一个为 C++11 量身打造的轻量级 config 库,轻松完成 JSON 解析和序列化功能,并和 C++ 输入输出流交互。
- 仅头文件,低接入成本
- STL-like,低学习成本
- 与标准库 io 交互
- 非侵入式的序列化与反序列化
- Unicode与多编码支持(支持
char、wchar_t、char16_t和char32_t) - 可扩展的输入输出方式
注意:项目仍处于开发状态,可能有不兼容的修改。
项目此前叫做 jsonxx,现已更名为 configor!
在保证原有 API 可用的情况下,将在未来支持包括 JSON 在内的各种常见对象存储格式(如 YAML 等)。
如果您之前已经在使用 jsonxx,那么升级到 configor 将非常简单,只需要修改头文件的声明如下:
// 替换掉注释中的头文件,改为使用下方的头文件即可
// #include "jsonxx/json.hpp"
// using namespace jsonxx;
#include "configor/json.hpp"
using namespace configor;- 引入 configor 头文件
#include "configor/json.hpp"
using namespace configor;- 快速完成自定义类型与 JSON 转换
struct User {
std::string name;
int age;
// 一行代码完成字段绑定
CONFIGOR_BIND(json, User, REQUIRED(name), OPTIONAL(age))
};
// User 转换到 json
json j = User{"John", 18};
// json 转换到 User
User u = json({{"name", "John"}, {"age", 18}});- 使用 C++ 的方式的创建 JSON 对象
使用 operator[] 为 JSON 对象赋值
json j;
j["number"] = 1;
j["float"] = 1.5;
j["string"] = "this is a string";
j["boolean"] = true;
j["user"]["id"] = 10;
j["user"]["name"] = "Nomango";使用 std::initializer_list 为 JSON 对象赋值
// 使用初始化列表构造数组
json arr = { 1, 2, 3 };
// 使用初始化列表构造对象
json obj = {
{
"user", {
{ "id", 10 },
{ "name", "Nomango" }
}
}
};
// 第二个对象
json obj2 = {
{ "nul", nullptr },
{ "number", 1 },
{ "float", 1.3 },
{ "boolean", false },
{ "string", "中文测试" },
{ "array", { 1, 2, true, 1.4 } },
{ "object", {
{ "key", "value" },
{ "key2", "value2" },
}},
};使用辅助方法构造数组或对象
json arr = json::array({ 1 });
json obj = json::object({ { "user", { { "id", 1 }, { "name", "Nomango" } } } });- 判断 JSON 对象的值类型
// 判断 JSON 值类型
bool is_null();
bool is_bool();
bool is_integer();
bool is_float();
bool is_number(); // is_integer() || is_float()
bool is_string();
bool is_array();
bool is_object();- JSON 对象的取值与类型转换
通过 get 函数可以直接取值:
auto b = j.get<bool>(); // 仅当 j.is_bool() 时可用
auto i = j.get<int>(); // 仅当 j.is_integer() 时可用
auto i = j.get<int64_t>(); // 仅当 j.is_integer() 时可用
auto f = j.get<float>(); // 仅当 j.is_float() 时可用
auto d = j.get<double>(); // 仅当 j.is_float() 时可用
auto s = j.get<std::string>(); // 仅当 j.is_string() 时可用
// 对于实现了 config_bind 的自定义数据类型,也可以直接取值
// 详情请参考下方 `与自定义类型转换`
class MyObject;
auto myObj = j.get<MyObject>();注意:get函数会强校验数据类型(例如整形和浮点数不能自动转换),参数类型与值类型不同时会引发 configor_type_error 异常。
同时 get 支持取出引用和指针类型:
j.get<const std::string&>();
j.get<std::string&>();
j.get<const std::string*>();
j.get<std::string*>();通过有参数的 get 函数,可以传入对象引用来取值:
int n = 0;
if (j.get(n))
{
// 成功读取到 n 的值
}
else
{
// 读取 n 值失败
}通过 as 系列函数可以将数据类型尽可能的转换:
bool as_bool(); // 对bool直接返回,对数字类型判断是否非0,对null返回false,对其他类型返回empty()
int64_t as_integer(); // 对数字类型直接返回,对bool类型强转,对其他类型抛出
double as_float(); // 对数字类型直接返回,对bool类型强转,对其他类型抛出
std::string as_string(); // 对字符串类型直接返回,对数字类型和bool转换为字符串,对null返回空串,对其他类型抛出类型转换:
// 显式转换
bool b = (bool)j["boolean"];
int i = (int)j["number"];
float d = (float)j["float"];
// 对于实现了 config_bind 的自定义数据类型,也可以直接转换
// 详情请参考下方 `与自定义类型转换`
class MyObject;
MyObject myObj = (MyObject)j;
MyObject myObj = j;- size & empty & clear & count & ...
