Table of Contents generated with DocToc
nextTick 可以让我们在下次 DOM 更新循环结束之后执行延迟回调,用于获得更新后的 DOM。
在 Vue 2.4 之前都是使用的 microtasks,但是 microtasks 的优先级过高,在某些情况下可能会出现比事件冒泡更快的情况,但如果都使用 macrotasks 又可能会出现渲染的性能问题。所以在新版本中,会默认使用 microtasks,但在特殊情况下会使用 macrotasks,比如 v-on。
对于实现 macrotasks ,会先判断是否能使用 setImmediate ,不能的话降级为 MessageChannel ,以上都不行的话就使用 setTimeout
if (typeof setImmediate !== 'undefined' && isNative(setImmediate)) {
macroTimerFunc = () => {
setImmediate(flushCallbacks)
}
} else if (
typeof MessageChannel !== 'undefined' &&
(isNative(MessageChannel) ||
// PhantomJS
MessageChannel.toString() === '[object MessageChannelConstructor]')
) {
const channel = new MessageChannel()
const port = channel.port2
channel.port1.onmessage = flushCallbacks
macroTimerFunc = () => {
port.postMessage(1)
}
} else {
/* istanbul ignore next */
macroTimerFunc = () => {
setTimeout(flushCallbacks, 0)
}
}nextTick 同时也支持 Promise 的使用,会判断是否实现了 Promise
export function nextTick(cb?: Function, ctx?: Object) {
let _resolve
// 将回调函数整合进一个数组中
callbacks.push(() => {
if (cb) {
try {
cb.call(ctx)
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, ctx, 'nextTick')
}
} else if (_resolve) {
_resolve(ctx)
}
})
if (!pending) {
pending = true
if (useMacroTask) {
macroTimerFunc()
} else {
microTimerFunc()
}
}
// 判断是否可以使用 Promise
// 可以的话给 _resolve 赋值
// 这样回调函数就能以 promise 的方式调用
if (!cb && typeof Promise !== 'undefined') {
return new Promise(resolve => {
_resolve = resolve
})
}
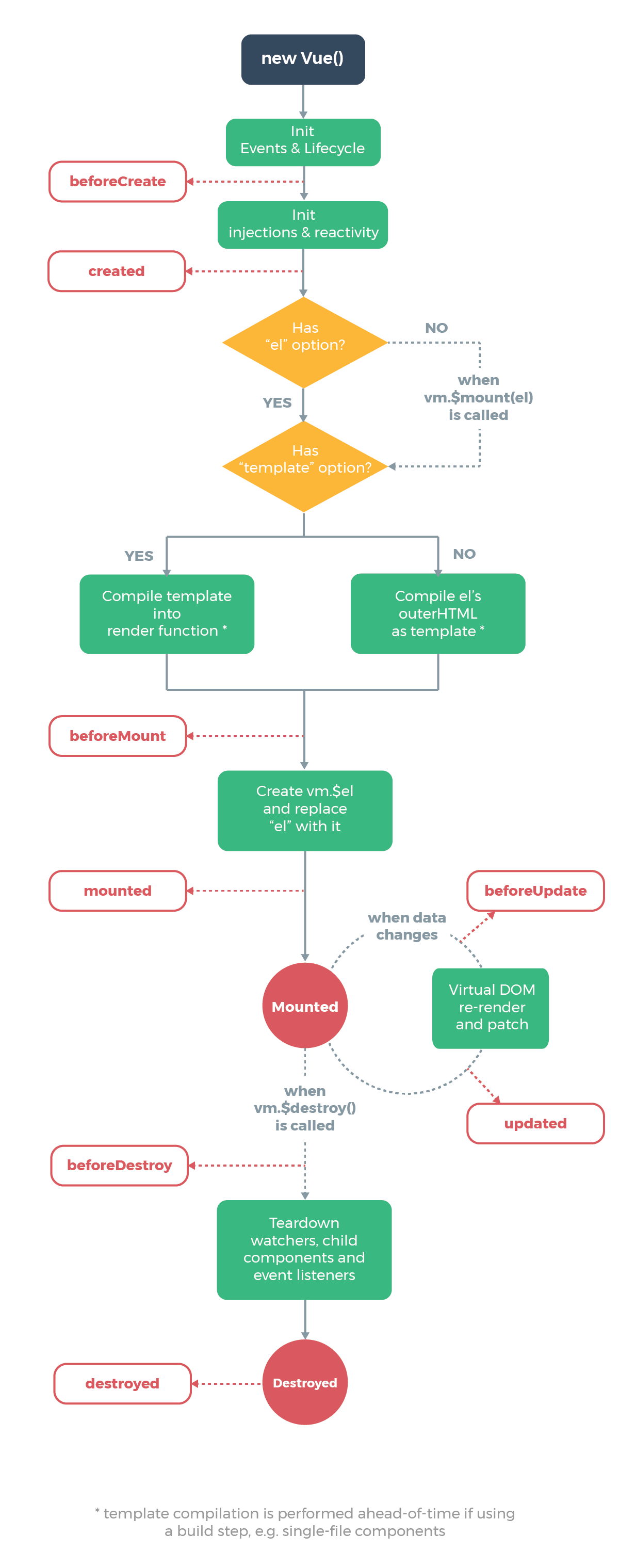
}生命周期函数就是组件在初始化或者数据更新时会触发的钩子函数。
在初始化时,会调用以下代码,生命周期就是通过 callHook 调用的
Vue.prototype._init = function(options) {
initLifecycle(vm)
initEvents(vm)
initRender(vm)
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate') // 拿不到 props data
initInjections(vm)
initState(vm)
initProvide(vm)
callHook(vm, 'created')
}可以发现在以上代码中,beforeCreate 调用的时候,是获取不到 props 或者 data 中的数据的,因为这些数据的初始化都在 initState 中。
接下来会执行挂载函数
export function mountComponent {
callHook(vm, 'beforeMount')
// ...
