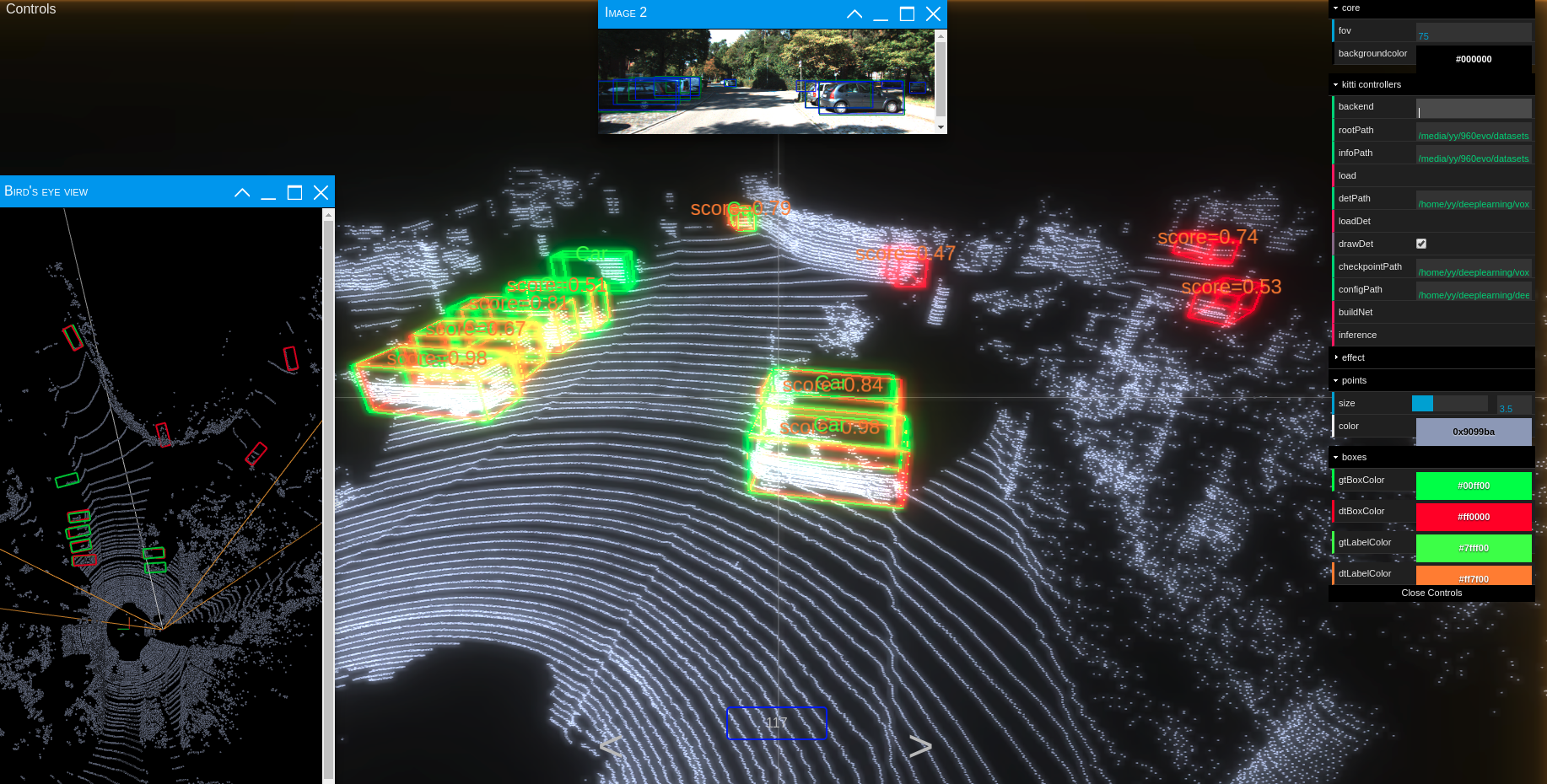
SECOND detector. Based on my unofficial implementation of VoxelNet with some improvements.
ONLY support python 3.6+, pytorch 0.4.1+. Don't support pytorch 0.4.0. Tested in Ubuntu 16.04/18.04.
- Ubuntu 18.04 have speed problem in my environment and may can't build/usr SparseConvNet.
Car [email protected], 0.70, 0.70:
bbox AP:90.80, 88.97, 87.52
bev AP:89.96, 86.69, 86.11
3d AP:87.43, 76.48, 74.66
aos AP:90.68, 88.39, 86.57
Car [email protected], 0.50, 0.50:
bbox AP:90.80, 88.97, 87.52
bev AP:90.85, 90.02, 89.36
3d AP:90.85, 89.86, 89.05
aos AP:90.68, 88.39, 86.57
git clone https://github.com/traveller59/second.pytorch.git
cd ./second.pytorch/secondIt is recommend to use Anaconda package manager.
pip install shapely fire pybind11 tensorboardX protobuf scikit-image numba pillowIf you don't have Anaconda:
pip install numbaFollow instructions in https://github.com/facebookresearch/SparseConvNet to install SparseConvNet.
Install Boost geometry:
sudo apt-get install libboost-all-devyou need to add following environment variable for numba.cuda, you can add them to ~/.bashrc:
export NUMBAPRO_CUDA_DRIVER=/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcuda.so
export NUMBAPRO_NVVM=/usr/local/cuda/nvvm/lib64/libnvvm.so
export NUMBAPRO_LIBDEVICE=/usr/local/cuda/nvvm/libdevice- Dataset preparation
Download KITTI dataset and create some directories first:
└── KITTI_DATASET_ROOT
├── training <-- 7481 train data
| ├── image_2 <-- for visualization
| ├── calib
| ├── label_2
| ├── velodyne
| └── velodyne_reduced <-- empty directory
└── testing <-- 7580 test data
├── image_2 <-- for visualization
├── calib
├── velodyne
└── velodyne_reduced <-- empty directory
- Create kitti infos:
python create_data.py create_kitti_info_file --data_path=KITTI_DATASET_ROOT- Create reduced point cloud:
python create_data.py create_reduced_point_cloud --data_path=KITTI_DATASET_ROOT- Create groundtruth-database infos:
python create_data.py create_groundtruth_database --data_path=KITTI_DATASET_ROOT- Modify config file
There is some path need to be configured in config file:
train_input_reader: {
...
database_sampler {
database_info_path: "/path/to/kitti_dbinfos_train.pkl"
...
}
kitti_info_path: "/path/to/kitti_infos_train.pkl"
kitti_root_path: "KITTI_DATASET_ROOT"
}
...
eval_input_reader: {
...
kitti_info_path: "/path/to/kitti_infos_val.pkl"
kitti_root_path: "KITTI_DATASET_ROOT"
}python ./pytorch/train.py train --config_path=./configs/car.config --model_dir=/path/to/model_dir-
Make sure "/path/to/model_dir" doesn't exist if you want to train new model. A new directory will be created if the model_dir doesn't exist, otherwise will read checkpoints in it.
-
training process use batchsize=3 as default for 1080Ti, you need to reduce batchsize if your GPU has less memory.
-
Currently only support single GPU training, but train a model only needs 20 hours (165 epoch) in a single 1080Ti and only needs 40 epoch to reach 74 AP in car moderate 3D in Kitti validation dateset.
python ./pytorch/train.py evaluate --config_path=./configs/car.config --model_dir=/path/to/model_dir- detection result will saved as a result.pkl file in model_dir/eval_results/step_xxx or save as official KITTI label format if you use --pickle_result=False.
Before using pretrained model, you need to modify some file in SparseConvNet because the pretrained model doesn't support SparseConvNet master:
- convolution.py
# self.weight = Parameter(torch.Tensor(
# self.filter_volume, nIn, nOut).normal_(
# 0,
# std))
self.weight = Parameter(torch.Tensor(
self.filter_volume * nIn, nOut).normal_(
0,
std))
# ...
# output.features = ConvolutionFunction.apply(
# input.features,
# self.weight,
output.features = ConvolutionFunction.apply(
input.features,
self.weight.view(self.filter_volume, self.nIn, self.nOut),- submanifoldConvolution.py
# self.weight = Parameter(torch.Tensor(
# self.filter_volume, nIn, nOut).normal_(
# 0,
# std))
self.weight = Parameter(torch.Tensor(
self.filter_volume * nIn, nOut).normal_(
0,
std))
# ...
# output.features = SubmanifoldConvolutionFunction.apply(
# input.features,
# self.weight,
output.features = SubmanifoldConvolutionFunction.apply(
input.features,
self.weight.view(self.filter_volume, self.nIn, self.nOut),You can download pretrained models in google drive. The car model is corresponding to car.config, the car_tiny model is corresponding to car.tiny.config and the people model is corresponding to people.config.
You can use a prebuilt docker for testing:
docker pull scrin/second-pytorch
Then run:
nvidia-docker run -it --rm -v /media/yy/960evo/datasets/:/root/data -v $HOME/pretrained_models:/root/model --ipc=host second-pytorch:latest
python ./pytorch/train.py evaluate --config_path=./configs/car.config --model_dir=/root/model/car
...
Currently there is a problem that training and evaluating in docker is very slow.
-
run
python ./kittiviewer/backend.py main --port=xxxxin your server/local. -
run
cd ./kittiviewer/frontend && python -m http.serverto launch a local web server. -
open your browser and enter http://127.0.0.1:8000.
-
input backend (http://your_server:your_backend_port)
-
input root path, info path and det path (optional)
-
click load, loadDet (optional), then click plot.
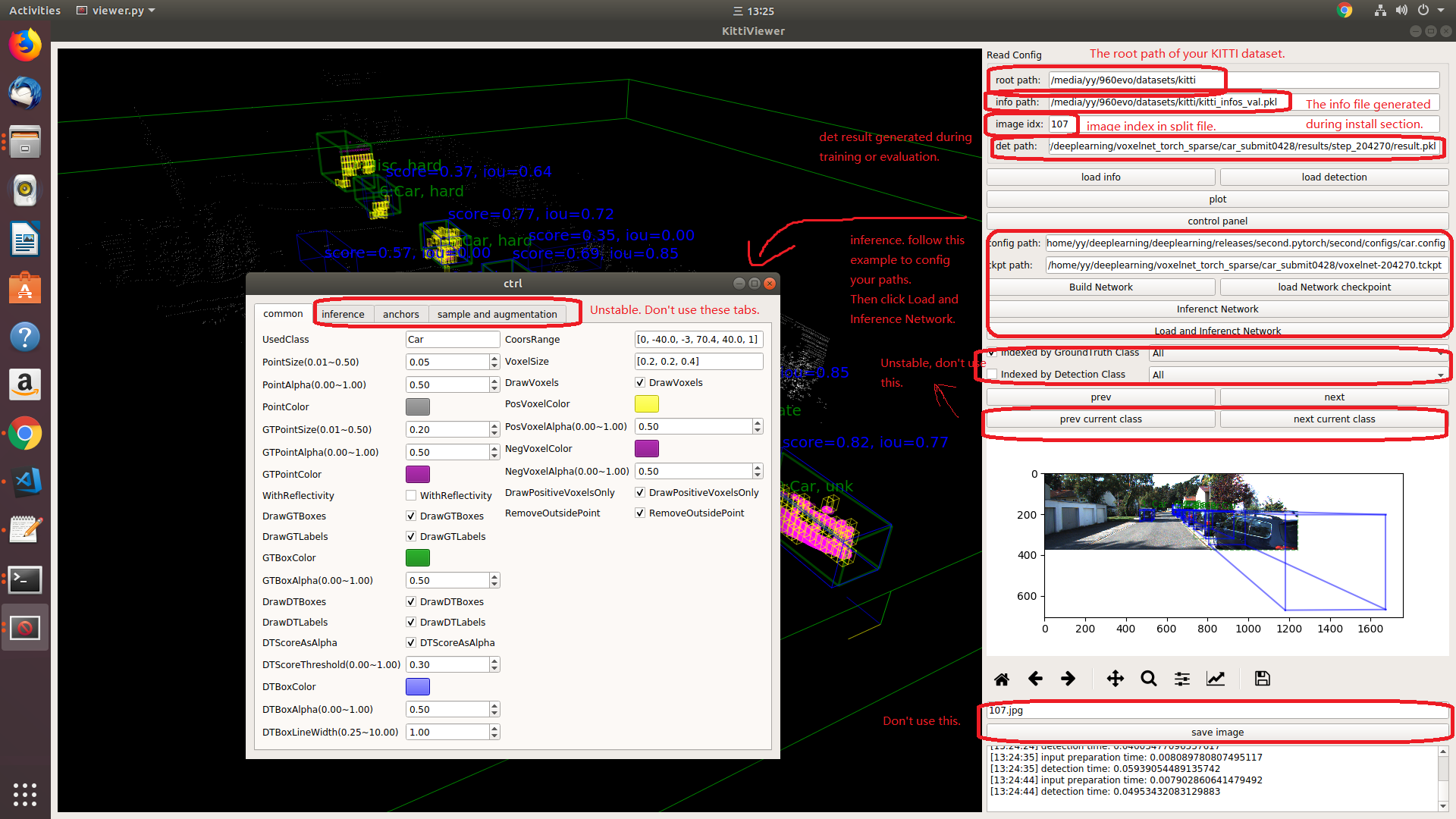
You should use kitti viewer based on pyqt and pyqtgraph to check data before training.
run python ./kittiviewer/viewer.py, check following picture to use kitti viewer:
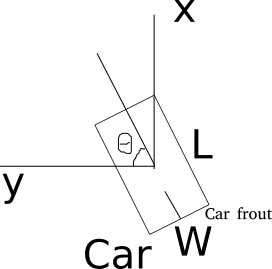
- Kitti lidar box
A kitti lidar box is consist of 7 elements: [x, y, z, w, l, h, rz], see figure.
All training and inference code use kitti box format. So we need to convert other format to KITTI format before training.
- Kitti camera box
A kitti camera box is consist of 7 elements: [x, y, z, l, h, w, ry].