In 2017, the US government released over 34,000 pages of documents relating to the CIA investigation of the JFK assasination. These files contain a huge volume of unstructured data - typed and handwritten notes, photos and other data that standard search solutions are unable to parse.
This lab will show you how you can leverage AI and Cognitive Search, to extract meaning from this data. You can watch a demo of the lab contents in action in a short online video or explore the JFK files yourself with our online demo.
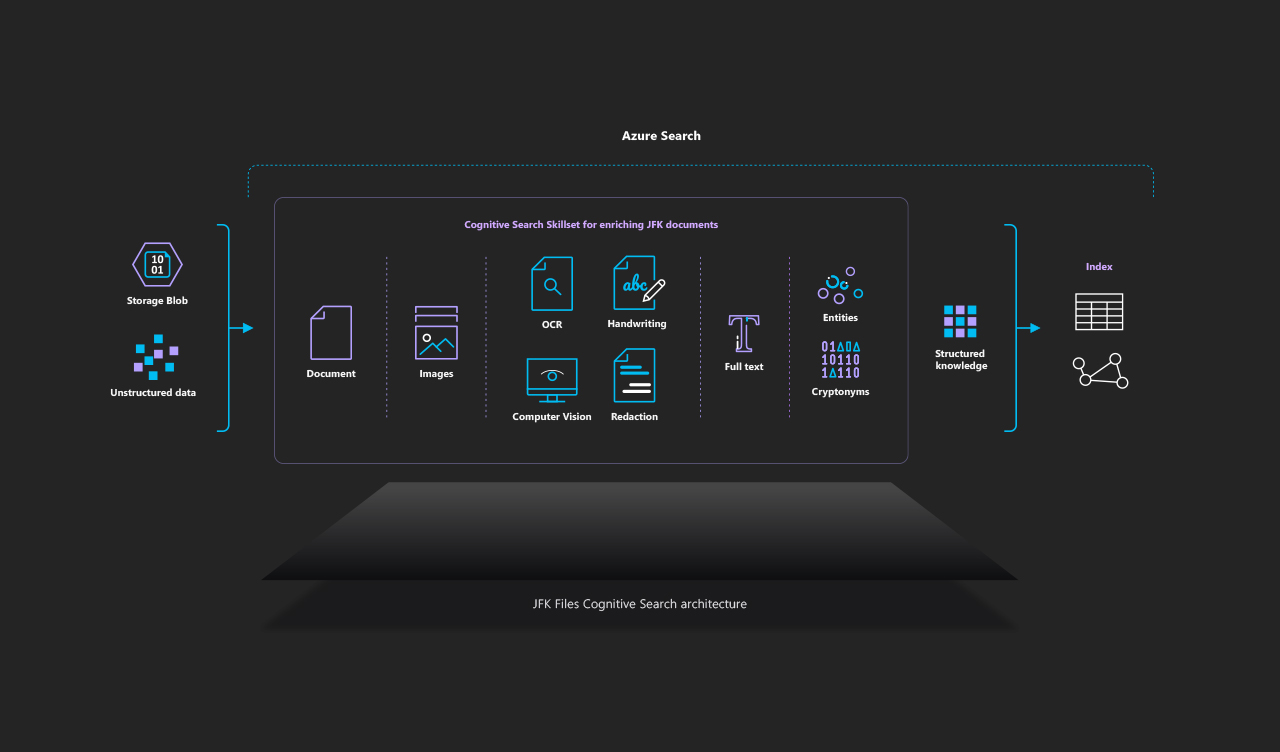
Cognitive Search is an Azure service that ingests your data from almost any datasource; enriches it using a set of cognitive skills, and finally enables you explore the data using Azure Search.
