Detecting lane lines is the first step towards building a self driving car. The goal of the project is to develop an algorithm using Open Source Computer Vision (OpenCV).
The goals / steps of this project are the following:
- Make a pipeline that finds lane lines on the road
- Improve drawing of lanes by averaging and extrapolating lanes detected
- Reflect on your work in a written report
1. Describe your pipeline. As part of the description, explain how you modified the draw_lines() function.
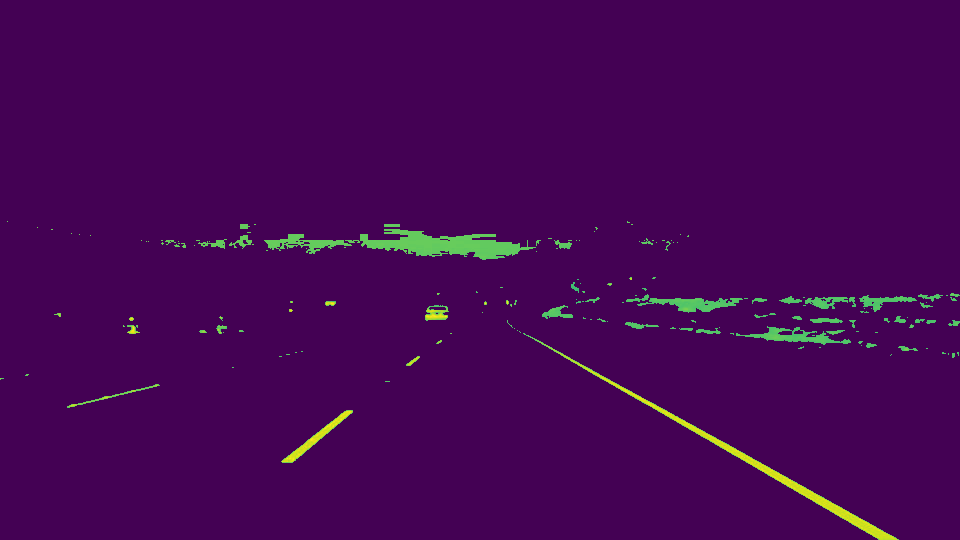
ORIGINAL IMAGE
My pipeline consisted of 5 steps. First, I converted the images to grayscale, then I ....
STEP-1: Color Selection
The very first step is to create a mask with range of colors which may appear in lanes. Usually lanes appear in a range of yellow to white. This allows for more accurate lane detection and accounts for variations in colors of lane.
STEP-2: Convert to Grayscale
Converting the image to gray scale allows to highlight features we care about and reduce background noise.
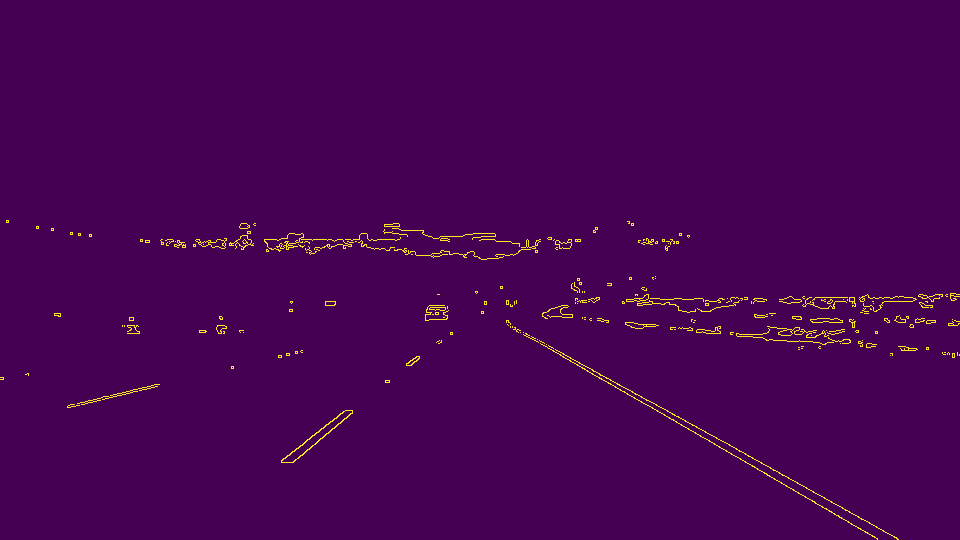
STEP-3: Apply Canny Edge Detector
Applying this technique helps extract structural information from the image. This step also reduces the amount of data which needs to be processed. The thickness of edges are based on strength of gradients at that point.
