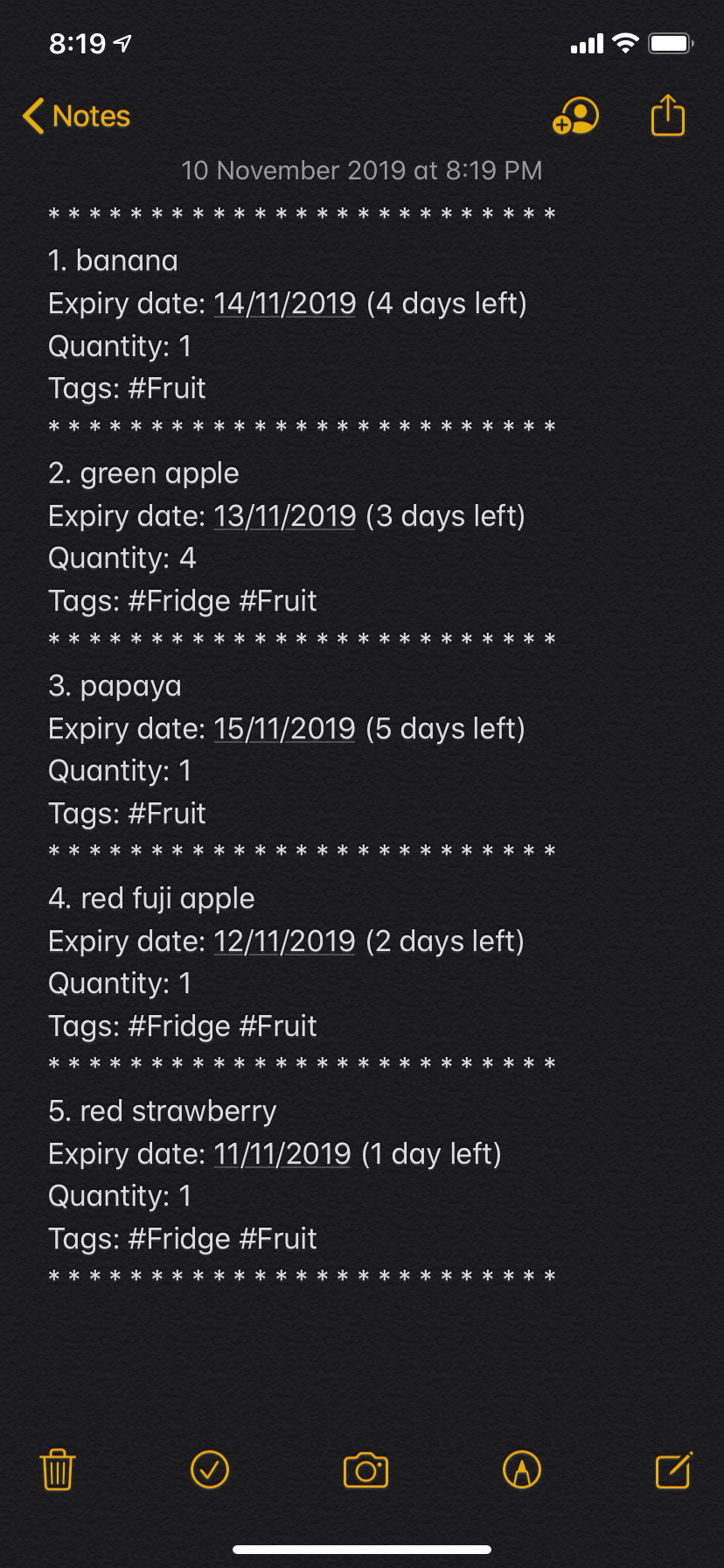
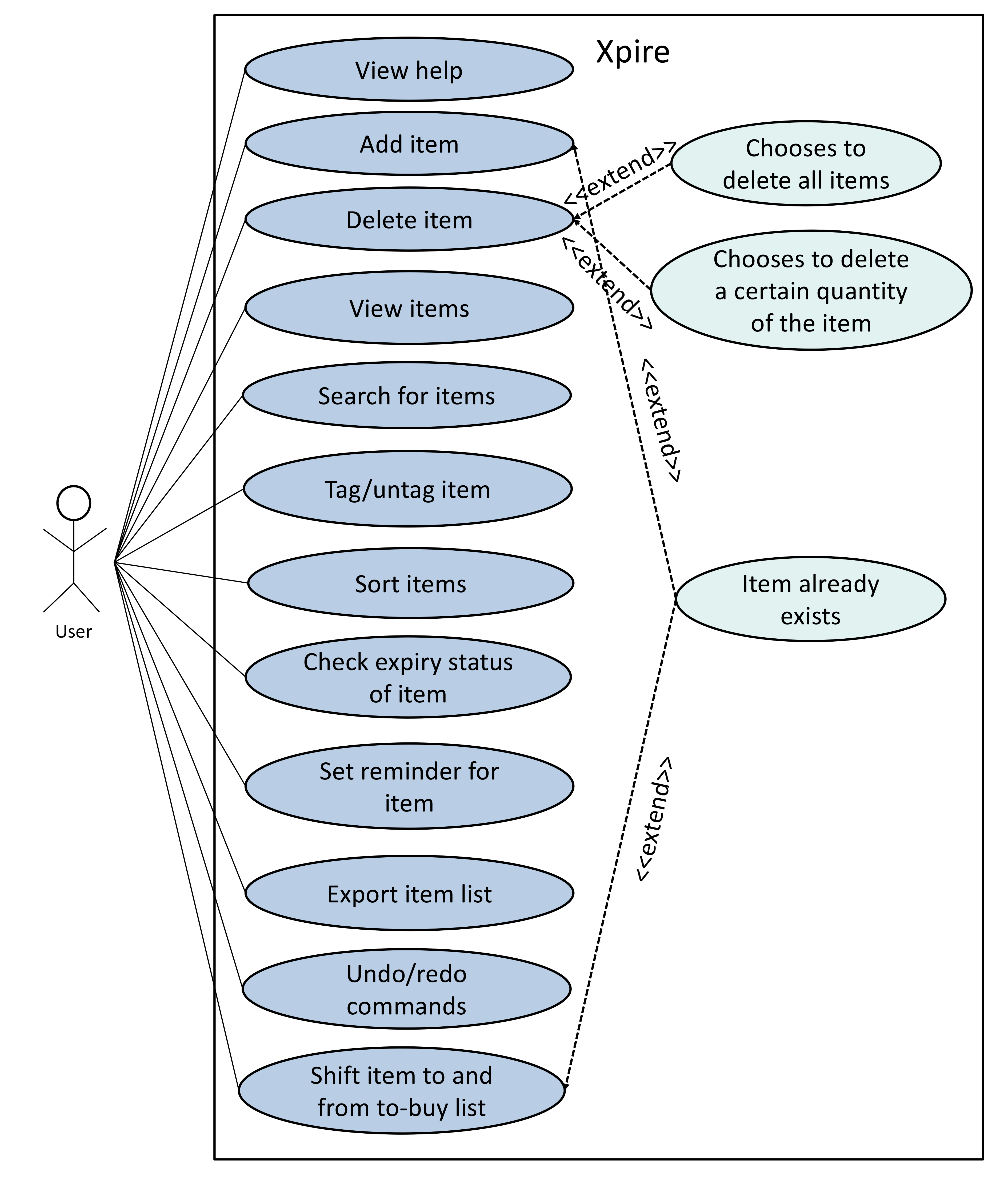
Xpire is a desktop application used for tracking expiry dates of items. The user interacts with it using a Command Line Interface (CLI), and it has a Graphical User Interface (GUI) created with JavaFX.
Xpire is developed as part of a CS2103T software engineering team project and it is a brownfield project that is morphed from Address Book (Level 3).
Xpire is mainly targeted at students living on campus and some of the features of Xpire include an item expiry date tracker, a reminder system to notify users when an item is expiring or has already expired, and an export functionality to share the tracking list with other devices.
|
Note
|
The symbol on the left is used to highlight crucial information. |
set reminder:
Words that are highlighted in grey (a form of markup) indicates a command line input that can be supplied
to the application and be executed. In addition, this notation is also used to represent a class,
component or object in the architecture.
