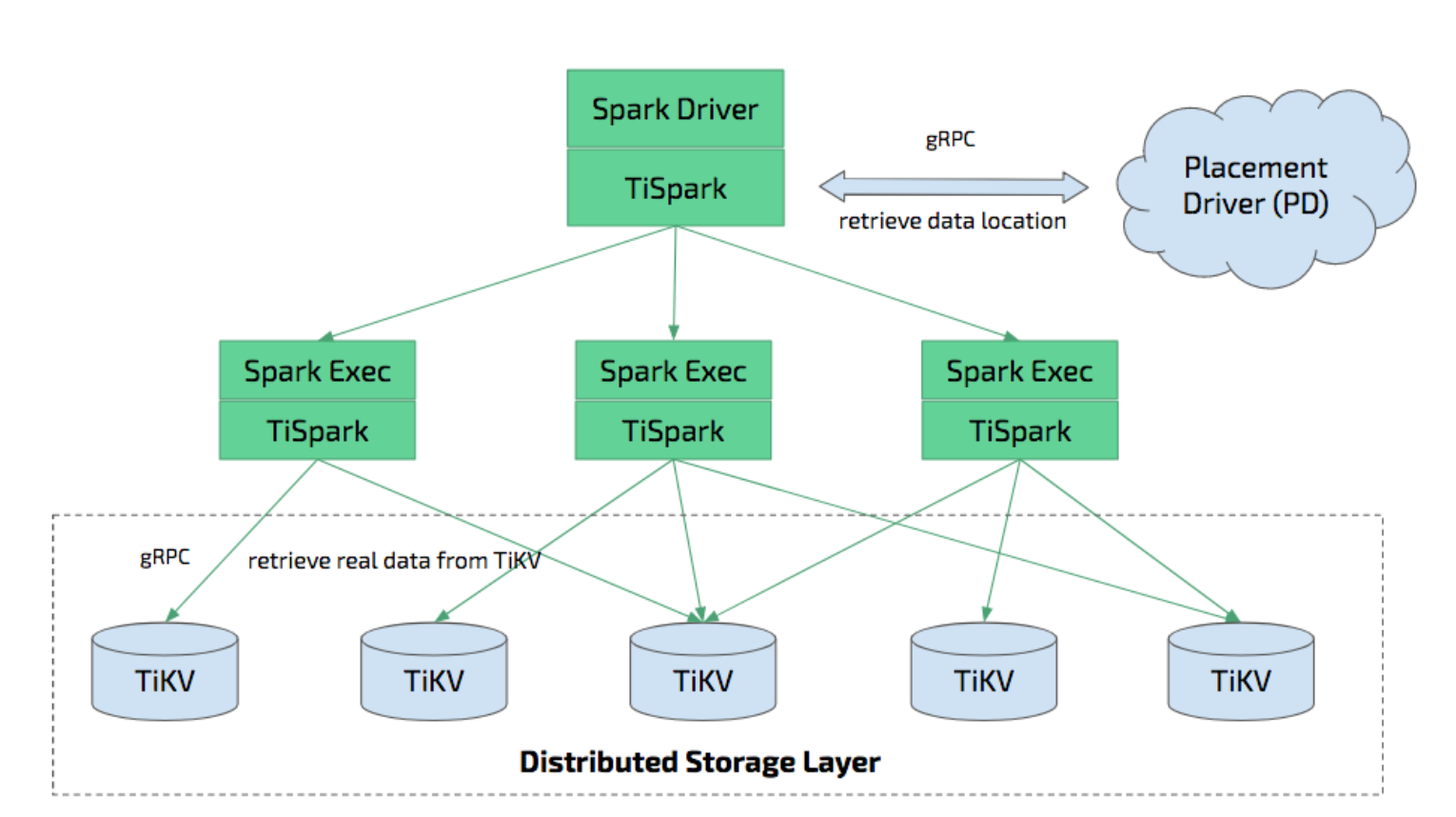
TiSpark is a thin layer built for running Apache Spark on top of TiDB/TiKV to answer the complex OLAP queries. It takes advantages of both the Spark platform and the distributed TiKV cluster, at the same time, seamlessly glues to TiDB, the distributed OLTP database, to provide a Hybrid Transactional/Analytical Processing (HTAP) to serve as a one-stop solution for online transactions and analysis.
-
TiSpark integrates with Spark Catalyst Engine deeply. It provides precise control of the computing, which allows Spark read data from TiKV efficiently. It also supports index seek, which improves the performance of the point query execution significantly.
-
It utilizes several strategies to push down the computing to reduce the size of dataset handling by Spark SQL, which accelerates the query execution. It also uses the TiDB built-in statistical information for the query plan optimization.
