SecretScanner has been integrated into ThreatMapper 1.3.0, and also remains as this standalone project.
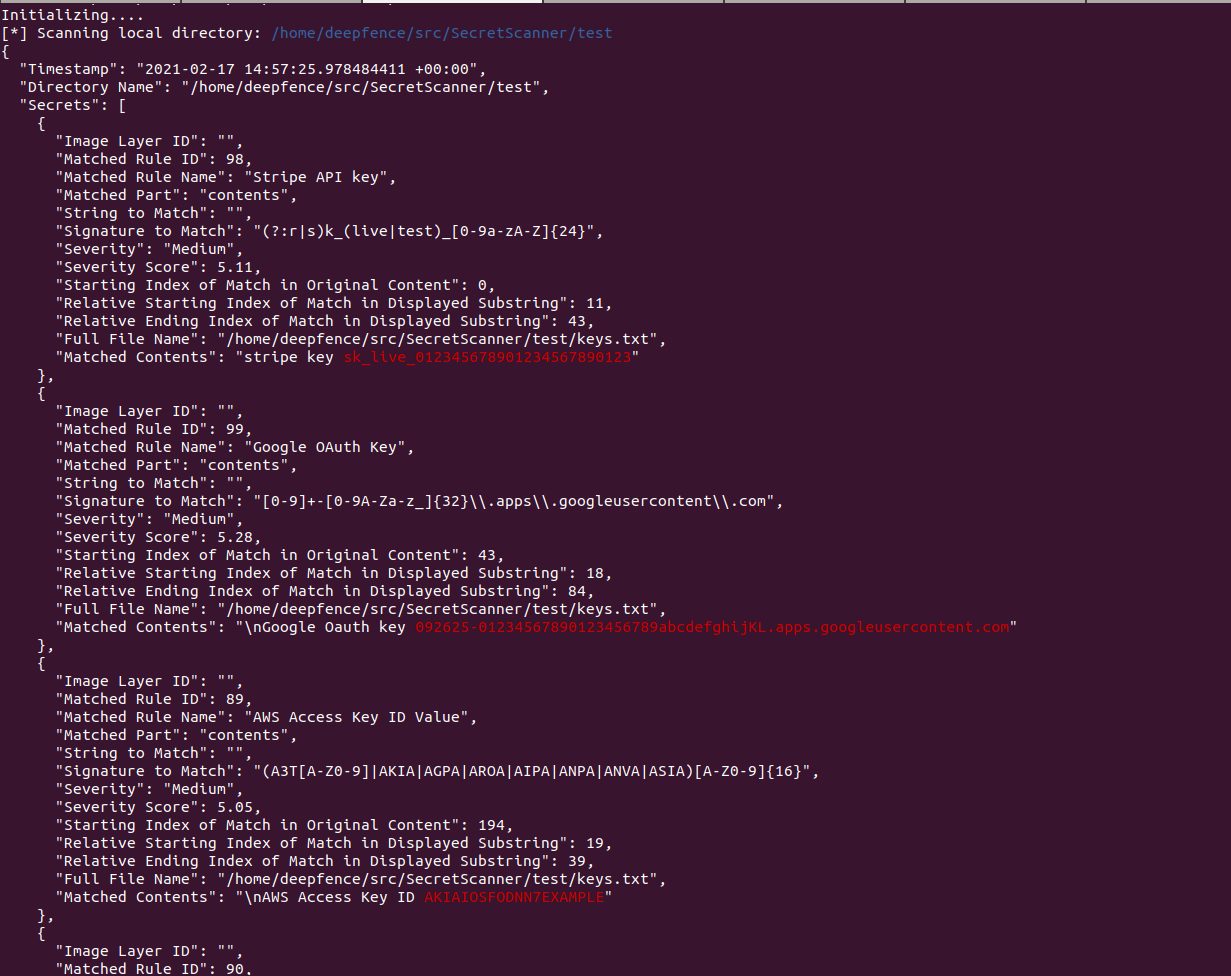
Deepfence SecretScanner can find unprotected secrets in container images or file systems.
- SecretScanner is a standalone tool that retrieves and searches container and host filesystems, matching the contents against a database of approximately 140 secret types.
- SecretScanner is also included in ThreatMapper, an open source scanner that identifies vulnerable dependencies and unprotected secrets in cloud native applications, and ranks these vulnerabilities based on their risk-of-exploit (example)
Secrets are any kind of sensitive or private data which gives authorized users permission to access critical IT infrastructure (such as accounts, devices, network, cloud based services), applications, storage, databases and other kinds of critical data for an organization. For example, passwords, AWS access IDs, AWS secret access keys, Google OAuth Key etc. are secrets. Secrets should be strictly kept private. However, sometimes attackers can easily access secrets due to flawed security policies or inadvertent mistakes by developers. Sometimes developers use default secrets or leave hard-coded secrets such as passwords, API keys, encryption keys, SSH keys, tokens etc. in container images, especially during rapid development and deployment cycles in CI/CD pipeline. Also, sometimes users store passwords in plain text. Leakage of secrets to unauthorized entities can put your organization and infrastructure at serious security risk.