Content enclosed in this markup indicates additional information for you to take note of.
This section shows a summary of my coding, documentation and other helpful contributions to the team project. |
-
Major enhancement: Added the ability to export the item list through a QR code
-
What it does: It allows users to export the list of items that are currently being tracked to any devices with QR code scanner, such as mobile phones and iPads.
-
Justification: This feature enhances the product significantly as it enables the users to keep a copy of the list of items in Xpire for easy reference. This is so that users can view the list and keep track of the items at anywhere and anytime.
-
Highlights: This enhancement requires knowledge of handling image data as well as an in-depth understanding of the need to convert between png data and byte array. Additional challenges include building a JavaFX component to render the QR code as a popup window and increasing the resolution of the QR code image to reduce the chances of failure when scanning the code.
-
Credits: Google ZXing
-
-
Major enhancement: Added the ability to perform AND search
-
What it does: It allows user to perform an AND search instead of the typical OR search. e.g. an AND search is akin to searching for items that contain "cold" AND "red" AND "cake" in its name while an OR search will be similar to searching for items that contain either "cold" OR "red" OR "cake" in its name.
-
Justification: This feature improves the product significantly as it allows users to perform more restrictive searches. This makes it easier and faster for the users to search for the items they are looking for, especially when there is a lot of items in the list.
-
Highlights: This enhancement requires a remodelling of the
Model's architecture as well as writing a new Application Programming Interface (API) since the current implementation of Address Book (Level 3) does not support AND search. In other words, an in-depth analysis of theModel's design architecture is required so that the new API written to support AND search does not break any other existing features. This requires thorough testing and meticulous integration skills and techniques.