-
From the data integration point of view, TiSpark + TiDB provides a solution runs both transaction and analysis directly on the same platform without building and maintaining any ETLs. It simplifies the system architecture and reduces the cost of maintenance.
-
In addition, you can deploy and utilize tools from the Spark ecosystem for further data processing and manipulation on TiDB. For example, using TiSpark for data analysis and ETL; retrieving data from TiKV as a machine learning data source; generating reports from the scheduling system and so on.
TiSpark depends on the existence of TiKV clusters and PDs. It also needs to setup and use Spark clustering platform.
A thin layer of TiSpark. Most of the logic is inside tikv-java-client library. https://github.com/pingcap/tikv-client-lib-java
Uses as below
./bin/spark-shell --jars /wherever-it-is/tispark-${version}-jar-with-dependencies.jar
import org.apache.spark.sql.TiContext
val ti = new TiContext(spark)
// Map all TiDB tables from database tpch as Spark SQL tables
ti.tidbMapDatabase("tpch")
spark.sql("select count(*) from lineitem").show
If you are using spark-shell, you need to manually load schema information as decribed above.
If you have too many tables, you might choose to disable histogram preparison and loading will be faster.
ti.tidbMapDatabase("tpch", autoLoadStatistics = true)
If you have two tables with same name in different databases, you might choose to append database name as prefix for table name:
ti.tidbMapDatabase("tpch", dbNameAsPrefix = true)
If you have too many tables and use only some of them, to speed up meta loading process, you might manually load only tables you use:
ti.tidbTable("tpch", "lineitem")
If you have newly created table which is not yet synchronized into TiSpark between refresh period, you can manually refresh schema metadata:
ti.meta.reloadMeta
ti.version
or
spark.sql("select ti_version()").show
Below configurations can be put together with spark-defaults.conf or passed in the same way as other Spark config properties.
| Key | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| spark.tispark.pd.addresses | 127.0.0.1:2379 | PD Cluster Addresses, split by comma |
| spark.tispark.grpc.framesize | 268435456 | Max frame size of GRPC response |
| spark.tispark.grpc.timeout_in_sec | 10 | GRPC timeout time in seconds |
| spark.tispark.meta.reload_period_in_sec | 60 | Metastore reload period in seconds |
| spark.tispark.plan.allow_agg_pushdown | true | If allow aggregation pushdown (in case of busy TiKV nodes) |
| spark.tispark.plan.allow_index_read | false | If allow index read (which might cause heavy pressure on TiKV) |
| spark.tispark.index.scan_batch_size | 20000 | How many row key in batch for concurrent index scan |
| spark.tispark.index.scan_concurrency | 5 | Maximal threads for index scan retrieving row keys (shared among tasks inside each JVM) |
| spark.tispark.table.scan_concurrency | 512 | Maximal threads for table scan (shared among tasks inside each JVM) |
| spark.tispark.request.command.priority | "Low" | "Low", "Normal", "High" which impacts resource to get in TiKV. Low is recommended for not disturbing OLTP workload |
| spark.tispark.coprocess.streaming | false | Whether to use streaming for response fetching |
| spark.tispark.plan.unsupported_pushdown_exprs | "" | A comma separated list of expressions. In case you have very old version of TiKV, you might disable some of the expression push-down if not supported |
| spark.tispark.plan.downgrade.index_threshold | 10000 | If index scan ranges on one region exceeds this limit in original request, downgrade this region's request to table scan rather than original planned index scan |
| spark.tispark.type.unsupported_mysql_types | "time,enum,set,year,json" | A comma separated list of mysql types TiSpark does not support currently, refer to Unsupported MySQL Type List below |
| spark.tispark.request.timezone.offset | Local Timezone offset | An integer, represents timezone offset to UTC time(like 28800, GMT+8), this value will be added to requests issued to TiKV |
| Mysql Type |
|---|
| time |
| enum |
| set |
| year |
| json |
If you want to know how TiSpark could benefit from TiDB's statistic information, read more here.
Read the Quick Start.
To build all TiSpark modules :
mvn clean install -Dmaven.test.skip=true
Remember to add -Dmaven.test.skip=true to skip all the tests if you don't need to run them.
We use docker-compose to provide tidb cluster service which allows you to run test across different platforms. It is recommended to install docker in order to test locally, or you can set up your own TiDB cluster locally as you wish.
If you prefer the docker way, you can use docker-compose up -d to launch tidb cluster service under tispark home directory. If you want to see tidb cluster's log you can launch via docker-compose up. You can use docker-compose down to shutdown entire tidb cluster service. All data is stored in data directory at the root of this project. Feel free to change it.
You can read more about test here.
TiSpark is under the Apache 2.0 license. See the LICENSE file for details.