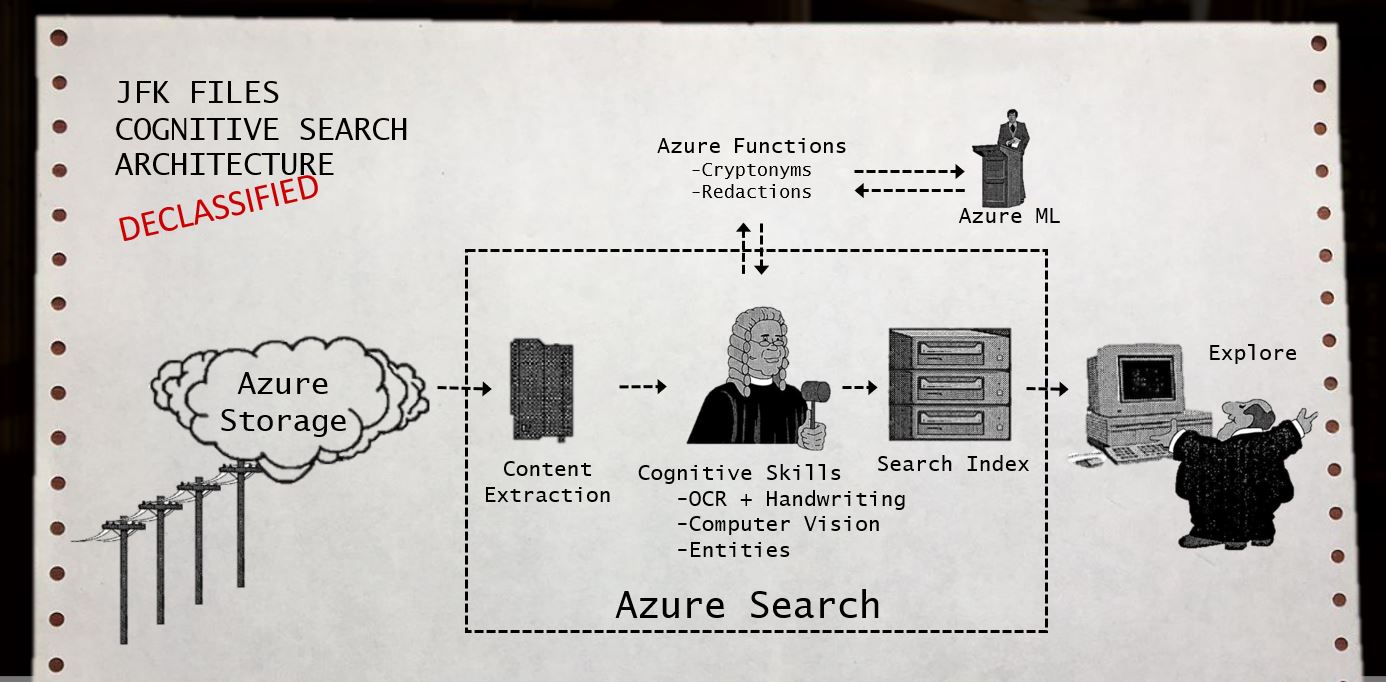
The JFK files example leverages the built-in Cognitive Skills inside of Azure Search and combines it with custom skills using extensibility. The architecture below showcases how the new Cognitive Search capabilities of Azure enable you to easily create structure from almost any datasource.
Note: This diagram of visuals are inspired by the CIA's JFK document management system in 1997 included in the JFK files.
This project includes the following capabilities for you to build your own version of the JFK files.
- We have provided a small subset of the JFK PDF documents and images that have been uploaded to the cloud into Azure Blob Storage.
- An Azure Search service is used to index the content and power the UX experience. We use the new Cognitive Search capabilities to apply pre-built cognitive skills to the content, and we also use the extensibility mechanism to add custom skills using Azure Functions.
- Uses the Cognitive Services Vision API to extract text information from the image via OCR, handwriting, and image captioning,
- Applies Named Entity Recognition to extract named entities from the documents,
- Annotates text using a custom CIA Cryptonyms skill,
- Generates HOCR content based on results.
- A standalone website to search the index and explore the documents
- This is a lab to showcase a Cognitive Search use case. It is not intended to be a framework or scalable architecture for all scenarios, though it can give you an idea of what your scenario might end up looking like.