-
-
Minor enhancement: Added shorthand commands as an alternative to the full commands. e.g.
searchcan also be inputted asse. This caters to users who wants to manage the items quickly using the application. -
Minor enhancement: Added partial search by name/exact search by tag(s). e.g.
search|foo|#Fruitwill search for any item with name that partially matchesfooor with tag(s) that exactly matches#Fruit. -
Other contributions:
-
Project management:
-
Managed releases
v1.2.1andv1.3on GitHub
-
-
Dev Ops:
-
Contributions to team members' enhancements:
-
Wrote a
DateUtilclass to provide helper functions to manage dates (see code) -
Helped to wrote
SetReminderCommandandSetReminderCommandParserfor a teammate’s feature (Pull request #10) -
Rewrote
ModelManagerclass to accommodate the new API (Pull request #194) -
Integrated new API with all existing commands (Pull request #194)
-
-
Enhancements to existing features:
-
Added more test cases (Pull request #221)
-
-
Community:
-
Given below are sections I contributed to the User Guide. They showcase my ability to write documentation targeting end-users. |
Thinking of viewing the list of currently tracked items on your mobile phone? Want to have a
copy of the to-buy items on your mobile phone so that you can refer to it while shopping?
With Xpire’s export feature, you can easily transfer the list of items to any platform
by simply scanning the generated QR code.
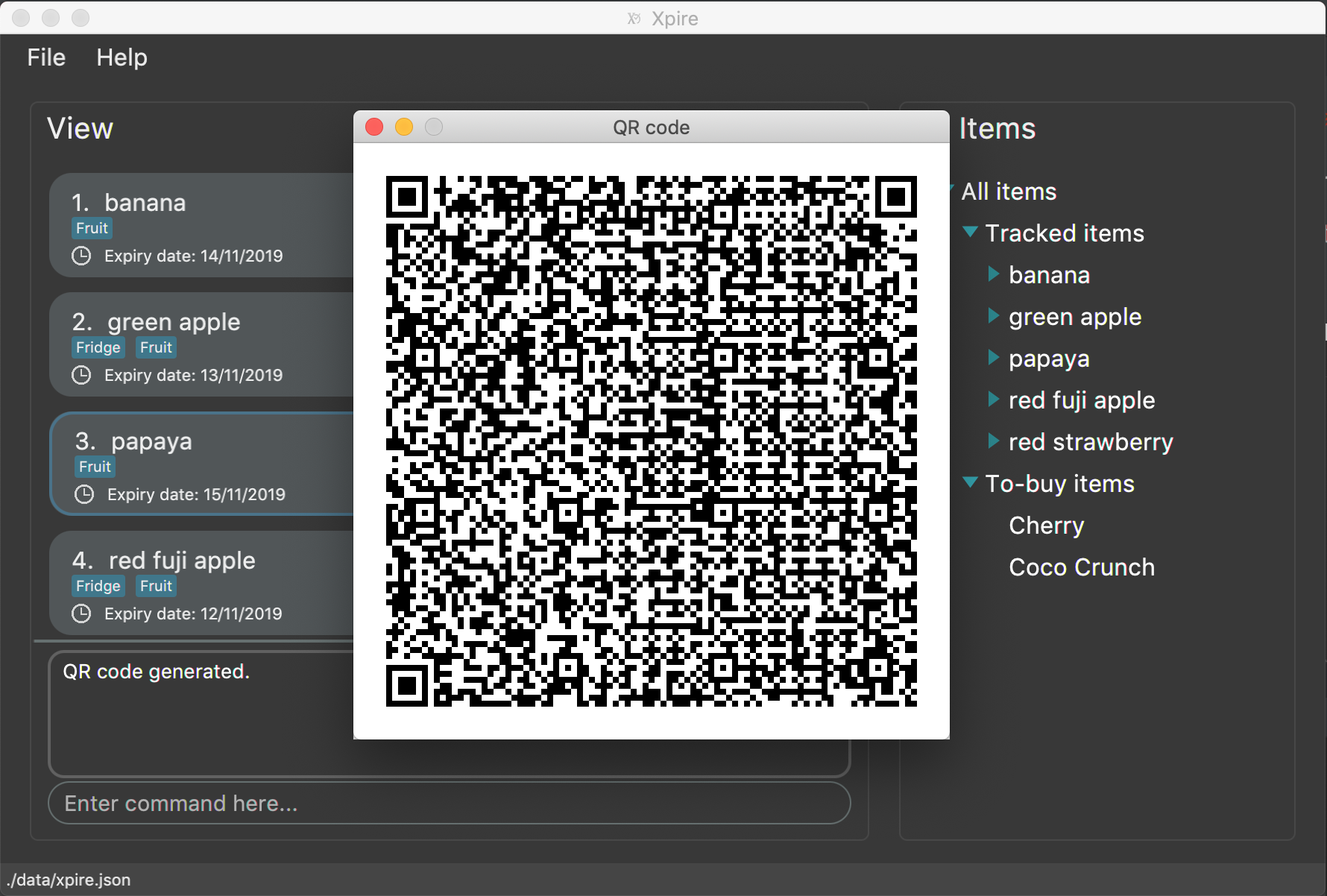
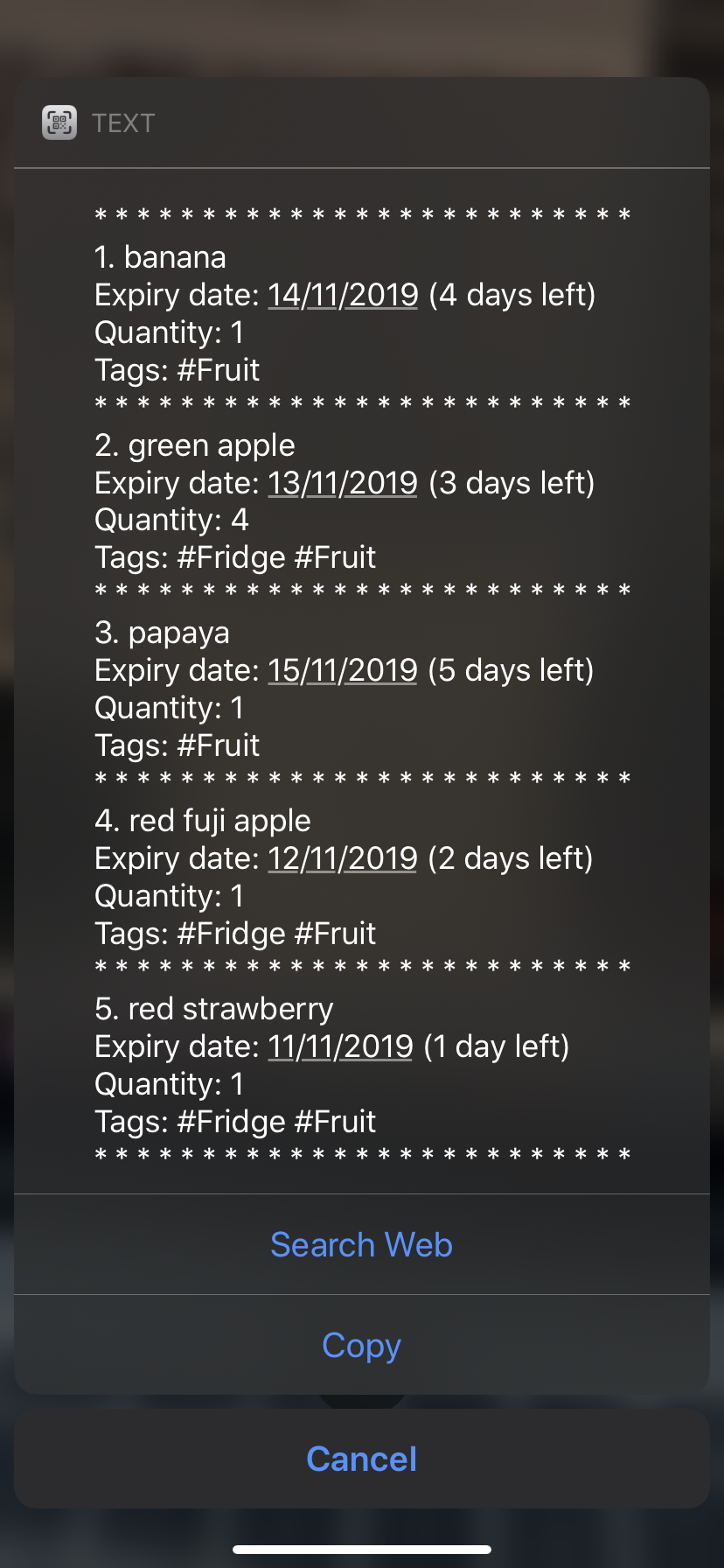
Xpire can not only help you track your items' expiry dates, it can also export the current list of items through a QR code (see Figure 1). Any device with a QR code reader will be able to download the list of items (see Figure 2).
Format: export
|
Note
|
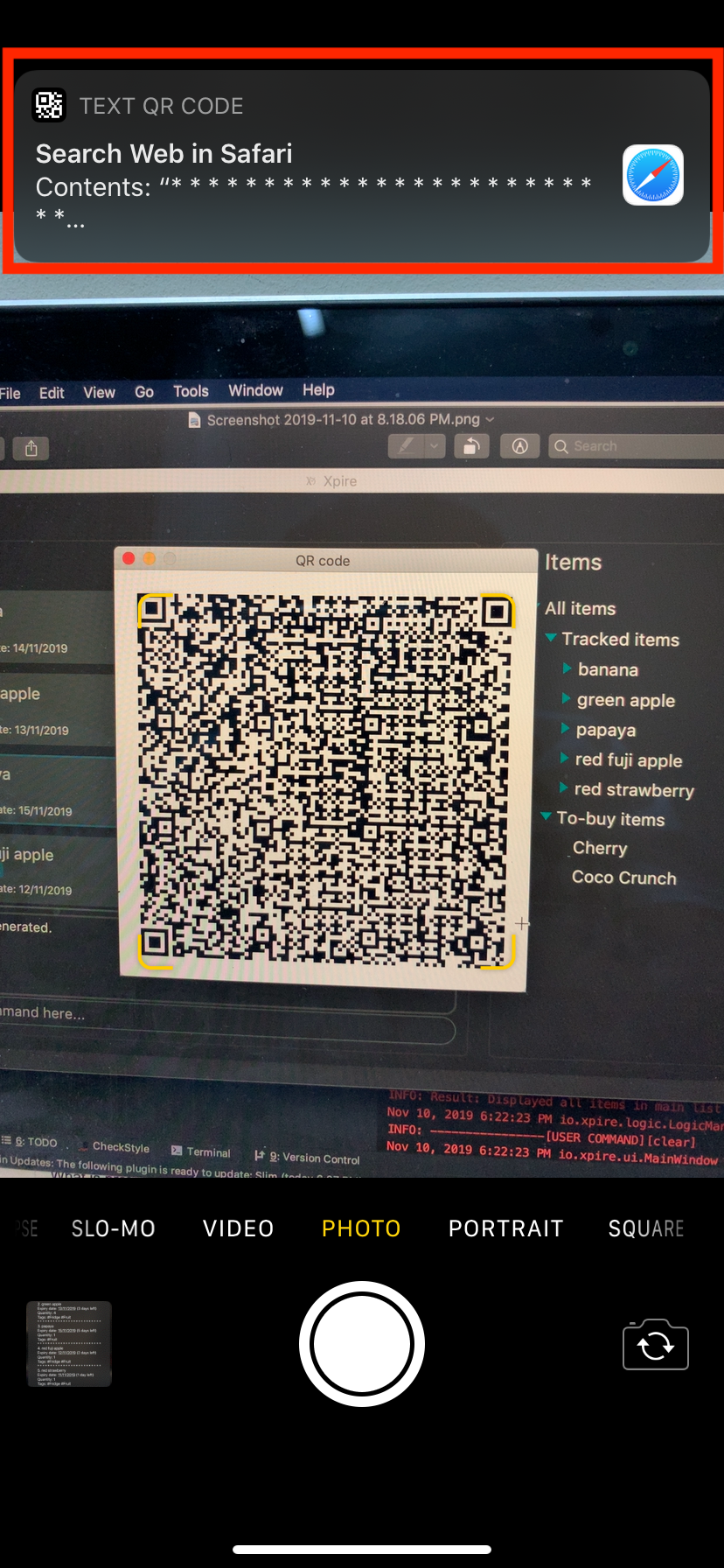
Depending on the operating system of your mobile phone, you may be directed to a google search page after scanning the QR code. Follow the steps below to rectify this issue if necessary. |
-
Upon scanning the QR code, you may see a pop-up prompt suggesting to you to search the content received on the web (see Figure 3).
