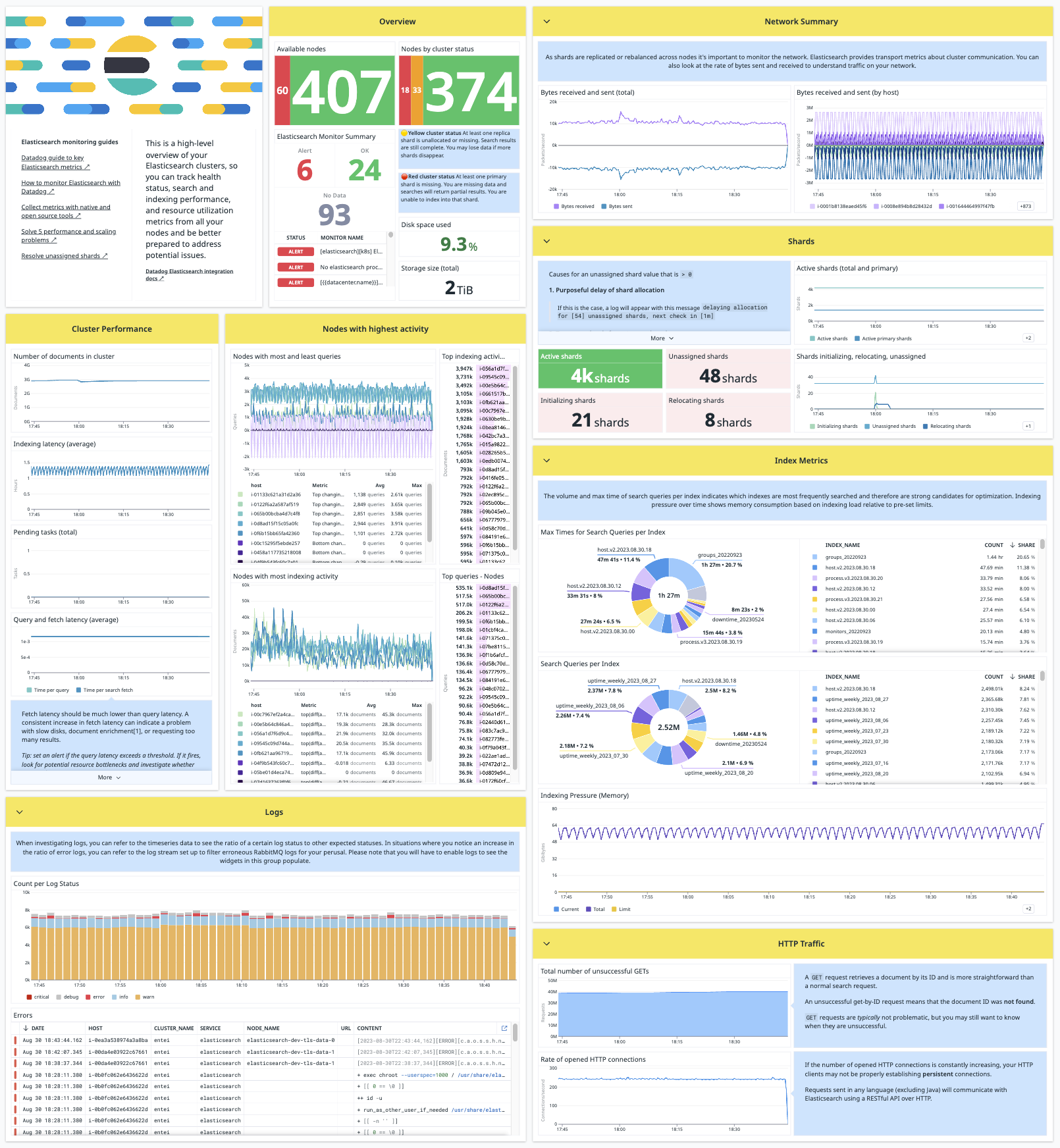
Stay up-to-date on the health of your Elasticsearch cluster, from its overall status down to JVM heap usage and everything in between. Get notified when you need to revive a replica, add capacity to the cluster, or otherwise tweak its configuration. After doing so, track how your cluster metrics respond.
The Datadog Agent's Elasticsearch check collects metrics for search and indexing performance, memory usage and garbage collection, node availability, shard statistics, disk space and performance, pending tasks, and many more. The Agent also sends events and service checks for the overall status of your cluster.
The Elasticsearch check is included in the Datadog Agent package. No additional installation is necessary.
