The Azure Content Delivery Network (CDN) offers developers a global solution for delivering high-bandwidth content by caching blobs and static content of compute instances at physical nodes in the United States, Europe, Asia, Australia and South America. For a current list of CDN node locations, see Azure CDN Node Locations.
This task includes the following steps:
- Step 1: Create a storage account
- Step 2: Create a new CDN endpoint for your storage account
- Step 3: Access your CDN content
- Step 4: Remove your CDN content
The benefits of using CDN to cache Azure data include:
- Better performance and user experience for end users who are far from a content source, and are using applications where many 'internet trips' are required to load content
- Large distributed scale to better handle instantaneous high load, say, at the start of an event such as a product launch
Existing CDN customers can now use the Azure CDN in the Azure Management Portal. The CDN is an add-on feature to your subscription and has a separate billing plan.
Use the following procedure to create a new storage account for a Azure subscription. A storage account gives access to Azure storage services. The storage account represents the highest level of the namespace for accessing each of the Azure storage service components: Blob services, Queue services, and Table services. For more information about the Azure storage services, see Using the Azure Storage Services.
To create a storage account, you must be either the service administrator or a co-administrator for the associated subscription.
[AZURE.NOTE] For information about performing this operation by using the Azure Service Management API, see the Create Storage Account reference topic.
To create a storage account for an Azure subscription
-
Log into the Azure Management Portal.
-
In the lower left corner, click New. In the New Dialog, select Data Services, then click Storage, then Quick Create.
The Create Storage Account dialog appears.
-
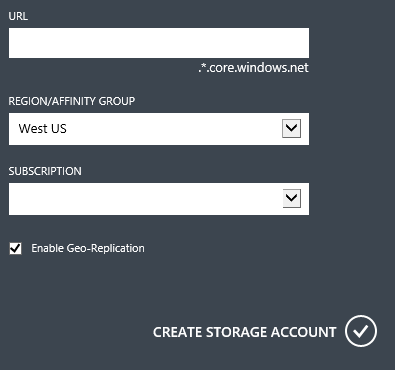
In the URL field, type a subdomain name. This entry can contain from 3-24 lowercase letters and numbers.
This value becomes the host name within the URI that is used to address Blob, Queue, or Table resources for the subscription. To address a container resource in the Blob service, you would use a URI in the following format, where <StorageAccountLabel> refers to the value you typed in Enter a URL:
http://<StorageAcountLabel>.blob.core.windows.net/<mycontainer>
Important: The URL label forms the subdomain of the storage account URI and must be unique among all hosted services in Azure.
This value is also used as the name of this storage account in the portal, or when accessing this account programmatically.
-
From the Region/Affinity Group drop-down list, select a region or affinity group for the storage account. Select an affinity group instead of a region if you want your storage services to be in the same data center with other Windows Azure services that you are using. This can improve performance, and no charges are incurred for egress.
Note: To create an affinity group, open the Settings area of the Management Portal, click Affinity Groups, and then click either Add an affinity group or Add. You can also create and manage affinity groups using the Windows Azure Service Management API. For more information, see [Operations on Affinity Groups].
-
From the Subscription drop-down list, select the subscription that the storage account will be used with.
-
Click Create Storage Account. The process of creating the storage account might take several minutes to complete.
-
To verify that the storage account was created successfully, verify that the account appears in the items listed for Storage with a status of Online.
Once you enable CDN access to a storage account or hosted service, all publicly available objects are eligible for CDN edge caching. If you modify an object that is currently cached in the CDN, the new content will not be available via the CDN until the CDN refreshes its content when the cached content time-to-live period expires.
To create a new CDN endpoint for your storage account
-
In the Azure Management Portal, in the navigation pane, click CDN.
-
On the ribbon, click New. In the New dialog, select App Services, then CDN, then Quick Create.
-
In the Origin Domain dropdown, select the storage account you created in the previous section from the list of your available storage accounts.
-
Click the Create button to create the new endpoint.
-
Once the endpoint is created, it appears in a list of endpoints for the subscription. The list view shows the URL to use to access cached content, as well as the origin domain.
The origin domain is the location from which the CDN caches content. The origin domain can be either a storage account or a cloud service; a storage account is used for the purposes of this example. Storage content is cached to edge servers according either to a cache-control setting that you specify, or to the default heuristics of the caching network. See How to Manage Expiration of Blob Content for more information.
[AZURE.NOTE] The configuration created for the endpoint will not immediately be available; it can take up to 60 minutes for the registration to propagate through the CDN network. Users who try to use the CDN domain name immediately may receive status code 400 (Bad Request) until the content is available via the CDN.
To access cached content on the CDN, use the CDN URL provided in the portal. The address for a cached blob will be similar to the following:
http://<CDNNamespace>.vo.msecnd.net/<myPublicContainer>/<BlobName>
If you no longer wish to cache an object in the Azure Content Delivery Network (CDN), you can take one of the following steps:
- For an Azure blob, you can delete the blob from the public container.
- You can make the container private instead of public. See Restrict Access to Containers and Blobs for more information.
- You can disable or delete the CDN endpoint using the Management Portal.
- You can modify your hosted service to no longer respond to requests for the object.
An object already cached in the CDN will remain cached until the time-to-live period for the object expires. When the time-to-live period expires, the CDN will check to see whether the CDN endpoint is still valid and the object still anonymously accessible. If it is not, then the object will no longer be cached.
The ability to immediately purge content is currently not supported on Azure Management Portal. Please contact Azure support if you need to immediately purge content.