Deepfence SecretScanner helps users scan their container images or local directories on hosts and outputs a JSON file with details of all the secrets found.
Check out our blog for more details.
$ ./SecretScanner --help
Usage of ./SecretScanner:
-config-path string
Searches for config.yaml from given directory. If not set, tries to find it from SecretScanner binary's and current directory
-debug-level string
Debug levels are one of FATAL, ERROR, IMPORTANT, WARN, INFO, DEBUG. Only levels higher than the debug-level are displayed (default "ERROR")
-image-name string
Name of the image along with tag to scan for secrets
-json-filename string
Output json file name. If not set, it will automatically create a filename based on image or dir name
-local string
Specify local directory (absolute path) which to scan. Scans only given directory recursively.
-max-multi-match uint
Maximum number of matches of same pattern in one file. This is used only when multi-match option is enabled. (default 3)
-max-secrets uint
Maximum number of secrets to find in one container image or file system. (default 1000)
-maximum-file-size uint
Maximum file size to process in KB (default 256)
-multi-match
Output multiple matches of same pattern in one file. By default, only one match of a pattern is output for a file for better performance
-output-path string
Output directory where json file will be stored. If not set, it will output to current directory
-temp-directory string
Directory to process and store repositories/matches (default "/tmp")
-threads int
Number of concurrent threads (default number of logical CPUs)
-socket-path string
The gRPC server socket path
Install docker and run SecretScanner on a container image using the following instructions:
- Build SecretScanner:
./bootstrap.sh
docker build --rm=true --tag=deepfenceio/deepfence_secret_scanner:latest -f Dockerfile .- Or, pull the latest build from docker hub by doing:
docker pull deepfenceio/deepfence_secret_scanner:latest- Pull a container image for scanning:
docker pull node:8.11-
Run SecretScanner as a standalone:
-
Scan a container image:
docker run -it --rm --name=deepfence-secretscanner -v $(pwd):/home/deepfence/output -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock -v /run/containerd/containerd.sock:/run/containerd/containerd.sock deepfenceio/deepfence_secret_scanner:latest -image-name node:8.11 -
Scan a local directory:
docker run -it --rm --name=deepfence-secretscanner -v /:/deepfence/mnt -v $(pwd):/home/deepfence/output -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock -v /run/containerd/containerd.sock:/run/containerd/containerd.sock deepfenceio/deepfence_secret_scanner:latest -host-mount-path /deepfence/mnt -local /deepfence/mnt
-
-
Or run SecretScanner as a gRPC server:
docker run -it --rm --name=deepfence-secretscanner -v $(pwd):/home/deepfence/output -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock -v /run/containerd/containerd.sock:/run/containerd/containerd.sock -v /tmp/sock:/tmp/sock deepfenceio -socket-path /tmp/sock/s.sock-
Scan a container image:
grpcurl -plaintext -import-path ./agent-plugins-grpc/proto -proto secret_scanner.proto -d '{"image": {"name": "node:8.11"}}' -unix '/tmp/sock.sock' secret_scanner.SecretScanner/FindSecretInfo
-
Scan a local directory:
grpcurl -plaintext -import-path ./agent-plugins-grpc/proto -proto secret_scanner.proto -d '{"path": "/tmp"}' -unix '/tmp/sock.sock' secret_scanner.SecretScanner/FindSecretInfo
-
By default, SecretScanner will also create json files with details of all the secrets found in the current working directory. You can explicitly specify the output directory and json filename using the appropriate options.
Please note that you can use nerdctl as an alternative to docker in the commands above.
- Run boostrap.sh
- Install Docker
- Install Hyperscan
- Install go for your platform (version 1.14)
- Install go modules, if needed:
gohs,yaml.v3andcolor go get github.com/deepfence/SecretScannerwill download and build SecretScanner automatically in$GOPATH/binor$HOME/go/bindirectory. Or, clone this repository and rungo build -v -ito build the executable in the current directory.- Edit config.yaml file as needed and run the secret scanner with the appropriate config file directory.
For reference, the Install file has commands to build on an ubuntu system.
./SecretScanner --help
./SecretScanner -config-path /path/to/config.yaml/dir -local test
./SecretScanner -config-path /path/to/config.yaml/dir -image-name node:8.11./SecretScanner -socket-path /path/to/socket.sockSee "Quickly-Try-Using-Docker" section above to see how to send requests.
We have built upon the configuration file from shhgit project.
This tool is not meant to be used for hacking. Please use it only for legitimate purposes like detecting secrets on the infrastructure you own, not on others' infrastructure. DEEPFENCE shall not be liable for loss of profit, loss of business, other financial loss, or any other loss or damage which may be caused, directly or indirectly, by the inadequacy of SecretScanner for any purpose or use thereof or by any defect or deficiency therein.