| title | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
20. Sending ETH |
|
Recently, I have been revisiting Solidity, consolidating the finer details, and writing "WTF Solidity" tutorials for newbies.
Twitter: @0xAA_Science | @WTFAcademy_
Community: Discord|Wechat|Website wtf.academy
Codes and tutorials are open source on GitHub: github.com/AmazingAng/WTFSolidity
There are three ways of sending ETH in Solidity: transfer(), send() and call(), in which call() is recommended.
Let's deploy a contract ReceiveETH to receive ETH. ReceiveETH has an event Log, which logs the received ETH amount and the remaining gas. Along with two other functions, one is the receive() function, which is executed when receiving ETH, and emits the Log event; the other is the getBalance() function that is used to get the balance of the contract.
contract ReceiveETH {
// Receiving ETH event, log the amount and gas
event Log(uint amount, uint gas);
// receive() is executed when receiving ETH
receive() external payable{
emit Log(msg.value, gasleft());
}
// return the balance of the contract
function getBalance() view public returns(uint) {
return address(this).balance;
}
}After deploying ReceiveETH, call the getBalance() function, we can see the balance is 0 Ether.
We will implement three ways to send ETH to the ReceiveETH contract. First thing first, let's make the constructor of the SendETH contract payable, and add the receive() function, so we can transfer ETH to our contract at deployment and after.
contract SendETH {
// constructor, make it payable so we can transfer ETH at deployment
constructor() payable{}
// receive() function, called when receiving ETH
receive() external payable{}
}- Usage:
receiverAddress.transfer(value in Wei). - The
gaslimit oftransfer()is2300, which is enough to make the transfer, but not if the receiving contract has a gas-consumingfallback()orreceive(). - If
