A prototype of a new verinice version.
- Install Java 11.
- If you are using an IDE (Eclipse, IntelliJ, VSCode,...) you need to run it with the lombok compile time preprocessor. Simply download lombok.jar (i.e. from Maven Central) and run the helper: "java -jar lombok.jar". This will add the required parameter to your eclipse.ini or other configuration. If you want to do it by hand, add the following parameter at the end of your eclipse.ini:
-javaagent:/home/user/eclipse/lombok.jar
git clone ssh://[email protected]:7999/rd/v2020.git
cd v2020export JAVA_HOME=/path/to/jdk-11
./gradlew build [-x test]If you want to build a Docker image, you can then run
docker build --build-arg VEO_VERSON='0.1.0-SNAPSHOT' .You can configure the application by changing properties either as system environment variables, Java system property or by setting the properties in an application.properties file. Which means the following are equivalent:
-
System Environment:
export spring_datasource_url=jdbc:postgresql://127.0.0.1:5432/v2020 java -jar ./veo-rest/build/libs/veo-rest-0.1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar -
Java system property value:
java -Dspring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://127.0.0.1:5432/v2020 -jar ./veo-rest/build/libs/veo-rest-0.1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar -
Adding the line to application.properties:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://127.0.0.1:5432/v2020
The system environment variable approach has the advantage, that it works when running the built jar.
Note The system environment variable name is the same as the name of the property except dots are replaced by underscore, i.e.
The following sections describe commonly changed properties.
The database connection can be modified by setting the following properties as needed:
export spring_datasource_url=jdbc:postgresql://127.0.0.1:5432/v2020
export spring_datasource_username=verinice
export spring_datasource_password=verinice
export spring_datasource_driver-class-name=org.postgresql.Driver
export spring_jpa_database-platform=org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQLDialectYou can change the logging level per package by setting the property logging.level.<qualified package name>, e.g.
export logging_level_org_veo_rest_security=DEBUG
export logging_level_org_veo=TRACENote that you have to replace the dots in the package name with underscores.
This even works for specific test runs:
env 'logging_level_org_veo=DEBUG' ./gradlew veo-rest:test --tests 'AuthenticationMockMvcITSpec'Valid logging levels in ascending order are
ALLTRACEDEBUGINFOWARNERRORFATALOFF
You can log to files by setting the property logging.file, e.g.
export logging_file=/var/log/veo.logOf course if you want to see the logs and pipe them to a file you can always run
./gradlew sR | tee /var/log/veo.logThis also works for specific test runs:
env 'logging_file=/tmp/test.log' 'logging_level_org_veo=DEBUG' ./gradlew veo-rest:test --tests 'AuthenticationMockMvcITSpec'To configure more complex setups you can reference a logback.xml configuration file, by setting
the property logging.config
export logging_config=/etc/veo/logback.xmlWhen you do so, you may like to enable configuration auto scanning by setting
the scanPeriod attribute of the configuration tag.
e.g. you could change the logging level in the following logback.xml from error to debug
while the application is running:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration scan="true" scanPeriod="30 seconds" >
<include
resource="org/springframework/boot/logging/logback/base.xml" />
<logger name="org.veo" level="error" />
</configuration>- Install Java 11.
- Install MySQL, MariaDB or PostgreSQL
- Create an empty database v2020
Set your database properties in file veo-vna-import/src/main/resources/application.properties and rebuild the application.
./gradlew veo-vna-import:bootJar
java -jar veo-vna-import/build/libs/veo-vna-import-0.1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar \
-f /path/to/verinice-archive-file.vnaSet your database properties in file veo-rest/src/main/resources/application.properties and rebuild the application.
./gradlew veo-rest:bootRunor
./gradlew veo-rest:jar
java -jar veo-rest/build/libs/veo-rest-0.1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar./gradlew jmGui
./gradlew jmRun
The Swagger-UI is available after strarting the REST service at:
http://localhost:8070/swagger-ui.html
CAUTION: this URL will redirect you to http://localhost:8070/swagger-ui/index.html?configUrl=/v3/api-docs/swagger-config. Do NOT use this URL directly or the redirects for OpenID Connect authentication will not work.