if (vm.$vnode == null) {
vm._isMounted = true
callHook(vm, 'mounted')
}
}beforeMount 就是在挂载前执行的,然后开始创建 VDOM 并替换成真实 DOM,最后执行 mounted 钩子。这里会有个判断逻辑,如果是外部 new Vue({}) 的话,不会存在 $vnode ,所以直接执行 mounted 钩子了。如果有子组件的话,会递归挂载子组件,只有当所有子组件全部挂载完毕,才会执行根组件的挂载钩子。
接下来是数据更新时会调用的钩子函数
function flushSchedulerQueue() {
// ...
for (index = 0; index < queue.length; index++) {
watcher = queue[index]
if (watcher.before) {
watcher.before() // 调用 beforeUpdate
}
id = watcher.id
has[id] = null
watcher.run()
// in dev build, check and stop circular updates.
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && has[id] != null) {
circular[id] = (circular[id] || 0) + 1
if (circular[id] > MAX_UPDATE_COUNT) {
warn(
'You may have an infinite update loop ' +
(watcher.user
? `in watcher with expression "${watcher.expression}"`
: `in a component render function.`),
watcher.vm
)
break
}
}
}
callUpdatedHooks(updatedQueue)
}
function callUpdatedHooks(queue) {
let i = queue.length
while (i--) {
const watcher = queue[i]
const vm = watcher.vm
if (vm._watcher === watcher && vm._isMounted) {
callHook(vm, 'updated')
}
}
}上图还有两个生命周期没有说,分别为 activated 和 deactivated ,这两个钩子函数是 keep-alive 组件独有的。用 keep-alive 包裹的组件在切换时不会进行销毁,而是缓存到内存中并执行 deactivated 钩子函数,命中缓存渲染后会执行 actived 钩子函数。
最后就是销毁组件的钩子函数了
Vue.prototype.$destroy = function() {
// ...
callHook(vm, 'beforeDestroy')
vm._isBeingDestroyed = true
// remove self from parent
const parent = vm.$parent
if (parent && !parent._isBeingDestroyed && !vm.$options.abstract) {
remove(parent.$children, vm)
}
// teardown watchers
if (vm._watcher) {
vm._watcher.teardown()
}
let i = vm._watchers.length
while (i--) {
vm._watchers[i].teardown()
}
// remove reference from data ob
// frozen object may not have observer.
if (vm._data.__ob__) {
vm._data.__ob__.vmCount--
}
// call the last hook...
vm._isDestroyed = true
// invoke destroy hooks on current rendered tree
vm.__patch__(vm._vnode, null)
// fire destroyed hook
callHook(vm, 'destroyed')
// turn off all instance listeners.
