只找当前最优,不再进行回溯,不记录曾经走过的路;可能达不到最优解,但如果可以使用贪心算法得到最优结果,则贪心算法的探索过程一定是最优的,因为其没有额外的内存消耗,且时间方面也是最优的。
问题的关键是什么情况下可以使用贪心算法?
1、
2、
贪心就在于:面对20元找零时,优先用掉10元面额的,逗人呢?
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
public boolean lemonadeChange(int[] bills) {
if(bills == null || bills.length == 0) {
return true;
}
map.put(5, 0);
map.put(10, 0);
map.put(20, 0);
//模拟付账
for (int i = 0; i < bills.length; i++) {
int curPrice = bills[i];
int returnCount = 0;
map.put(curPrice, map.get(curPrice)+1);
if(curPrice == 5) continue;
if(curPrice == 10) {
if(map.get(5) == 0) {
return false;
}
map.put(5, map.get(5)-1);
} else { //curPrice == 20
if(map.get(10) > 0 && map.get(5) > 0) { // 1.第一种能通过的情况
map.put(10,map.get(10)-1);
map.put(5,map.get(5)-1);
} else if(map.get(10) == 0 && map.get(5) >= 3) { //2. 第二种能通过的情况
map.put(5,map.get(5)-3);
} else { // 通不过的情况
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}思路:
只要后者比前者大,则有利润,
//最大利润:
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
if (prices == null) return 0;
int profit = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
if(prices[i] > prices[i-1]) {
profit += prices[i] - prices[i-1];
}
}
return profit;
}思路:1、饼干满足最小需求;2、饼干和需求尽可能相近;
public int findContentChildren(int[] g, int[] s) {
if(g == null || g.length == 0 || s == null || s.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int gLen = g.length;
int sLen = s.length;
int i= 0;
int j= 0;
Arrays.sort(g);
Arrays.sort(s);
int count = 0;
while (i < gLen && j < sLen) {
if(g[i] <= s[j]) {
count++;
i++;
j++;
} else {
j++;
}
}
return count;
}public int robotSim(int[] commands, int[][] obstacles) {
if(commands == null || commands.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int result = 0;
int x = 0,y = 0,direction = 0; //x,y代表当前坐标
int[][] xy = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}}; //北移、东移、西移、南移
//存储到set中进行判断
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int[] array:obstacles) {
set.add(array[0]+","+array[1]);
}
for (int com:commands) {
if(com == -2) {
// 左转
direction = (direction+3)%4; //相当于右转了三次
} else if(com == -1) {
// 右转
direction = (direction+1)%4;
} else {
//在指定方向前进com步
for (int i = 1; i <= com; i++) {
int newX = x+xy[direction][0];
int newY = y+xy[direction][1];
//判断是否是障碍物
if(set.contains(newX+","+newY)) {
break;
}
//没有障碍物
x = newX;
y = newY;
result = Math.max(result,x*x+y*y);
}
}
}
return result;
}思路:如何判断某一个位置可以达到?
在每个节点处最远可到达下标为:当前下标 i + nums[i]
怎么能到达 j 下标? j <= 最远可到达的位置
public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return false;
}
int len = nums.length;
int maxGet = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if(i <= maxGet) {
//能够到达
maxGet = Math.max(maxGet, i+nums[i]);
} else {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}//反向查找,查找第一个离终点最近的点
public int jump(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int end = nums.length-1;
int step = 0;
while (end > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < end; i++) {
if (i + nums[i] >= end) {
end = i;
step++;
break;
}
}
}
return step;
}//正向贪心查找
public int jump1(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int step = 0;
int locMax = 0;
int end = 0; //记录当前边界
//作用:探索当前能够达到的最大
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length-1; i++) {
locMax = Math.max(locMax, i+nums[i]);
if(i == end) { //到达边界
step++;
end = locMax; //新边界变为当前能够到达的最远
}
}
return step;
}使用条件:
- 单调
- 存在上下界
- 索引访问
在满足上面三者调价下才可以使用,在一些半有序的情况下有时也可以使用。
- 暴力求解
public int mySqrt(int x) {
int i = x / 2 +1;
for (long j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
if(j*j == x) {
//找到了
return (int)j;
} else if(j*j > x) {
return (int)j-1;
}
}
return -1;
}- 二分查找求解
public int mySqrt1(int x) {
if(x==0 || x==1) {
return x;
}
int left = 1;
int right = x/2;
while (left < right) {
int mid = left+(right-left)/2;
if(mid*mid > x) {
right = mid-1;
} else {
left = mid+1;
}
}
return right;
}- 牛顿迭代法
int s;
//牛顿迭代法
public int mySqrt3(int x) {
s = x;
s=x;
if(x==0) return 0;
return ((int)(sqrts(x)));
}
public double sqrts(double x){
double res = (x + s / x) / 2;
if (res == x) {
return x;
} else {
return sqrts(res);
}
}- 牛顿迭代法的优雅实现方式
public int mySqrt4(int x) {
long s = x;
while (s*s > x) {
s = (s+x/s)/2;
}
return (int)s;
}要注意Integer越界问题:mid*mid可能大于Integer.MAX_VALUE
public boolean isPerfectSquare(int num) {
if(num == 1) {
return true;
}
int left = 1;
int right = num/2;
while (left <= right) {
long mid = left + (right-left)/2;
if(mid*mid == num) {
return true;
} else if(mid*mid > num) {
right = (int)mid - 1;
} else if(mid*mid < num) {
left = (int)mid + 1;
}
}
return false;
}- 牛顿迭代法
public boolean isPerfectSquare(int num) {
if (num < 2) return true;
long x = num / 2;
while (x * x > num) {
x = (x + num / x) / 2;
}
return (x * x == num);
}- 一次二分查找
思路:将矩阵拼接(即整体计算,需要横纵坐标时,再进行计算),通过一次二分查找寻找target。
class Solution {
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
int low = 0, high = m * n - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (high - low) / 2 + low;
int x = matrix[mid / n][mid % n];
if (x < target) {
low = mid + 1;
} else if (x > target) {
high = mid - 1;
} else {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}- 两次二分查找
思路:先按列进行二分查找,找rowIndex,找到后,再按普通的二分查找找结果。
class Solution {
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
int rowIndex = binarySearchFirstColumn(matrix, target);
if (rowIndex < 0) {
return false;
}
return binarySearchRow(matrix[rowIndex], target);
}
public int binarySearchFirstColumn(int[][] matrix, int target) {
int low = -1, high = matrix.length - 1;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (high - low + 1) / 2 + low;
if (matrix[mid][0] <= target) {
low = mid;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return low;
}
public boolean binarySearchRow(int[] row, int target) {
int low = 0, high = row.length - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (high - low) / 2 + low;
if (row[mid] == target) {
return true;
} else if (row[mid] > target) {
high = mid - 1;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return false;
}
}- 使用二分查找,寻找一个半有序数组 [4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2] 中间无序的地方 说明:同学们可以将自己的思路、代码写在第 3 周的学习总结中
动态规划四步走:
1、dp数组:存什么?要多大?每个元素代表什么?是一维还是二维?是dp[n+1] 还是dp[m][n]还是dp[m+1][n+1]?