json arr = json::array({ 1, 2, 3 });
arr.size(); // 3
arr.empty(); // false
arr.erase(0); // 第一个元素被删除
arr.clear();
json obj = json::object({ { "one", 1 }, { "two", 2 } });
obj.size(); // 2
obj.empty(); // false
obj.count("one"); // 1
obj.count("missing"); // 0
obj.erase("one"); // one 被删除
obj.clear();- 比较运算符
j["boolean"] == true
j["number"] == 1
j["number"] != 2
j["number"] > 0
j["float"] < 3- JSON 对象类型和数组类型的遍历
// 增强 for 循环
for (auto& j : obj) {
std::cout << j << std::endl;
}// 使用迭代器遍历
for (auto iter = obj.begin(); iter != obj.end(); iter++) {
std::cout << iter.key() << ":" << iter.value() << std::endl;
}- 序列化为字符串
// 序列化为字符串
std::string json_str = j.dump();
// 美化输出,使用 4 个空格对输出进行格式化
std::string pretty_str = j.dump(4, ' ');- 序列化到文件
std::ofstream ofs("output.json");
ofs << j << std::endl;// 将 JSON 内容输出到文件,并美化
std::ofstream ofs("pretty.json");
ofs << std::setw(4) << j << std::endl;- 序列化到输出流
json j;
std::cout << j; // 可以使用 std::setw(4) 对输出内容美化- 从字符串中解析
json j = json::parse("{ \"happy\": true, \"pi\": 3.141 }");- 从文件中读取
std::ifstream ifs("sample.json");
json j;
ifs >> j;- 从用户输入中读取
json j;
std::cin >> j;configor 具有完备的 unicode 支持,同時支持 char、wchar_t、char16_t和char32_t。
对于 wchar_t 类型,可使用下面的别名来使用宽字符版本:
json // char
wjson // wchar_t宽字符版本示例代码:
wjson j = wjson::parse(L"{ \"name\": \"中文测试\" }");
std::wstring str = j[L"name"].get<std::wstring>();对 char16_t 和 char32_t 字符类型需要使用下面的别名
struct u16json_args : json_tpl_args
{
using char_type = char16_t;
};
struct u32json_args : json_tpl_args
{
using char_type = char32_t;
};
// char16_t
using u16json = configor::basic_value<u16json_args>;
// char32_t
using u32json = configor::basic_value<u32json_args>;由于C++标准库并不支持 char16_t 和 char32_t 的IO流,在不同的平台和编译器上可能会有不同表现。
对于 Clang 编译器来说,您可能需要自己实现 std::ctype<char16_t> 和 std::ctype<char32_t> 才能让 configor 正常工作。
- 将自定义类型与 JSON 绑定
configor 提供了 CONFIGOR_BIND 宏,可以用一行代码快速完成 json 绑定:
struct User
{
int user_id;
std::string user_name;
CONFIGOR_BIND(
json, User, // 将 User 类绑定到 json
CONFIGOR_REQUIRED(user_id), // user_id 字段必填,空值会引发异常
CONFIGOR_OPTIONAL(user_name) // user_name 字段非必填,空值会被忽略
);
};
// 对私有成员变量同样适用
class User
{
private:
int user_id;
std::string user_name;
public:
// 绑定私有字段,支持 REQUIRED 和 OPTIONAL 的简写
CONFIGOR_BIND(json, User, REQUIRED(user_id), OPTIONAL(user_name));
};
// 指定与 C++ 字段名不同的 JSON 名
class User
{
private:
int user_id_;
std::string user_name_;
public:
// 为 JSON 指定不同的名称,使 User 可以接受如 {"id": 1, "name": "John"} 这样的 JSON 内容
CONFIGOR_BIND(json, User, REQUIRED(user_id_, "id"), OPTIONAL(user_name_, "name"));
};与 JSON 绑定后,可以方便的将自定义类型与 JSON 进行转换:
json j;
User user;
// 将 User 转换为 json
j = user;
// 将 json 转换为 User
user = (User)j;同时会默认支持 User 的智能指针、std::vector<User>、std::map<std::string, User> 等类型的自动转换。
例如,下面的代码是正确的:
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<User>> user_list;
json j = user_list; // 可以正确处理复合类型的转换对于第三方库的类型,由于无法侵入式的在其内部声明 JSON_BIND,可以通过特化实现 config_bind 类,非侵入式的绑定到 JSON。
特化实现 config_bind 的例子:
// 用户类
struct User
{
int user_id;
