Allows for easy implementation of smooth scrolling for same-page links.
+Note: Version 2.0+ of this plugin requires jQuery version 1.7 or greater.
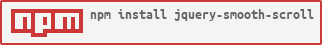
Using npm:
-1 npm install jquery-smooth-scroll
+1 npm install jquery-smooth-scroll
The old-fashioned way:
Go to the following URL in your browser and copy/paste the code into your own file:
@@ -92,13 +93,13 @@
$.fn.smoothScroll
Exclude links if they are within a containing element: $('#container a').smoothScroll({excludeWithin: ['.container2']});
Exclude links if they match certain conditions: $('a').smoothScroll({exclude: ['.rough','#chunky']});
Adjust where the scrolling stops: $('.backtotop').smoothScroll({offset: -100});
-Add a callback function that is triggered before the scroll starts: `$('a').smoothScroll({beforeScroll: function() { alert('ready to go!'); }});
+Add a callback function that is triggered before the scroll starts: $('a').smoothScroll({beforeScroll: function() { alert('ready to go!'); }});
Add a callback function that is triggered after the scroll is complete: $('a').smoothScroll({afterScroll: function() { alert('we made it!'); }});
-Add back button support by including a history management plugin such as Ben Alman's BBQ. See demo/bbq.html for an example of how to implement this.
+Add back button support by using a hashchange event listener. You can also include a history management plugin such as Ben Alman's BBQ for ancient browser support (IE < 8), but you'll need jQuery 1.8 or earlier. See demo/hashchange.html or demo/bbq.html for an example of how to implement.
Options
The following options, shown with their default values, are available for both $.fn.smoothScroll and $.smoothScroll:
-12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728293031323334 { offset: 0, // one of 'top' or 'left' direction: 'top', // only use if you want to override default behavior scrollTarget: null, // string to use as selector for event delegation (Requires jQuery >=1.4.2) delegateSelector: null, // fn(opts) function to be called before scrolling occurs. // `this` is the element(s) being scrolled beforeScroll: function() {}, // fn(opts) function to be called after scrolling occurs. // `this` is the triggering element afterScroll: function() {}, easing: 'swing', // speed can be a number or 'auto' // if 'auto', the speed will be calculated based on the formula: // (current scroll position - target scroll position) / autoCoeffic speed: 400, // autoCoefficent: Only used when speed set to "auto". // The higher this number, the faster the scroll speed autoCoefficient: 2, // $.fn.smoothScroll only: whether to prevent the default click action preventDefault: true }
+12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728293031323334353637 { offset: 0, // one of 'top' or 'left' direction: 'top', // only use if you want to override default behavior scrollTarget: null, // string to use as selector for event delegation delegateSelector: null, // fn(opts) function to be called before scrolling occurs. // `this` is the element(s) being scrolled beforeScroll: function() {}, // fn(opts) function to be called after scrolling occurs. // `this` is the triggering element afterScroll: function() {}, // easing name. jQuery comes with "swing" and "linear." For others, you'll need an easing plugin // from jQuery UI or elsewhere easing: 'swing', // speed can be a number or 'auto' // if 'auto', the speed will be calculated based on the formula: // (current scroll position - target scroll position) / autoCoeffic speed: 400, // autoCoefficent: Only used when speed set to "auto". // The higher this number, the faster the scroll speed autoCoefficient: 2, // $.fn.smoothScroll only: whether to prevent the default click action preventDefault: true }
The options object for $.fn.smoothScroll can take two additional properties:
exclude and excludeWithin. The value for both of these is an array of
@@ -115,7 +116,7 @@
$.smoothScroll
document.body)
Doesn't automatically fire, so you need to bind it to some other user
interaction. For example:
-1234567 $('button.scrollsomething').on('click', function() { $.smoothScroll({ scrollElement: $('div.scrollme'), scrollTarget: '#findme' }); return false;});
+1234567 $('button.scrollsomething').on('click', function() { $.smoothScroll({ scrollElement: $('div.scrollme'), scrollTarget: '#findme' }); return false;});
The $.smoothScroll method can take one or two arguments.
