This is official PyTorch implementation of LGNet: Local-and-Global Feature Adaptive Network for 3D Interacting Hand Mesh Reconstruction.
In this supplementary material, we provide additional experiments, discussions, and other details that could not be included in the main text due to lack of space. The content is summarized as follows:
- Detailed explanation of feature definitions
- Detailed architecture of LGNet
- Detailed experiments
- Discussion
Note that all the notation and abbreviations here are consistent with the main manuscript.
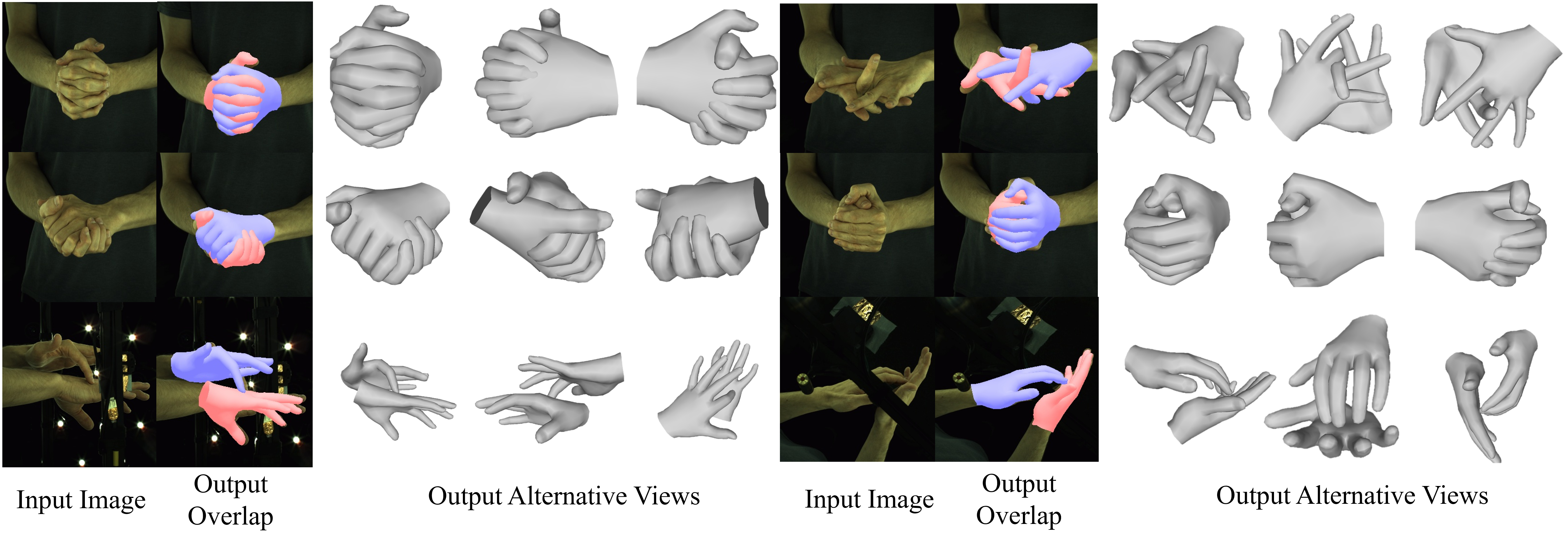
Accurate 3D interacting hand mesh reconstruction from RGB images is crucial for applications such as robotics, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR). Especially in the field of robotics, accurate interacting hand mesh reconstruction can significantly improve the accuracy and naturalness of human-robot interaction. This task requires accurate understanding of complex interactions between two hands and ensuring reasonable alignment of the hand mesh with the image. Recent Transformer-based methods directly utilise the features of the two hands as input tokens, ignoring the correlation between local and global features of the interacting hands, leading to hand ambiguity, self-obscuration and self-similarity problems.We propose LGNet, Local and Global Feature Adaptive Network, by decoupling the hand mesh reconstruction task into three stages: a joint stage for predicting hand joints; a mesh stage for predicting a rough hand mesh; and a refine stage for fine-tuning the mesh image alignment using an offset mesh. LGNet enables high-quality fingertip-level mesh image alignment, effectively models the spatial relationship between two hands, and supports real-time prediction. Extensive quantitative and qualitative results on benchmark datasets show that LGNet outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of mesh accuracy and image alignment, and demonstrates strong generalisation capabilities in experiments on in-the-wild images. Our source code will be made available to the community.