std::string user_name;
};
// 与 json 绑定
namespace configor
{
template <>
struct value_binder<User>
{
static void to_value(json& j, const User& v)
{
j = { { "user_id", v.user_id }, { "user_name", v.user_name } };
}
static void from_value(const json& j, User& v)
{
j["user_id"].get(v.user_id);
j["user_name"].get(v.user_name);
}
};
}- 将自定义类型以 JSON 格式与输入输出流交互
使用 json::wrap 函数可以让任意类型实现序列化与反序列化,并与输入输出流交互
std::stringstream s;
// 把 obj 序列化,并输入到 s 流中
s << json::wrap(obj);
// 从 s 流中读取,并把 obj 反序列化
s >> json::wrap(obj);- 实现自定义User类的序列化与反序列化
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <configor/json.hpp>
using namespace configor;
// 用户类
struct User
{
int user_id;
std::string user_name;
CONFIGOR_BIND(json, User, REQUIRED(user_id), OPTIONAL(user_name));
};
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
std::stringstream s("{\"user_id\": 10001, \"user_name\": \"John\"}");
// 解析json内容,并反序列化到user对象
User user;
s >> json::wrap(user);
// 序列化user对象并输出
std::cout << json::wrap(user) << std::endl; // {"user_id":10001,"user_name":"John"}
return 0;
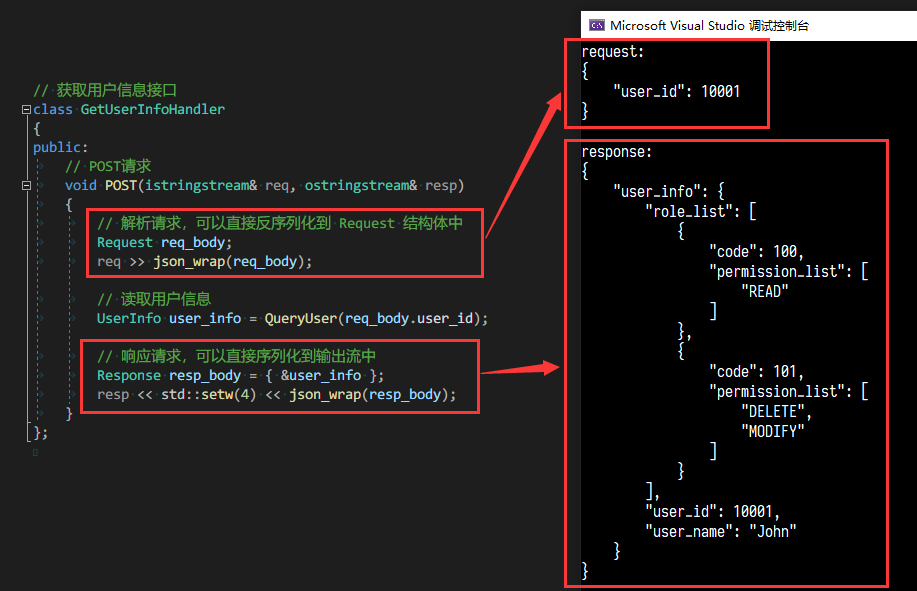
}- 一个HTTP接口的伪代码
抛出异常 config deserialization error: unexpected token 'end_of_input'
往往是读取文件失败导致的,请检查文件路径是否正确。
Windows 下中文乱码
这是由于在中文环境下,Visual Studio 和 Windows 终端使用的编码都是 gb2312,而 configor 仅支持 unicode。
Visual Studio 使用 utf-8 非常困难,建议直接忽略编码,对中文不做处理:
using namespace configor;
// 使用 encoding::ignore 忽略编码
json j = json::parse<encoding::ignore>("{\"chinese\":\"一些带有中文的JSON字符串\"}");
std::cout << j.dump<encoding::ignore>() << std::endl;或使用自定义的json类:
struct my_json_args : configor::json_tpl_args
{
// 使用 encoding::ignore 忽略编码
template <typename _CharTy>
using default_encoding = configor::encoding::ignore<_CharTy>;
};
using json = configor::basic_value<my_json_args>;如何保证 JSON 序列化时按 key 的插入顺序输出?
configor 内部使用 std::map 存储 kv 对象,默认是按 key 的字符串大小排序的。
建议用第三方库替换 std::map,比如 nlohmann/fifo_map,然后声明 fifo_json 替换 json 来保证插入序
struct fifo_json_args : json_tpl_args
{
template <class _Kty, class _Ty, class... _Args>
using object_type = nlohmann::fifo_map<_Kty, _Ty>;
};
// fifo_json 是按插入序排列的
using fifo_json = configor::basic_value<fifo_json_args>;若你需要将 JSON 解析和序列化应用到非 std::basic_stream 流中,可以通过实现自定义 oadapter 和 iadapter 的方式。
一个 oadapter 的例子:
struct myadapter : public oadapter
{
// 实现 write 接口,写入一个字符
virtual void write(const char ch) override
{
// 直接输出到屏幕
std::cout << ch;
}
};
// 使用方式
myadapter ma;
oadapterstream os{ ma };
j.dump(os); // 将 json j 序列化输出到屏幕上一个 iadapter 的例子:
struct myadapter : public iadapter
{
// 实现 read 接口,读取一个字符
virtual char read() override
{
// 直接从用户输入读取字符,读到换行符结束
char ch = std::cin.get();
if (ch == '\n')
return std::char_traits<char>::eof();
return ch;
}
};
// 使用方式
myadapter ma;
iadapterstream is{ ma };
json j = json::parse(is); // 读取用户输入,并反序列化详细内容请参考 json_stream.hpp
- 完全的 unicode 支持
- 单测覆盖率达到 85% 以上
- 支持注释
- 支持 json 和自定义类型的隐式转换(has_to_json限定)
- optional 返回值的支持(作为模板参数并允许替换)
- 错误信息完善
- SAX工具
感谢 nlohmann 的 JSON for Modern C++ 项目,本仓库的许多概念和灵感都来源于此。