This integration monitors your Cloudera Data Platform through the Datadog Agent, allowing you to submit metrics and service checks on the health of your Cloudera Data Hub clusters, hosts, and roles.
Follow the instructions below to install and configure this check for an Agent running on a host. For containerized environments, see the Autodiscovery Integration Templates for guidance on applying these instructions.
The Cloudera check is included in the Datadog Agent package. No additional installation is needed on your server.
The Cloudera check requires version 7 of Cloudera Manager.
-
In Cloudera Data Platform, navigate to the Management Console and click on the User Management tab.
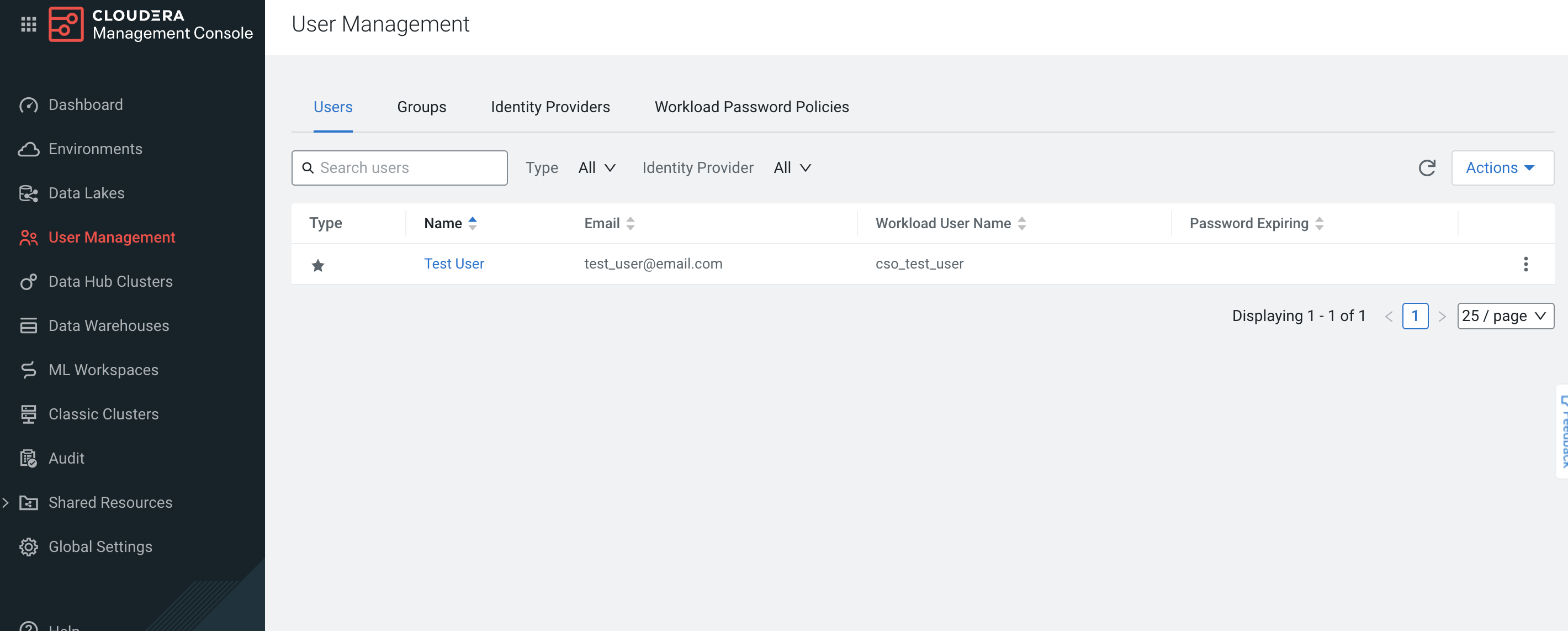
-
Click on Actions, then Create Machine User to create the machine user that queries the Cloudera Manager through the Datadog Agent.