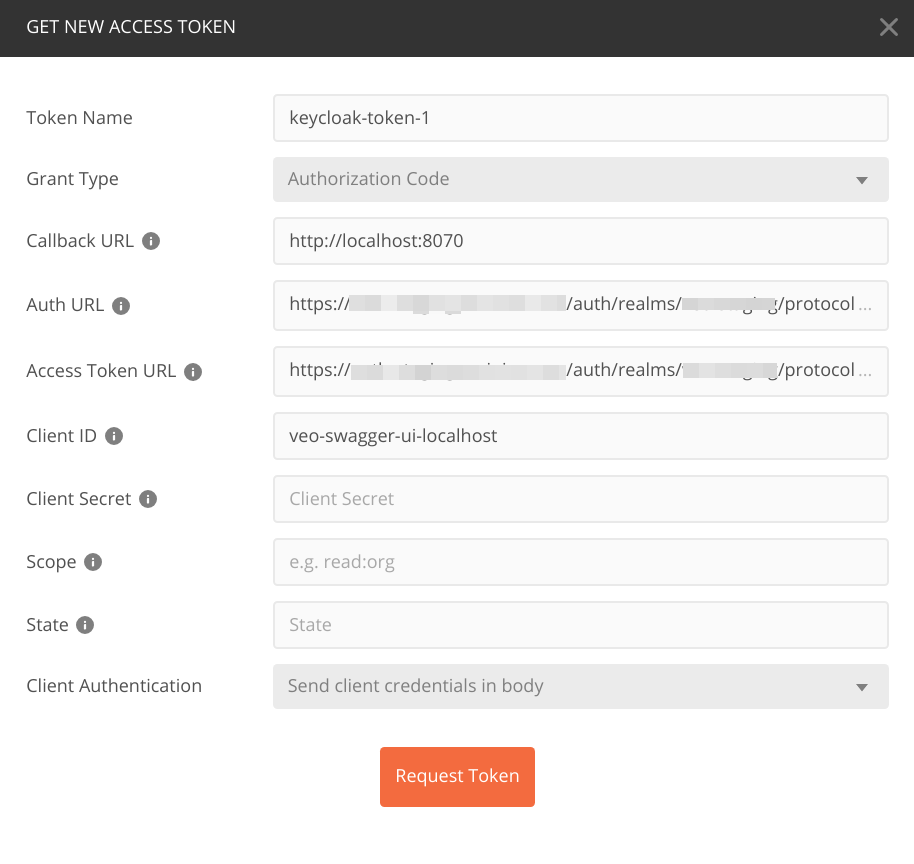
You can use postman to access and test the REST API. To set up the necessary authentication, got to the tab 'Authoization -> Get new access token'.
Enter the following details:
Use the following values:
- Auth URL: https://<KEYCLOAK_SERVER>/auth/realms/<REALM>/protocol/openid-connect/auth
- Access Token URL: https://<KEYCLOAK_SERVER>/auth/realms/<REALM>/protocol/openid-connect/token
Click on 'Request Token'. Enter your credentials. Then select the aquired token in the dropdown box 'Available Tokens'.
You can now send your HTTP request. The access token will time out (usually after 1-5 minutes) nad has to be requested again for another request.
This module contains the JAXB class files for accessing SNCA.xml from verinice.
This module contains the implementation of the REST services of the REST API.
The JSON schemas accepted by the API can be found in ${veo.basedir}/schemas/. If this directory does not exist, built-in schema files will be served as default.
veo.basedir can be set in application.properties and is /var/lib/veo by
default. The gradle task bootRun sets veo.basedir to
$HOME/.local/share/veo.
This module contains an importer for verinice archives (VNAs). It has to be fixed to work with the new data model.
Entity–relationship model of the database:
veo-rest uses OIDC to authorize users. To get an access token and access the API you can use any library supporting oAuth2. To test on the command line you can also use the script
misc/scripts/authenticate
to log in and get an access token and
misc/scripts/authorize
to use the access token and send a HTTP request to the API. See misc/scripts/README or
call ./misc/scripts/authenticate -h for more details.
(See the section on using postman for another alternative.)
Code styles are enforced using the gradle plugins pmd and spotless.
To verify your code run
./gradlew pmdMain
./gradlew spotlessCheck
or just
./gradlew check
You can find formatting settings for IDEs in misc/eclipse.
Spotless can fix code formatting violations by running
./gradlew spotlessApply
For some reason the ktlint plugin cannot apply fixes. To automatically format Kotlin files
you can install ktlint and run
ktlint -F
In the project root.
Sample git hooks are provided in misc/git, e.g. pre-commit, which checks the code style on each commit. To install, copy the file to .git/hooks/pre-commit, etc. Make sure the scripts are executable.