python3 train_SVM.py
- for real-time person detection :
python3 visualize_real_time.py
Histogram of oriented gradients (HOG) is a feature descriptor used to detect objects in computer vision and image processing. The HOG descriptor technique counts occurrences of gradient orientation in localized portions of an image - detection window, or region of interest (ROI).
Implementation of the HOG descriptor algorithm is as follows:
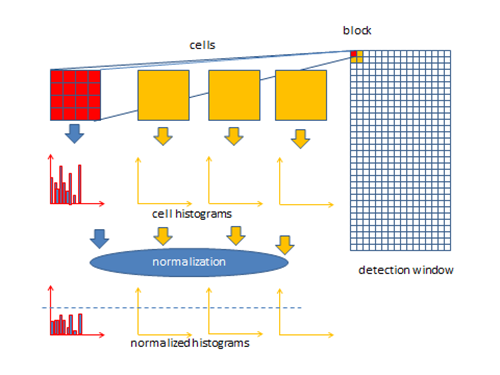
Divide the image into small connected regions called cells, and for each cell compute a histogram of gradient directions or edge orientations for the pixels within the cell. Discretize each cell into angular bins according to the gradient orientation. Each cell's pixel contributes weighted gradient to its corresponding angular bin. Groups of adjacent cells are considered as spatial regions called blocks. The grouping of cells into a block is the basis for grouping and normalization of histograms.Normalized group of histograms represents the block histogram. The set of these block histograms represents the descriptor.
The following figure demonstrates the algorithm implementation scheme:
Computation of the HOG descriptor requires the following basic configuration parameters:
Masks to compute derivatives and gradients
Geometry of splitting an image into cells and grouping cells into a block
Block overlapping
Normalization parameters
According to (Source : https://lear.inrialpes.fr/people/triggs/pubs/Dalal-cvpr05.pdf) the recommended values for the HOG parameters are:
1D centered derivative mask [-1, 0, +1]
Detection window size is 64x128
Cell size is 8x8
Block size is 16x16 (2x2 cells)