- The OCR technology is not perfect and the handwriting capability is in preview. The results will vary greatly by scan and image quality.
- Most file formats and datasources are supported, however some scanned and native PDF formats may not be parsed correctly.
- Cognitive Search is currently only available in public preview in the South Central US and West Europe Azure regions, so the Azure Search service you use with this demo must be provisioned in one of these two regions.
This lab requires an Azure subscription. If you delete the resources at the end of the session, total charges will be less than $1 so we strongly recommend using an existing subscription if available.
If you need a new Azure subscription, then there are a couple of options to get a free subscription:
- The easiest way to sign up for an Azure subscription is with VS Dev Essentials and a personal Microsoft account (like @outlook.com). This does require a credit card; however, there is a spending limit in the subscription so it won't be charged unless you explicitly remove the limit.
- Open Microsoft Edge and go to the Microsoft VS Dev Essentials site.
- Click Join or access now.
- Sign in using your personal Microsoft account.
- If prompted, click Confirm to agree to the terms and conditions.
- Find the Azure tile and click the Activate link.
- Alternatively, if the above isn't suitable, you can sign up for a free Azure trial.
- Open Microsoft Edge and go to the free Azure trial page.
- Click Start free.
- Sign in using your personal Microsoft account.
- Complete the Azure sign up steps and wait for the subscription to be provisioned. This usually only takes a couple of minutes.
This lab uses Postman to interact with the Azure Search REST API. Other similar tools can be used e.g. Fiddler, Charles. The free Postman desktop app can be downloaded and installed for most operating systems. See the Azure Search documentation for more information on using Postman.
Download the sample code provided for this lab, it includes the following:
- Sample JFK file documents
- JSON request files for configuring the Cognitive Search Service
- A set of custom Cognitive skills
- The frontend JFK search app
To Download:
- Click Clone or download from this repo.
- You can clone the repo using git or click Download ZIP to directly download the code from your browser.
In this module, you'll learn how to create your own Cognitive Search pipeline. You'll use the 'OCR cognitive skill' to perform character recognition on the source documents.
In order to speed up the lab we provide an Azure Template to deploy the required resources for this lab. The template will provision the following services:
- An Azure Search service.
- An Azure Blob Storage Account.
- An Azure App Service plan.
- An Azure Web App Service to deploy the front-end.
- An Azure Function instance.
Follow the next steps to create the resources:
-
Click the following link to deploy the template: // TODO: Replace template url
-
You will be redirected to Azure, provide your credentials to login.
-
Provide the required information:
- Subscription: select your subscription.
- Create a new resource group with the name:
ai-labs-<your initials>. - Location:
South Central US.
[!NOTE] At the time of writing, Azure Search with Cognitive Services is only available in the
South Central USregion. -
Select the checkbox for "I agree to the terms and conditions stated above".
-
Click Purchase. This step might take a few seconds.
-
Once the deployment is complete, you will see a Deployment succeeded notification.
Save the configuration values required to use these services:
- Go to Resource groups in the left pane and search for your resource group:
jfk-labs-<your initials>. - Click on the resource.
- Click on Deployments.
- Click on the Deployment Name Microsoft.Template from the first result.
- Click on Outputs.
- Copy all the values in Notepad.
[!NOTE] These settings are required to connect to the services later in the lab.
We'll need a set of documents for testing the capabilities of cognitive search. Let's upload the sample files.
Create the blob container:
-
Go to All Resources in the left pane and search for the storage:
jfkstorage. -
Click on the resource.
-
Click on the Blob option.
-
Click on +Container and provide the required information:
- Name:
jfkfiles. - Public access level:
Container.
- Name:
-
Click on the newly created container.
-
Click the Upload button.
-
Select the following files from the lab materials:
resources\documents. -
Click Upload and wait for the process to complete.
A data source is the mechanism by which Azure Search indexers ingest data. You can pull data from supported Azure data sources using indexers and schedule data refreshes of a target index.