-
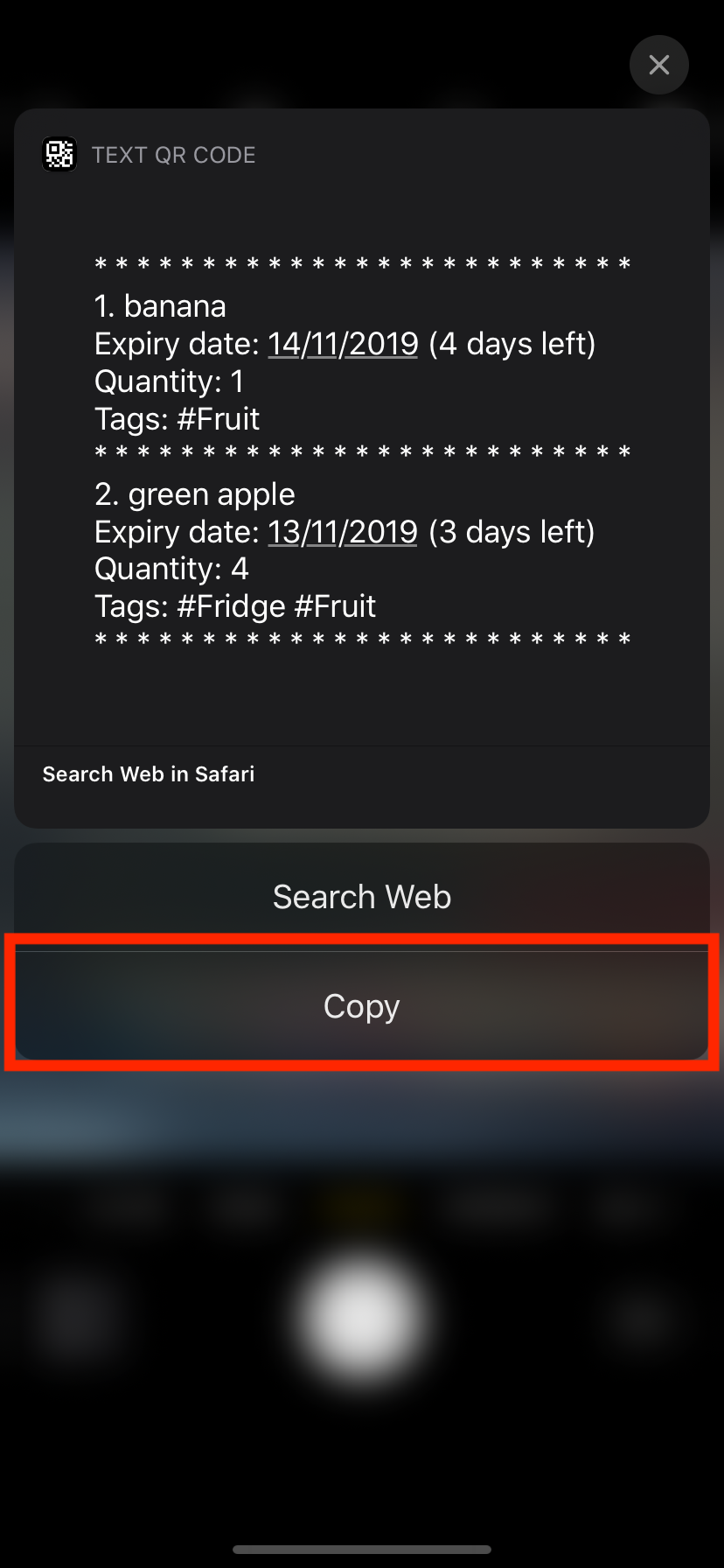
Instead of immediately accepting the suggestion, press and hold on the prompt to reveal the other options available (see Figure 4). Choose "Copy" or any other similar options.
-
Once the content has been copied, you can simply paste and save the content on Notes or any other notepad application on your mobile phone (see Figure 5).
Having a hard time looking for an item in Xpire? Not to worry, Xpire provides a search functionality to aid you in finding your items with ease.
With search, you can simply input any words or phrases and Xpire will display all items whose names or tag(s) contain any of the given keywords.
Format: search|<keyword>[|<other keywords>]…
|
Note
|
search is designed to work only on the current view list. In other words, search will only
display matching items which exists in the current view list.
|
|
Tip
|
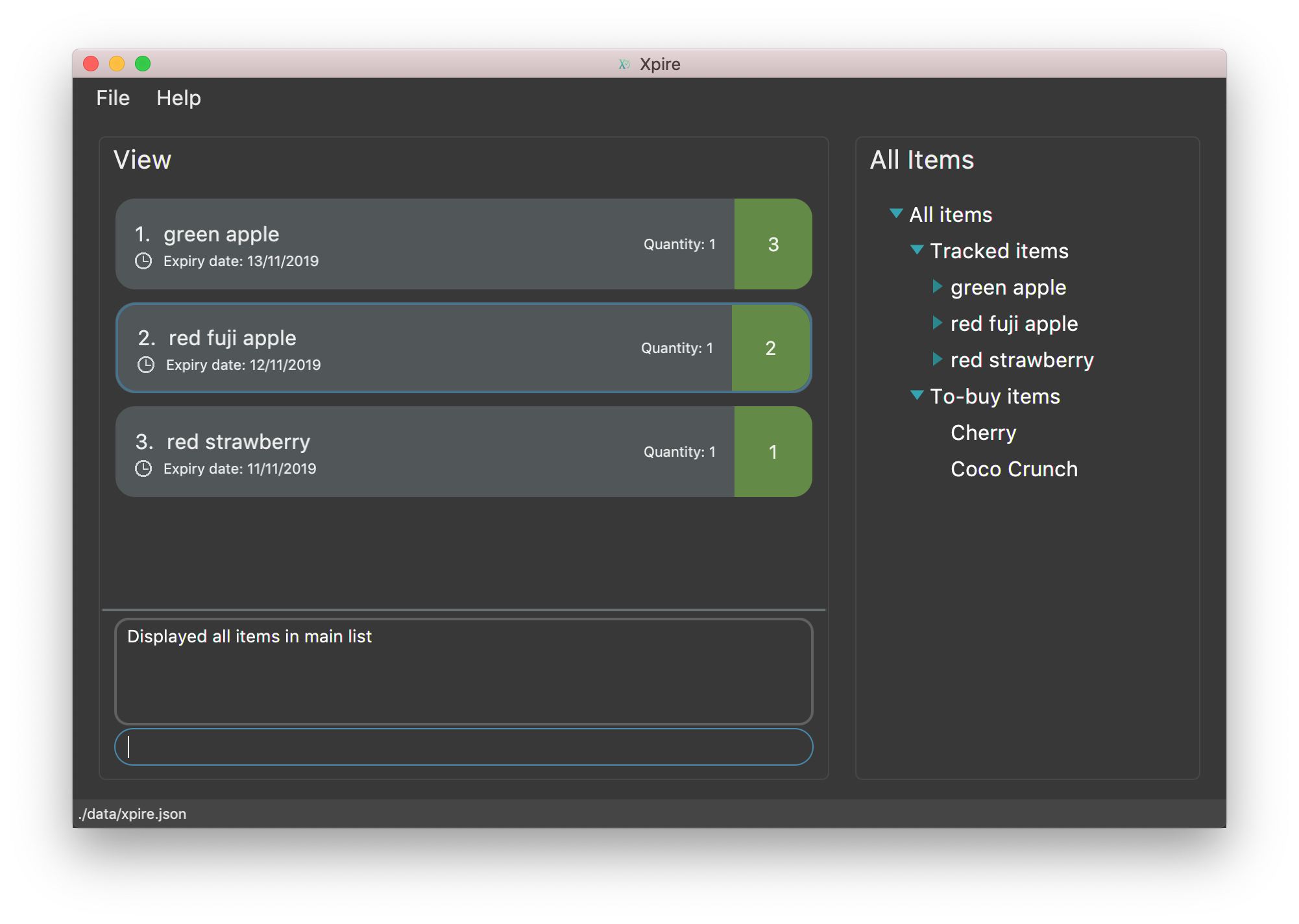