2、基本状态是什么?dp[i][j]代表的含义是什么?
基本状态确定了,进行初始化;
dp[i]有两种含义:
1、 dp[i]为前[0,i]中最大...的和,即最后的结果为dp[i]
2、dp[i]为以nums[i]为结尾的最...,即最终的结果还需要将dp数组进行遍历获取最大值。
dp[i][j]的含义是到第(i,j)位的什么值? 这里有两种定义方式同上
3、基本状态初始化后,需要确定迭代的方向:
dp[n] : 从左往右
dp[m][n]:
1、从左往右,从上至下
2、从下至上,从左往右
确定遍历的原则为:已经求出来的解,在接下来的迭代中能够被使用。
4、 确定最后的返回值
- 组合数学方式
m行n列:向下走m-1步,向右走n-1步;从(m-1+n-1)中选出m-1步向下走;即采用排列组合中的组合方式:$C_{m+n-2}^{m-1}$.
排列组合公式:
排列:
组合:
但要担心计算过程中超出int 和 long的范围
class Solution {
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
//组合数学方式 C m+n-2 m-1
return (int)(factorial(m+n-2)/factorial(m-1)/factorial(n-1));
}
private long factorial(int i) {
long sum = 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
sum *= j;
}
return sum;
}
}出错原因:超出了long的范围
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
int N = n + m - 2;
double res = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) //巧妙
res = res * (N - (m - 1) + i) / i;
return (int) res;
}
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-paths/solution/dong-tai-gui-hua-di-gui-gong-shi-deng-3z-9mp1/- 自顶向下:
傻递归
//递归方式:自顶向下方式
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
return recursion(0, 0, m, n);
}
//进行递归,计算[i,j]到[m-1,n-1]的路径条数
private int recursion(int i, int j, int m, int n) {
if (i == m - 1 || j == n - 1) {
return 1;
}
return recursion(i + 1, j, m, n) + recursion(i, j + 1, m, n);
}递归+记忆化搜索
思想:
//递归方式:自顶向下方式 + 记忆化搜索
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
int[][] dp= new int[m][n]; //递归不需要dp数组
//基础状态处理
//处理最后一列,列不变,行变
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
dp[i][n-1] = 1;
}
//处理最后一行,行不变,列变
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dp[m-1][i] = 1;
}
//进行递归,来填充dp数组
recursion(0, 0, dp);
for (int[] array:dp) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
return dp[0][0];
}
//进行递归,计算[i,j]到[m-1,n-1]的路径条数
private int recursion(int i, int j, int[][] dp) {
//不需要进行这个结束判断
/*if (i == dp.length - 1 || j == dp[0].length - 1) {
return 1;
}*/
if(dp[i][j] == 0) {
dp[i][j] = recursion(i + 1, j, dp) + recursion(i, j + 1, dp);
}
return dp[i][j];
}自底向上:使用动态规划思路
1、基础状态
2、存储中间状态
3、寻找状态转移方程
动态规划:这种方式好理解
//自底向上:动态规划递推方式 空间复杂度为:O(mn)
public int uniquePaths3(int m, int n) {
//从左上到右下 == 从右下走到左上
int[][] dp = new int[m][n];
//初始化状态
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) dp[i][0] = 1; //行变,列不变
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) dp[0][i] = 1; //列变,行不变
//递推:dp[i][j] = dp[i+1][j] + dp[i][j+1]
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + dp[i][j-1];
}
}
return dp[m-1][n-1];
}优化:空间复杂度O(n)
class Solution {
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
int[] cur = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(cur,1);
for (int i = 1; i < m;i++){
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++){
cur[j] += cur[j-1] ;
}
}
return cur[n-1];
}
}思考:关键点在于处理障碍物节点,构建dp数组时进行限制,限制那个点的值为0
class Solution {
public int uniquePathsWithObstacles(int[][] obstacleGrid) {
int m = obstacleGrid.length;
int n = obstacleGrid[0].length;
//创建dp数组
int[][] dp = new int[m][n];
//构建基本状态
for (int i = 0; i < dp.length;i++) {
if(obstacleGrid[i][0]==1) {
break;
}
dp[i][0] = 1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < dp[0].length; i++) {
if(obstacleGrid[0][i]==1) {
break;
}
dp[0][i] = 1;
}
//递推:dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j]+dp[i][j-1] 但要排除obstacleGrid[i][j] == 1
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
if(obstacleGrid[i][j] == 0) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j]+dp[i][j-1];
}
}
}
return dp[m-1][n-1];
}
}求一个最长公共子序列的问题 转换为 二维数组递推问题:如何能够定义动态规划问题的状态
dp方程:
//有时这种方式不太好理解
public int longestCommonSubsequence1(String text1, String text2) {
int m = text1.length();
int n = text2.length();
int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1]; //不需要初始化,默认初始化为0
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (text1.charAt(i - 1) == text2.charAt(j - 1)) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}- 应用空格技巧的动态规划
即在所需处理的字符串前增加一个空格,防止越界,也方便了dp数组的初始化。
//应用空格技巧的动态规划
public int longestCommonSubsequence(String text1, String text2) {
int m = text1.length();
int n = text2.length();
text1 = " "+text1;
text2 = " "+text2;
int[][] dp = new int[m+1][n+1];
//dp数组初始化
for (int i = 0; i < m+1; i++) dp[i][0] = 1; //行变列不变
for (int i = 0; i < n+1; i++) dp[0][i] = 1; //列变行不变
//进行递推
for (int i = 1; i < m+1; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < n+1; j++) {
if(text1.charAt(i) == text2.charAt(j)) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1]+1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]);
}
}
}
return dp[m][n]-1; //最终减去空字符所引起的重复
}tag:滑动窗口
- 题目
输入:nums = [1,3,5,4,7]
输出:3
解释:最长连续递增序列是 [1,3,5], 长度为3。
尽管 [1,3,5,7] 也是升序的子序列, 但它不是连续的,因为 5 和 7 在原数组里被 4 隔开。 - 想法
1、连续的递增子序列,递增序列是连续的,所以可以记录每个递增子序列的长度,然后最终结果为最长的那个保留下来。
怎么记录每个递增子序列的长度? i-index+1 即为个数
遍历的方式,i不断的向后探索,再来一个指针记录最开始的那个index、
什么时候索引发生改变?
后者<=前者的时候,进行改变初始索引位置- 解答
// 通式,思路清晰
class Solution {
public int findLengthOfLCIS(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length <= 1) {
return nums.length;
}
int count = 0;
int start = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(nums[i] <= nums[i-1]) {
start = i;
}
count = Math.max(count, i-start+1);
}
return count;
}
}- 另一种解
//一种笨拙的dp方式
public int findLengthOfLCIS(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int n = nums.length;
//dp[i]: 代表到达nums[i]当前这个值时,最大连续递增子序列为dp[i],最终结果还要从中找最大
//而不是前[0,i]位的最大连续递增子序列
int[] dp = new int[n];
dp[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if(nums[i] > nums[i-1]) {
dp[i] = dp[i-1]+1;
} else {
dp[i] = 1;
}
}
//遍历查找最大
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
max = dp[i]>max?dp[i]:max;
}
return max;
}输入:nums = [10,9,2,5,3,7,101,18]
输出:4
解释:最长递增子序列是 [2,3,7,101],因此长度为 4 。
- 想法
不连续的递增子序列,无法使用滑动窗口的思路,使用dp的思路
1、dp数组是一维还是二维? 需要两头操作才使用二维,这里dp[n]
2、dp[i]代表什么? 两种定义方式:1、以nums[i]结尾的递增子序列的长度;2、[0,i]中的最长序列长度
两种定义方式区别:1、在遍历一遍nums后得到dp[i]后,需要重新遍历获得dp数组的最大值
2、若dp[i]代表nums[0,i]的最长递增序列,则最终返回的为dp[n-1]
采用1方式:dp[i] = 找左侧第一位比nums[i]小的,dp[j]+1,一直迭代到最后即可
找左侧第一位比nums[i]小的,并不一定是最长的子序列数组,因为第一位小的并不一定是最长的子序列,前边可能有有比当前这位小的,但是更长的子序列。
采用第2种:前一位nums[i-1]<nums[i]时:dp[i] = dp[i-1]+1
前一位nums[i-1]>=nums[i]时:也应该为dp[i] = dp[i-1],但dp[i]并不是只跟它的前1位有关,这种方式,只可以处理连续的递增子序列,无法处理不连续的递增子序列。
3、确定采用dp[i]的第一种含义
4、初始状态: dp[0] = 1
5、最优子结构: dp[]
- 解答
public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0) return 0;
int[] dp = new int[nums.length];
Arrays.fill(dp,1); //用1进行填充
//构建dp数组中的每一个值
for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++) {
//负责填充dp[i]->dp[nums.length-1]
for(int j=0; j<i; j++) {//确定每一个dp[i]的值
if(nums[i] > nums[j]) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i],dp[j]+1);
}
}
}
//获取最长子序列长度:即为dp数组的最大值
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i<dp.length; i++) {
res = Math.max(res,dp[i]);
}
return res;
}tag:困难 动态规划
- 题目描述
给你一个二维整数数组 envelopes ,其中 envelopes[i] = [wi, hi] ,表示第 i 个信封的宽度和高度。
当另一个信封的宽度和高度都比这个信封大的时候,这个信封就可以放进另一个信封里,如同俄罗斯套娃一样。
请计算 最多能有多少个 信封能组成一组“俄罗斯套娃”信封(即可以把一个信封放到另一个信封里面)。
注意:不允许旋转信封。
输入:envelopes = [[5,4],[6,4],[6,7],[2,3]]
输出:3
解释:最多信封的个数为 3, 组合为: [2,3] => [5,4] => [6,7]。
输入:envelopes = [[1,1],[1,1],[1,1]]
输出:1- 思路
求最大值问题,最大能套多少?使用dp方式
可以使用先对envelopes按照第一个元素排序,排好后就按照数组第二位,求取最长子序列
- 解答
class Solution {
public int maxEnvelopes(int[][] envelopes) {
//先排序
Arrays.sort(envelopes, new Comparator<int[]>() { //先按第
@Override
public int compare(int[] o1, int[] o2) {
return o1[0]-o2[0];
}
});
int len = envelopes.length;
int[] dp = new int[len];
Arrays.fill(dp,1); //用1进行填充
//构建dp数组中的每一个值
for(int i=0; i<len; i++) {
//负责填充dp[i]->dp[nums.length-1]
for(int j=0; j<i; j++) {//确定每一个dp[i]的值
if (envelopes[i][0] > envelopes[j][0] && envelopes[i][1] > envelopes[j][1]) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i],dp[j]+1);
}
}
}
//获取最长子序列长度:即为dp数组的最大值
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i<dp.length; i++) {
res = Math.max(res,dp[i]);
}
return res;
}
}tag:简单 动态规划
- 题目
输入一个整型数组,数组中的一个或连续多个整数组成一个子数组。求所有子数组的和的最大值。要求时间复杂度为O(n)。
示例1:
输入: nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4]
输出: 6
解释: 连续子数组 [4,-1,2,1] 的和最大,为 6。- 思路
没法用滑动窗口,因为不确定多会收缩左侧索引- 解答
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
if(nums==null || nums.length==0) {
return 0;
}
int n = nums.length;
int[] dp = new int[n];
// dp[i]:代表以nums[i]为尾的最大连续子数组的和,最终遍历一遍
//另一种表现含义:dp[i]:第i位时的最大连续子数组的和,最终返回dp[n-1]
//初始状态:全都为0
dp[0] = nums[0];
//dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i-1],)
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i-1]+nums[i],nums[i]);
}
int res = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res = res>dp[i]?res:dp[i];
}
return res;
}
}tag:动态规划 hard
- 题目
给你两个单词 word1 和 word2,请你计算出将 word1 转换成 word2 所使用的最少操作数 。
你可以对一个单词进行如下三种操作:
插入一个字符
删除一个字符
替换一个字符
示例 1:
输入:word1 = "horse", word2 = "ros"
输出:3
解释:
horse -> rorse (将 'h' 替换为 'r')
rorse -> rose (删除 'r')
rose -> ros (删除 'e')
示例 2:
输入:word1 = "intention", word2 = "execution"
输出:5
解释:
intention -> inention (删除 't')
inention -> enention (将 'i' 替换为 'e')
enention -> exention (将 'n' 替换为 'x')
exention -> exection (将 'n' 替换为 'c')
exection -> execution (插入 'u')- 思路
两个字符串,从一个变为另一个,一般两个字符串用i、j两个指针,从后往前一步步往前走,缩小问题的规模。
- 方法1:递归方式 -> 超出了时间限制
//1.使用递归的方式
public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
if (word1 == null || word1.length() == 0) return word2.length();
if (word2 == null || word2.length() == 0) return word1.length();