vm.$off()
// remove __vue__ reference
if (vm.$el) {
vm.$el.__vue__ = null
}
// release circular reference (#6759)
if (vm.$vnode) {
vm.$vnode.parent = null
}
}在执行销毁操作前会调用 beforeDestroy 钩子函数,然后进行一系列的销毁操作,如果有子组件的话,也会递归销毁子组件,所有子组件都销毁完毕后才会执行根组件的 destroyed 钩子函数。
在开始之前,推荐大家 clone 一份源码对照着看。因为篇幅较长,函数间的跳转也很多。
使用路由之前,需要调用 Vue.use(VueRouter),这是因为让插件可以使用 Vue
export function initUse (Vue: GlobalAPI) {
Vue.use = function (plugin: Function | Object) {
// 判断重复安装插件
const installedPlugins = (this._installedPlugins || (this._installedPlugins = []))
if (installedPlugins.indexOf(plugin) > -1) {
return this
}
const args = toArray(arguments, 1)
// 插入 Vue
args.unshift(this)
// 一般插件都会有一个 install 函数
// 通过该函数让插件可以使用 Vue
if (typeof plugin.install === 'function') {
plugin.install.apply(plugin, args)
} else if (typeof plugin === 'function') {
plugin.apply(null, args)
}
installedPlugins.push(plugin)
return this
}
}接下来看下 install 函数的部分实现
export function install (Vue) {
// 确保 install 调用一次
if (install.installed && _Vue === Vue) return
install.installed = true
// 把 Vue 赋值给全局变量
_Vue = Vue
const registerInstance = (vm, callVal) => {
let i = vm.$options._parentVnode
if (isDef(i) && isDef(i = i.data) && isDef(i = i.registerRouteInstance)) {
i(vm, callVal)
}
}
// 给每个组件的钩子函数混入实现
// 可以发现在 `beforeCreate` 钩子执行时
// 会初始化路由
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate () {
// 判断组件是否存在 router 对象,该对象只在根组件上有
if (isDef(this.$options.router)) {
// 根路由设置为自己
this._routerRoot = this
this._router = this.$options.router
// 初始化路由
this._router.init(this)
// 很重要,为 _route 属性实现双向绑定
// 触发组件渲染
Vue.util.defineReactive(this, '_route', this._router.history.current)
} else {
// 用于 router-view 层级判断
this._routerRoot = (this.$parent && this.$parent._routerRoot) || this
}
registerInstance(this, this)
},
destroyed () {
registerInstance(this)
}
})
// 全局注册组件 router-link 和 router-view
Vue.component('RouterView', View)
Vue.component('RouterLink', Link)
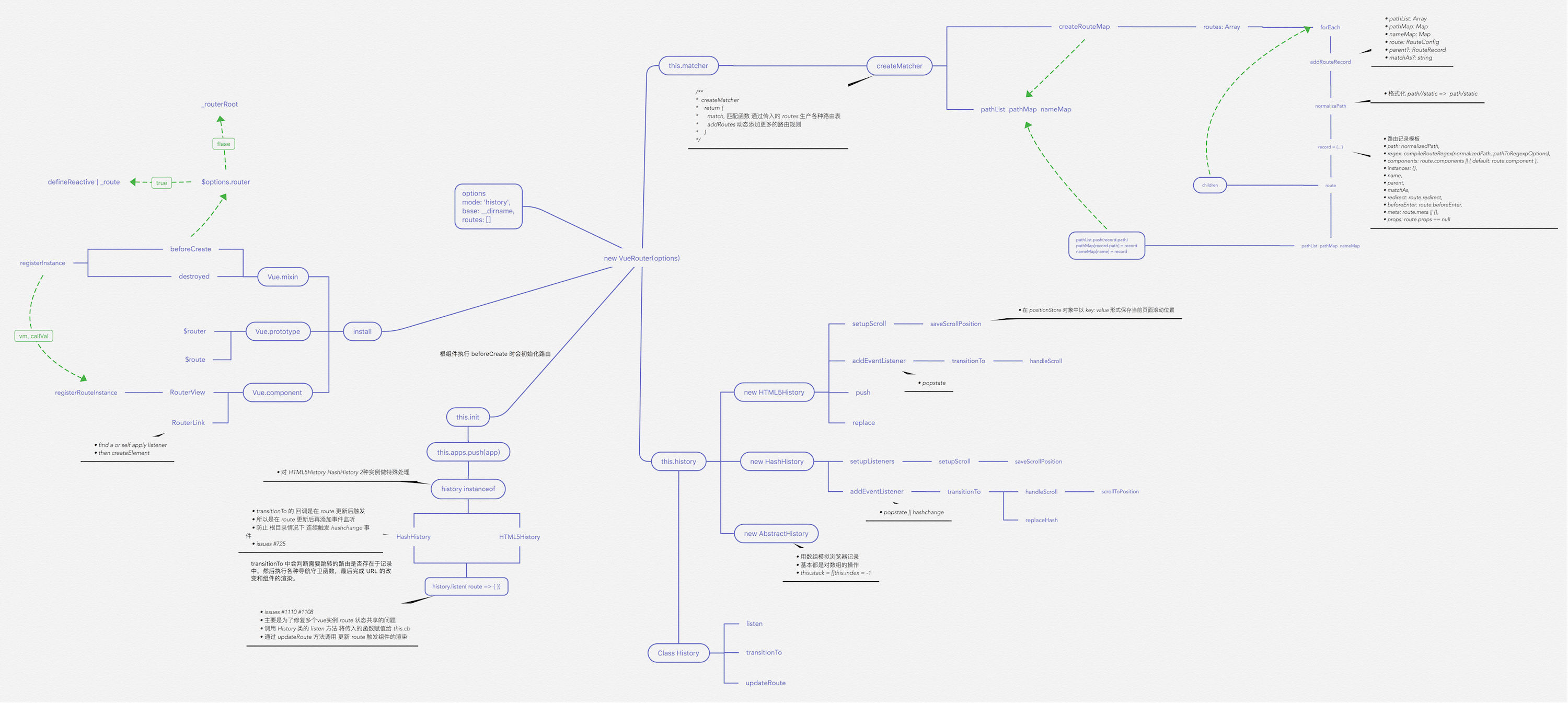
}对于路由注册来说,核心就是调用 Vue.use(VueRouter),使得 VueRouter 可以使用 Vue。然后通过 Vue 来调用 VueRouter 的 install 函数。在该函数中,核心就是给组件混入钩子函数和全局注册两个路由组件。
在安装插件后,对 VueRouter 进行实例化。
const Home = { template: '<div>home</div>' }
const Foo = { template: '<div>foo</div>' }
const Bar = { template: '<div>bar</div>' }
// 3. Create the router
const router = new VueRouter({
mode: 'hash',
base: __dirname,
routes: [
{ path: '/', component: Home }, // all paths are defined without the hash.