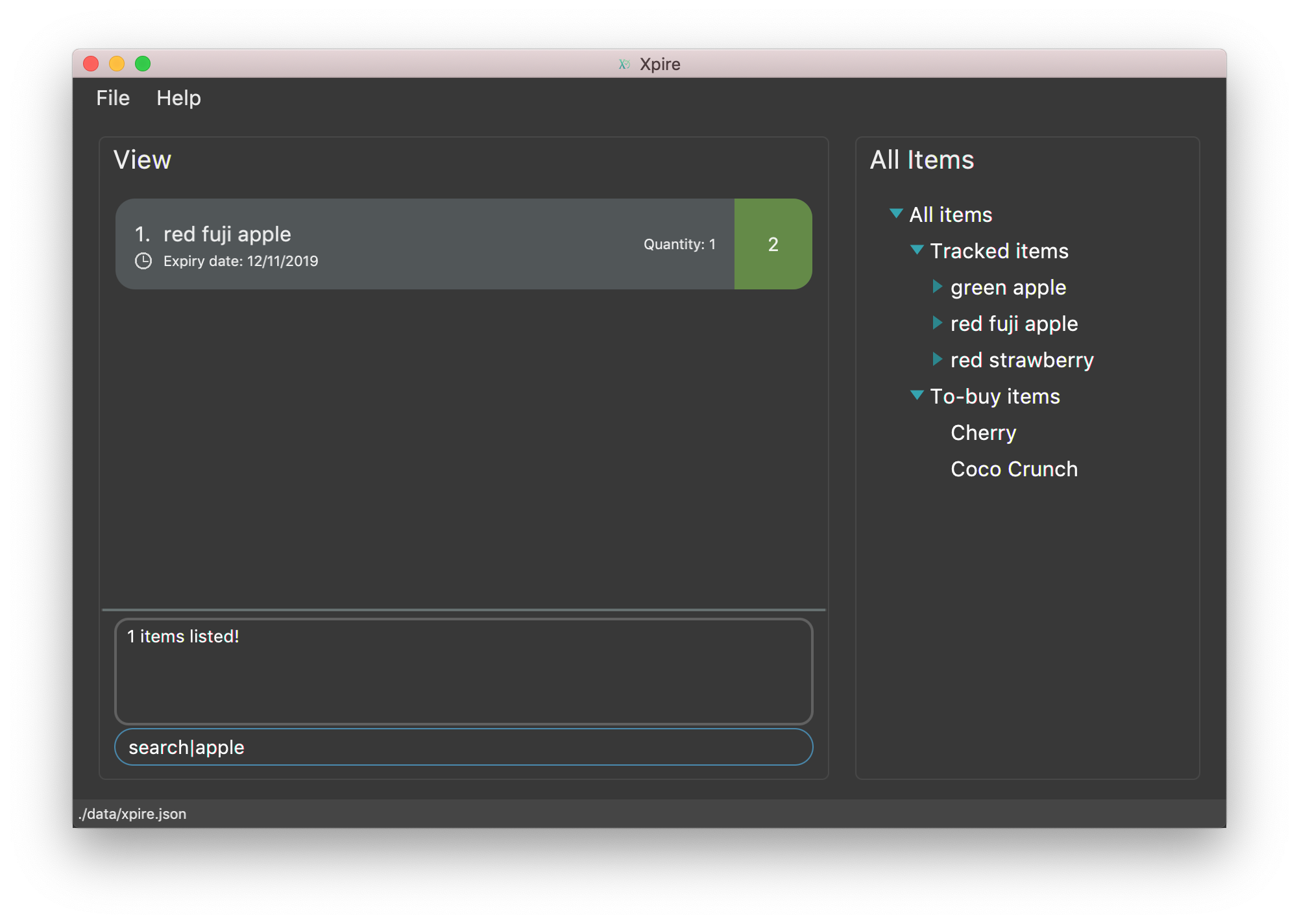
You can do an AND search, e.g. search for items that contains BOTH red and apple in its name,
by keying search|red and then search|apple. Suppose there are only 3 items in your list, e.g.
red fuji apple, red strawberry and green apple (see Figure 7), the above commands will display only red
fuji apple (see Figure 8).
|
-
The search is case insensitive. e.g
hamwill matchHamand#fruitwill match#Fruit. -
The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
Turkey Ham|Applewill matchApple|Turkey Ham. -
Only the name and tag fields, if any, are searched.
-
For name search, partial words can be matched e.g.
Papawill matchPapayas. -
For tag search, only exact words will be matched e.g.
#Fruitwill match#Fruitbut#Fruwill not match#Fruit. -
Items matching at least one keyword will be returned (an OR search). e.g.
Apple|Pearwill returnGranny Smith AppleandJapanese Pear. -