Setup Postman:
-
Open Postman from the Start Menu.
-
Click on Import from the toolbar.
-
Click on Import files and select the collection file at
resources\AI Labs - Azure Search.postman_collection.json. -
Click the gear icon in the upper right corner and select "Manage Environments".
-
Click the Import button at the bottom of the modal and select the file
resources\AI Labs - Azure Search.postman_environment.json. -
Click on the environment name to reveal a key-value editor to add, edit, and delete the environment variables.
-
Set the value of the following variables:
- searchServiceName: paste the SEARCH SERVICE NAME value obtained in the deployment's output.
- searchServiceKey: paste the SEARCH SERVICE API KEY value obtained in the deployment's output.
-
Click on Update and close the modal window.
-
Select
AI Labs - Azure Searchfrom the environment list in the top right corner.
Make the request:
-
Click the Create Data Source request from the collection.
-
Click on Body and specify the following values:
- name:
jfklabds. - type:
azureblob. - credentials: set the connectionString using the Blob Storage account connection string obtained in the deployment's output.
- name:
-
Click on Send and wait for the response. If the request is successful you should see a status code
201 Created.
A Skillset is a set of Cognitive Skills that are used to extract and enrich data from the source documents to make it searchable in Azure Search. The service provides a set of predefined cognitive skills to extract data using techniques like entity recognition, language detection, key phrase extraction, text manipulation, and image detection, for more information follow this link.
-
Click the Create Skillset request from the collection in Postman.
-
Review the request url and replace the value [skillset_name] with
jfklabskillset. -
Click on Body and check the value, it contains two predefined skills:
- An OCR Skill to extract the text from printed content.
- A Text Merger Skill to merge the textual representation from the OCR skill into the finalText field.
-
Click on Send and wait for the response. For a successful request, you should see status code
201 Created.
Creating an index specifies the schema and metadata that are required to store documents in Azure Search.
- Click the Create Index request from the collection in Postman.
- Review the request url and replace the value [index_name] with
jfklabindex. - Click on Body and check the value, it contains the index definition.
[!NOTE] The body of the request contains the schema definition, which includes the list of data fields within documents that will be fed into this index.
- Click on Send and wait for the response. For a successful request, you should see status code
201 Created.
Indexers are specific to Azure data storage, they are used for crawling data in the data source and populating the Azure Search index.
-
Click the Create Indexer request from the collection in Postman.
-
Review the request url and replace the value [indexer_name] with
jfklabindexer. -
Click on Body and replace the [IndexerName] with
jfklabindexer. -
Replace the following values:
- [IndexName]: set the value of the index previously created (
jfklabindex). - [DataSourceName]: set the value of the data source previously created (
jfklabds). - [SkillSetName]: : set the value of the Skillset previously created (
jfklabskillset).
- [IndexName]: set the value of the index previously created (
-
Click on Send and wait for the response. For a successful request, you should see status code
201 Created.
- Return to the Azure Portal.
- Go to All Resources in the left pane and search for the Search resource:
jfk-lab-search-service. - Click on the resource. This will provide an overview of the service, from this view you can access the indexes, indexers, data sources and perform other operations on the service.
- Click on Indexers and check the status of your newly created Indexer, wait for the status to be Success. This process might take a few minutes to complete.
- Return to the Search service overview.
- Click the Search Explorer from the toolbar.
- In the search box type:
$top=10&$count=true. - Click the Search button. You will see the 7 documents that we initially uploaded to the storage, and the content of the documents in the text field.
- On the search box displayed type:
JFK&$count=true. - Click the Search button.
- Review the results and look for the text that matches your search criteria. The service will retrieve 5 documents for this query.
[!NOTE] Use
CTRL+Fto search through the document content if you can't find the content that matches your query.
In this module, you'll learn how create a custom skill that can be plugged into the Cognitive Search pipeline.
Building a custom skill gives you a way to insert specific transformations to your content and apply whatever enrichment process you require.
