Covered in this guide:
- How to install Metabase
- How to upgrade Metabase
- Tips for troubleshooting various issues
- Configuring the application database
- Migrating from using the H2 database to MySQL or Postgres
- Running database migrations manually
- Backing up Metabase Application Data
- Customizing the Metabase Jetty Webserver
- Changing password complexity
- Handling Timezones
Metabase is built and packaged as a Java jar file and can be run anywhere that Java is available. Below we provide detailed instructions on how to install and run Metabase in a variety of common configurations.
This is the simplest and most basic way of running Metabase. Here we'll cover the general requirements for running Metabase and provide some information about how to customize your installation for any scenario.
Metabase provides a binary Mac OS X application for users who are interested in trying Metabase on a Mac system.
If you are using Docker containers and prefer to manage your Metabase installation that way then we've got you covered. This guide discusses how to use the Metabase Docker image to launch a container running Metabase.
Step-by-step instructions on how to deploy Metabase on Elastic Beanstalk using RDS. This is the most common way to run Metabase in production.
Currently in beta. We've run Metabase on Heroku and it works just fine, but it's not hardened for production use just yet. If you're up for it then give it a shot and let us know how we can make it better!
Community support only at this time, but we have reports of Metabase instances running on Cloud66!
Before you attempt to upgrade Metabase, you should make a backup of the database just in case. While it is unlikely you will need to rollback, it will do wonders for your peace of mind.
How you upgrade Metabase depends on how you are running it. See below for information on how to update Metabase on managed platforms.
If you are running it via docker, then you simply kill the docker process, and start a new container with the latest image. On startup, Metabase will perform any upgrade tasks it needs to perform, and once it is finished, you'll be running the new version.
If you are running the JVM Jar file directly, then you simply kill the process, and restart the server. On startup, Metabase will perform any upgrade tasks it needs to perform, and once it is finished, you'll be running the new version.
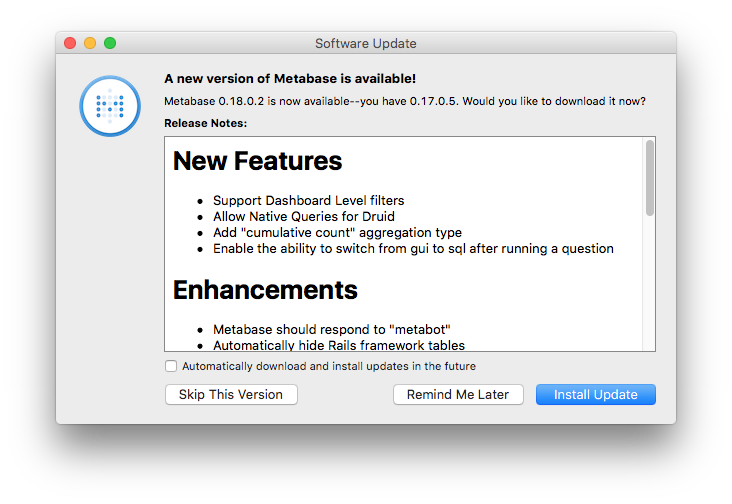
If you are using the Metabase app, you will be notified when there is a new version available. You will see a dialog displaying the changes in the latest version and prompt you to upgrade.
Step-by-step instructions on how to upgrade Metabase running on Elastic Beanstalk using RDS.
Step-by-step instructions on how to upgrade Metabase running on Heroku.
Sometimes Metabase will fail to complete its startup due to a database lock that was not cleared properly.
When this happens, go to a terminal where Metabase is installed and run:
java -jar metabase.jar migrate release-locks
in the command line to manually clear the locks. Then restart your Metabase instance.
The application database is where Metabase stores information about users, saved questions, dashboards, and any other data needed to run the application. The default settings use an embedded H2 database, but this is configurable.
NOTE: you cannot change the application database while the application is running. these values are read only once when the application starts up and will remain constant throughout the running of the application.
NOTE: currently Metabase does not provide automated support for migrating data from one application database to another, so if you start with H2 and then want to move to Postgres you'll have to dump the data from H2 and import it into Postgres before relaunching the application.
H2 (default)
To use the H2 database for your Metabase instance you don't need to do anything at all. When the application is first launched it will attempt to create a new H2 database in the same filesystem location the application is launched from.