To configure this check for an Agent running on a host:
-
Edit the
elastic.d/conf.yamlfile, in theconf.d/folder at the root of your Agent's configuration directory to start collecting your Elasticsearch metrics. See the sample elastic.d/conf.yaml for all available configuration options.init_config: instances: ## @param url - string - required ## The URL where Elasticsearch accepts HTTP requests. This is used to ## fetch statistics from the nodes and information about the cluster health. # - url: http://localhost:9200
Notes:
-
If you're collecting Elasticsearch metrics from just one Datadog Agent running outside the cluster, such as using a hosted Elasticsearch, set
cluster_statstotrue. -
Agent-level tags are not applied to hosts in a cluster that is not running the Agent. Use integration level tags in
<integration>.d/conf.yamlto ensure ALL metrics have consistent tags. For example:init_config: instances: - url: "%%env_MONITOR_ES_HOST%%" username: "%%env_MONITOR_ES_USER%%" password: ********* auth_type: basic cluster_stats: true tags: - service.name:elasticsearch - env:%%env_DD_ENV%%
-
To use the Agent's Elasticsearch integration for the AWS Elasticsearch services, set the
urlparameter to point to your AWS Elasticsearch stats URL. -
All requests to the Amazon ES configuration API must be signed. See the Making and signing OpenSearch Service requests for details.
-
The
awsauth type relies on boto3 to automatically gather AWS credentials from.aws/credentials. Useauth_type: basicin theconf.yamland define the credentials withusername: <USERNAME>andpassword: <PASSWORD>. -
You must create a user and a role (if you don't already have them) in Elasticsearch with the proper permissions to monitor. This can be done through the REST API offered by Elasticsearch, or through the Kibana UI.
-
If you have enabled security features in Elasticsearch, you can use
monitorormanageprivilege while using the API to make the calls to the Elasticsearch indices. -
Include the following properties in the created role:
name = "datadog" indices { names = [".monitoring-*", "metricbeat-*"] privileges = ["read", "read_cross_cluster", "monitor"] } cluster = ["monitor"]
Add the role to the user:
roles = [<created role>, "monitoring_user"]For more information, see create or update roles and create or update users.
-
The Elasticsearch integration allows you to collect custom metrics through custom queries by using the custom_queries configuration option.
Note: When running custom queries, use a read only account to ensure that the Elasticsearch instance does not change.
custom_queries:
- endpoint: /_search
data_path: aggregations.genres.buckets
payload:
aggs:
genres:
terms:
field: "id"
columns:
- value_path: key
name: id
type: tag
- value_path: doc_count
name: elasticsearch.doc_count
tags:
- custom_tag:1The custom query sends as a GET request. If you use an optional payload parameter, the request sends as a POST request.
value_path may either be string keys or list indices. Example:
{
"foo": {
"bar": [
"result0",
"result1"
]
}
}value_path: foo.bar.1 returns the value result1.
Datadog APM integrates with Elasticsearch to see the traces across your distributed system. Trace collection is enabled by default in the Datadog Agent v6+. To start collecting traces:
- Enable trace collection in Datadog.
- Instrument your application that makes requests to Elasticsearch.
Available for Agent versions >6.0
-
Collecting logs is disabled by default in the Datadog Agent, enable it in the
datadog.yamlfile with:logs_enabled: true
-
To collect search slow logs and index slow logs, configure your Elasticsearch settings. By default, slow logs are not enabled.
-
To configure index slow logs for a given index
<INDEX>:curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/<INDEX>/_settings?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' { "index.indexing.slowlog.threshold.index.warn": "0ms", "index.indexing.slowlog.threshold.index.info": "0ms", "index.indexing.slowlog.threshold.index.debug": "0ms", "index.indexing.slowlog.threshold.index.trace": "0ms", "index.indexing.slowlog.level": "trace", "index.indexing.slowlog.source": "1000" }'
-
To configure search slow logs for a given index
<INDEX>:curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/<INDEX>/_settings?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' { "index.search.slowlog.threshold.query.warn": "0ms", "index.search.slowlog.threshold.query.info": "0ms", "index.search.slowlog.threshold.query.debug": "0ms", "index.search.slowlog.threshold.query.trace": "0ms", "index.search.slowlog.threshold.fetch.warn": "0ms", "index.search.slowlog.threshold.fetch.info": "0ms", "index.search.slowlog.threshold.fetch.debug": "0ms", "index.search.slowlog.threshold.fetch.trace": "0ms" }'
-
-
Add this configuration block to your
elastic.d/conf.yamlfile to start collecting your Elasticsearch logs:logs: - type: file path: /var/log/elasticsearch/*.log source: elasticsearch service: "<SERVICE_NAME>"
-
Add additional instances to start collecting slow logs:
- type: file path: "/var/log/elasticsearch/\ <CLUSTER_NAME>_index_indexing_slowlog.log" source: elasticsearch service: "<SERVICE_NAME>" - type: file path: "/var/log/elasticsearch/\ <CLUSTER_NAME>_index_search_slowlog.log" source: elasticsearch service: "<SERVICE_NAME>"
Change the
pathandserviceparameter values and configure them for your environment.