The overall architecture of Local-and-Global Feature Adaptive Network (LGNet).
The joint stage aims to extract hand features (F_R or F_L) from the input image, fuse them into global interaction features, and adapt them to each hand (F_R* or F_L*). Subsequently, the joint feature extractor derives the predicted 2.5D joint coordinates (J_R or J_L) and joint features (F_JR or F_JL) for each hand from the adapted features (F_R* or F_L*).
The mesh stage feeds the augmented joint features (F_JR* or F_JL*) to the regressor for recovering the rough 3D hand mesh (V_R or V_L).
The refine stage fuses the image features, local interaction features, and global interaction features from the joint stage and passes them to the graph convolutional layer (GCN) to regress the offset mesh ΔM and generate the final hand mesh M_f = M_r + ΔM.
The overall architecture of Local-and-Global Feature Adaptive Block (LGBlock).
Step 1. Local unit for hand local interaction feature extraction. Local interaction features F_inter^local are extracted by fusing two hand features (F_R and F_L).
Step 2. Global unit for global interaction feature adaptation. The global interaction feature F_inter^global is obtained by fusing the local interaction feature (F_interR and F_interL) and adapted to each hand.
Visualization of attention maps in pseudo color. Ten independent examples are shown. In each example, from left to right is the input image, local stage attention map overlaid on the image, and global stage attention map. For the local stage attention map, red represents attention from the right hand, and blue represents attention from the left hand. Brighter colors indicate stronger attention. For the global attention map, brighter colors indicate stronger cross-hand attention. All attention maps have been normalized for better visualization.
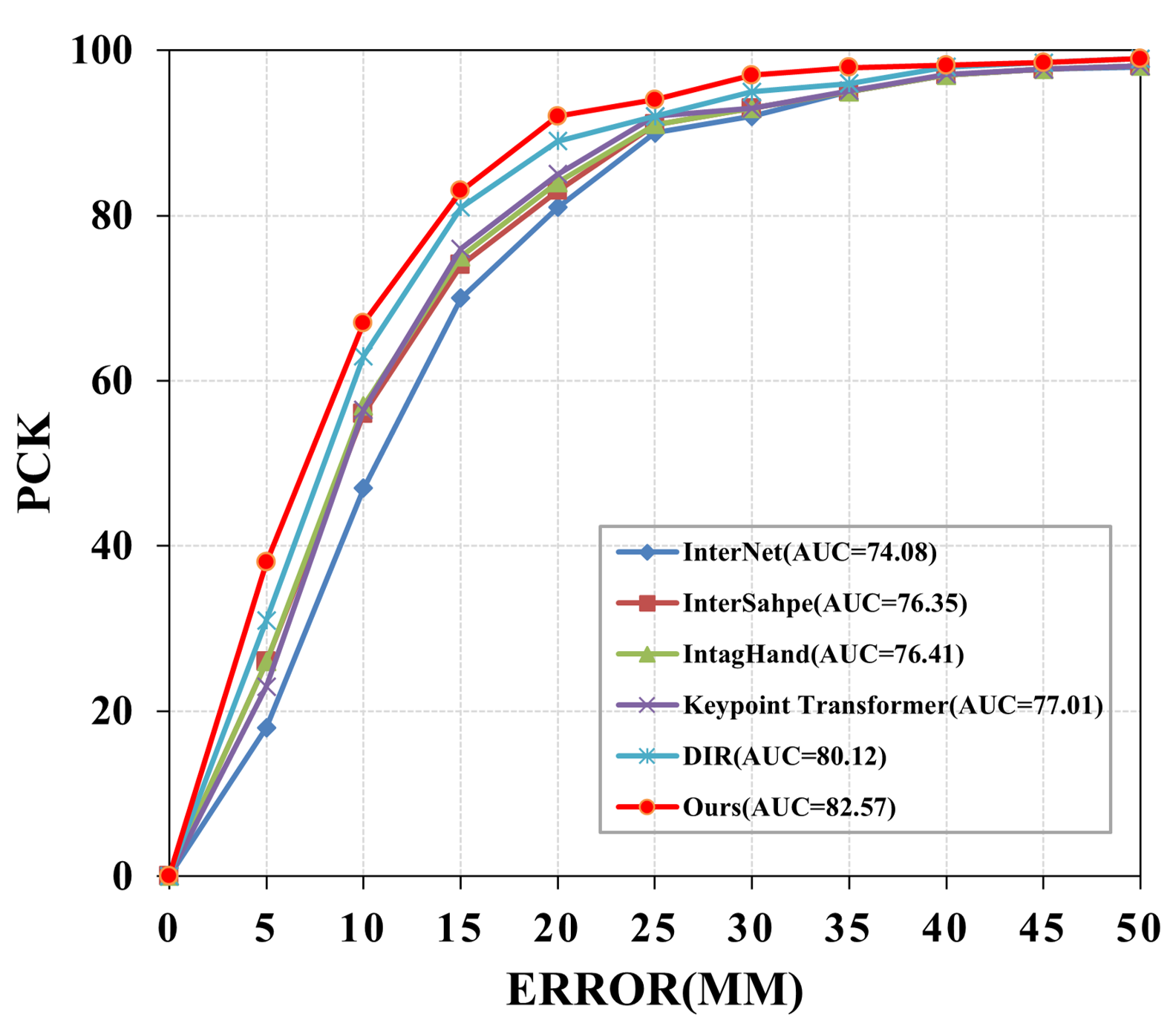
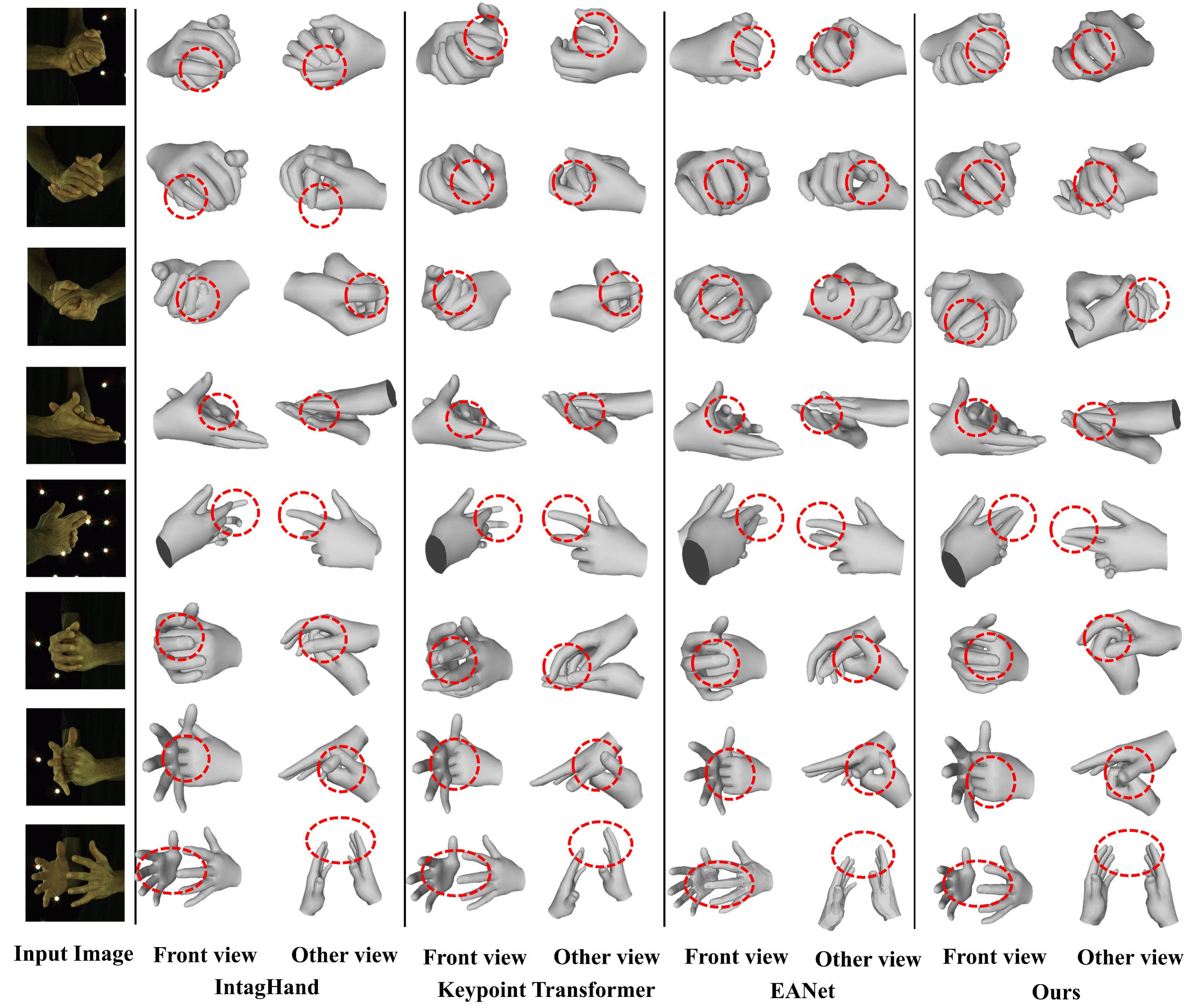
Comparison with SOTA methods on InterHand2.6M.