In this example we will create a custom skill that annotates documents that contain CIA "Cryptonym" code words. e.g The CIA assigned the cryptonym GPFLOORto Lee Harvey Oswald, so any documents containing that Cryptonym will be linked with Oswald.
The only requirement for a skill is the ability to accept inputs and emit outputs. Currently, the only mechanism for interacting with a custom skill is through a Web API interface. Although this example uses an Azure Function to host a web API, it is not required as long as you meet the interface requirements for a cognitive skill. Click here for more information.
- Open Visual Studio from the Start Menu.
- Click Open Project/Solution and select
JfkWebApiSkills\JfkWebApiSkills.sln. - Right-click the Solution.
- Click Restore NuGet Packages.
- Open the file
JfkWebApiSkills. - Add the following function method.
[FunctionName("link-cryptonyms")]
public static IActionResult RunCryptonymLinker([HttpTrigger(AuthorizationLevel.Function, "post", Route = null)]HttpRequest req, TraceWriter log, ExecutionContext executionContext)
{
}
- Add the following code snippet to the function method to get the input records:
string skillName = executionContext.FunctionName;
// Get the batch of input records from the request
var requestRecords = WebApiSkillHelpers.GetRequestRecords(req);
if (requestRecords == null)
{
return new BadRequestObjectResult($"{skillName} - Invalid request record array.");
}
- Add the following code at the end of the method, this will process all the records and put the results in the output:
// Process each record and set the cryptonym to the output if found
WebApiSkillResponse response = WebApiSkillHelpers.ProcessRequestRecords(skillName, requestRecords,
(inRecord, outRecord) => {
string word = inRecord.Data["word"] as string;
if (word.All(Char.IsUpper) && cryptonymLinker.Cryptonyms.TryGetValue(word, out string description))
{
outRecord.Data["cryptonym"] = new { value = word, description };
}
return outRecord;
});
return (ActionResult)new OkObjectResult(response);
[!NOTE] The
ProcessRequestRecordsmethod sets the description of each cryptonym, it reads the values from the json fileCryptonymLinker\cia-cryptonyms.json. Open this file to see the list of available cryptonyms.
For the purposes of our demo, we'll be deploying directly from Visual Studio.
- Check your current connected account in the top right corner of Visual Studio.
[!ALERT] Ensure you are signed in with the same credentials you used to sign in to Azure. This will connect Visual Studio to your Azure subscription.
- Select JfkWebApiSkills from the Projects dropdown list in the toolbar.
- Select
Release. - Right-click the JfkWebApiSkills project.
- Click Build and wait for it to finish.
- Right-click the JfkWebApiSkills project.
- Click Publish.
- Mark the option Select Existing.
- Click Publish.
- Select the Web App previously created for the function:
jfk-lab-function-app. - Click OK and wait for the deployment to complete. This step might take a few minutes.
[!NOTE] If you are prompted to update the Functions Version on Azure click Yes.
- Check the Output window until you see the Publish completed message.
- In the Azure portal, search for your function app resource: :
jfk-lab-function-app. - Click on Function app settings.
- Select the Copy icon for the master host key. Paste this value in Notepad as you'll need it later.
- Click on the Platform features option.
- Click on SSL.
[!NOTE] All Azure Functions created after June 30th, 2018 have disabled TLS 1.0, which is not currently compatible with custom skills.
- After selecting SSL, ensure the Minimum TLS version is set to 1.0.
[!ALERT] TLS 1.2 functions are not yet supported as custom skills.
-
Click on the Overview option.
-
Click on Configuration.
-
Click on + New Application Settings Verify and add the following setting:
- name:
MSDEPLOY_RENAME_LOCKED_FILES. - value:
1.
- name:
-
Scroll to the top and click the Save button.
-
Return to Postman.
-
Click the Test Custom Skill request from the collection in Postman.
-
Review the request url and replace the following values:
- [function_app_name] with the
AZURE FUNCTION SITE NAMEvalue from the initial Deployment Output. - [function_host_key] with the Host key previously obtained.