If no items are found, any closely related keywords, if any, will be displayed.
Examples:
-
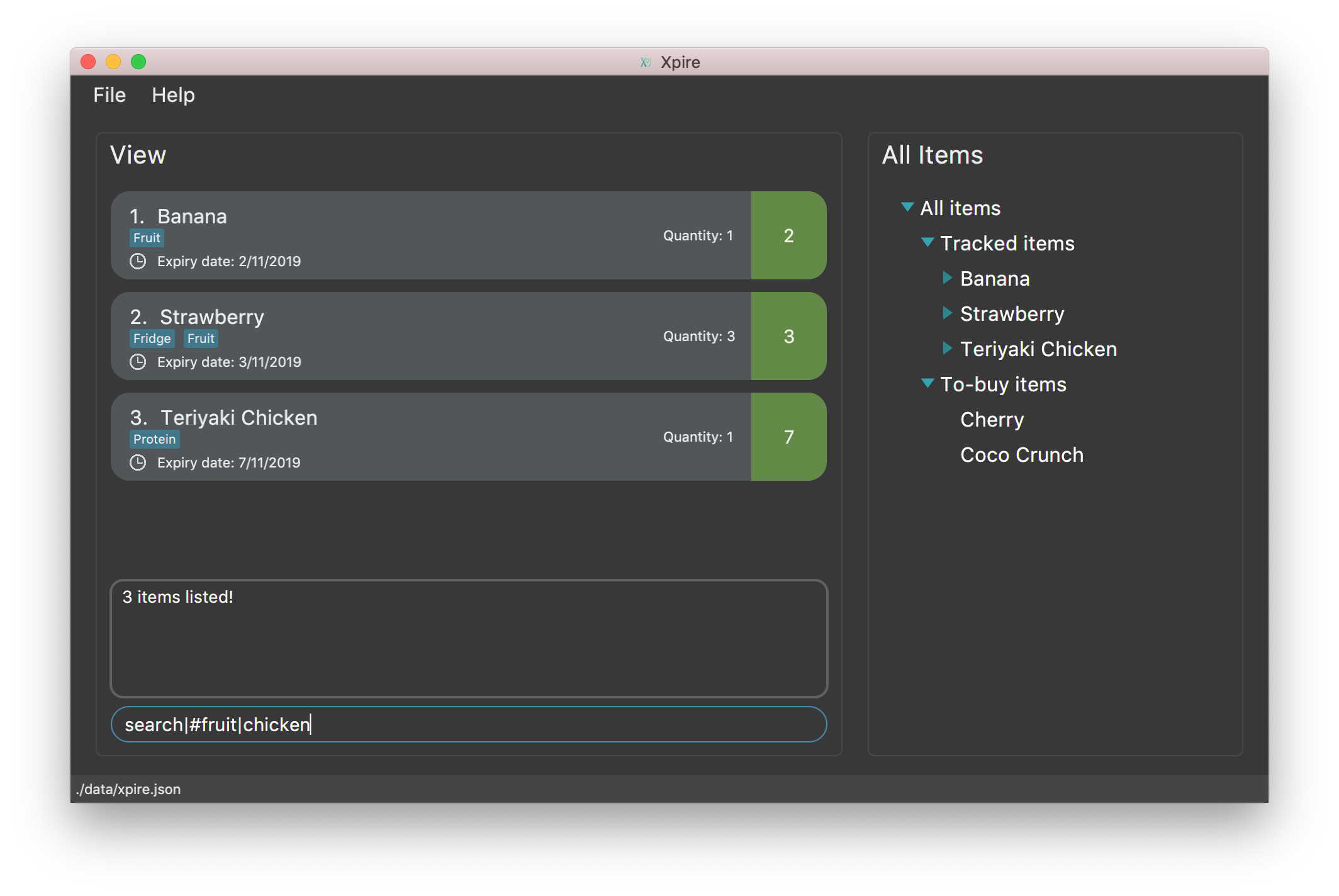
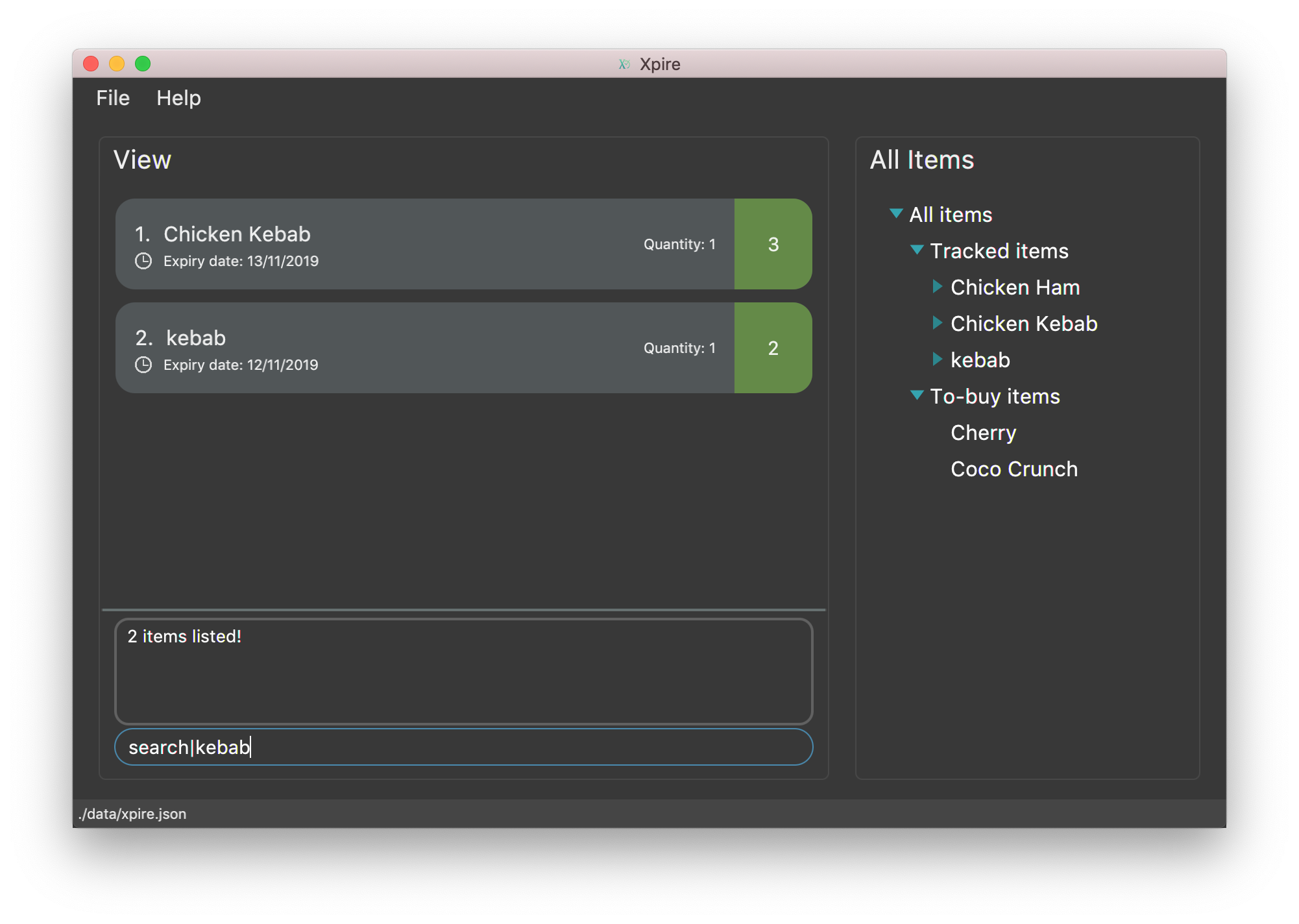
search|kebabwill displayChicken Kebabandkebab(see Figure 9).
-
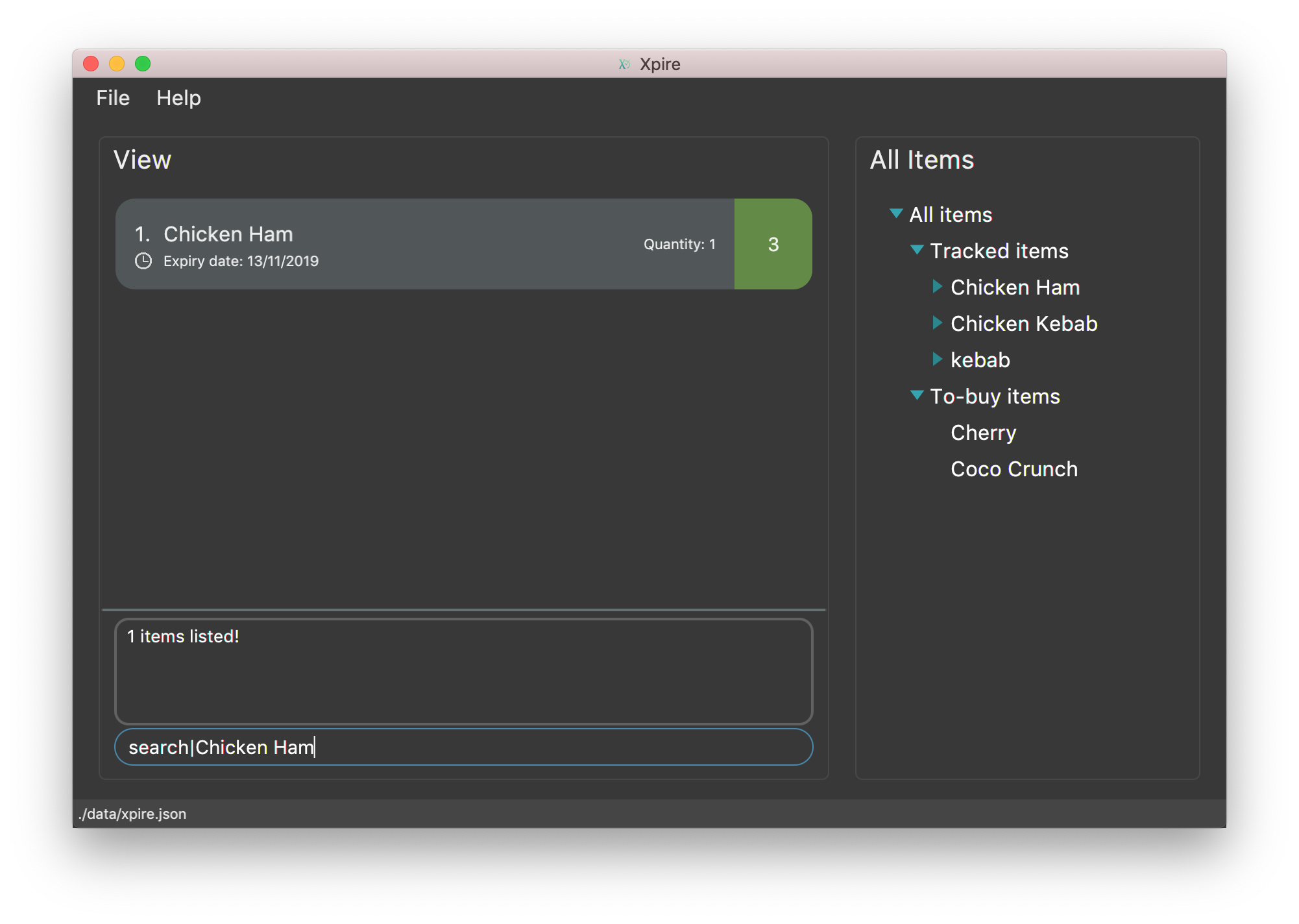
search|Chicken Hamwill displayChicken Ham(see Figure 10).
-
search|milk|tea|#Drinkwill display any items with names containingmilkortea, or with the tag#Drink.
Given below are sections I contributed to the Developer Guide. They showcase my ability to write technical documentation and the technical depth of my contributions to the project. |
This feature allows users to export the items in the current view list to other devices through a QR code. Any device with a QR code reader will be able to download the list of items.
This implementation is under Logic and Model components, and it uses a helper method from StringUtil.
