A cloud is a combination of services, networks, hardware, storage, and interfaces that helps in delivering computing as a service. It broadly has three users. These are the end-user, business management user, and cloud service, provider. The end-user is the one who uses the services provided by the cloud. The responsibility of the data and the services provided by the cloud is taken by the business management user in the cloud. The one who takes care of or is responsible for the maintenance of the IT assets of the cloud is the cloud service provider. The cloud acts as a common center for its users to fulfill their computing needs.
The following are some of the key features of cloud computing:
- Agility: Helps in quick and inexpensive re-provisioning of resources.
- Location Independence: This means that the resources can be accessed from everywhere.
- Multi-Tenancy: The resources are shared amongst a large group of users.
- Reliability: Resources and computation can be dependable for accessibility.
- Scalability: Dynamic provisioning of data helps in scaling.
Cloud delivery models are models that represent the computing environments. These are as follows:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is the delivery of services, including an operating system, storage, networking, and various utility software elements, on a request basis.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a mechanism for combining Infrastructure as a Service with an abstracted set of middleware services, software development, and deployment tools. These allow the organization to have a consistent way to create and deploy applications on a cloud or on-premises environment.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Software as a Service (SaaS) is a business application created and hosted by a provider in a multi-tenant model.
- Function as a Service (FaaS): Function as a Service (FaaS) gives a platform for customers to build, manage and run app functionalities without the difficulty of maintaining infrastructure. One can thus achieve a "serverless" architecture.
There are two primary deployment models of the cloud: Public and Private.
- Public Cloud: The set of hardware, networking, storage, services, applications, and interfaces owned and operated by a third party for use by other companies or individuals is the public cloud. These commercial providers create a highly scalable data center that hides the details of the underlying infrastructure from the consumer. Public clouds are viable because they offer many options for computing, storage, and a rich set of other services.
- Private Cloud: The set of hardware, networking, storage, services, applications, and interfaces owned and operated by an organization for the use of its employees, partners, or customers is the private cloud. This can be created and managed by a third party for the exclusive use of one enterprise. The private cloud is a highly controlled environment not open for public consumption. Thus, it sits behind a firewall.
- Hybrid Cloud: Most companies use a combination of private computing resources and public services, called the hybrid cloud environment.
- Multi-Cloud: Some companies, in addition, also use a variety of public cloud services to support the different developer and business units – called a multi-cloud environment
The parts of the cloud ecosystem that determine how you view the cloud architecture are:
- Cloud consumers
- Direct customers
- Cloud service providers
The individuals and groups within your business unit that use different types of cloud services to get a task accomplished. A cloud consumer could be a developer using compute services from a public cloud
Users who often take advantage of services that your business has created within a cloud environment. The end-users of your service have no idea that you're using a public or private cloud. As long as the users are concerned, they're interacting directly with the services and value
Cloud service providers are the commercial vendors or companies that create their own capabilities. The commercial vendors sell their services to cloud consumers. In contrast to this, a company might decide to become an internal cloud service provider to its own partners, employees, and customers, either as an internal service or as a profit center. Cloud service providers also create applications or services for such environments.
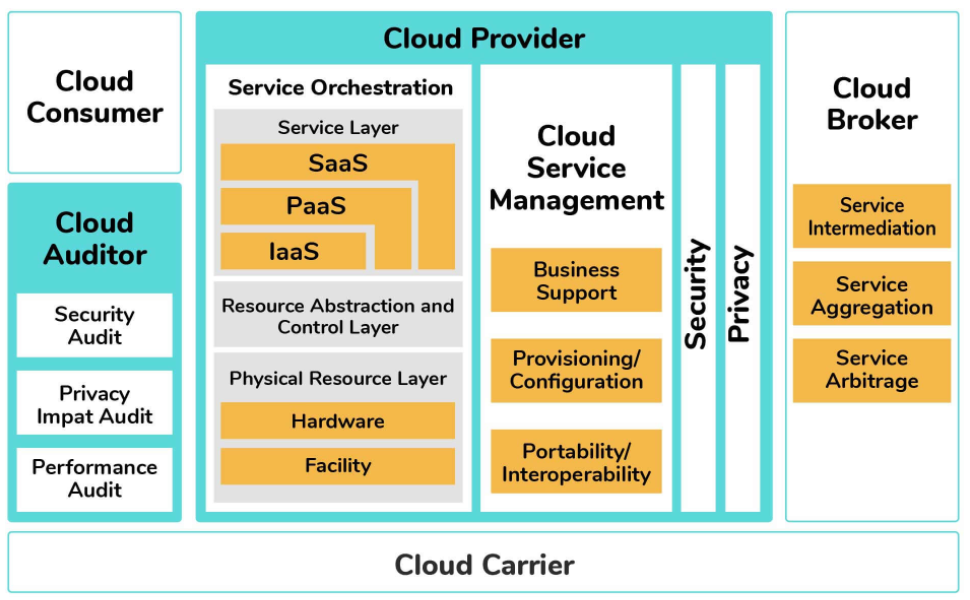
The cloud computing architecture is all the components of a cloud model that fit together from an architectural perspective. The figure below depicts how the various cloud services are related to support the needs of businesses. On the left side, the cloud service consumer represents the types of uses of cloud services. No matter what the requirements of the particular constituent are, it is important to bring the right type of services together that can support both internal and external users. Management of the consumers should be able to make services readily available to support the changing business needs. The applications, middleware, infrastructure, and services that are built based on on-premises computing models are within this category. In addition to this, the model depicts the role of a cloud auditor. This organization provides an oversight either by an internal or external group which makes sure that the consumer group meets its obligations.