- [function_app_name] with the
-
Click on Body and check the content, we'll be sending 2 cryptonyms to the function.
-
Click on Send and wait for the response. For a successful request, you should see status code
200 OK. -
Check the descriptions for each cryptonym in the response body.
- Click the Create Skillset request from the collection in Postman.
- Review the request url and replace the value [skillset_name] with
jfklabskillset. - Click on the Body and add the new skill to the end of the skills array:
{
"@odata.type": "#Microsoft.Skills.Custom.WebApiSkill",
"description": "Cryptonym linker",
"uri": "https://[function_app_name].azurewebsites.net/api/link-cryptonyms?code=[default_host_key]",
"context": "/document/normalized_images/*/layoutText/words/*/text",
"inputs": [
{
"name": "word",
"source": "/document/normalized_images/*/layoutText/words/*/text"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"name": "cryptonym",
"targetName": "cryptonym"
}
]
}
[!NOTE] Replace the
[function_app_name]and[default_host_key]with the values used in the previous section.
- Click on Send and wait for the response. For a successful request, you should see status code
204 No Content. - Click the Get Skillset request from the collection in Postman.
- Review the request url and replace the value [skillset_name] with
jfklabskillset. - Click on Send and wait for the response. Check the response and search for the newly added skill in the results.
Include the cryptonyms field in the Indexer:
- Click the Create Indexer request from the collection.
- Add the following code snippet to the
outputFieldMappingssection:
{
"sourceFieldName": "/document/normalized_images/*/layoutText/words/*/text/cryptonym/value",
"targetFieldName": "cryptonyms"
}
- Click on Send and wait for the response.
We have to re-run the indexer to apply the new skill to the source documents.
- Go to All Resources in the left pane and search for the Search resource:
jfk-lab-search-service. - Click on the resource. This will provide an overview of the service, from this view you can access the indexes, indexers, data sources and perform other operations on the service.
- Click on Indexers and check the status of the newly created Indexer, wait for the status to be Success. This process might take a few minutes to complete.
- Return to the Azure Portal.
- Go to All Resources in the left pane and search for the Search resource:
jfk-lab-search-service. - Click on the resource.
- Click on Indexers and click on the first indexer displayed.
- Click the Run button, it will prompt for confirmation, click Yes.
- Return to the Search service overview.
- Click the Search Explorer from the toolbar.
- On the search box displayed type:
WILSON&$count=true. - Click the Search button.
- Review the results and look for the
cryptonymsfield, you will see the AM cryptonym in the results.
In this module, you'll create a more advanced pipeline, using the custom skill from the previous module and include more cognitive skills in the pipeline.
Let's take a look at our source data and see which data is not being extracted:
- Go to your lab directory and open the document at
resources\documents\104-10013-10234.pdf. - Notice the handwritten text at the bottom.
- Go back to the Search explorer in Azure.
- On the search box displayed type:
FBI. - Click the Search button.
- Try finding the 104-10013-10234 in the results, you will see that it is not being recognized by our current skillset.
- Go to your lab directory and open the document at
resources\documents\photo_oswald.jpeg. - On the search box displayed type:
oswald. - Click the Search button.
- Try finding the picture file in the results, you will see that is not being recognized either.
We'll use a query key to query the Search service from the front-end. Query keys grant read-only access to indexes and documents, and are typically distributed to client applications that issue search requests. In the next steps we'll create a new query key. You can create up to 50 query keys per service.
-
Follow this link to create the query key.
-
Login with the same credentials you used to sign in to Azure.
-
Review the request url and provide the following parameters:
- subscriptionId: copy the value from the initial deployment output.
- resourceGroupName: your resource group name.
- searchServiceName: copy the value from the initial deployment output.
- name:
my_query_key.
-
Click on Run.
-
Check the response body, copy the key value as you will need it later.