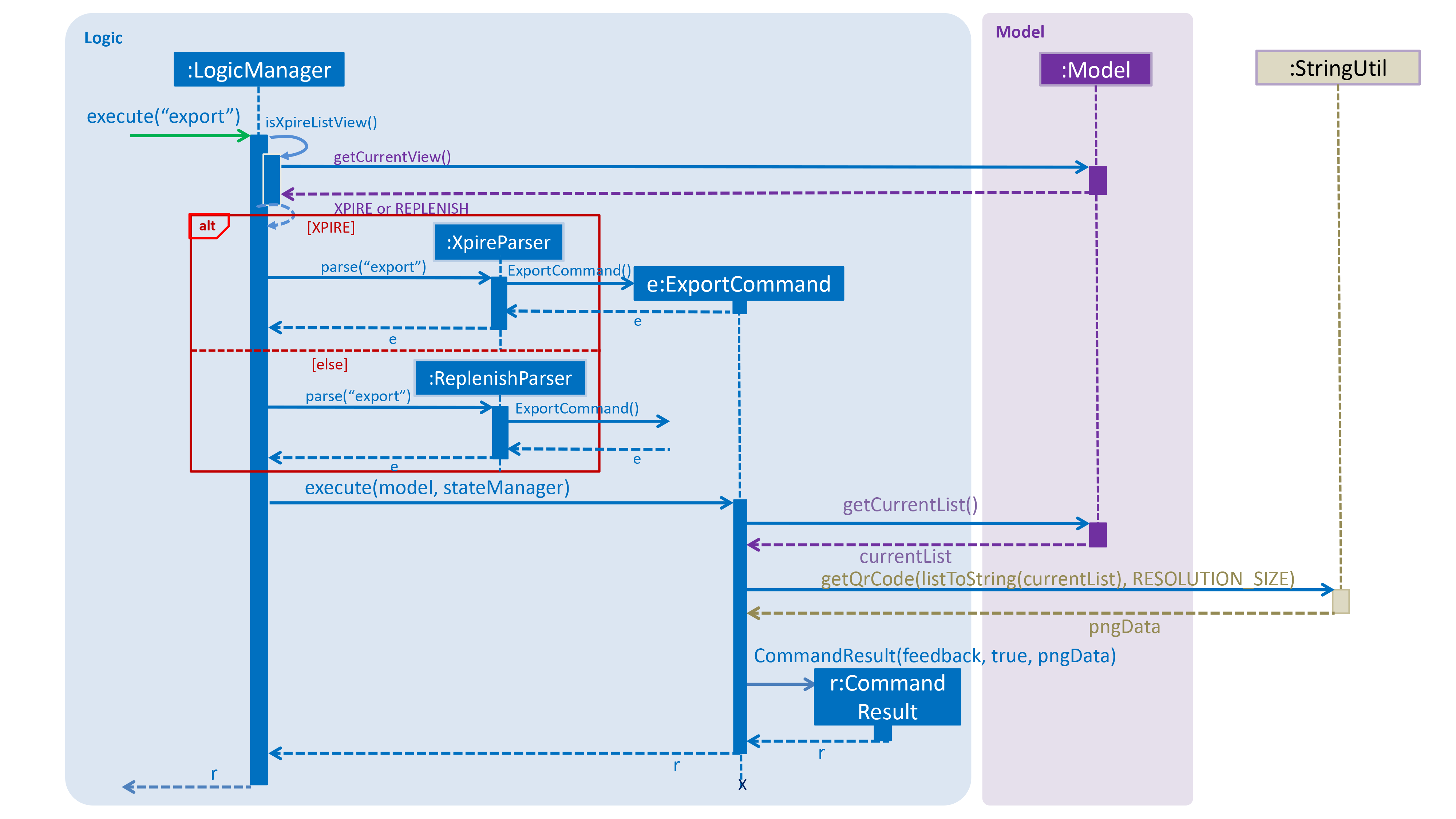
Below is the UML sequence diagram and a step-by-step explanation of an example usage scenario.
Example usage scenario:
Step 1. User enters command export. The command is received by the LogicManager’s `execute method which
then calls the getCurrentView method of Model to determine which item list is currently being displayed, XPIRE
or REPLENISH.
Step 2. Depending on which item list is currently being displayed, either XpireParser 's or ReplenishParser 's parse
method will be called to create a ExportCommand object. The ExportCommand object will be returned to the LogicManager.
Step 3. The LogicManager then calls the returned ExportCommand object’s execute method which calls the
getCurrentList method of Model to retrieve the list of items in the current view list.
Step 4. The items in the current view list is then converted to its string representation and then passed into the getQrCode
method in StringUtil.
Step 5. The getQrCode method uses Google ZXing library to process the input string
into a QR code and this QR code is subsequently converted to a byte array (pngData) so that it can be passed around easily.
Step 6. Upon successful creation of the QR code data, a CommandResult object will be created by ExportCommand to encapsulate
a feedback message and the QR code data, which will be rendered and shown to the user. The CommandResult will then be returned to the LogicManager.
The following UML activity diagram will further demonstrate the high-level workflow of the export command.
|
Note
|
The selection of parser and the creation of ExportCommand object is omitted for brevity.
|
As illustrated in Figure 12, the export functionality also considers the case where the current view list
is empty and there will be a feedback to the user to inform him/her that the export command is not executed
successfully.
Below highlights the essential design consideration while implementing this feature.
-
Option 1: Export to a csv file.
-
Pros:
-
Easily transferable and shared to other computers.
-
Easily allows user to edit the exported data.
-
-
Cons:
-
Does not work well on other platforms such as mobile phones and iPads.
-
Slow to transfer the data to other computers. Have manually transfer the csv file through email, thumb drive or cloud drive.
-
-
-
Option 2 (current choice): Export through QR code.
-
Pros:
-
Allows data to be easily transferred to any device with QR code scanner.
-
Instantaneous data transfer upon scanning the QR code.
-
-
Cons:
-
Hard to be shared to other computers since computers generally do not have QR code scanner.
-
Focuses more on ready-only rather than editing the data.
-
-
Since Xpire is an application that helps users keep track of items' expiry dates as well as maintain a list of to-buy items for users' reference, its exported data should focus more on conveniently showing users the items' information rather than emphasise on editing the data.
As such, due to the nature of this application, option 2 was chosen since it can precisely meet the needs of the users, which is to be able to easily view the exported data anywhere and anytime through their mobile phones.
This feature allows users to filter out specific items either by name or by tag(s) through providing the relevant keyword(s). Items which contain any of the keywords will be shown on the view panel. For search by name, partial words can be matched. For search by tag, only exact words will be matched.
This implementation is under Logic and Model components.
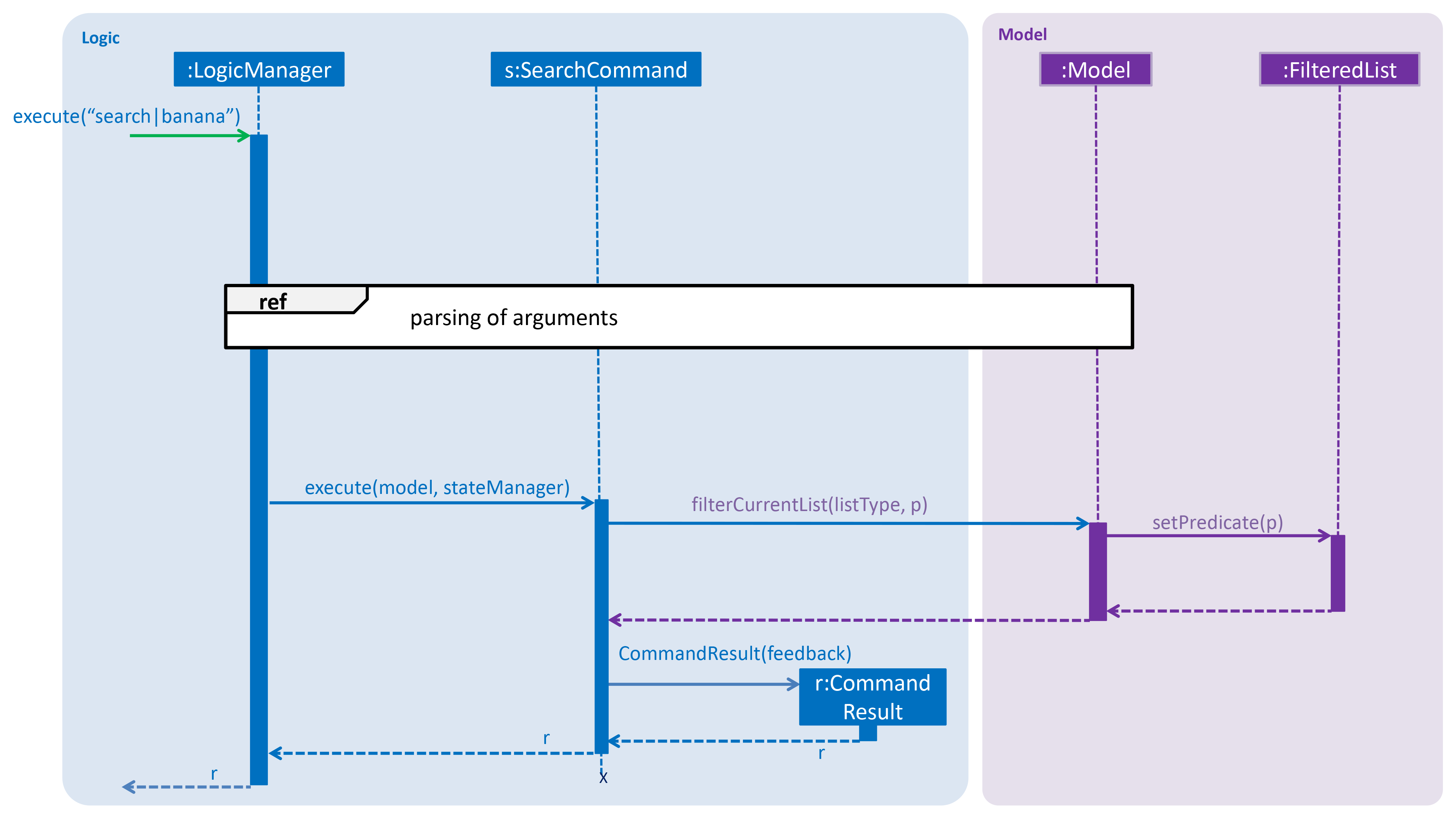
Below are the UML sequence diagrams an example usage scenario.
