To be updated soon. This work springboards from the PyNEMO Project.
Steps to take to install PyNEMO, creating a specific conda virtual environment is highly recommended. click here for more about virtual enviroments
Clone PyNEMO repository:
$ export PYNEMO_DIR=$PWD/PyNEMO $ git clone https://github.com/NOC-MSM/PyNEMO.git
Create conda environment for PyNEMO:
$ cd $PyNEMO_DIR $ conda env create -f pynemo_39.yml
Activate the new virtual environment:
$ source activate pynemo
To deactivate:
$ conda deactivate
Make sure the Java Runtime Environment is set (e.g. livljobs*):
$ export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8.0-openjdk-1.8.0.322.b06-1.el7_9.x86_64/
Install PyNEMO:
$ python setup.py build $ python setup.py install
This should result in PyNEMO being installed in the virtual environment, and can be checked by entering:
$ pynemo -v
Resulting in a help usage prompt:
$ usage: pynemo -g -s <namelist.bdy>
To use PyNEMO, the following command is entered: (the example will run an benchmarking test):
$ pynemo -s /path/to/namelist/file (e.g. ./inputs/namelist_remote.bdy)
The PyNEMO module can be tested using the bench marking namelist bdy file in the inputs folder. To check the outputs of the benchmark test, these can be visualised using the plotting script within the test_scripts folder. The following steps are required,
Run PyNEMO using the namelist file in the inputs folder (namelist_remote.bdy) e.g.:
$ pynemo -s /path/to/namelist/file
This will create two output files coordinates.bdy.nc and NNA_R12_bdyT_y1979)m11.nc in an outputs folder
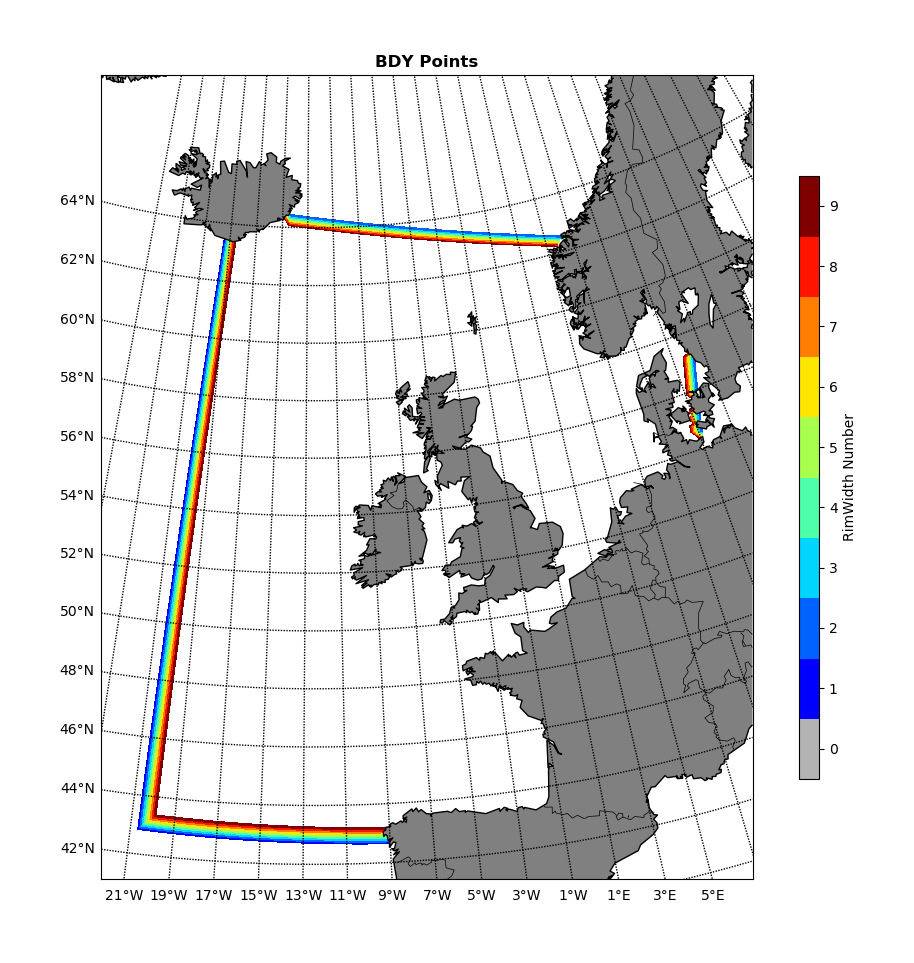
To check the coordinates.bdy.nc has the correct boundary points, the script bdy_coords_plot.py will plot the domain boundaries and shown the different locations of the rim width (increasing number should go inwards) This script is located in the test_scripts folder.
The result should look like this (if using the current benchmark data)