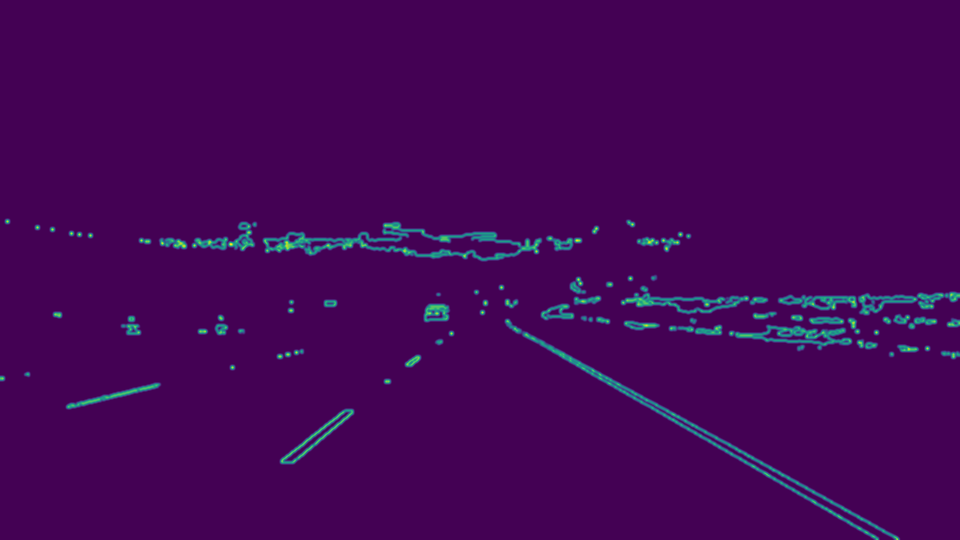
STEP-4: Gaussian Blur
Eventhough the canny filter involves applying gaussian filter as the very first step. Its recommended to apply it once again as it would help reduce noise.
STEP-5: Create a region of interest mask
This step is important to narrow down your search area. This will reduce help reduce complexity and improve accuracy. Goal here was to find vertices for a polygon that generalizes well for all images.
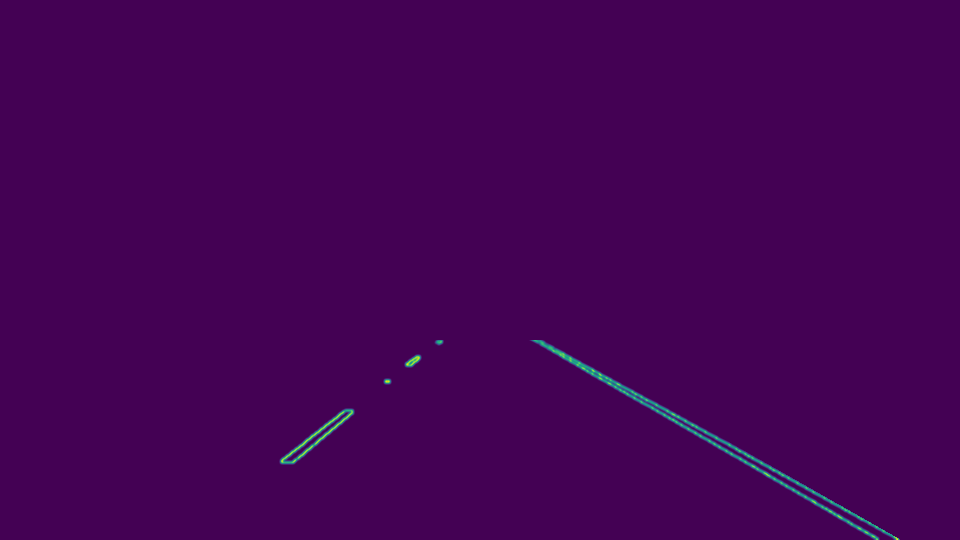
STEP-6: Generate Hough Lines
This step is crucial towards accurate lane detection. Applying the Hough transform allows for feature extraction. A line in an image appears as a dot in Hough's Space. Hence, a dot appears as a line in Hough Space. We choose to use polar coordinates due to problem of infinite slope.
