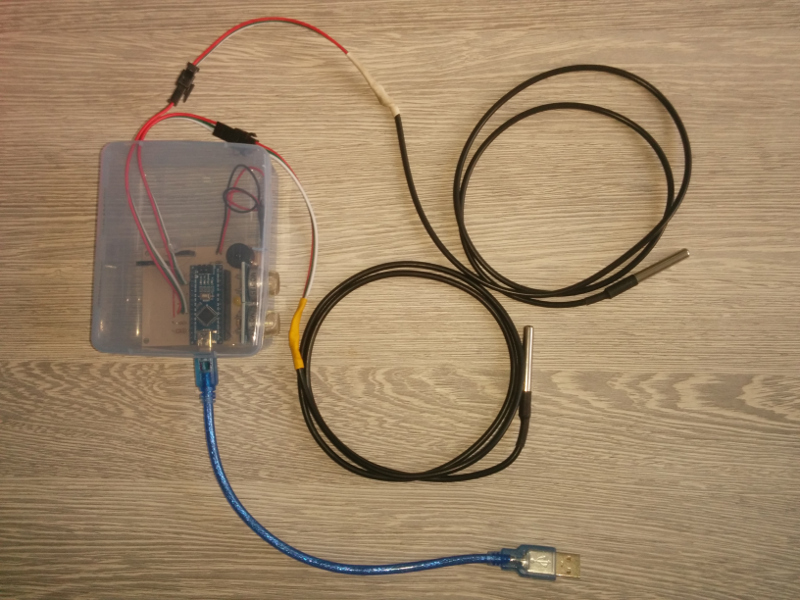
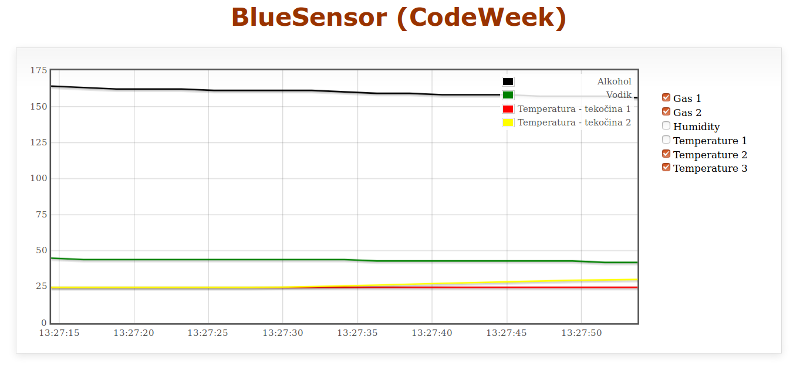
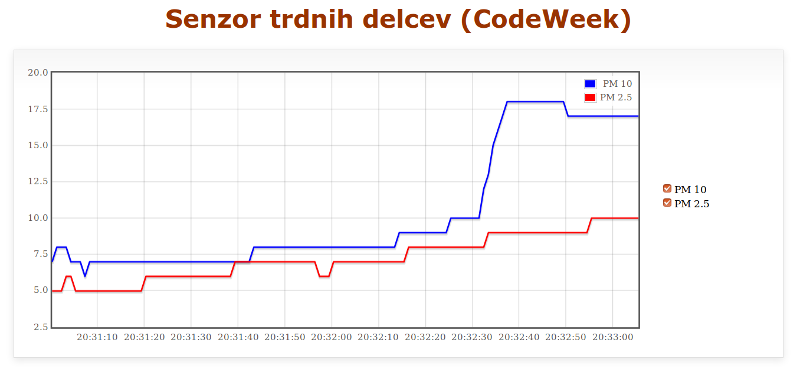
Arduino based device for temperature, air humidity and gas concentration measurment.
PCB dimension is 70mm x 55mm. Schematics is available in two PDF files (BlueSensor_v1.1_PCB_top.pdf and BlueSensor_v1.1_PCB_top_miror.pdf). PCB can be manufactured with chemo transfer method invented by Volk Darko. In that case mirror image should be used. Schematics have been developed by Darko Volk.
Needed materials:
- 1 x Arduino Nano
- 2 x MQ2-x gas sensors*
- 1 x DHT-22 (AM2302) humidity and temperature sensor
- 2 x (max 4 x) DS12B20 temperature sensor (on a cable)
- 1 x buzzer
- 1 x LED diode
- 1 x 4.7k Ohm resistor
- 1 x 270 Ohm resistor
- 1 x 100 Ohm resistor
- 1 x battery case (for 4 x AAA batteries)
PCB is designed to additionally connect:
- 1 x HC-05 Bluetooth module
- 1 x 2k Ohm resistor
- 1 x 4.6k Ohm resistor
However, in future versions Bluetooth will not be supported.
MQ-x gas sensor are cheap sensors for detecting leakage of various gases:
- MQ-2: combustible gases
- MQ-3: alcohol
- MQ-4: CH4, natural gas
- MQ-5: LPG, natural gas, coal gas
- MQ-6: LPG
- MQ-7: carbon monoxide
- MQ-8: hydrogen
- MQ-9: carbon monoxide and combustible gases
- MQ-135: air quality sensor
They have analog output and are not calibrated.
Python application bluesensor-server.py is used for displaying data from BlueSensor or SDS dust sensor in a web application. Appication runs web server on a localhost and calls data reader.
Currently there are two data readers available:
- read-serial (in read-serial.py), which reads JSON data from BlueSensor connected to USB port;
- read-dust (in read-dust.py), which reads data from SDS011, SDS018 or SDS021 dust sensor connected to USB port, and formats it to JSON;
- read-raw-serial (in read-raw-serial.py), which reads raw (tab-delimited) data from device connected to USB port, and formats them to JSON (you can use this for any sensor device which does not support our JSON format);
First you need to install Tornado Python web server. Od Ubuntu/Debian based systems you can do it with:
sudo pip install tornado
Then you connect BlueSensor or SDS dust reader to USB port and run:
- for reading data from BlueSensor connected to ttyUSB0:
python bluesensor-server.py read-serial 0 - for reading data from SDS dust reader (dust reader should always be connected to ttyUSB0):
python bluesensor-server.py read-dust
When application is started, you can open URL which is printed in console:
- for BlueSensor data from ttyUSB0: http://localhost:8080/
- for BlueSensor data from ttyUSB1: http://localhost:8081/, etc...
- for SDS dust sensor data: http://localhost:8089/
Arduino firmware for BlueSensor is available in a file BlueSensor_JSON.ino. Output data from BlueSensor are printed in JSON format. Dust reader already uses JSON formatting.
Data from sensor devices are presented in JSON format, which self-describes sensor device and sonnected sensors. Here is the example of it:
{
"metadata": {
"device_name": "BlueSensor",
"device_id": "BlueSensor1",
"device_location": "Slovenia",
"sensors": {
"temperature1": ["Room temperature", "DHT-22", "°C", "orange", "not ready"],
"humidity": ["Humidity", "DHT-22", "%", "blue", "not ready"],
"temperature2": ["Liquid 1 temperature", "DS18B20", "°C", "red", "ready"],
"temperature3": ["Liquid 2 temperature", "DS18B20", "°C", "yellow", "ready"],
"gas1": ["Alcohol", "MQ-3", "raw value", "green", "ready"],
"gas2": ["Combustible gases", "MQ-2", "raw value", "violet", "ready"]
}
},
"time": 0,
"data": {
"temperature1": "none",
"humidity": "none",
"temperature2": "none",
"temperature3": 25.0625,
"gas1": 296,
"gas2": 282
}
}