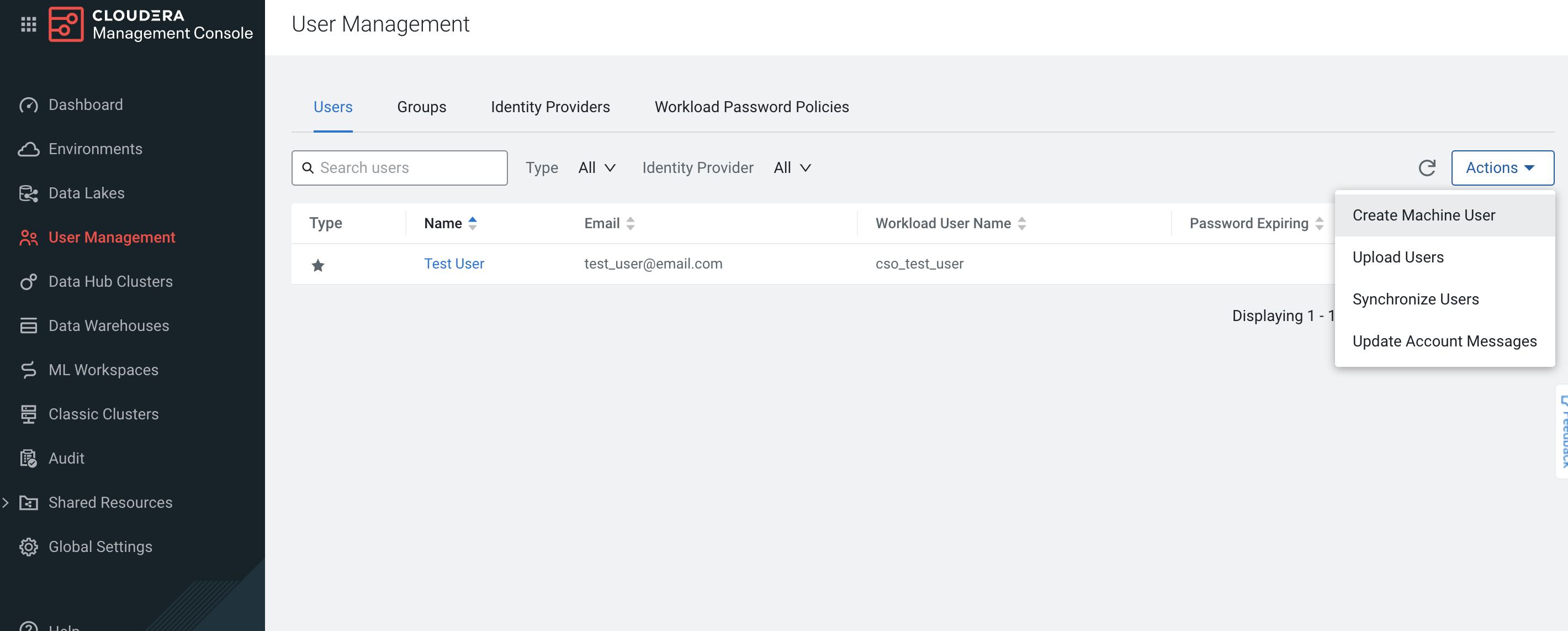
-
If the workload password hasn't been set, click on Set Workload Password after the user is created.
