Binary search is a search algorithm that finds the position of a target value within a sorted array.
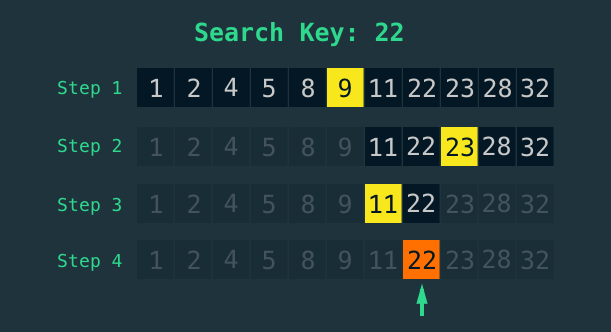
Let us understand this algorithm with a example. We are finding 22 in a sorted list (1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 9, 11, 22, 23, 28, 32)
- Here, mid element is 9 and 22 is greater than 9. So, it is in other half.
- Then, new mid element is 23, 22 is less than 22 than means it is among indices between element 9 and 23.
- Now mid is 11, that means it right of 11 or left of 23.
- Finally found.
Given an array A of n elements with values or records A0 ... An−1 and target value T, the following subroutine uses binary search to find the index of T in A.[6]
Set L to 0 and R to n − 1.
If L > R, the search terminates as unsuccessful. Set m (the position of the middle element) to the floor of (L + R) / 2.
If Am < T, set L to m + 1 and go to step 2.
If Am > T, set R to m − 1 and go to step 2.
If Am = T, the search is done; return m.
Binary search works on sorted arrays. A binary search begins by comparing the middle element of the array with the target value. If the target value matches the middle element, its position in the array is returned. If the target value is less or more than the middle element, the search continues the lower or upper half of the array respectively with a new middle element, eliminating the other half from consideration.
The pseudocode for binary search algorithm is as follows:
Procedure binary_search
A ← sorted array
n ← size of array
x ← value to be searched
Set lowerBound = 1
Set upperBound = n
while upperBound >= lowerBound
set midPoint = lowerBound + (upperBound - lowerBound) / 2
if A[midPoint] < x then
set lowerBound = midPoint + 1
else if A[midPoint] > x then
set upperBound = midPoint - 1
else if A[midPoint] = x then
return x found at location midPoint
endif
end while
/* That is upperBound > lowerBound but element is not found,
Hence, it implies element is not present in list */
return x not found
end procedure
Time complexity - О(log n), where n is the number of items being sorted.
Space complexity - O(1), due to auxillary space only.
🚀 Compile Online 🚀
🚀 Compile Online 🚀
🚀 Compile Online 🚀
🚀 Compile Online 🚀
🚀 Compile Online 🚀
🚀 Compile Online 🚀
🚀 Compile Online 🚀