You can see these database files from the terminal:
ls metabase.*
You should see the following files:
metabase.db.h2.db
metabase.db.trace.db
If for any reason you want to use an H2 database file in a separate location from where you launch Metabase you can do so using an environment variable. For example:
export MB_DB_TYPE=h2
export MB_DB_FILE=/the/path/to/my/h2.db
java -jar metabase.jar
For production installations of Metabase we recommend that users replace the H2 database with a more robust option such as Postgres. This offers a greater degree of performance and reliability when Metabase is running with many users.
You can change the application database to use Postgres using a few simple environment variables. For example:
export MB_DB_TYPE=postgres
export MB_DB_DBNAME=metabase
export MB_DB_PORT=5432
export MB_DB_USER=<username>
export MB_DB_PASS=<password>
export MB_DB_HOST=localhost
java -jar metabase.jar
This will tell Metabase to look for its application database using the supplied Postgres connection information.
If you prefer to use MySQL we've got you covered. You can change the application database to use MySQL using these environment variables. For example:
export MB_DB_TYPE=mysql
export MB_DB_DBNAME=metabase
export MB_DB_PORT=3306
export MB_DB_USER=<username>
export MB_DB_PASS=<password>
export MB_DB_HOST=localhost
java -jar metabase.jar
This will tell Metabase to look for its application database using the supplied MySQL connection information.
If you decide to use the default application database (H2) when you initially start using Metabase, but decide later that you'd like to switch to a more production ready database such as MySQL or Postgres we make the transition easy for you.
Metabase provides a custom migration command for upgrading H2 application database files by copying their data to a new database. Here's what you'll want to do:
- Shutdown your Metabase instance so that it's not running. This ensures no accidental data gets written to the db while migrating.
- Make a backup copy of your H2 application database by following the instructions in Backing up Metabase Application Data. Safety first!
- Run the Metabase data migration command using the appropriate environment variables for the target database you want to migrate to. You can find details about specifying MySQL and Postgres databases at Configuring the application database. Here's an example of migrating to Postgres.
export MB_DB_TYPE=postgres
export MB_DB_DBNAME=metabase
export MB_DB_PORT=5432
export MB_DB_USER=<username>
export MB_DB_PASS=<password>
export MB_DB_HOST=localhost
java -jar metabase.jar load-from-h2 <path-to-metabase-h2-database-file>
It is expected that you will run the command against a brand new (empty!) database and Metabase will handle all of the work of creating the database schema and migrating the data for you.
- It is required that wherever you are running this migration command can connect to the target MySQL or Postgres database. So if you are attempting to move the data to a cloud database make sure you take that into consideration.
- The code that handles these migrations uses a Postgres SQL command that is only available in Postgres 9.4 or newer versions. Please make sure you Postgres database is version 9.4 or newer.
When Metabase is starting up it will typically attempt to determine if any changes are required to the application database and it will execute those changes automatically. If for some reason you wanted to see what these changes are and run them manually on your database then we let you do that.
Simply set the following environment variable before launching Metabase:
export MB_DB_AUTOMIGRATE=false
When the application launches, if there are necessary database changes, you'll receive a message like the following which will indicate that the application cannot continue starting up until the specified upgrades are made:
2015-12-01 12:45:45,805 [INFO ] metabase.db :: Database Upgrade Required
NOTICE: Your database requires updates to work with this version of Metabase. Please execute the following sql commands on your database before proceeding.
-- *********************************************************************
-- Update Database Script
-- *********************************************************************
-- Change Log: migrations/liquibase.yaml
-- Ran at: 12/1/15 12:45 PM
-- Against: @jdbc:h2:file:/Users/agilliland/workspace/metabase/metabase/metabase.db
-- Liquibase version: 3.4.1
-- *********************************************************************
-- Create Database Lock Table
CREATE TABLE PUBLIC.DATABASECHANGELOGLOCK (ID INT NOT NULL, LOCKED BOOLEAN NOT NULL, LOCKGRANTED TIMESTAMP, LOCKEDBY VARCHAR(255), CONSTRAINT PK_DATABASECHANGELOGLOCK PRIMARY KEY (ID));
...
Once your database is updated try running the application again.