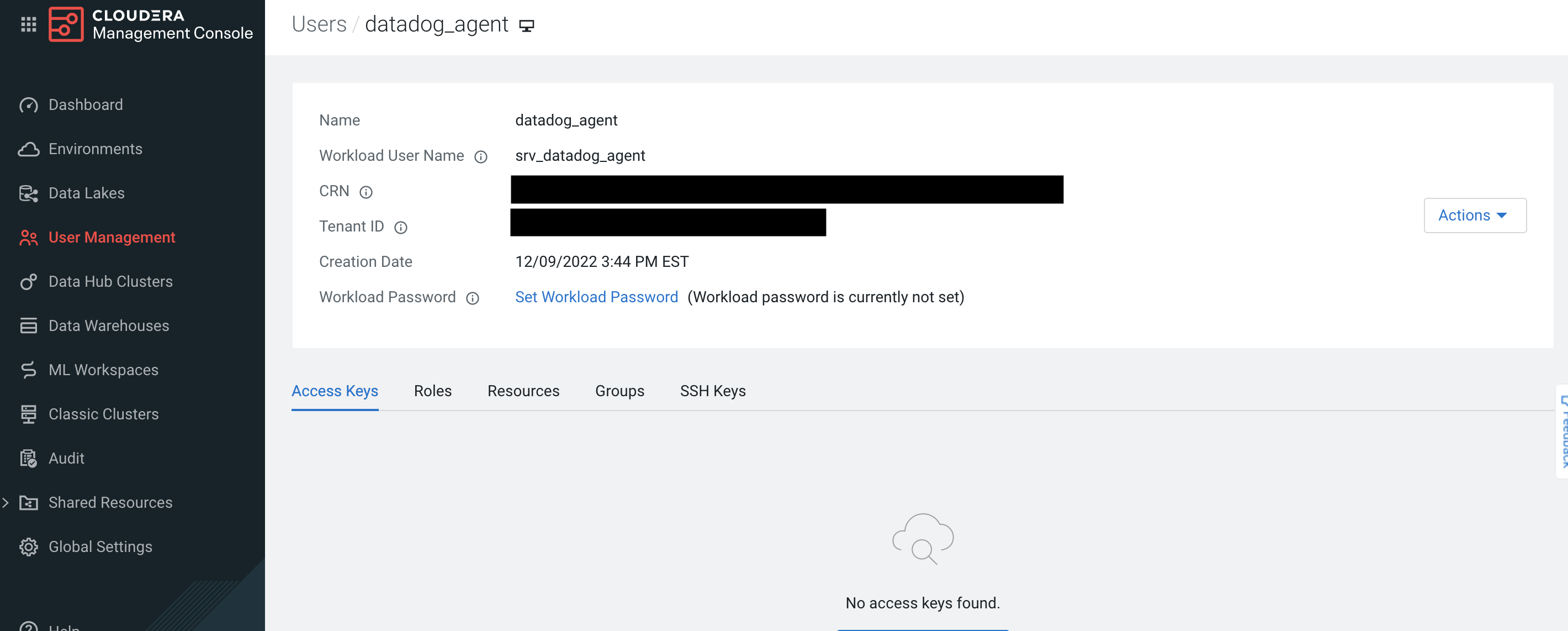
-
Edit the
cloudera.d/conf.yamlfile, in theconf.d/folder at the root of your Agent's configuration directory to start collecting your Cloudera cluster and host data. See the sample cloudera.d/conf.yaml for all available configuration options.
Note: Theapi_urlshould contain the API version at the end.init_config: ## @param workload_username - string - required ## The Workload username. This value can be found in the `User Management` tab of the Management ## Console in the `Workload User Name`. # workload_username: <WORKLOAD_USERNAME> ## @param workload_password - string - required ## The Workload password. This value can be found in the `User Management` tab of the Management ## Console in the `Workload Password`. # workload_password: <WORKLOAD_PASSWORD> ## Every instance is scheduled independently of the others. # instances: ## @param api_url - string - required ## The URL endpoint for the Cloudera Manager API. This can be found under the Endpoints tab for ## your Data Hub to monitor. ## ## Note: The version of the Cloudera Manager API needs to be appended at the end of the URL. ## For example, using v48 of the API for Data Hub `cluster_1` should result with a URL similar ## to the following: ## `https://cluster1.cloudera.site/cluster_1/cdp-proxy-api/cm-api/v48` # - api_url: <API_URL>
-
Restart the Agent to start collecting and sending Cloudera Data Hub cluster data to Datadog.