transfer()fails, the transaction willrevert.
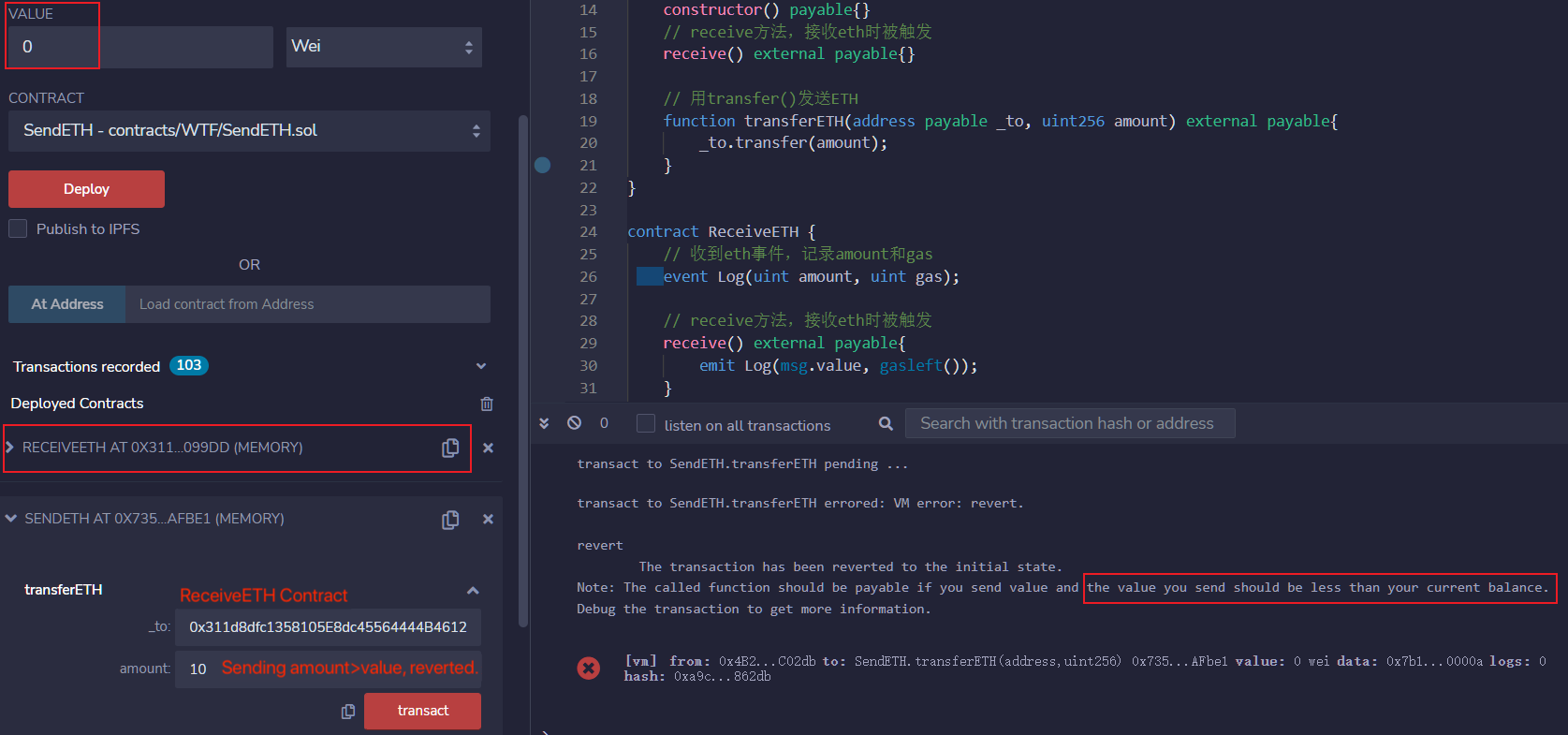
Sample code: note that _to is the address of the ReceiveETH contract, and amount is the value you want to send.
// sending ETH with transfer()
function transferETH(address payable _to, uint256 amount) external payable{
_to.transfer(amount);
}After deploying the SendETH contract, we can send ETH to the ReceiveETH contract. If amount is 10, and value is 0, amount>value, the transaction fails and gets reverted.
If amount is 10, and value is 10, amount<=value, then the transaction will go through.
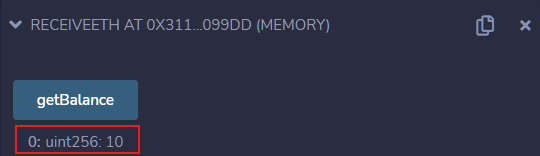
In the ReceiveETH contract, when we call getBalance(), we can see the balance of the contract is 10 Wei.
- Usage:
receiverAddress.send(value in Wei). - The
gaslimit ofsend()is2300, which is enough to make the transfer, but not if the receiving contract has a gas-consumingfallback()orreceive(). - If
send()fails, the transaction will bereverted. - The return value of
send()isbool, which is the status of the transaction, you can choose to act on that.
Sample Code:
// sending ETH with send()
function sendETH(address payable _to, uint256 amount) external payable{
// check result of send(),revert with error when failed
bool success = _to.send(amount);
if(!success){
revert SendFailed();
}
}Now we send ETH to the ReceiveETH contract, if amount is 10, and value is 0, amount>value, the transaction fails, since we handled the return value, the transaction will be reverted.
If amount is 10, and value is 11, amount<=value, the transaction is successful.
- Usage:
receiverAddress.call{value: value in Wei}(""). - There is no
gaslimit forcall(), so it supports more operations infallback()orreceive()of the receiving contract. - If
call()fails, the transaction will not bereverted. - The return value of
call()is(bool, data), in whichboolis the status of the transaction, you can choose to act on that.