2015-12-01 12:46:39,489 [INFO ] metabase.core :: Metabase Shutting Down ...
You can then take the supplied SQL script and apply it to your database manually. Once that's done just restart Metabase and everything should work normally.
If you are using Metabase in a production environment or simply want to make sure you don't lose any of the work that you've done, then backups are what you need.
Metabase uses a single SQL database for all of its runtime application data, so all you need to do is backup that database and you're good to go. From a database back-up you can restore any Metabase installation.
If you launched Metabase on a laptop or PC the application will create an embedded H2 database in the directory it is being run in. Navigate to the directory where you started Metabase from and find the file named metabase.db.h2.db. Simply copy that file somewhere safe and you are all backed up!
NOTE: If your Metabase is currently running it's best to shut down the Metabase process before making a backup copy of the file. Then, restart the application.
Amazon has its own best practices on how to backup and restore RDS databases, so we'll defer to them. We recommend that you enable automated RDS Backups.
Instructions can be found in the Amazon RDS User Guide.
Simply follow the same instructions you would use for making any normal database backup. It's a large topic more fit for a DBA to answer, but as long as you have a dump of the Metabase database you'll be good to go.
In most cases there will be no reason to modify any of the settings around how Metabase runs its embedded Jetty webserver to host the application, but if you wish to run HTTPS directly with your Metabase server or if you need to run on another port, that's all configurable.
By default Metabase will launch on port 3000, but if you prefer to run the application on another port you can do so by setting the following environment variable:
export MB_JETTY_PORT=12345
java -jar metabase.jar
In this example once the application starts up you will access it on port 12345 instead of the default port of 3000.
By default, Metabase will be listening on localhost. In some production environments you may want to listen on a different interface, which can be done by using the MB_JETTY_HOST environment variable:
export MB_JETTY_HOST=0.0.0.0
java -jar metabase.jar
If you have an ssl certificate and would prefer to have Metabase run over HTTPS directly using its webserver you can do so by using the following environment variables:
export MB_JETTY_SSL="true"
export MB_JETTY_SSL_Port="8443"
export MB_JETTY_SSL_Keystore="path/to/keystore.jks"
export MB_JETTY_SSL_Keystore_Password="storepass"
java -jar metabase.jar
With the above settings applied you will be running Metabase on port 8443 over HTTPS using the supplied certificate. #secured
Metabase offers a couple controls for administrators who prefer to increase the password requirements on their user accounts.
export MB_PASSWORD_COMPLEXITY=strong
export MB_PASSWORD_LENGTH=10
The settings above can be used independently, so it's fine to use only one or the other. By default Metabase use complexity = normal and a password length of 6. The following options are available for complexity choice:
weak= no character constraintsnormal= at least 1 digitstrong= minimum 8 characters w/ 2 lowercase, 2 uppercase, 1 digit, and 1 special character
Metabase does its best to ensure proper and accurate reporting in whatever timezone you desire, but timezones are a complicated beast so it's important to abide by some recommendations listed below to ensure your reports come out as intended.
The following places where timezones are set can all impact the data you see:
Database- includes global database timezone settings, specific column type settings, and even individual data values.OS & JVM- on whatever system is running Metabase the timezone settings of the Operating System as well as the Java Virtual Machine can impact your reports.Metabase- inside Metabase the reporting timezone setting (if set) will influence how your data is reported.
To ensure proper reporting it's important that timezones be set consistently in all places. Metabase recommends the following settings:
- Make sure all of your database columns are properly setup to include timezone awareness.
- Unless you have a special need it's best to set your database reporting timezone to UTC and store all of your date/time related values in UTC.
- Configure your JVM to use the same timezone you want to use for reporting, which ideally should also match the timezone of your database.
- Set the Metabase
Report Timezoneto match the timezone you want to see your reports in, again, this should match the rest of the timezone settings you've made.
Common Pitfalls:
- Your database is using date/time columns without any timezone information. Typically when this happens your database will assume all the data is from whatever timezone the database is configured in or possible just default to UTC (check your database vendor to be sure).
- Your JVM timezone is not the same as your Metabase
Report Timezonechoice. This is a very common issue and can be corrected by launching java with the-Duser.timezone=<timezone>option properly set to match your Metabase report timezone.