Please send a pull request to the branch named with your student ID during the submission periods (see below).
For Parts 1 and 2, please put the required items under lsv_fall_2021/pa1, i.e., this folder.
For Part 3, please develop your code under src/ext-lsv.
- Parts 1 and 2: 2021/10/08 11:00-13:00
- Part 3: 2021/10/22 11:00-13:00
(10%)
(a) Use BLIF manual to create a BLIF file representing a four-number serial adder.
(b) Perform the following steps to practice using ABC:
- read the BLIF file into ABC (command
read) - check statistics (command
print_stats) - visualize the network structure (command
show) - convert to AIG (command
strash) - visualize the AIG (command
show) - convert to BDD (command
collapse) - visualize the BDD (command
show_bdd -g; note thatshow_bddonly shows the first PO; option-gcan be applied to show all POs )
(10%)
In ABC there are different ways to represent Boolean functions.
(a) Compare the following differences with the four-number serial adder example.
- logic network in AIG (by command
aig) vs. structurally hashed AIG (by commandstrash) - logic network in BDD (by command
bdd) vs. collapsed BDD (by commandcollapse)
(b) Given a structurally hashed AIG, find a sequence of ABC command(s) to covert it to a logic network with node function expressed in sum-of-products (SOP).
- The BLIF file.
- A PDF report containing:
- results of
showandshow_bdd -gafter step 3,5,7 in Part 1 - answers of question (a),(b) in Part 2.
- results of
(80%)
Write a procedure in ABC that find maximum single-fanout cones (MSFCs) that covers all nodes (excluding PIs and POs) of a given AIG.
Integrate this procedure into ABC, so that after reading in a circuit by the command read, running the command lsv_print_msfc would invoke your code.
The maximum single-fanout cone (MSFC) (c.f. maximum fanout free cone (MFFC)
of node v, denoted C(v), is the maximum set of nodes such that u ∈ C(v) if and only if 1) u = v, or 2) |FO(u)| = 1 and FO(u) ⊆ C(v).
For example, given an AIG in the following figure,
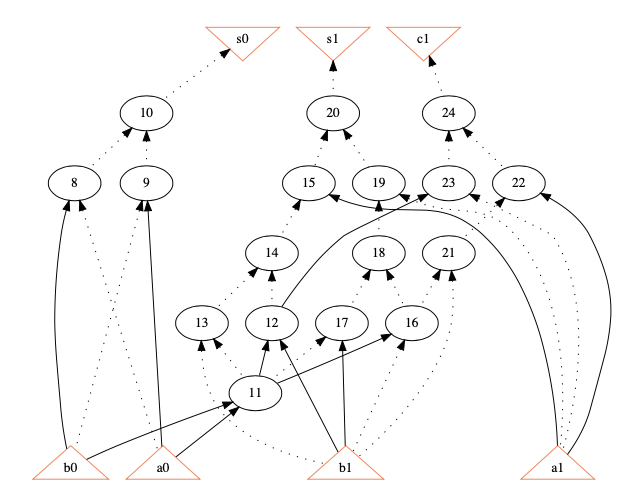
we have the following decomposition:
MSFC 0: n8,n9,n10
MSFC 1: n11
MSFC 2: n12
MSFC 3: n13,n14,n15,n17,n18,n19,n20
MSFC 4: n16
MSFC 5: n21,n22,n23,n24
In each line of MSFC i:, print the names of nodes returned by function Abc ObjName(), and sort the nodes in an increasing order with respect to their object IDs returned by function Abc ObjId().
Lines of MSFCs are printed in an increasing order with respect to the smallest object ID of each MSFC.
Make sure that only internal nodes (non-PI and non-PO nodes) are printed, and each node is printed only once.