Cloud storage device mechanisms provide common levels of data storage, such as:
- Files – These are collections of data that are grouped into files that are located in folders.
- Blocks – A block is the smallest unit of data that is individually accessible. It is the lowest level of storage and the closest to the hardware.
- Datasets – Data sets organized into a table-based, delimited, or record format.
- Objects – Data and the associated metadata with it are organized as web-based resources. Each of the above data storage levels is associated with a certain type of technical interface. This interface corresponds to a particular type of cloud storage device and the cloud storage service used to expose its API.
Serverless components in cloud computing allow the building of applications to take place without the complexity of managing the infrastructure. One can write code without having provision to a server.
Serverless machines take care of virtual machines and container management. Multithreading, hardware allocating are also taken care of by the serverless components.
Serverless computing has the following advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages:
- It is cost-effective.
- The operations on serverless computing are simplified.
- Serverless computing helps boost productivity.
- It offers scaling options.
- It involves zero server management.
Disadvantages:
- Serverless code can cause response latency.
- It is not ideal for high-computing operations because of resource limitations.
- For serverless computing, the responsibility of security comes under the service company and not the consumer, which might be more vulnerable.
- Debugging serverless code is a bit more challenging.
There are several areas of technology that contribute to modern-day cloud-based platforms. These are known as cloud-enabling technologies. Some of the cloud-enabling technologies are:
- Broadband Networks and Internet Architecture
- Data Center Technology
- (Modern) Virtualization Technology
- Web Technology
- Multitenant Technology
- Service Technology
Microservices is a process of developing applications that consist of code that is independent of each other and of the underlying developing platform. Each microservice runs a unique process and communicates through well-defined and standardized APIs, once created. These services are defined in the form of a catalog so that developers can easily locate the right service and also understand the governance rules for usage
The reason why microservices are so important for a true cloud environment is because of these four key benefits:
- Each microservice is built to serve a specific and limited purpose, and hence application development is simplified. Small development teams can then focus on writing code for some of the narrowly defined and easily understood functions.
- Code changes will be smaller and less complex than with a complex integrated application, making it easier and faster to make changes, whether to fix a problem or to upgrade service with new requirements.
- Scalability — Scalability makes it easier to deploy an additional instance of a service or change that service as needs evolve.
- Microservices are fully tested and validated. When new applications leverage existing microservices, developers can assume the integrity of the new application without the need for continual testing.
The cloud usage monitor mechanism is an autonomous and lightweight software program that is responsible for collecting and processing the IT resource usage data.
Cloud usage monitors can exist in different formats depending on what type of usage metrics these are designed to collect and how the usage data needs to be collected. The following points describe 3 common agent-based implementation formats.
- Monitoring Agent
- Resource Agent
- Polling Agent
An intermediary and an event-driven program that exists as a service agent and resides along the existing communication paths is a monitoring agent. It transparently monitors and analyzes dataflows. Commonly, the monitoring agent is used to measure the network traffic and also message metrics.
A processing module that is used to collect usage data by having event-driven interactions with the specialized resource software, is a resource agent. This agent is applied to check the usage metrics based on pre-defined, observable events at the resource software level, like initiating, suspending, resuming, and vertical scaling.