{ path: '/foo', component: Foo },
{ path: '/bar', component: Bar }
]
})来看一下 VueRouter 的构造函数
constructor(options: RouterOptions = {}) {
// ...
// 路由匹配对象
this.matcher = createMatcher(options.routes || [], this)
// 根据 mode 采取不同的路由方式
let mode = options.mode || 'hash'
this.fallback =
mode === 'history' && !supportsPushState && options.fallback !== false
if (this.fallback) {
mode = 'hash'
}
if (!inBrowser) {
mode = 'abstract'
}
this.mode = mode
switch (mode) {
case 'history':
this.history = new HTML5History(this, options.base)
break
case 'hash':
this.history = new HashHistory(this, options.base, this.fallback)
break
case 'abstract':
this.history = new AbstractHistory(this, options.base)
break
default:
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
assert(false, `invalid mode: ${mode}`)
}
}
}在实例化 VueRouter 的过程中,核心是创建一个路由匹配对象,并且根据 mode 来采取不同的路由方式。
export function createMatcher (
routes: Array<RouteConfig>,
router: VueRouter
): Matcher {
// 创建路由映射表
const { pathList, pathMap, nameMap } = createRouteMap(routes)
function addRoutes (routes) {
createRouteMap(routes, pathList, pathMap, nameMap)
}
// 路由匹配
function match (
raw: RawLocation,
currentRoute?: Route,
redirectedFrom?: Location
): Route {
//...
}
return {
match,
addRoutes
}
}createMatcher 函数的作用就是创建路由映射表,然后通过闭包的方式让 addRoutes 和 match 函数能够使用路由映射表的几个对象,最后返回一个 Matcher 对象。
接下来看 createMatcher 函数时如何创建映射表的
export function createRouteMap (
routes: Array<RouteConfig>,
oldPathList?: Array<string>,
oldPathMap?: Dictionary<RouteRecord>,
oldNameMap?: Dictionary<RouteRecord>
): {
pathList: Array<string>;
pathMap: Dictionary<RouteRecord>;
nameMap: Dictionary<RouteRecord>;
} {
// 创建映射表
const pathList: Array<string> = oldPathList || []
const pathMap: Dictionary<RouteRecord> = oldPathMap || Object.create(null)
const nameMap: Dictionary<RouteRecord> = oldNameMap || Object.create(null)
// 遍历路由配置,为每个配置添加路由记录
routes.forEach(route => {
addRouteRecord(pathList, pathMap, nameMap, route)
})
// 确保通配符在最后
for (let i = 0, l = pathList.length; i < l; i++) {
if (pathList[i] === '*') {
pathList.push(pathList.splice(i, 1)[0])
l--
i--
}
}
return {
pathList,
pathMap,
nameMap
}
}
// 添加路由记录
function addRouteRecord (
pathList: Array<string>,
pathMap: Dictionary<RouteRecord>,
nameMap: Dictionary<RouteRecord>,
route: RouteConfig,
parent?: RouteRecord,
matchAs?: string
) {
// 获得路由配置下的属性
const { path, name } = route
const pathToRegexpOptions: PathToRegexpOptions = route.pathToRegexpOptions || {}
// 格式化 url,替换 /
const normalizedPath = normalizePath(
path,
parent,
pathToRegexpOptions.strict
)
// 生成记录对象
const record: RouteRecord = {
path: normalizedPath,
regex: compileRouteRegex(normalizedPath, pathToRegexpOptions),
components: route.components || { default: route.component },
instances: {},
name,
parent,
matchAs,
redirect: route.redirect,
beforeEnter: route.beforeEnter,
meta: route.meta || {},
props: route.props == null
? {}
: route.components
? route.props
: { default: route.props }
}
if (route.children) {
// 递归路由配置的 children 属性,添加路由记录
route.children.forEach(child => {
const childMatchAs = matchAs
? cleanPath(`${matchAs}/${child.path}`)
: undefined
addRouteRecord(pathList, pathMap, nameMap, child, record, childMatchAs)
})
}
// 如果路由有别名的话
// 给别名也添加路由记录
if (route.alias !== undefined) {
const aliases = Array.isArray(route.alias)
? route.alias
: [route.alias]
aliases.forEach(alias => {
const aliasRoute = {
path: alias,