In order to speed up the lab process we'll use a console app to recreate the different components in the pipeline. This will include more cognitive skills like handwritting and image analysis for categories, faces, image type, adult content and others.
-
Return to Visual Studio.
-
Open the file
App.configfrom theJfkInitializerproject.. -
Add the configuration values, use the values obtained in previous steps.
-
Open the
Program.csfile. -
Go to the
CreateAdvancedPipelineAsyncmethod. -
Check the list of components being re-created.
- Skillset
- Index
- Indexer
- Synonyms: this is a map that you define and upload to your service to define synonyms. These map constitute an independent resource (like indexes or data sources), and can be used by any searchable field in any index in your search service.
- Blob Container for image store: used to store annotations from image data.
-
Let's implement the synonyms map, go to the method
CreateSynonyms. -
Add the following code snippet where indicated:
try
{
SynonymMap synonyms = new SynonymMap(SynonymMapName, SynonymMapFormat.Solr,
@"GPFLOOR,oswold,ozwald,ozwold,oswald
silvia, sylvia
sever, SERVE, SERVR, SERVER
novenko, nosenko, novenco, nosenko");
await _searchClient.SynonymMaps.CreateAsync(synonyms);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("Error creating synonym map: {0}", ex.Message);
return false;
}
- Right click on the
JfkInitializerproject and click Debug > Start new instance.
[!NOTE] Click Continue Debugging (Don't ask again) if prompted.
- A console window will be opened, it will display the process output.
-
Open the file explorer in the lab materials directory and replace the following files:
- Copy
resources\advanced-pipeline\JfkWebApiSkills.cstosrc\JfkWebApiSkills\JfkWebApiSkills. - Copy
resources\advanced-pipeline\cia-cryptonyms.jsontosrc\JfkWebApiSkills\JfkWebApiSkills\CryptonymLinker.
- Copy
-
Replace the file and open it in Visual Studio. The file contains the following functions:
- facet-graph-nodes.
- link-cryptonyms: the custom skill created in previous section.
- link-cryptonyms-list: similar to the previous skill but returns a list of cryptonyms per word.
- image-store: uploads image data to blob storage.
- hocr-generator: transforms ocr metadata to the hocr open standard (data representation for formatted text obtained from OCR).
-
Right-click the JfkWebApiSkills project.
-
Click Rebuild and wait for it to finish.
-
Right-click the JfkWebApiSkills project.
-
Click Publish.
-
Click Publish again.
-
Review the deployment result in the Output window and wait for the operation to complete.
[!Note] If your deployment fails due ERROR_FILE_IN_USE, return to Azure and open your function app resource, click Restart from the Overview page and try the deployment again.
-
Go to the
Mainmethod. -
Replace the following line:
bool result = CreateAdvancedPipelineAsync().GetAwaiter().GetResult();with
bool result = DeployFrontEndAsync().GetAwaiter().GetResult(); -
Right click on the
JfkInitializerproject and click Debug > Start new instance. -
It will open a Console App, wait until it requests to build the Website.
-
Open a Terminal and navigate to the
frontenddirectory in you lab folder. -
Execute the following commands:
npm installnpm run build:prod
[!NOTE] Check that a dist folder was created in your frontend directory.
-
Return to the Console App and press any key to continue.
-
Wait for deployment to complete, this might take a few seconds.
-
Copy the Website url and press any key to finish.
- Open the Website url in a Browser.
- Search
ozwold. - Click the Search button.
- Check the results and see the picture recognized as Oswald, this is done by using the Image Analysis (Computer Vision) skill.
[!NOTE] Notice how the Synonyms map allows to match the ozwold word to oswald.
- Review the list of entities at the left pane.
- Click on FBI, you will see 2 results containing that entity.
- Click on the first document, you will be able to see the document details.
- Search the FBI word on the right pane, see how we can highlight the word in the original document using the image metadata.
- Change the search criteria and search for
FBI. - Click the Search button.
- Click on the document 104-10013-10234.
- Review how the pipeline is extracting the FBI word from handwritten text.