There are two types of classical Chinese poetry: Jueju(绝句), Lvshi(律诗).The Jueju contains four lines in the whole poem. The Lvshi contains eight lines in the whole poem.Each line contains five or seven Chinese characters. There are four types in total, see the table below.
| Jueju | Lvshi | |
|---|---|---|
| five characters | wujue | wulv |
| seven characters | qijue | qilv |
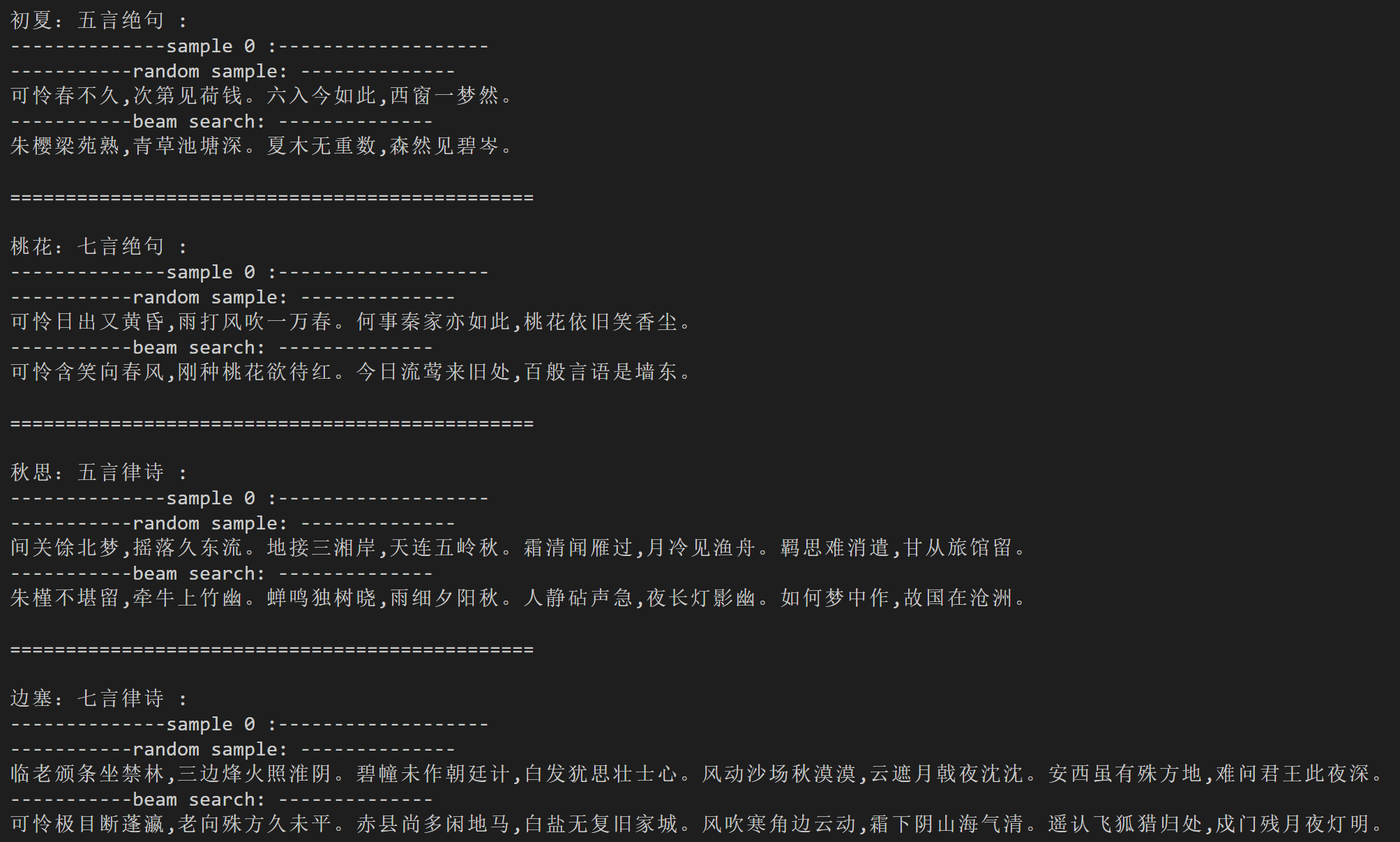
"桃花:七言绝句"
"可怜含笑向春风,刚种桃花欲待红。今日流莺来旧处,百般言语是墙东。"
Input the code in commandline to train:
cd ./examples/glm_poetry_generation
python ./train.py
1)Define the file reading function:
The sample data is in FlagAI/examples/glm_poetry_generation/data/
You need to define the data loading process in train.py, and get the list of src and tgt:
def read_file():
src = []
tgt = []
## src = ["春晓:五言绝句", "标题:五言律诗",......]
## tgt = ["春眠不觉晓,处处闻啼鸟。夜来风雨声,花落知多少。", "诗句...", ......]
## no matter what data you use, you need to construct the right src and tgt.
with open(src_dir, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in f:
line = line.strip()
if ":" in line:
l = line.split(":") #line eg:"初夏:五言绝句"
#if there are more than one ':', get title before the first ':'
title, style = l[0], l[-1]
if len(title) > 20:
title = title[:20] #cut the longer title
line = ":".join([title, style])
src.append(line)
with open(tgt_dir, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in f:
tgt.append(line.strip())
assert len(src) == len(tgt), 'lines not equal!'