@@ -129,7 +130,7 @@ $.smoothScroll
Additional Option
The following option, in addition to those listed for $.fn.smoothScroll above, is available
for $.smoothScroll:
-
12345 { // jQuery set of elements you wish to scroll. // if null (default), $('html, body').firstScrollable() is used. scrollElement: null}
+12345 { // jQuery set of elements you wish to scroll. // if null (default), $('html, body').firstScrollable() is used. scrollElement: null}
$.fn.scrollable
@@ -150,19 +151,19 @@ $.fn.firstScrollable
Examples
Smooth scrolling on page load
-If you want to scroll to an element when the page loads, use $.smoothScroll() in a script at the end of the body or use $(document).ready(). To prevent the browser from automatically scrolling to the element on its own, your link on page 1 will need to include a fragment identifier that does not match an element id on page 2. To ensure that users without JavaScript get to the same element, you should modify the link's hash on page 1 with JavaScript. Your script on page 2 will then modify it back to the correct one when you call $.smoothScroll().
+If you want to scroll to an element when the page loads, use $.smoothScroll() in a script at the end of the body or use $(document).ready(). To prevent the browser from automatically scrolling to the element on its own, your link on page 1 will need to include a fragment identifier that does not match an element id on page 2. To ensure that users without JavaScript get to the same element, you should modify the link's hash on page 1 with JavaScript. Your script on page 2 will then modify it back to the correct one when you call $.smoothScroll().
For example, let's say you want to smooth scroll to <div id="scrolltome"></div> on page-2.html. For page-1.html, your script might do the following:
-12345 $('a[href="page-2.html#scrolltome"]').attr('href', function() { var hrefParts = this.href.split(/#/); hrefParts[1] = 'smoothScroll' + hrefParts[1]; return hrefParts.join('#');});
+12345 $('a[href="page-2.html#scrolltome"]').attr('href', function() { var hrefParts = this.href.split(/#/); hrefParts[1] = 'smoothScroll' + hrefParts[1]; return hrefParts.join('#');});
-Then for page-2.html, your script would do this:
-12345678 // Call $.smoothScroll if location.hash starts with "#smoothScroll"var reSmooth = /^#smoothScroll/;var id;if (reSmooth.test(location.hash)) { // Strip the "#smoothScroll" part off (and put "#" back on the beginning) id = '#' + location.hash.replace(reSmooth, ''); $.smoothScroll({scrollTarget: id});}
+Then for page-2.html, your script would do this:
+12345678 // Call $.smoothScroll if location.hash starts with "#smoothScroll"var reSmooth = /^#smoothScroll/;var id;if (reSmooth.test(location.hash)) { // Strip the "#smoothScroll" part off (and put "#" back on the beginning) id = '#' + location.hash.replace(reSmooth, ''); $.smoothScroll({scrollTarget: id});}
Focus element after scrolling to it.
Imagine you have a link to a form somewhere on the same page. When the user clicks the link, you want the user to be able to begin interacting with that form. With the smoothScroll plugin, you can use the afterScroll callback function. Here is an example that focuses the first input within the form after scrolling to the form:
-12345 $('a.example').smoothScroll({ afterScroll: function(options) { $(options.scrollTarget).find('input')[0].focus(); }});
+12345 $('a.example').smoothScroll({ afterScroll: function(options) { $(options.scrollTarget).find('input')[0].focus(); }});
For accessibility reasons, it might make sense to focus any element you scroll to, even if it's not a natively focusable element. To do so, you could add a tabIndex attribute to the target element:
-12345678 $('a.example').smoothScroll({ afterScroll: function(options) { var $tgt = $(options.scrollTarget); $tgt.attr('tabIndex', '0'); // Using $tgt[0] allows us to call .focus() on the DOM node itself, not the jQuery collection $tgt[0].focus(); }});
+12345678 $('a.example').smoothScroll({ afterScroll: function(options) { var $tgt = $(options.scrollTarget); $tgt.attr('tabIndex', '0'); // Using $tgt[0] allows us to call .focus() on the DOM node itself, not the jQuery collection $tgt[0].focus(); }});
Notes
diff --git a/package.json b/package.json
index c52888a..021ba5c 100644
--- a/package.json
+++ b/package.json
@@ -19,7 +19,7 @@
"demo": "http://plugins.learningjquery.com/smooth-scroll/demo/",
"license": "MIT",
"dependencies": {
- "jquery": ">=1.4.2"
+ "jquery": ">=1.7.0"
},
"devDependencies": {
"grunt": "^0.4.5",