children: route.children
}
addRouteRecord(
pathList,
pathMap,
nameMap,
aliasRoute,
parent,
record.path || '/' // matchAs
)
})
}
// 更新映射表
if (!pathMap[record.path]) {
pathList.push(record.path)
pathMap[record.path] = record
}
// 命名路由添加记录
if (name) {
if (!nameMap[name]) {
nameMap[name] = record
} else if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !matchAs) {
warn(
false,
`Duplicate named routes definition: ` +
`{ name: "${name}", path: "${record.path}" }`
)
}
}
}以上就是创建路由匹配对象的全过程,通过用户配置的路由规则来创建对应的路由映射表。
当根组件调用 beforeCreate 钩子函数时,会执行以下代码
beforeCreate () {
// 只有根组件有 router 属性,所以根组件初始化时会初始化路由
if (isDef(this.$options.router)) {
this._routerRoot = this
this._router = this.$options.router
this._router.init(this)
Vue.util.defineReactive(this, '_route', this._router.history.current)
} else {
this._routerRoot = (this.$parent && this.$parent._routerRoot) || this
}
registerInstance(this, this)
}接下来看下路由初始化会做些什么
init(app: any /* Vue component instance */) {
// 保存组件实例
this.apps.push(app)
// 如果根组件已经有了就返回
if (this.app) {
return
}
this.app = app
// 赋值路由模式
const history = this.history
// 判断路由模式,以哈希模式为例
if (history instanceof HTML5History) {
history.transitionTo(history.getCurrentLocation())
} else if (history instanceof HashHistory) {
// 添加 hashchange 监听
const setupHashListener = () => {
history.setupListeners()
}
// 路由跳转
history.transitionTo(
history.getCurrentLocation(),
setupHashListener,
setupHashListener
)
}
// 该回调会在 transitionTo 中调用
// 对组件的 _route 属性进行赋值,触发组件渲染
history.listen(route => {
this.apps.forEach(app => {
app._route = route
})
})
}在路由初始化时,核心就是进行路由的跳转,改变 URL 然后渲染对应的组件。接下来来看一下路由是如何进行跳转的。
transitionTo (location: RawLocation, onComplete?: Function, onAbort?: Function) {
// 获取匹配的路由信息
const route = this.router.match(location, this.current)
// 确认切换路由
this.confirmTransition(route, () => {
// 以下为切换路由成功或失败的回调
// 更新路由信息,对组件的 _route 属性进行赋值,触发组件渲染
// 调用 afterHooks 中的钩子函数
this.updateRoute(route)
// 添加 hashchange 监听
onComplete && onComplete(route)
// 更新 URL
this.ensureURL()
// 只执行一次 ready 回调
if (!this.ready) {
this.ready = true
this.readyCbs.forEach(cb => { cb(route) })
}
}, err => {
// 错误处理
if (onAbort) {
onAbort(err)
}
if (err && !this.ready) {
this.ready = true
this.readyErrorCbs.forEach(cb => { cb(err) })
}
})
}在路由跳转中,需要先获取匹配的路由信息,所以先来看下如何获取匹配的路由信息
function match (
raw: RawLocation,
currentRoute?: Route,
redirectedFrom?: Location
): Route {
// 序列化 url
// 比如对于该 url 来说 /abc?foo=bar&baz=qux#hello
// 会序列化路径为 /abc
// 哈希为 #hello
// 参数为 foo: 'bar', baz: 'qux'
const location = normalizeLocation(raw, currentRoute, false, router)
const { name } = location
// 如果是命名路由,就判断记录中是否有该命名路由配置
if (name) {
const record = nameMap[name]
// 没找到表示没有匹配的路由
if (!record) return _createRoute(null, location)
const paramNames = record.regex.keys
.filter(key => !key.optional)
.map(key => key.name)
// 参数处理
if (typeof location.params !== 'object') {
location.params = {}
}
if (currentRoute && typeof currentRoute.params === 'object') {
for (const key in currentRoute.params) {
if (!(key in location.params) && paramNames.indexOf(key) > -1) {
location.params[key] = currentRoute.params[key]
}
}
}
if (record) {
location.path = fillParams(record.path, location.params, `named route "${name}"`)
return _createRoute(record, location, redirectedFrom)
}
} else if (location.path) {
// 非命名路由处理
location.params = {}
for (let i = 0; i < pathList.length; i++) {
// 查找记录
const path = pathList[i]