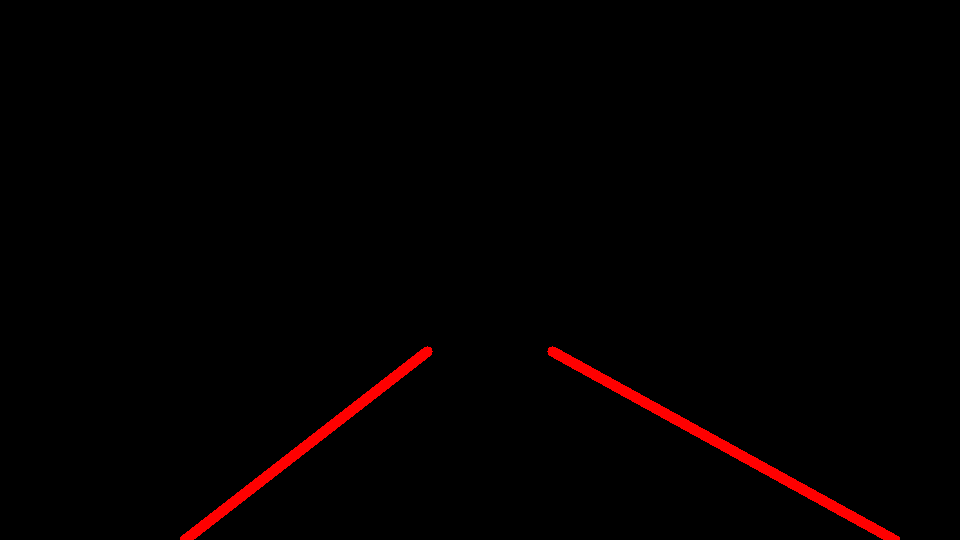
To draw more accurate lines we apply averaging and extrapolation techniques to generalize the lanes detected. Here are the steps towards it:
- Iterate through the lines and extract cordinates from each line
- Find slope and intercepts (y = mx + c), m = (y2-y1)/(x2-x1)
- Find length of each line
- Seperate right lane and left lane lines
- Find average of lane slope and intercept
- Fix the 'y' cordinates
- Find corresponding 'x' coordinates for both lanes, x = (y-c)/m
- Create array of combined lines. An array of just two lines, one for each lane. Shape (2,1,4)
- Draw Lines
STEP-7: Combine the image containing drawn lines with original image
Finally, overlay lines drawn on the original image to verify visually how accurately lanes were detected.
Potential shortcomings would be:
- Curvy roads: The video that the algorithm is run on has reletively gradual turns. This algorithm might not be so accurate with sharp turns. This is due to low polynomail rank in the fit function. This is why the algorithm performs bad on the challenge video.
- Algorithm Scaling: The algorithm doesnt scale well due to the pixelwise operation in houghs transform which can be computationally expensive.
Improvments:
- Add aditional features in the algorithm for better accuracy
- Experiment with additonal colors for color selection mask
- Add complexity by choosing an higher order polynomail