Sample Code:
// sending ETH with call()
function callETH(address payable _to, uint256 amount) external payable{
// check result of call(),revert with error when failed
(bool success, ) = _to.call{value: amount}("");
if(!success){
revert CallFailed();
}
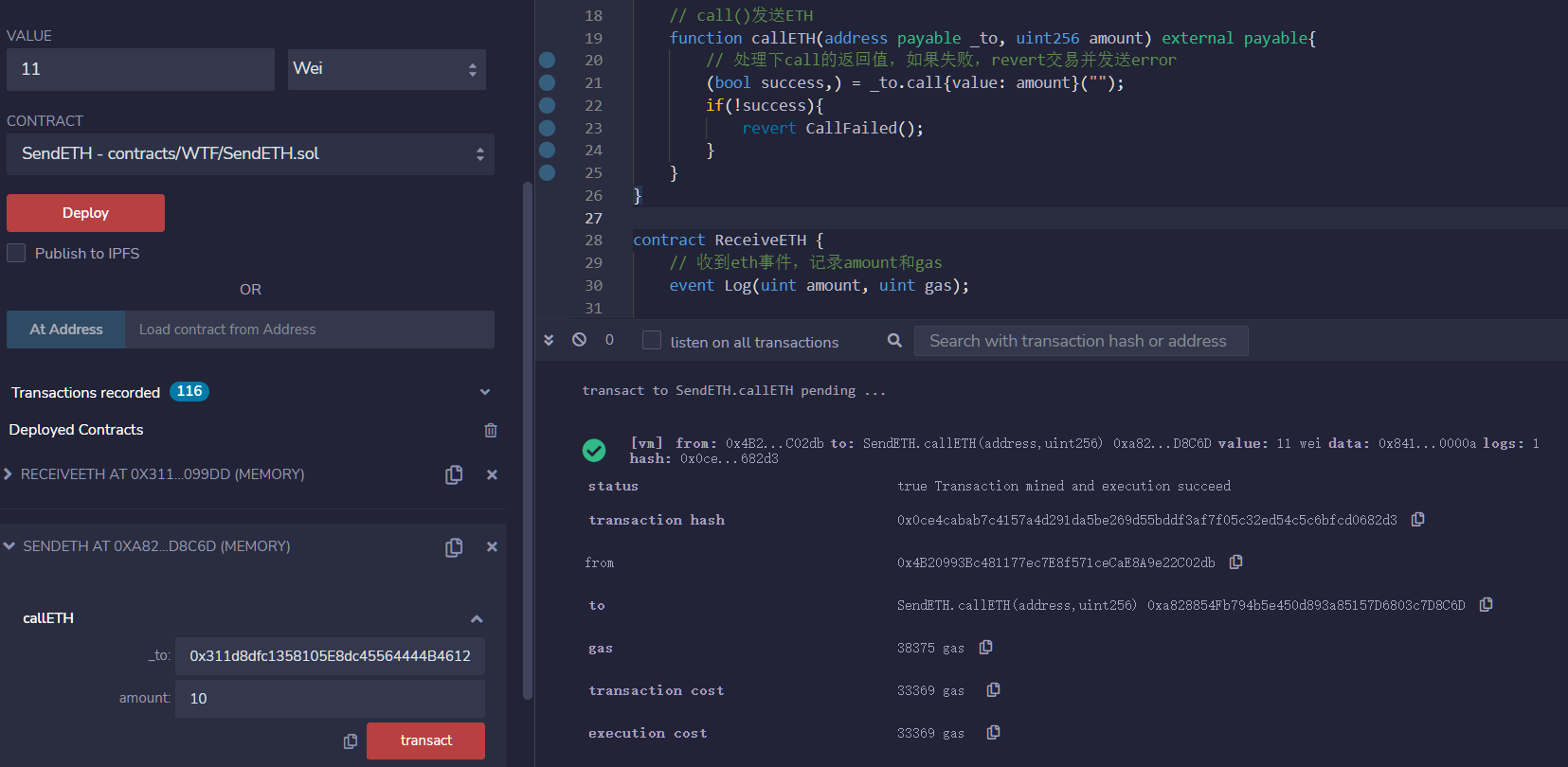
}Now we send ETH to the ReceiveETH contract, if amount is 10, and value is 0, amount>value, the transaction fails, since we handled the return value, the transaction will be reverted.
If amount is 10, and value is 11, amount<=value, the transaction is successful.
With any of these three methods, we send ETH to the ReceiveETH contract successfully.
In this tutorial, we talked about three ways of sending ETH in solidity:
transfer, send and call.
- There is no
gaslimit forcall, which is the most flexible and recommended way; - The
gaslimit oftransferis2300 gas, transaction will berevertedif it fails, which makes it the second choice; - The
gaslimit ofsendis2300, the transaction will not berevertedif it fails, which makes it the worst choice.