A processing module that gathers cloud service usage data by polling IT resources is called a polling agent. The polling agent has also been used to timely monitor the IT resource status, like uptime and downtime. Each of these can be designed to forward collected usage data to a log database for post-processing and for reporting purposes.
‘Cloud native' is a software framework designed with containers, microservices, dynamic orchestration, and also continuous delivery of software. Every part of the cloud-native application has within it its own container and is dynamically orchestrated with other containers to optimize the way the resources are utilized.
The Cloud Native Computing Foundation gives a clear definition of cloud-native:
- Container packaged: This means a standard way to package applications that is resource-efficient. By using a standard container format, more applications can be densely packed.
- Dynamically managed: This means a standard way to discover, deploy, and scale up and down containerized applications.
- Microservices oriented: This means a method to decompose the application into modular, independent services that interact through well-defined service contracts
Edge and cloud are complementary. These are both parts of a broader concept called the distributed cloud. A majority of those pursuing edge computing strategies are now viewing edge as part of their overall cloud strategy.
Edge computing, unlike cloud computing, is all about the physical location and issues related to latency. Cloud and edge combine the strengths of a centralized system, along with the advantages of distributed operations at the physical location where things and people connect. In IoT scenarios, the edge is very common. Cloud is different from the edge, in that it has never been about location. As opposed, it has always been about the independence of location.
The popular scenarios are where you have cloud and edge together, and the cloud provider controls to run and defines the architecture for what is out at the edge
An API gateway allows multiple APIs to act together as a single gateway to provide a uniform experience to the user. In this, each API call is processed reliably. The API gateway manages the APIs centrally and provides enterprise-grade security. Common tasks of the API services can be handled by the API gateway. These tasks include services like statistics, rate limiting, and user authentication.
Rate Limiting is a way to limit the network traffic. Rate limiting runs within the app rather than the server. It typically tracks the IP addresses and the time between each request.
It can eliminate certain suspicious and malicious activities. Bots that impact a website can also be stopped by Rate Limiting. This protects against API overuse which is important to prevent
A container is a packaged software code along with all of its dependencies so that it can run consistently across clouds and on-premises. This packaging up of code is often called encapsulation. Encapsulating code is important for developers as they don't have to develop code based on each individual environment
Cloud computing is made up of various data centers put together in a grid form. It consists of the data centers like:
- Containerized Data Centers
- Low-Density Data Centers
Containerized Data Centers are the traditional data centers that allow a high level of customization with servers, mainframes, and other resources. These require planning, cooling, networking, and power to access and work.
Low-Density Data Centers are optimized to give high performance. The space constraint is being removed and there is an increased density in these data centers. One drawback it has is that with high density the heat issue also creeps in. These data centers are quite suitable to develop the cloud infrastructure.
Following are some of the issues of cloud computing:
- Security Issues: As it would be in any other computing paradigms, security is as much of a concern as Cloud computing. Cloud Computing is vaguely defined as the outsourcing of services, which in turn causes users to lose significant control over their data. With the public Cloud, there is also a risk of seizure associated.
- Legal and Compliance Issues: Sometimes, clouds are bounded by geographical boundaries. The provision of different services is not location-dependent. Because of this flexibility Clouds face Legal & Compliance issues. Though these issues affect the end-users, they are related mainly to the vendors.
- Performance and Quality of Service (QoS) Related Issues: Paradigm performance is of utmost importance for any computing. The Quality of Service (QoS) varies as the user requirements may vary. One of the critical Quality of Service-related issues is the optimized way in which commercial success can be achieved using Cloud computing. If a provider is unable to deliver the promised QoS it may tarnish its reputation. One faces the issue of Memory and Licensing constraints which directly hamper the performance of a system, as Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) deals with the provision of software on virtualized resources,
- Data Management Issues: An important use case of Cloud Computing is to put almost the entire data on the Cloud with minimum infrastructure requirements for the end-users. The main problems related to data management are scalability of data, storage of data, data migration from one cloud to another, and also different architectures for resource access. It is of utmost importance to manage these data effectively, as data in Cloud computing also includes highly confidential information.
Resource Replication is the creation of multiple instances of the same IT resource. It is typically performed when an IT resource's availability and performance are needed to be enhanced. The virtualization technology is adopted to implement the resource replication mechanism in order to replicate the cloud-based IT resources.