const record = pathMap[path]
// 如果匹配路由,则创建路由
if (matchRoute(record.regex, location.path, location.params)) {
return _createRoute(record, location, redirectedFrom)
}
}
}
// 没有匹配的路由
return _createRoute(null, location)
}接下来看看如何创建路由
// 根据条件创建不同的路由
function _createRoute(
record: ?RouteRecord,
location: Location,
redirectedFrom?: Location
): Route {
if (record && record.redirect) {
return redirect(record, redirectedFrom || location)
}
if (record && record.matchAs) {
return alias(record, location, record.matchAs)
}
return createRoute(record, location, redirectedFrom, router)
}
export function createRoute (
record: ?RouteRecord,
location: Location,
redirectedFrom?: ?Location,
router?: VueRouter
): Route {
const stringifyQuery = router && router.options.stringifyQuery
// 克隆参数
let query: any = location.query || {}
try {
query = clone(query)
} catch (e) {}
// 创建路由对象
const route: Route = {
name: location.name || (record && record.name),
meta: (record && record.meta) || {},
path: location.path || '/',
hash: location.hash || '',
query,
params: location.params || {},
fullPath: getFullPath(location, stringifyQuery),
matched: record ? formatMatch(record) : []
}
if (redirectedFrom) {
route.redirectedFrom = getFullPath(redirectedFrom, stringifyQuery)
}
// 让路由对象不可修改
return Object.freeze(route)
}
// 获得包含当前路由的所有嵌套路径片段的路由记录
// 包含从根路由到当前路由的匹配记录,从上至下
function formatMatch(record: ?RouteRecord): Array<RouteRecord> {
const res = []
while (record) {
res.unshift(record)
record = record.parent
}
return res
}至此匹配路由已经完成,我们回到 transitionTo 函数中,接下来执行 confirmTransition
transitionTo (location: RawLocation, onComplete?: Function, onAbort?: Function) {
// 确认切换路由
this.confirmTransition(route, () => {}
}
confirmTransition(route: Route, onComplete: Function, onAbort?: Function) {
const current = this.current
// 中断跳转路由函数
const abort = err => {
if (isError(err)) {
if (this.errorCbs.length) {
this.errorCbs.forEach(cb => {
cb(err)
})
} else {
warn(false, 'uncaught error during route navigation:')
console.error(err)
}
}
onAbort && onAbort(err)
}
// 如果是相同的路由就不跳转
if (
isSameRoute(route, current) &&
route.matched.length === current.matched.length
) {
this.ensureURL()
return abort()
}
// 通过对比路由解析出可复用的组件,需要渲染的组件,失活的组件
const { updated, deactivated, activated } = resolveQueue(
this.current.matched,
route.matched
)
function resolveQueue(
current: Array<RouteRecord>,
next: Array<RouteRecord>
): {
updated: Array<RouteRecord>,
activated: Array<RouteRecord>,
deactivated: Array<RouteRecord>
} {
let i
const max = Math.max(current.length, next.length)
for (i = 0; i < max; i++) {
// 当前路由路径和跳转路由路径不同时跳出遍历
if (current[i] !== next[i]) {
break
}
}
return {
// 可复用的组件对应路由
updated: next.slice(0, i),
// 需要渲染的组件对应路由
activated: next.slice(i),
// 失活的组件对应路由
deactivated: current.slice(i)
}
}
// 导航守卫数组
const queue: Array<?NavigationGuard> = [].concat(
// 失活的组件钩子
extractLeaveGuards(deactivated),
// 全局 beforeEach 钩子
this.router.beforeHooks,
// 在当前路由改变,但是该组件被复用时调用
extractUpdateHooks(updated),
// 需要渲染组件 enter 守卫钩子
activated.map(m => m.beforeEnter),
// 解析异步路由组件
resolveAsyncComponents(activated)
)
// 保存路由
this.pending = route
// 迭代器,用于执行 queue 中的导航守卫钩子
const iterator = (hook: NavigationGuard, next) => {
// 路由不相等就不跳转路由
if (this.pending !== route) {
return abort()
}
try {
// 执行钩子
hook(route, current, (to: any) => {
// 只有执行了钩子函数中的 next,才会继续执行下一个钩子函数
// 否则会暂停跳转
// 以下逻辑是在判断 next() 中的传参
if (to === false || isError(to)) {