For containerized environments, see the Autodiscovery Integration Templates for guidance on applying the parameters below.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
<INTEGRATION_NAME> |
cloudera |
<INIT_CONFIG> |
{"workload_username": "<WORKLOAD_USERNAME>", 'workload_password": "<WORKLOAD_PASSWORD>"} |
<INSTANCE_CONFIG> |
{"api_url": <API_URL>"} |
You can configure how your clusters are discovered with the clusters configuration option with the following parameters:
-
limit: Maximum number of items to be autodiscovered.
Default value:None(all clusters will be processed) -
include: Mapping of regular expression keys and component config values to autodiscover.
Default value: empty map -
exclude: List of regular expressions with the patterns of components to exclude from autodiscovery.
Default value: empty list -
interval: Validity time in seconds of the last list of clusters obtained through the endpoint.
Default value:None(no cache used)
Examples:
Process a maximum of 5 clusters with names that start with my_cluster:
clusters:
limit: 5
include:
- 'my_cluster.*'Process a maximum of 20 clusters and exclude those with names that start with tmp_:
clusters:
limit: 20
include:
- '.*'
exclude:
- 'tmp_.*'You can configure the Cloudera integration to collect custom metrics that are not be collected by default by running custom timeseries queries. These queries use the tsquery language to retrieve data from Cloudera Manager.
Example:
Collect JVM garbage collection rate and JVM free memory with cloudera_jvm as a custom tag:
custom_queries:
- query: select last(jvm_gc_rate) as jvm_gc_rate, last(jvm_free_memory) as jvm_free_memory
tags: cloudera_jvmNote: These queries can take advantage of metric expressions, resulting in queries such as total_cpu_user + total_cpu_system, 1000 * jvm_gc_time_ms / jvm_gc_count, and max(total_cpu_user). When using metric expressions, make sure to also include aliases for the metrics, otherwise the metric names may be incorrectly formatted. For example, SELECT last(jvm_gc_count) results in the metric cloudera.<CATEGORY>.last_jvm_gc_count. You can append an alias like in the following example: SELECT last(jvm_gc_count) as jvm_gc_count to generate the metric cloudera.<CATEGORY>.jvm_gc_count.
Run the Agent's status subcommand and look for cloudera under the Checks section.
See metadata.csv for a list of metrics provided by this integration.
The Cloudera integration collects events that are emitted from the /events endpoint from the Cloudera Manager API. The event levels are mapped as the following:
| Cloudera | Datadog |
|---|---|
UNKNOWN |
error |
INFORMATIONAL |
info |
IMPORTANT |
info |
CRITICAL |
error |
See service_checks.json for a list of service checks provided by this integration.
To install the Datadog Agent on a Cloudera host, make sure that the security group associated with the host allows SSH access.
Then, you need to use the root user cloudbreak when accessing the host with the SSH key generated during the environment creation:
sudo ssh -i "/path/to/key.pem" cloudbreak@<HOST_IP_ADDRESS>
The workload username and password can be used to access Cloudera hosts through SSH, although only the cloudbreak user can install the Datadog Agent.
Trying to use any user that is not cloudbreak may result in the following error:
<NON_CLOUDBREAK_USER> is not allowed to run sudo on <CLOUDERA_HOSTNAME>. This incident will be reported.
If you see something similar to the following in the Agent status when collecting metrics from your Cloudera host:
Config Errors
==============
zk
--
open /etc/datadog-agent/conf.d/zk.d/conf.yaml: permission denied
You need to change the ownership of the conf.yaml to dd-agent:
[cloudbreak@<CLOUDERA_HOSTNAME> ~]$ sudo chown -R dd-agent:dd-agent /etc/datadog-agent/conf.d/zk.d/conf.yaml
Need help? Contact Datadog support.
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: