分支:simple-bean-container
定义一个简单的bean容器BeanFactory,内部包含一个map用以保存bean,只有注册bean和获取bean两个方法
public class BeanFactory {
private Map<String, Object> beanMap = new HashMap<>();
public void registerBean(String name, Object bean) {
beanMap.put(name, bean);
}
public Object getBean(String name) {
return beanMap.get(name);
}
}
测试:BeanFactoryTest
@Test
public void testGetBean() throws Exception {
BeanFactory beanFactory = new BeanFactory();
beanFactory.registerBean("helloService", new HelloService());
HelloService helloService = (HelloService) beanFactory.getBean("helloService");
assertThat(helloService).isNotNull();
assertThat(helloService.sayHello()).isEqualTo("hello");
}
class HelloService {
public String sayHello() {
System.out.println("hello");
return "hello";
}
}
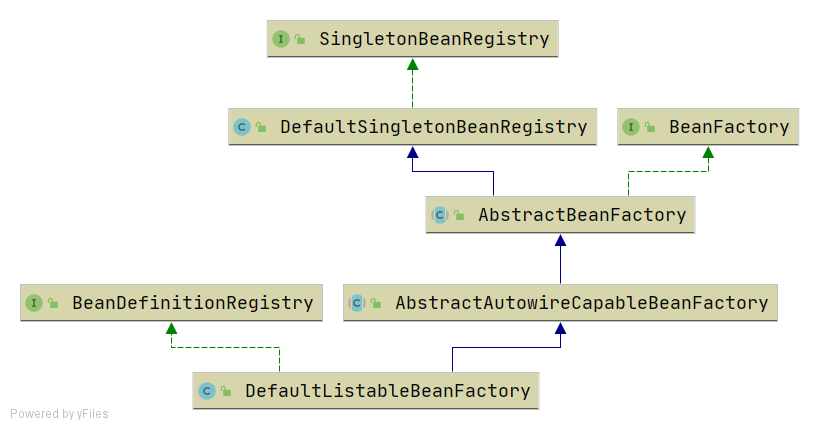
分支:bean-definition-and-bean-definition-registry
主要增加如下类:
- BeanDefinition,顾名思义,用于定义bean信息的类,包含bean的class类型、构造参数、属性值等信息,每个bean对应一个BeanDefinition的实例。简化BeanDefition仅包含bean的class类型。
- BeanDefinitionRegistry,BeanDefinition注册表接口,定义注册BeanDefintion的方法。
- SingletonBeanRegistry及其实现类DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry,定义添加和获取单例bean的方法。
bean容器作为BeanDefinitionRegistry和SingletonBeanRegistry的实现类,具备两者的能力。向bean容器中注册BeanDefintion后,使用bean时才会实例化。
测试:BeanFactoryTest
@Test
public void testBeanFactory() throws Exception {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition(HelloService.class);
beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition("helloService", beanDefinition);
HelloService helloService = (HelloService) beanFactory.getBean("helloService");
helloService.sayHello();
}
class HelloService {
public String sayHello() {
System.out.println("hello");
return "hello";
}
}
分支:instantiation-strategy
现在bean是在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean方法中用beanClass.newInstance()来实例化,仅适用于bean有无参构造函数的情况。针对bean的实例化,抽象出一个实例化策略的接口InstantiationStrategy,有两个实现类:
- SimpleInstantiationStrategy,使用bean的构造函数来实例化
- CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy,使用CGLIB动态生成子类
分支:populate-bean-with-property-values
在BeanDefinition中增加和bean属性对应的PropertyVales,实例化bean之后,为bean填充属性(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#applyPropertyValues)。 测试:BeanFactoryTest
@Test
public void testBeanFactory() throws Exception {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
PropertyValues propertyValues = new PropertyValues();
propertyValues.addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue("foo", "hello"));
propertyValues.addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue("bar", "world"));
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition(HelloService.class, propertyValues);
beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition("helloService", beanDefinition);
HelloService helloService = (HelloService) beanFactory.getBean("helloService");
System.out.println(helloService.toString());
assertThat(helloService.getFoo()).isEqualTo("hello");
assertThat(helloService.getBar()).isEqualTo("world");
}
public class HelloService {
private String foo;
private String bar;
public String getFoo() {
return foo;
}
public void setFoo(String foo) {
this.foo = foo;
}
public String getBar() {
return bar;
}
public void setBar(String bar) {
this.bar = bar;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HelloService{" +
"foo='" + foo + '\'' +
", bar='" + bar + '\'' +
'}';
}
}