return recursion(word1, word2, word1.length() - 1, word2.length() - 1);
}
private int recursion(String s1, String s2, int i, int j) {
//结束状态
if (i < 0) return j + 1;
if (j < 0) return i + 1;
//子结构
if (s1.charAt(i) == s2.charAt(j)) {
return recursion(s1, s2, i - 1, j - 1);
} else {
return Math.min(Math.min(
recursion(s1, s2, i - 1, j) + 1, //删除
recursion(s1, s2, i, j - 1)+1 //添加
), recursion(s1, s2, i - 1, j - 1) + 1 );//替换
}
}- 方法2:递归优化 -> 加dptable,记录每个过程中产生的值
题目:
思路:
双指针方式,扩展中心法,以每个值为基,进行处理,保存最长的串。
这里需要考虑奇、偶回文情况;然后选取最长的。
class Solution {
public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
if(s==null || s.length()==0||s.length()==1) {
return s;
}
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
String res = "";
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
//以i为基的最长
String oddRes = getMaxLengthSubStr(s,i,i);
String evenRes = getMaxLengthSubStr(s,i,i+1);
//int len = Math.max(oddRes.length(), evenRes.length());
if(oddRes.length()>evenRes.length() && oddRes.length()>res.length()) {
res = oddRes;
} else if(oddRes.length()<=evenRes.length() && evenRes.length()>res.length()){
res = evenRes;
}
}
return res;
}
private String getMaxLengthSubStr(String s, int l, int r) {
while(l>=0 && r<s.length()&& s.charAt(l) == s.charAt(r)) {
l--;
r++;
}
return s.substring(l+1, r);
}
}//思路:存到hashMap中<c,count>,遍历hash表,偶数位+;奇数位不管,最后加1
public int longestPalindrome(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() == 1) {
return s.length();
}
//遍历,存到hashMap
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
HashMap<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
//System.out.println(map.get(chars[i]) == null?0:map.get(chars[i]));
map.put(chars[i], (map.get(chars[i]) == null ? 0 : map.get(chars[i])) + 1);
}
//遍历map
Set<Character> keys = map.keySet();
int sum = 0;
int odd = 0; //是否有奇数
for (Character c : keys) {
if(map.get(c)%2 == 0) {
sum += map.get(c);
} else { //奇数
//sum += (map.get(c)/2*2);//有多少个成对的
sum = sum + map.get(c)-1;
odd = 1;
}
}
return sum+odd;
}正着读和反着读都一样的序列,必须是子序列
- 单个序列使用二维dp数组
思路:
dp(i,j) 表示以 (i, j)(i,j) 为右下角且只包含 1 的正方形的边长最大值。如果我们能计算出所有 \textit{dp}(i, j)dp(i,j) 的值,那么其中的最大值即为矩阵中只包含 1 的正方形的边长最大值,其平方即为最大正方形的面积。
计算 dp 中的每个元素值呢?对于每个位置 (i, j),检查在矩阵中该位置的值:
如果该位置的值是 0,则 dp(i, j) = 0dp(i,j)=0,因为当前位置不可能在由 11 组成的正方形中;
如果该位置的值是 1,则 dp(i,j) 的值由其上方、左方和左上方的三个相邻位置的 dp 值决定。具体而言,当前位置的元素值等于三个相邻位置的元素中的最小值加 1,状态转移方程如下: dp(i,j)=min(dp(i−1,j),dp(i−1,j−1),dp(i,j−1))+1
作者:LeetCode-Solution 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximal-square/solution/zui-da-zheng-fang-xing-by-leetcode-solution/ 来源:力扣(LeetCode) 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
class Solution {
public int maximalSquare(char[][] matrix) {
int maxSide = 0;
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
return maxSide;
}
int rows = matrix.length, columns = matrix[0].length;
int[][] dp = new int[rows][columns]; //dp数组
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < columns; j++) {
if (matrix[i][j] == '1') {
if (i == 0 || j == 0) {
dp[i][j] = 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.min(Math.min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]), dp[i - 1][j - 1]) + 1;
}
maxSide = Math.max(maxSide, dp[i][j]);
}
}
}
int maxSquare = maxSide * maxSide;
return maxSquare;
}
}- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/climbing-stairs/description/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/triangle/description/
- https://leetcode.com/problems/triangle/discuss/38735/Python-easy-to-understand-solutions-(top-down-bottom-up)
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-subarray/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-product-subarray/description/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/coin-change/description/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/climbing-stairs/description/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/triangle/description/
- https://leetcode.com/problems/triangle/discuss/38735/Python-easy-to-understand-solutions-(top-down-bottom-up)
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-subarray/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-product-subarray/description/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/coin-change/description/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/house-robber/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/house-robber-ii/description/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock/#/description
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-ii/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-iii/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-with-cooldown/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-iv/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-with-transaction-fee/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock/solution/yi-ge-fang-fa-tuan-mie-6-dao-gu-piao-wen-ti-by-l-3/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/perfect-squares/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/edit-distance/ (重点)
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/jump-game/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/jump-game-ii/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-paths/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-paths-ii/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-paths-iii/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/coin-change/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/coin-change-2/
注意:请大家先消化前面的实战题目,高级 DP 的方法和题解会在课程后面解锁。
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-valid-parentheses/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-path-sum/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/edit-distance/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/decode-ways
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximal-square/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/max-sum-of-rectangle-no-larger-than-k/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/frog-jump/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/split-array-largest-sum
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/student-attendance-record-ii/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/task-scheduler/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindromic-substrings/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-window-substring/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/burst-balloons/
树的定义:
二叉搜索树:
- 二叉搜索树中序遍历是有序的。
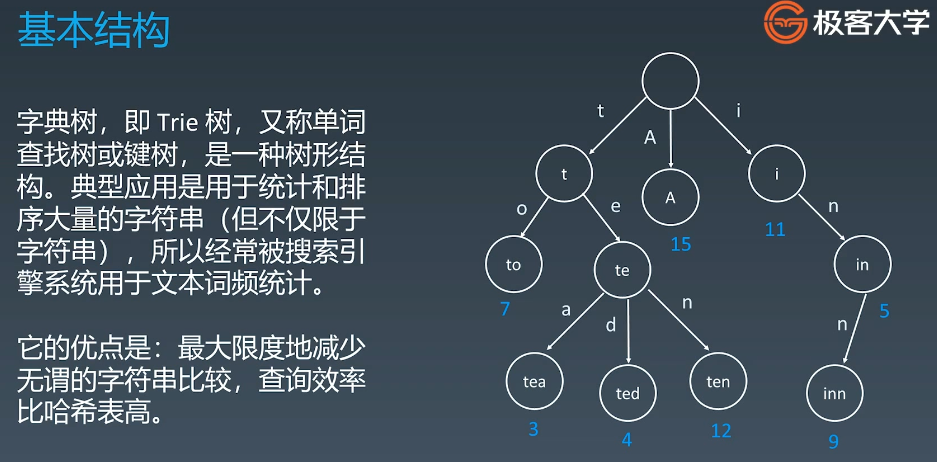
现实中的一个实际问题:根据词频进行推荐显示,用什么数据结构?二叉搜索树便于搜索而不便于插入。
在这里使用字典树(也称Trie树)
- 多叉树
- 根节点不存储字符,根节点存储去往每个字符的路径**(图示中的单词只是作示范,并非真正的存储效果)**
- 空间换时间
- 叶子节点才存储词频
1、节点本身不存储完整单词;
2、从根节点到某一节点,路径上经过的字符串连接起来,为该节点对应的字符串;
3、每个节点的所有子节点路径都不同;
4、节点可以存储额外的信息,如出现的频次,通过频次可以进行推荐信息
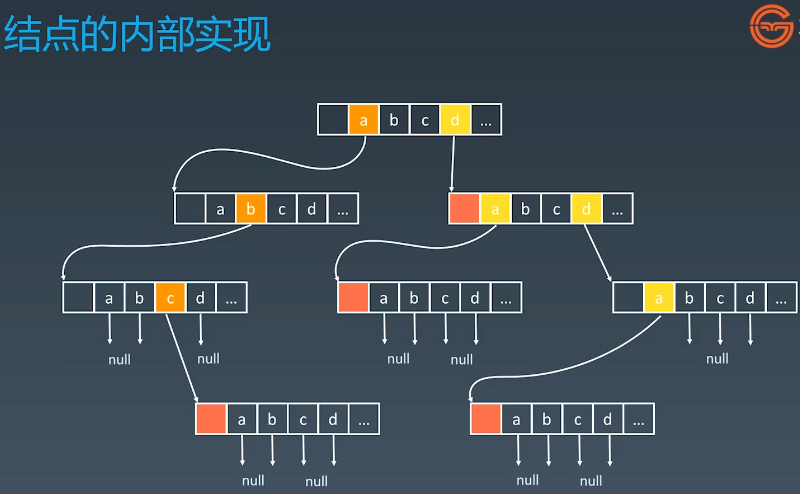
查询次数:等于单词有多少个字符
1、Trie树的核心思想是空间换时间
2、利用字符串的公共前缀来降低查询时候的时间开销以达到提高效率的目的
- python版
- Java版
采用数组方式存储子Trie,每个子节点均为Trie数组,共有0-25个位置,分别代表a-z这25个字符,不为null代表该位置所代表的单词有值,isEnd来标识是否到达一个单词的末尾。
class Trie {
Trie[] children;
Boolean isEnd;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public Trie() {
children = new Trie[26];
isEnd = false;
}
/** Inserts a word into the trie. */
public void insert(String word) {
Trie node = this;
Integer len = word.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char c = word.charAt(i);
int index = c-'a';
if(node.children[index] == null) {
node.children[index] = new Trie();
}
node = node.children[index];
}
node.isEnd = true;
}
public Trie searchPrefix(String word) {
//返回最终的那个node
Trie node = this;
Integer len = word.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char c = word.charAt(i);
int index = c-'a';
if(node.children[index] != null) {
node = node.children[index];
} else {
return null;
}
}
return node;
}
/** Returns if the word is in the trie. */
public boolean search(String word) {
Trie node = searchPrefix(word);
return node!= null && node.isEnd;
}
/** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
return searchPrefix(prefix)!= null;
}
}复杂版(可以不看)
class Trie {
Trie[] children;
Boolean isEnd;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public Trie() {
children = new Trie[26];
isEnd = false;
}
/** Inserts a word into the trie. */
public void insert(String word) {
Trie node = this;
Integer len = word.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char c = word.charAt(i);
int index = c-'a';
if(node.children[index] == null) {
node.children[index] = new Trie();
}
node = node.children[index];
}
node.isEnd = true;
}
/** Returns if the word is in the trie. */
public boolean search(String word) {
Trie node = this;
Integer len = word.length();
int index = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char c = word.charAt(i);
index = c-'a';
if(node.children[index] != null) {
node = node.children[index];
} else {
return false;
}
}
if(node.isEnd) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
/** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
Trie node = this;