-
To configure this check for an Agent running on a container:
Set Autodiscovery Integrations Templates as Docker labels on your application container:
LABEL "com.datadoghq.ad.check_names"='["elastic"]'
LABEL "com.datadoghq.ad.init_configs"='[{}]'
LABEL "com.datadoghq.ad.instances"='[{"url": "http://%%host%%:9200"}]'Collecting logs is disabled by default in the Datadog Agent. To enable it, see Docker Log Collection.
Then, set Log Integrations as Docker labels:
LABEL "com.datadoghq.ad.logs"='[{"source":"elasticsearch","service":"<SERVICE_NAME>"}]'APM for containerized apps is supported on Agent v6+ but requires extra configuration to begin collecting traces.
Required environment variables on the Agent container:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
<DD_API_KEY> |
api_key |
<DD_APM_ENABLED> |
true |
<DD_APM_NON_LOCAL_TRAFFIC> |
true |
See Tracing Kubernetes Applications and the Kubernetes Daemon Setup for a complete list of available environment variables and configuration.
Then, instrument your application container and set DD_AGENT_HOST to the name of your Agent container.
To configure this check for an Agent running on Kubernetes:
Set Autodiscovery Integrations Templates as pod annotations on your application container. Aside from this, templates can also be configured with a file, a configmap, or a key-value store.
Annotations v1 (for Datadog Agent < v7.36)
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: elasticsearch
annotations:
ad.datadoghq.com/elasticsearch.check_names: '["elastic"]'
ad.datadoghq.com/elasticsearch.init_configs: '[{}]'
ad.datadoghq.com/elasticsearch.instances: |
[
{
"url": "http://%%host%%:9200"
}
]
spec:
containers:
- name: elasticsearchAnnotations v2 (for Datadog Agent v7.36+)
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: elasticsearch
annotations:
ad.datadoghq.com/elasticsearch.checks: |
{
"elastic": {
"init_config": {},
"instances": [
{
"url": "http://%%host%%:9200"
}
]
}
}
spec:
containers:
- name: elasticsearchCollecting logs is disabled by default in the Datadog Agent. To enable it, see the Kubernetes Log Collection.
Then, set Log Integrations as pod annotations. This can also be configured with a file, a configmap, or a key-value store.
Annotations v1/v2
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: elasticsearch
annotations:
ad.datadoghq.com/elasticsearch.logs: '[{"source":"elasticsearch","service":"<SERVICE_NAME>"}]'
spec:
containers:
- name: elasticsearchAPM for containerized apps is supported on hosts running Agent v6+ but requires extra configuration to begin collecting traces.
Required environment variables on the Agent container:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
<DD_API_KEY> |
api_key |
<DD_APM_ENABLED> |
true |
<DD_APM_NON_LOCAL_TRAFFIC> |
true |
See Tracing Kubernetes Applications and the Kubernetes Daemon Setup for a complete list of available environment variables and configuration.
Then, instrument your application container and set DD_AGENT_HOST to the name of your Agent container.
To configure this check for an Agent running on ECS:
Set Autodiscovery Integrations Templates as Docker labels on your application container:
{
"containerDefinitions": [{
"name": "elasticsearch",
"image": "elasticsearch:latest",
"dockerLabels": {
"com.datadoghq.ad.check_names": "[\"elastic\"]",
"com.datadoghq.ad.init_configs": "[{}]",
"com.datadoghq.ad.instances": "[{\"url\": \"http://%%host%%:9200\"}]"
}
}]
}Collecting logs is disabled by default in the Datadog Agent. To enable it, see ECS Log Collection.
Then, set Log Integrations as Docker labels:
{
"containerDefinitions": [{
"name": "elasticsearch",
"image": "elasticsearch:latest",
"dockerLabels": {
"com.datadoghq.ad.logs": "[{\"source\":\"elasticsearch\",\"service\":\"<SERVICE_NAME>\"}]"
}
}]
}APM for containerized apps is supported on Agent v6+ but requires extra configuration to begin collecting traces.
Required environment variables on the Agent container:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
<DD_API_KEY> |
api_key |
<DD_APM_ENABLED> |
true |
<DD_APM_NON_LOCAL_TRAFFIC> |
true |
See Tracing Kubernetes Applications and the Kubernetes Daemon Setup for a complete list of available environment variables and configuration.
Then, instrument your application container and set DD_AGENT_HOST to the EC2 private IP address.
Run the Agent's status subcommand and look for elastic under the Checks section.
By default, not all of the following metrics are sent by the Agent. To send all metrics, configure flags in elastic.yaml as shown above.
pshard_statssends elasticsearch.primaries.* and elasticsearch.indices.count metricsindex_statssends elasticsearch.index.* metricspending_task_statssends elasticsearch.pending_* metricsslm_statssends elasticsearch.slm.* metrics
See metadata.csv for a list of metrics provided by this integration.
The Elasticsearch check emits an event to Datadog each time the overall status of your Elasticsearch cluster changes - red, yellow, or green.
See service_checks.json for a list of service checks provided by this integration.