return src, tgt
return src,tgt2)Define the DataLoader:
class GLMPoetryDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, sents_src, sents_tgt):
super(GLMPoetryDataset, self).__init__()
self.sents_src = sents_src
self.sents_tgt = sents_tgt
def __getitem__(self, i):
source_text = self.sents_src[i]
target_text = self.sents_tgt[i]
data=tokenizer.encode_plus(source_text,
target_text=target_text)
return data
def __len__(self):
return len(self.sents_src)The tokenizer.encode_plus() method converts the source and target strings into input data of the GLM model such as the source token id.
3)Define the collate_fn in DataLoader to pad a batch of data into a uniform size
class GLMPoetryDynamicCollateFN():
def __init__(self, pad_id):
self.pad_id = pad_id
def pad_token(self, tokens, max_length):
pad_len = max_length-len(tokens)
tokens += [self.pad_id]*pad_len
return tokens
def pad_position_ids(self, position_ids, max_length):
pad_len = max_length-len(position_ids[0])
position_ids[0] += [len(position_ids[0])+x for x in range(pad_len)]
position_ids[1] += [1] * pad_len
return position_ids
def pad_loss_mask(self, loss_mask, max_length):
pad_len = max_length-len(loss_mask)
loss_mask += [0] * pad_len
return loss_mask
def __call__(self, batch):
input_ids = [data["input_ids"] for data in batch]
target_ids = [data["target_ids"] for data in batch]
position_ids = [data["position_ids"] for data in batch]
attention_mask = [data['attention_mask'] for data in batch]
loss_mask = [data['loss_mask'] for data in batch]
max_length = max([len(t) for t in input_ids])
for i in range(len(input_ids)):
input_ids[i] = self.pad_token(input_ids[i], max_length)
target_ids[i] = self.pad_token(target_ids[i], max_length)
position_ids[i] = self.pad_position_ids(position_ids[i], max_length)
loss_mask[i] = self.pad_loss_mask(loss_mask[i], max_length)
return {
'input_ids': torch.LongTensor(input_ids),
'target_ids': torch.LongTensor(target_ids),
'position_ids': torch.LongTensor(position_ids),
'attention_mask': torch.LongTensor(attention_mask),
'loss_mask': torch.LongTensor(loss_mask)
}4)Get training data
train_src, train_tgt = read_file()
print('-----------train data length:', len(train_src))
my_collate_fn = GLMPoetryDynamicCollateFN(pad_id=tokenizer.get_command_id('pad'))
train_dataset = GLMPoetryDataset(train_src,
train_tgt)from flagai.auto_model.auto_loader import AutoLoader
# the model dir, which contains the 1.config.json, 2.pytorch_model.bin, 3.vocab.txt,
# or we will download these files from the model hub to this dir.
model_dir = "./state_dict/glm/"
# Autoloader can build the model and tokenizer automatically.
# 'seq2seq' is the task_name.
AutoLoader("seq2seq",model_name="GLM-large-ch",model_dir=model_dir)
model = auto_loader.get_model()
tokenizer = auto_loader.get_tokenizer()Instantiate the Trainer, and set the training parameters.
from flagai.trainer import Trainer
trainer = Trainer(
env_type="pytorch",
experiment_name="glm_poetry",
batch_size=4,
gradient_accumulation_steps=1,
lr=2e-4,
weight_decay=2e-8,
epochs=100,
log_interval=10,
tensorboard_dir="tbsummary",
eval_interval=2000000,
load_dir=None,
save_dir="checkpoints_poetry",
save_interval=1,
)Pass the model, data, and collate_fn into the trainer to start training:
trainer.train(model,
train_dataset=train_dataset,
collate_fn=my_collate_fn)Modify the model configuration path model_dir and the saved model path model_save_path before running. Run the command at the command line:
cd ./examples/glm_poetry_generation
python ./generate.py
You can choose between two generation methods: random sampling based on probability screening or beam search
print(predictor.predict_generate_randomsample(text,out_max_length=66, top_k=10, top_p=.1,
repetition_penalty=4.0, temperature=1.2))
print(predictor.predict_generate_beamsearch(text, out_max_length=66, beam_size=10))