// next(false)
this.ensureURL(true)
abort(to)
} else if (
typeof to === 'string' ||
(typeof to === 'object' &&
(typeof to.path === 'string' || typeof to.name === 'string'))
) {
// next('/') 或者 next({ path: '/' }) -> 重定向
abort()
if (typeof to === 'object' && to.replace) {
this.replace(to)
} else {
this.push(to)
}
} else {
// 这里执行 next
// 也就是执行下面函数 runQueue 中的 step(index + 1)
next(to)
}
})
} catch (e) {
abort(e)
}
}
// 经典的同步执行异步函数
runQueue(queue, iterator, () => {
const postEnterCbs = []
const isValid = () => this.current === route
// 当所有异步组件加载完成后,会执行这里的回调,也就是 runQueue 中的 cb()
// 接下来执行 需要渲染组件的导航守卫钩子
const enterGuards = extractEnterGuards(activated, postEnterCbs, isValid)
const queue = enterGuards.concat(this.router.resolveHooks)
runQueue(queue, iterator, () => {
// 跳转完成
if (this.pending !== route) {
return abort()
}
this.pending = null
onComplete(route)
if (this.router.app) {
this.router.app.$nextTick(() => {
postEnterCbs.forEach(cb => {
cb()
})
})
}
})
})
}
export function runQueue (queue: Array<?NavigationGuard>, fn: Function, cb: Function) {
const step = index => {
// 队列中的函数都执行完毕,就执行回调函数
if (index >= queue.length) {
cb()
} else {
if (queue[index]) {
// 执行迭代器,用户在钩子函数中执行 next() 回调
// 回调中判断传参,没有问题就执行 next(),也就是 fn 函数中的第二个参数
fn(queue[index], () => {
step(index + 1)
})
} else {
step(index + 1)
}
}
}
// 取出队列中第一个钩子函数
step(0)
}接下来介绍导航守卫
const queue: Array<?NavigationGuard> = [].concat(
// 失活的组件钩子
extractLeaveGuards(deactivated),
// 全局 beforeEach 钩子
this.router.beforeHooks,
// 在当前路由改变,但是该组件被复用时调用
extractUpdateHooks(updated),
// 需要渲染组件 enter 守卫钩子
activated.map(m => m.beforeEnter),
// 解析异步路由组件
resolveAsyncComponents(activated)
)第一步是先执行失活组件的钩子函数
function extractLeaveGuards(deactivated: Array<RouteRecord>): Array<?Function> {
// 传入需要执行的钩子函数名
return extractGuards(deactivated, 'beforeRouteLeave', bindGuard, true)
}
function extractGuards(
records: Array<RouteRecord>,
name: string,
bind: Function,
reverse?: boolean
): Array<?Function> {
const guards = flatMapComponents(records, (def, instance, match, key) => {
// 找出组件中对应的钩子函数
const guard = extractGuard(def, name)
if (guard) {
// 给每个钩子函数添加上下文对象为组件自身
return Array.isArray(guard)
? guard.map(guard => bind(guard, instance, match, key))
: bind(guard, instance, match, key)
}
})
// 数组降维,并且判断是否需要翻转数组
// 因为某些钩子函数需要从子执行到父
return flatten(reverse ? guards.reverse() : guards)
}
export function flatMapComponents (
matched: Array<RouteRecord>,
fn: Function
): Array<?Function> {
// 数组降维
return flatten(matched.map(m => {
// 将组件中的对象传入回调函数中,获得钩子函数数组
return Object.keys(m.components).map(key => fn(
m.components[key],
m.instances[key],
m, key
))
}))
}第二步执行全局 beforeEach 钩子函数
beforeEach(fn: Function): Function {
return registerHook(this.beforeHooks, fn)
}
function registerHook(list: Array<any>, fn: Function): Function {
list.push(fn)
return () => {
const i = list.indexOf(fn)
if (i > -1) list.splice(i, 1)
}
}在 VueRouter 类中有以上代码,每当给 VueRouter 实例添加 beforeEach 函数时就会将函数 push 进 beforeHooks 中。
第三步执行 beforeRouteUpdate 钩子函数,调用方式和第一步相同,只是传入的函数名不同,在该函数中可以访问到 this 对象。
第四步执行 beforeEnter 钩子函数,该函数是路由独享的钩子函数。
第五步是解析异步组件。
export function resolveAsyncComponents (matched: Array<RouteRecord>): Function {
return (to, from, next) => {
let hasAsync = false
let pending = 0
let error = null
// 该函数作用之前已经介绍过了
flatMapComponents(matched, (def, _, match, key) => {
// 判断是否是异步组件
if (typeof def === 'function' && def.cid === undefined) {
hasAsync = true