Integer len = prefix.length();
int index = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char c = prefix.charAt(i);
index = c-'a';
if(node.children[index] != null) {
node = node.children[index];
} else {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}- 使用map+结束字符
使用map来存储,<key,value>结构为<char,Trie>,方便查询,而且节省空间
class Trie {
Map<Character, Trie> children;
char end_of_word;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public Trie() {
children = new HashMap();
end_of_word = '#';
}
/** Inserts a word into the trie. */
public void insert(String word) {
Trie node = this;
for (char c: word.toCharArray()) {
if(node.children.get(c) == null) {
node.children.put(c,new Trie());
}
node = node.children.get(c);
}
node.end_of_word = '@';
}
public Trie searchPrefix(String word) {
Trie node = this;
for (char c: word.toCharArray()) {
if(node.children.get(c) == null) {
return null;
} else {
node = node.children.get(c);
}
}
return node;
}
/** Returns if the word is in the trie. */
public boolean search(String word) {
Trie node = searchPrefix(word);
return node!= null && node.end_of_word == '@';
}
/** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
return searchPrefix(prefix)!= null;
}
}标签:
四联通、trie树、字符串搜索、字符串匹配、DFS
- 暴力解法
直接采用回溯+dfs进行四联通查找,发现会超出时间限制。一个word一个word的进行查找,每个word都需要将board遍历一遍,在board遍历过程中还需要进行四联通的DFS查找,故非常耗时间,其时间复杂度为O(单词个数N*m*n*单词的平均长度^4);
int[] dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int[] dy = {0, -1, 0, 1};
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
//暴力方式:暴力查找
public List<String> findWords(char[][] board, String[] words) {
//List<String> resList = new ArrayList<>();
if (board.length == 0 || board[0].length == 0 || board == null || words == null) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
int m = board.length, n = board[0].length;
//遍历查找
for (String word : words) {
boolean[][] isUsed = new boolean[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
dfs(board, word, 0, i, j, isUsed);
}
}
}
return new ArrayList<>(set);
}
private void dfs(char[][] board, String word, int curIndex, int i, int j, boolean[][] isUsed) {
if (curIndex >= word.length()) {
set.add(word);
return;
}
int m = board.length, n = board[0].length;
if (i < 0 || i >= m || j < 0 || j >= n || isUsed[i][j]) {
return;
}
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
if (word.charAt(curIndex) == board[i][j]) {
isUsed[i][j] = true;
dfs(board, word, curIndex + 1, i + dx[k], j + dy[k], isUsed);
isUsed[i][j] = false; //修正回原先状态
}
}
// return; 没有添加return的必要
}思考怎么能够加缩减搜索的时间复杂度?
可以使用字典树Trie树,来存储words中的每个word,不依赖于word一个一个查找,而是依赖于board中的字符,去字典树中查找是否有到当前的前缀,没有即进行剪枝,查询下一个board的字符。
int[] dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int[] dy = {0, -1, 0, 1};
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
//使用dfs进行回溯
public List<String> findWords(char[][] board, String[] words) {
if (board.length == 0 || board[0].length == 0 || board == null || words == null) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
int m = board.length, n = board[0].length;
Trie trie = new Trie();
//插入words到Trie树中
for (String word : words) {
trie.insertWord(word);
}
boolean[][] isUsed = new boolean[m][n]; //确保用过的下次不会朝向原先的位置用
//遍历查找
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
dfs(board, i, j, trie, isUsed);
}
}
return new ArrayList<>(set);
}
//深度有限搜索
private void dfs(char[][] board, int i, int j, Trie node, boolean[][] isUsed) {
int m = board.length, n = board[0].length;
if (i < 0 || i >= m || j < 0 || j >= n || isUsed[i][j]) {
return;
}
char c = board[i][j];
if (node.children[c - 'a'] == null) {
return;
}
node = node.children[c - 'a'];
if (node.isEnd) {
set.add(node.val);
node.isEnd = true; //赋值是为了防止下一次过来,仍旧存储该值
// return; //这里不能用终止,是因为存在 word = ["oa","oaa"] 这种情况,使得前缀是一个单词的后续仍旧可以查询到。
}
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
isUsed[i][j] = true;
dfs(board, i + dx[k], j + dy[k], node, isUsed);
isUsed[i][j] = false; //修正回原先状态
}
}
// 构建字典树
class Trie {
Trie[] children;
boolean isEnd;
String val; //记录到当前位置的值
Trie() {
children = new Trie[26];
isEnd = false;
}
void insertWord(String word) {
int len = word.length();
Trie node = this;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char c = word.charAt(i);
int index = c - 'a';
if (node.children[index] == null) {
node.children[index] = new Trie();
}
node = node.children[index]; //往下移动一位
}
node.isEnd = true;
node.val = word; //记录
}
}- 分析单词搜索 2 用 Tire 树方式实现的时间复杂度,请同学们提交在第 6 周的学习总结中。
并查集:一种跳跃式的数据结构
适用场景:判断两两的元素是不是在一个集合中?两个人是不是朋友?这类问题直接使用并查集
组团和配对,a和b是不是朋友?
