As in any ML problem, data used to train models is indispensable to the model's performance and value. The same principle applies to Generative AI tasks. More precisely, in finetuning Large Language Models, one of the critical components in this course.
Thus, let's go over a few bullet points on why it might be essential for you to consider analyzing your dataset before finetuning any LLM model.
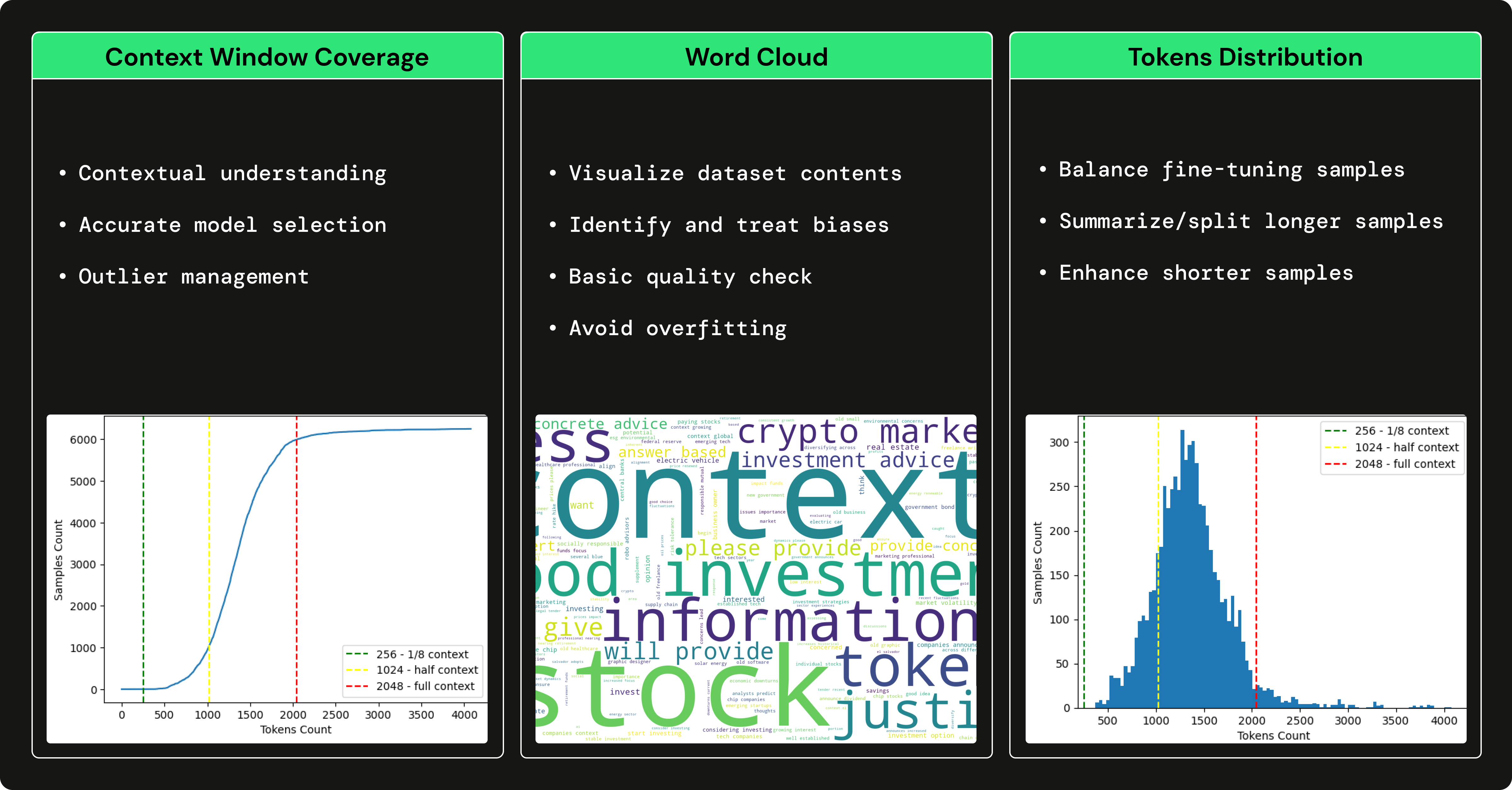
Here are the key steps of our EDA (Exploratory Data Analysis) on the prompts of the Q&A dataset:
-
Helps in selecting the optimal context window size for your dataset
-
Ensures that your model can capture the whole contextual meaning of your prompt.
-
Helps in accurately selecting a parameter size for your model (7B, 13B, 2B)
-
Helps in establishing the max_sequence_len, speeds up fine-tuning due to lower attention masking matmul’s.
-
Visual representation of most representative words
-
Helps in preventing bias towards a specific theme (overfit)
-
Helps in processing/removing irrelevant frequent words
-
Could serve as a primary quality check of your overall dataset vocabulary
-
Helps to balance the lengths of your dataset prompts
-
Easy to check for the Gaussian Bell distribution of lengths
-
Helps identify the samples that could be enhanced or summarised
-
Helps limit the input prompt to a specific size, allowing the completion sentence to be longer.
→ Check out the EDA notebook at dataset_analysis/prompts_eda.ipynb to see the complete analysis.