pending++
// 成功回调
// once 函数确保异步组件只加载一次
const resolve = once(resolvedDef => {
if (isESModule(resolvedDef)) {
resolvedDef = resolvedDef.default
}
// 判断是否是构造函数
// 不是的话通过 Vue 来生成组件构造函数
def.resolved = typeof resolvedDef === 'function'
? resolvedDef
: _Vue.extend(resolvedDef)
// 赋值组件
// 如果组件全部解析完毕,继续下一步
match.components[key] = resolvedDef
pending--
if (pending <= 0) {
next()
}
})
// 失败回调
const reject = once(reason => {
const msg = `Failed to resolve async component ${key}: ${reason}`
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(false, msg)
if (!error) {
error = isError(reason)
? reason
: new Error(msg)
next(error)
}
})
let res
try {
// 执行异步组件函数
res = def(resolve, reject)
} catch (e) {
reject(e)
}
if (res) {
// 下载完成执行回调
if (typeof res.then === 'function') {
res.then(resolve, reject)
} else {
const comp = res.component
if (comp && typeof comp.then === 'function') {
comp.then(resolve, reject)
}
}
}
}
})
// 不是异步组件直接下一步
if (!hasAsync) next()
}
}以上就是第一个 runQueue 中的逻辑,第五步完成后会执行第一个 runQueue 中回调函数
// 该回调用于保存 `beforeRouteEnter` 钩子中的回调函数
const postEnterCbs = []
const isValid = () => this.current === route
// beforeRouteEnter 导航守卫钩子
const enterGuards = extractEnterGuards(activated, postEnterCbs, isValid)
// beforeResolve 导航守卫钩子
const queue = enterGuards.concat(this.router.resolveHooks)
runQueue(queue, iterator, () => {
if (this.pending !== route) {
return abort()
}
this.pending = null
// 这里会执行 afterEach 导航守卫钩子
onComplete(route)
if (this.router.app) {
this.router.app.$nextTick(() => {
postEnterCbs.forEach(cb => {
cb()
})
})
}
})第六步是执行 beforeRouteEnter 导航守卫钩子,beforeRouteEnter 钩子不能访问 this 对象,因为钩子在导航确认前被调用,需要渲染的组件还没被创建。但是该钩子函数是唯一一个支持在回调中获取 this 对象的函数,回调会在路由确认执行。
beforeRouteEnter (to, from, next) {
next(vm => {
// 通过 `vm` 访问组件实例
})
}下面来看看是如何支持在回调中拿到 this 对象的
function extractEnterGuards(
activated: Array<RouteRecord>,
cbs: Array<Function>,
isValid: () => boolean
): Array<?Function> {
// 这里和之前调用导航守卫基本一致
return extractGuards(
activated,
'beforeRouteEnter',
(guard, _, match, key) => {
return bindEnterGuard(guard, match, key, cbs, isValid)
}
)
}
function bindEnterGuard(
guard: NavigationGuard,
match: RouteRecord,
key: string,
cbs: Array<Function>,
isValid: () => boolean
): NavigationGuard {
return function routeEnterGuard(to, from, next) {
return guard(to, from, cb => {
// 判断 cb 是否是函数
// 是的话就 push 进 postEnterCbs
next(cb)
if (typeof cb === 'function') {
cbs.push(() => {
// 循环直到拿到组件实例
poll(cb, match.instances, key, isValid)
})
}
})
}
}
// 该函数是为了解决 issus #750
// 当 router-view 外面包裹了 mode 为 out-in 的 transition 组件
// 会在组件初次导航到时获得不到组件实例对象
function poll(
cb: any, // somehow flow cannot infer this is a function
instances: Object,
key: string,
isValid: () => boolean
) {
if (
instances[key] &&
!instances[key]._isBeingDestroyed // do not reuse being destroyed instance
) {
cb(instances[key])
} else if (isValid()) {
// setTimeout 16ms 作用和 nextTick 基本相同
setTimeout(() => {
poll(cb, instances, key, isValid)
}, 16)
}
}第七步是执行 beforeResolve 导航守卫钩子,如果注册了全局 beforeResolve 钩子就会在这里执行。
第八步就是导航确认,调用 afterEach 导航守卫钩子了。
以上都执行完成后,会触发组件的渲染
history.listen(route => {
this.apps.forEach(app => {
app._route = route
})
})以上回调会在 updateRoute 中调用
updateRoute(route: Route) {
const prev = this.current
this.current = route
this.cb && this.cb(route)
this.router.afterHooks.forEach(hook => {
hook && hook(route, prev)
})
}至此,路由跳转已经全部分析完毕。核心就是判断需要跳转的路由是否存在于记录中,然后执行各种导航守卫函数,最后完成 URL 的改变和组件的渲染。