| title | description | services | documentationcenter | author | manager | editor | ms.assetid | ms.service | ms.workload | ms.tgt_pltfrm | ms.devlang | ms.topic | ms.date | ms.author |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Debug your Model in Azure Machine Learning | Microsoft Docs |
Explains how to How to debug your Model in Azure Machine Learning. |
machine-learning |
garyericson |
jhubbard |
cgronlun |
629dc45e-ac1e-4b7d-b120-08813dc448be |
machine-learning |
data-services |
na |
na |
article |
12/12/2016 |
bradsev;garye |
This article explains of how to debug your models in Microsoft Azure Machine Learning. Specifically, it covers the potential reasons why either of the following two failures might be encountered when running a model:
- the Train Model module produces an error
- the Score Model module produces incorrect results
[!INCLUDE machine-learning-free-trial]
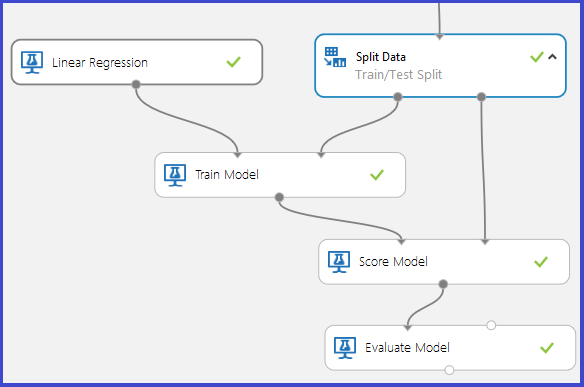
The Train Model Module expects the following two inputs:
- The type of Classification/Regression Model from the collection of models provided by Azure Machine Learning
- The training data with a specified Label column. The Label column specifies the variable to predict. The rest of the columns included are assumed to be Features.
This module produces an error in the following cases:
- The Label column is specified incorrectly because either more than one column is selected as the Label or an incorrect column index is selected. For example, the second case would apply if a column index of 30 was used with an input dataset which had only 25 columns.
- The dataset does not contain any Feature columns. For example, if the input dataset has only one column, which is marked as the Label column, there would be no features with which to build the model. In this case, the Train Model module produces an error.
- The input dataset (Features or Label) contains Infinity as a value.
In a typical training/testing graph for supervised learning, the Split Data module divides the original dataset into two parts: the part that is used to train the model and the part that is reserved to score how well the trained model performs on data it did not train on. The trained model is then used to score the test data, after which the results are evaluated to determine the accuracy of the model.
The Score Model module requires two inputs:
- A trained model output from Train Model module
- A scoring dataset that is different from the dataset used to train the model
It may happen that even though the experiment succeeds, the Score Model module produces incorrect results. Several scenarios may cause this to happen:
- If the specified Label is categorical and a regression model is trained on the data, an incorrect output would be produced by the Score Model module. This is because regression requires a continuous response variable. In this case, it would be more suitable to use a classification model.
- Similarly, if a classification model is trained on a dataset having floating point numbers in the Label column, it may produce undesirable results. This is because classification requires a discrete response variable that only allows values that range over a finite, and usually somewhat small, set of classes.
- If the scoring dataset does not contain all the features used to train the model, the Score Model produces an error.
- If a row in the scoring dataset contains a missing value or an infinite value for any of its features, the Score Model will not produce any output corresponding to that row.
- The Score Model may produce identical outputs for all rows in the scoring dataset. This could occur, for example, when attempting classification using Decision Forests if the minimum number of samples per leaf node is chosen to be more than the number of training examples available.