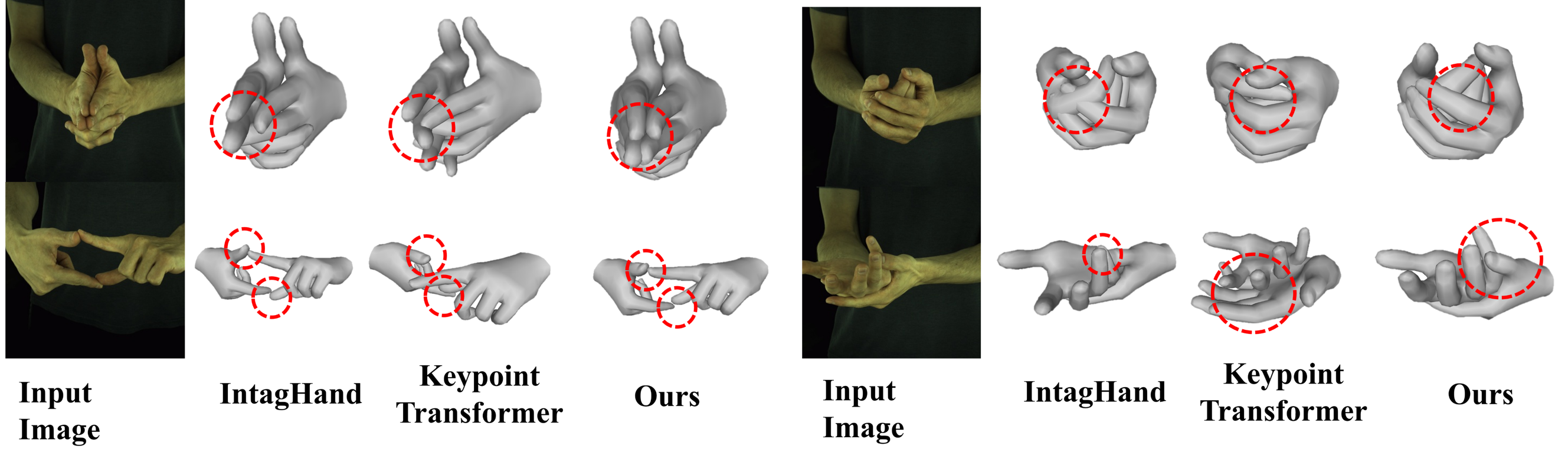
Robustness to asymmetric poses of two hands on InterHand2.6M.
-
Setup the conda environment
conda create --name lgnet python==3.8.11 conda activate lgnet conda install pytorch==1.10.1 torchvision==0.11.2 torchaudio==0.10.1 cudatoolkit=11.3 -c pytorch -c conda-forge pip install -r requirements.txt -
Download MANO model files from the website (requires login) and set the
smplx_pathinconfig.py -
Clone the Current Repo
git clone <curr_repo> cd lgnet cd main
The setup has been tested on NVIDIA 3090 GPU.
Depending on the dataset you intend to train/evaluate follow the instructions below for the setup.
- Download the dataset from the website
- In
config.py, setinterhand_anno_dirto point to the annotations directory - In
config.py, setinterhand_images_pathto point to the images directory - If you intend to use RootNet output for the
root joint translation, download the RootNet results for InterHand2.6M from here.
Set
root_net_output_pathinconfig.pyfor point to the RootNet outputs folder. Instead, if you intend to test with ground-truth relative translation, setroot_net_output_pathtoNone
To release
To release
To release