- 初始化:每个元素拥有一个parent数组指向自己。
- 查询:目的是为了找当前元素的带头元素(用带头元素来作为整个集合的代表);找其parent、再找其parent,直到其parent[i]==i,则找到了该带头元素
- 合并:分别找出两个集合的领头元素,将parent[e]指向a或者parent[a]指向e(这两种指向均可)
- 路径压缩:提升查询效率
- 实现方式
- 代码模板
class UnionFind {
private int count = 0;
private int[] parent;
public UnionFind(int n) {
count = n;
parent = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
}
public int find(int p) {
while (p != parent[p]) {
parent[p] = parent[parent[p]];
p = parent[p];
}
return p;
}
public void union(int p, int q) {
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
if (rootP == rootQ) return;
parent[rootP] = rootQ;
count--;
}
}- 并查集:路径压缩的
class UnionFind {
public int count = 0; //记录有几个群组,连通分量的个数
public int[] parent;
public UnionFind(int n) {
count = n;
parent = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
}
public int find(int p) { //找到p元素所在group的代表元素
int target = p;
while (p != parent[p]) { // 不断向上找,直到找到了p == parent[p],即找到了代表元素
//parent[p] = parent[parent[p]];
p = parent[p];
}
//路径压缩
while (target != parent[target]) {
int temp = target; //从底到 代表元素,
target = parent[target];
parent[temp] = p;
}
return p;
}
public void union(int p, int q) {
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
if (rootP == rootQ) return;
parent[rootP] = rootQ; //不相等的情况
count--;
}
}- dfs
//定义
int[][] directions = {{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}}; // 右、下两个方向
int count = 0;
boolean[][] visited;
int row;
int col;
//1. dfs方式
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
//判空
if(grid == null) {
return 0;
}
row = grid.length;
if(row == 0) {
return 0;
}
col = grid[0].length;
visited = new boolean[row][col];
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
if(grid[i][j] == '1' && !visited[i][j]) {
dfs(grid,i,j); //进行一次dfs,即代表一座岛屿
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
private void dfs(char[][] grid, int i, int j) {
//结束条件
if(grid[i][j] == '0' && !visited[i][j]) {
visited[i][j] = true;
return;
}
//根
visited[i][j] = true;
//多叉
for (int[] direction :directions) {
int newX = i+direction[0];
int newY = j+direction[1];
if(newX >= 0 && newX < row && newY >= 0 && newY < col && !visited[newX][newY]) {
dfs(grid, newX, newY);
}
}
}- bfs
class Solution {
//定义
int[][] directions = {{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}}; // 右、下两个方向
int count = 0;
boolean[][] visited;
int row;
int col;
//2. bfs方式
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
//判空
if(grid == null) {
return 0;
}
row = grid.length;
if(row == 0) {
return 0;
}
col = grid[0].length;
visited = new boolean[row][col];
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
if(grid[i][j] == '1' && !visited[i][j]) {
bfs(grid,i,j); //进行一次bfs,即代表一座岛屿
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
//迭代的方式
private void bfs(char[][] grid, int i, int j) {
Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList<>();
deque.addLast(i*col+j); //该编码必须在队列中唯一
visited[i][j] = true;
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
Integer first = deque.removeFirst(); // deque.poll()
int curX = first/col;
int curY = first%col;
//多叉
for (int[] direction :directions) {
int newX = curX+direction[0];
int newY = curY+direction[1];
if(newX >= 0 && newX < row && newY >= 0 && newY < col && !visited[newX][newY] && grid[newX][newY] == '1') {
deque.addLast(newX * col + newY); // deque.offer()
visited[newX][newY] = true;
}
}
}
}
}- 并查集方式
思路:
并查集中维护连通分量的个数,在遍历的过程中:
- 相邻的陆地(只需要向右看和向下看)合并,只要发生过合并,岛屿的数量就减少 1;
- 在遍历的过程中,同时记录空地的数量;
- 岛屿数量 = 并查集中连通分量的个数 - 空地的个数;
class Solution {
//1. 定义一些额外的需要的量
int[][] directions = {{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}}; // 右、下两个方向
int row;
int col;
//2. 定义并查集
class UnionFind {
public int count = 0; //记录有几个群组,连通分量的个数
public int[] parent;
public UnionFind(int n) {
count = n;
parent = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
}
public int find(int p) { //找到p元素所在group的代表元素
int target = p;
while (p != parent[p]) { // 不断向上找,直到找到了p == parent[p],即找到了代表元素
//parent[p] = parent[parent[p]];
p = parent[p];
}
//路径压缩
while (target != parent[target]) {
int temp = target; //从底到 代表元素,
target = parent[target];
parent[temp] = p;
}
return p;
}
public void union(int p, int q) {
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
if (rootP == rootQ) return;
parent[rootP] = rootQ; //不相等的情况
count--;
}
}
//3. 并查集
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
//判空
if (grid == null) {
return 0;
}
row = grid.length;
if (row == 0) {
return 0;
}
col = grid[0].length;
UnionFind unionFind = new UnionFind(row * col);
int spaces = 0; //记录0出现的次数,每个0相当于一个单独的连通分量
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == '0') {
spaces++;
} else {
for (int[] direction : directions) {
int newX = i + direction[0];
int newY = j + direction[1];
if (newX >= 0 && newX < row && newY >= 0 && newY < col && grid[newX][newY] == '1') {
unionFind.union(i*col+j, newX*col+newY);
}
}
}
}
}
return unionFind.count-spaces; //总的连通分量-0的个数(即0所代表的连通分量)
}
}BFS一般都是使用队列来实现,不通过递归来实现
优化方向:剪枝(剪掉重复、非最优的枝)
想法:
这是一个斐波那契数列得问题,直观的看每一项(n>2)都等于前两项之和。
- 直接递归:造成超时,时间复杂度太高
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if(n == 1 || n == 2) {
return n;
}
return climbStairs(n-1)+climbStairs(n-2);
}
}为什么直接递归那么耗费时间?可以画出直接递归的递归树,发现这是一颗二叉树,深度能够达到$2^n$,并且有很多重复的分支,是否可以通过记录的方式,来进行剪枝优化。
考虑如何能够提升效率?
