如果某个系统支持两个或者多个动作同时存在,那么这个系统就是一个并发系统。
如果某个系统支持两个或者多个动作同时执行,那么这个系统就是一个并行系统。
并发系统与并行系统这两个定义之间的关键差异在于“存在”这个词。
如果单核 CPU 并发执行任务,这些任务是同时存在的,CPU 会在不同任务之间进行切换,直到所有任务执行完成。并行意味着一定在多核 CPU 上,多个任务(线程)会被分配到独立的处理器上,因此可以同时运行。因此并行其实是并发的一个子集。
Object 中的方法:
- wait()
- notify()
- notifyAll()
关于等待与唤醒的例子,循环打印 ABC...:
public class PrintSamples {
public static class PrintTask {
private TaskEnum taskEnum;
public PrintTask(TaskEnum taskEnum) {
this.taskEnum = taskEnum;
}
public synchronized void printA() throws InterruptedException {
while (!taskEnum.equals(TaskEnum.A)) {
wait();
}
System.out.print("A");
taskEnum = TaskEnum.B;
notifyAll();
}
public synchronized void printB() throws InterruptedException {
while (!taskEnum.equals(TaskEnum.B)) {
wait();
}
System.out.print("B");
taskEnum = TaskEnum.C;
notifyAll();
}
public synchronized void printC() throws InterruptedException {
while (!taskEnum.equals(TaskEnum.C)) {
wait();
}
System.out.print("C");
taskEnum = TaskEnum.A;
notifyAll();
}
}
public enum TaskEnum {
A, B, C
}
}Thread 中的方法:
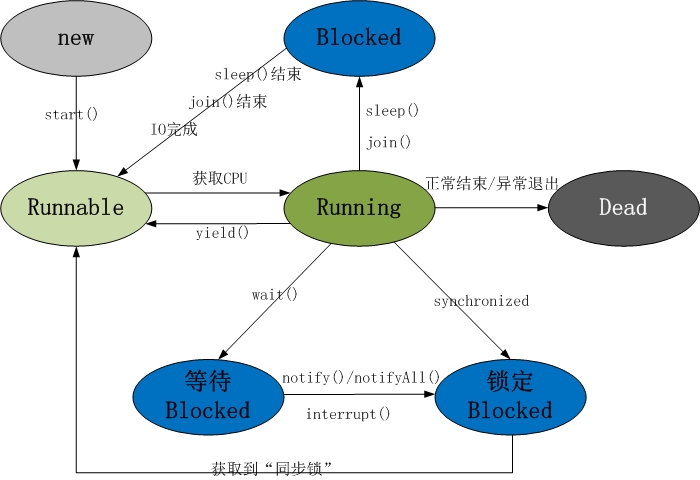
- yield():让出当前 CPU 的执行权,从”运行状态“进入到“就绪状态”,并不能保证在当前线程调用
yield()之后,其它具有相同优先级的线程就一定能获得执行权,也有可能是当前线程又进入到“运行状态”继续运行- wait() 让线程进入阻塞状态,并释放锁,而
yield()让线程进入执行状态,不会释放锁,会和其他线程共同竞争 CPU 资源
- wait() 让线程进入阻塞状态,并释放锁,而
- sleep():线程休眠,从“运行状态”进入“阻塞状态”,阻塞期间不会释放锁,时间过期后,进去“就绪状态”
- join():作用:在 A 线程中调用了 B 线程的
join()方法时,表示只有当 B 线程执行完毕时,A 线程才能继续执行- 底层调用
wait()方法,因此会释放锁
- 底层调用
- interrupt():中断,当一个线程调用该方法时,调用方与被调用方需要配合处理中断程序,如果中断的程序处于阻塞状态(wait、sleep、join),则抛出
InterruptedException异常 - isInterrupted():返回当前线程中断标识(true or false)
- interrupted():返回当前线程中断标识,并清除中断状态,抛出
InterruptedException异常同样会清除中断状态
原因:任意对象都可以作为锁。
这个问题和线程的 wait 与 notify 机制有很大的关系,当我们使用 synchronized 关键字加锁时这个锁可以是任何对象,并不一定是 Thread 才行,当一个线程 wait 时,一定是调用这个锁的 wait 方法,同样唤醒时也必须调用这个锁的 notify(notifyAll)方法。
下面是一个例子:
public class NotifySamples {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Object lock = new Object();
ThreadA t1 = new ThreadA("sub", lock);
synchronized (lock) {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " start t1");
t1.start();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " wait()");
lock.wait();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " continue");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
static class ThreadA extends Thread {
private final Object lock;
public ThreadA(String name, Object lock) {
super(name);
this.lock = lock;
}
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " call notify()");
// 唤醒当前的wait线程
lock.notify();
}
}
}
}public class ProducerConsumerSamples {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Resource resource = new Resource(new ArrayList<>(), 2);
new Thread(new Producer(resource)).start();
new Thread(new Producer(resource)).start();
new Thread(new Producer(resource)).start();
new Thread(new Consumer(resource)).start();
new Thread(new Consumer(resource)).start();
new Thread(new Consumer(resource)).start();
}
public static class Consumer implements Runnable {
private final Resource resource;
public Consumer(Resource resource) {
this.resource = resource;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
resource.consume();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static class Producer implements Runnable {
private final Resource resource;
public Producer(Resource resource) {
this.resource = resource;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
resource.produce();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
com.yunhu.erpsaas.client.service.StockService.getAvailableStockNumByItemIds("330110000011", "["SP20200207000012"]")
public static class Resource {
private final List<Integer> bufList;
private final Integer maxBufSize;
public Resource(List<Integer> bufList, Integer maxBufSize) {
this.bufList = bufList;
this.maxBufSize = maxBufSize;
}
public synchronized void produce() throws InterruptedException {
while (bufList.size() >= maxBufSize) {
System.out.println("装不下了");
wait();
}
int nextInt = new Random().nextInt(100) + 1;
bufList.add(nextInt);
System.out.println("进货:" + nextInt);
notifyAll();
}
public synchronized void consume() throws InterruptedException {
while (bufList.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("没有货了");
wait();
}
Integer remove = bufList.remove(0);
System.out.println("出货:" + remove);
notifyAll();
}
}
}