|
Note
|
Parsing of arguments is omitted from the diagram above to place greater emphasis on the filtering process. The diagram below further illustrates the parsing of arguments. |
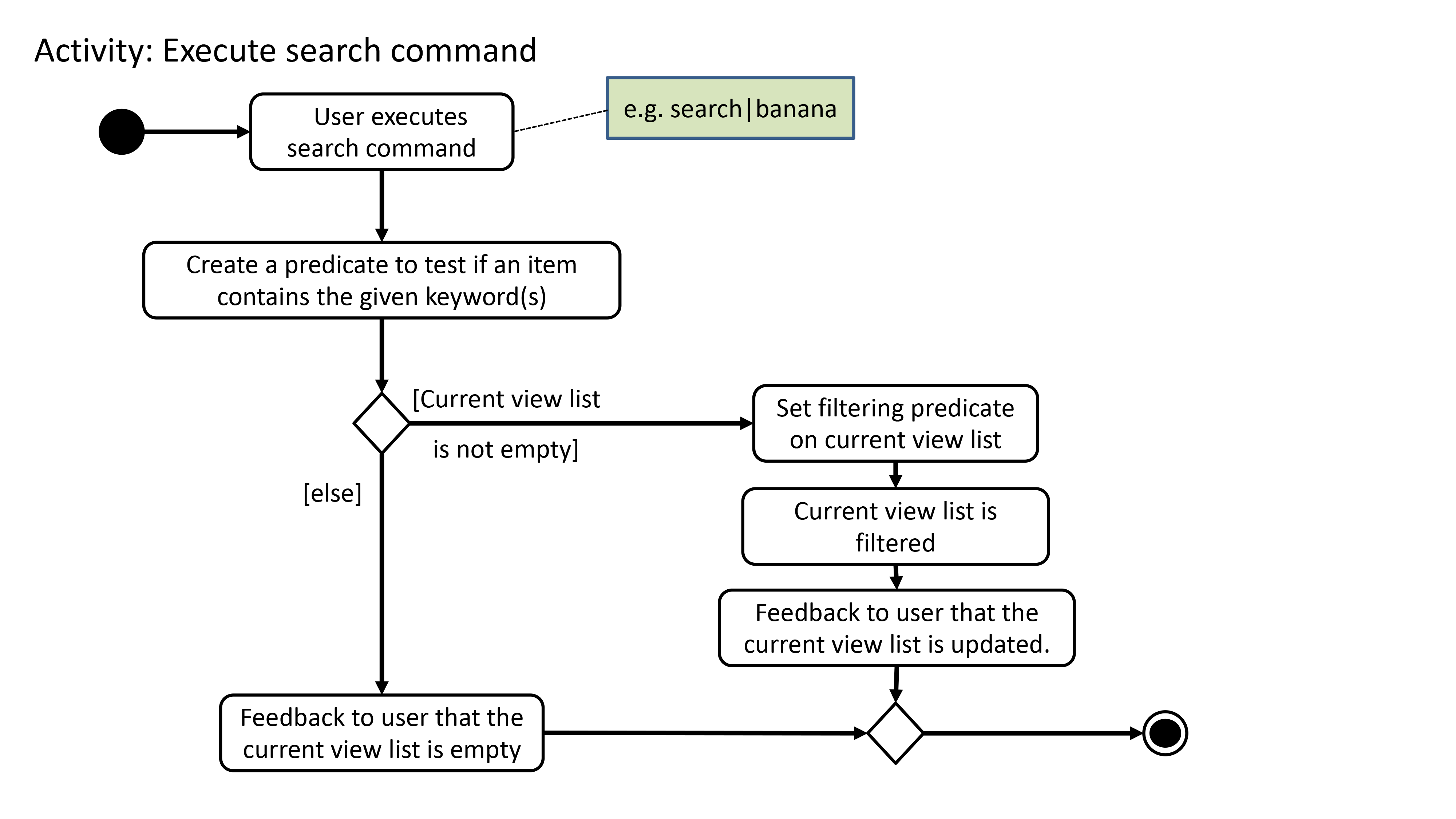
To further demonstrate the high-level workflow of the search command, the following UML activity diagram is provided:
|
Note
|
The selection of parser and the creation of SearchCommand object is omitted for brevity.
|
As illustrated in Figure 15, the search functionality also considers the case where the current view list
is empty and there will be a feedback to the user to inform him/her that the search command is not executed
successfully.
Below highlights the different considerations while implementing this feature.
-
Option 1 (initial choice): Modify the input command format to include "&" as a separator. The "&" separator will be placed between 2 keywords to signify an AND condition between the them.
-
Pros:
-
Requires only a single
searchcommand to do both AND and OR search. -
There is no need to change the original architecture for
Model.
-
-
Cons:
-
Complicates the input command format (since it has both "|" and "&" separators) and makes it not user-friendly.
-
Could be confusing to the user when they want to a mix of AND and OR conditions in a single
searchcommand. -
Could be difficult to parse correctly since there are 2 different separators.
-
Extra work has to be done to change the ContainsKeywordsPredicate to accept AND condition.
-
-
-
Option 2 (current choice): Make the
searchcommand "stackable". Everysearchcommand will now only execute on the current view list. e.g. the result of asearchcommand can be further filtered with anothersearchcommand.-
Pros:
-
Users can intuitively make an AND search of 2 or more keywords by first searching with 1 keyword and then search again with another keyword, and repeat again for more keywords.
-
There is no change to the input command format.
-
-
Cons:
-
Requires multiple
searchcommands to be executed for AND search. -
Have to figure out how to implement "stackable" commands.
-
-
-
Option 1 (current choice): Modify the
ModelManager.-
Pros:
-
Uses the separation of concerns principle. The commands do not need to know how the item list will behave when they are executed. They simply need to make the relevant Application Programming Interface (API) calls and the
ModelManagerwill handle the behaviour of the list. -
Adheres to the open-closed principle. The commands do not need to make any changes to its architecture and other commands can also be made "stackable" through using the API.
-
-
Cons:
-
Have to modify the
ModelManager's architecture to support the API that modifies the current view list.
-
-
-
Option 2: Modify the commands.
-
Pros:
-
Do not need to modify the API.
-
-
Cons:
-
Violates single responsibility principle. The commands will now handle both the execution algorithm and the behaviour of the item list.
-
Violates open-closed principle. The
Command's architecture will have to be modified to be "stackable".
-
-