两种思考角度,自顶向下和自底向上,中间冗余过程提前记录
- 自顶向下:从结果,一步步回退,直到获得最终结果
class Solution {
int[] array; //默认内部为0
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if( n == 1 || n == 2) {
return n;
}
array = new int[n+1];
array[1] = 1;
array[2] = 2;
process(n);
return array[n];
}
private void process(int n) {
if(array[n-2] == 0) {
process(n-2);
}
if(array[n-1] == 0) {
process(n-1);
}
array[n] = array[n-1]+array[n-2];
}
}- 自底向上
class Solution {
int[] array;
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if( n == 1 || n == 2) {
return n;
}
array = new int[n+1];
array[1] = 1;
array[2] = 2;
//迭代处理
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
array[i] = array[i-2] + array[i-1];
}
return array[n];
}
}不使用数组,采用两个中间变量来进行处理
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if( n == 1 || n == 2) {
return n;
}
int p = 1;
int q = 2;
int z = -1;
//迭代处理
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
z = p+q;
p = q;
q = z;
}
return q;
}
}将p、q、z置于外部:效率有提升
List<String> resultList = new ArrayList<>();
int n;
public List<String> generateParenthesis(int n) {
this.n = n;
if(n <= 0) {
return resultList;
}
int level = 1;
dfs("", 0, 0);
return resultList;
}
private void dfs(String str, int open, int close) {
//结束条件
if(str.length() == 2*n) {
resultList.add(str);
return;
}
//左
if(open < n) {
//放(
dfs(str+"(",open+1, close);
}
//右
if(open > close) {
//放)
dfs(str+")",open, close+1);
}
}思路:
遍历数组一次,全都存储到三个不同的数组中
public boolean isValidSudoku(char[][] board) {
int row = board.length;
int col = board[0].length;
boolean[][] rows = new boolean[9][9];
boolean[][] cols = new boolean[9][9];
boolean[][] boxs = new boolean[9][9];
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) { //双重循环解决:遍历一遍
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == '.') {
continue;
}
int num = board[i][j] - '1';
int boxIndex = (i / 3) * 3 + j / 3; //计算是第几个box
if (rows[i][num]) return false;
else rows[i][num] = true;
if (cols[j][num]) return false;
else cols[j][num] = true;
if (boxs[boxIndex][num]) return false;
else boxs[boxIndex][num] = true;
}
}
return true;
}思路:采用回溯方式
class Solution {
public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {
backtrack(board, 0, 0);
}
boolean backtrack(char[][] board, int r, int c) {
int m = 9, n = 9;
if (c == n) {
// 穷举到最后一列的话就换到下一行重新开始。
return backtrack(board, r + 1, 0);
}
if (r == m) {
// 找到一个可行解,触发 base case
return true;
}
// 就是对每个位置进行穷举
for (int i = r; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = c; j < n; j++) {
if (board[i][j] != '.') {
// 如果有预设数字,不用我们穷举
return backtrack(board, i, j + 1);
}
for (char ch = '1'; ch <= '9'; ch++) {
// 如果遇到不合法的数字,就跳过
if (!isValid(board, i, j, ch))
continue;
board[i][j] = ch;
// 如果找到一个可行解,立即结束
if (backtrack(board, i, j + 1)) {
return true;
}
board[i][j] = '.';
}
// 穷举完 1~9,依然没有找到可行解,此路不通
return false;
}
}
return false;
}
// 判断 board[i][j] 是否可以填入 n
boolean isValid(char[][] board, int r, int c, char n) {
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
// 判断行是否存在重复
if (board[r][i] == n) return false;
// 判断列是否存在重复
if (board[i][c] == n) return false;
// 判断 3 x 3 方框是否存在重复
if (board[(r/3)*3 + i/3][(c/3)*3 + i%3] == n) //获取3*3格中的索引
return false;
}
return true;
}
}- tips:9x9格分成9格3x3格时,其索引的遍历
int r; //本身行
int c; //本身列
for(int i=0; i<9; i++) {
int row = (r/3)*3 + i/3;
int col = (c/3)*3 + i%3;
System.out.println(board[row][col]);
}- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/shortest-path-in-binary-matrix/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sliding-puzzle/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sudoku-solver/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/number-of-1-bits/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/power-of-two/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-bits/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/n-queens/description/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/n-queens-ii/description/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/counting-bits/description/
- 布隆过滤器的原理和实现
- 使用布隆过滤器解决缓存击穿、垃圾邮件识别、集合判重
- 布隆过滤器 Python 代码示例
- 布隆过滤器 Python 实现示例
- 高性能布隆过滤器 Python 实现示例
- 布隆过滤器 Java 实现示例 1
- 布隆过滤器 Java 实现示例 2
- 十大经典排序算法
- 快速排序代码示例
- 归并排序代码示例
- 堆排序代码示例
- 直播课回顾: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1sFuZ8GjDCXy5mPCNLZhHxw 提取码: 2rdy
用自己熟悉的编程语言,手写各种初级排序代码,提交到第 7 周学习总结中。
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/relative-sort-array/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-anagram/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/design-a-leaderboard/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-intervals/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-pairs/
在第 8 周学习总结中,写出不同路径 2 这道题目的状态转移方程。
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-increasing-subsequence/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/decode-ways/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-valid-parentheses/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximal-rectangle/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/distinct-subsequences/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/race-car/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/to-lower-case/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/length-of-last-word/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/jewels-and-stones/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/first-unique-character-in-a-string/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/string-to-integer-atoi/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-common-prefix/description/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-string
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-string-ii/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-words-in-a-string/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-words-in-a-string-iii/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-only-letters/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-anagram/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/group-anagrams/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-all-anagrams-in-a-string/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-palindrome/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-palindrome-ii/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-palindromic-substring/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-common-subsequence/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/edit-distance/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-palindromic-substring/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/regular-expression-matching/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/regular-expression-matching/solution/ji-yu-guan-fang-ti-jie-gen-xiang-xi-de-jiang-jie-b/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/wildcard-matching/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/distinct-subsequences/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/first-unique-character-in-a-string/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/string-to-integer-atoi/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-string-ii/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-words-in-a-string/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-words-in-a-string-iii/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-only-letters/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-all-anagrams-in-a-string/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-palindromic-substring/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/isomorphic-strings/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-palindrome-ii/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/wildcard-matching
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-valid-parentheses
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/distinct-subsequences/