This code was written in 2019, and I was not very familiar with transformer model in that time. So don't trust this code too much because the code may have several bugs or wrong implementations. Currently I am not managing this code well, so please open pull requests if you find bugs in the code and want to fix.
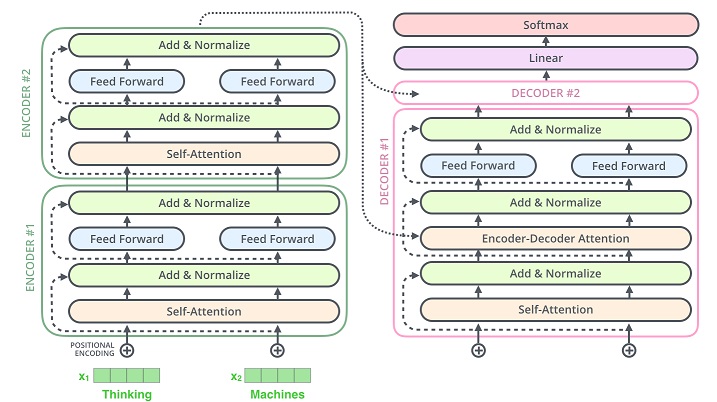
My own implementation Transformer model (Attention is All You Need - Google Brain, 2017)
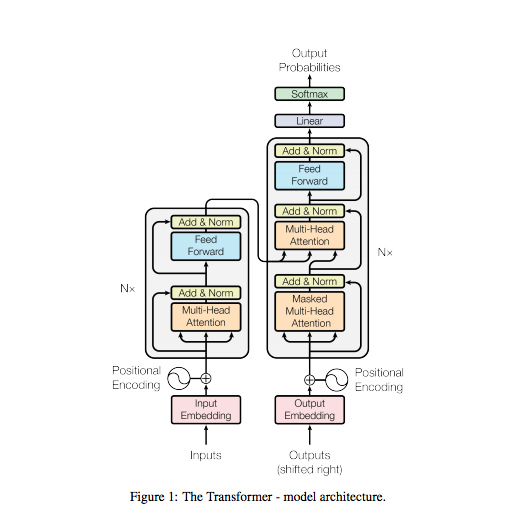
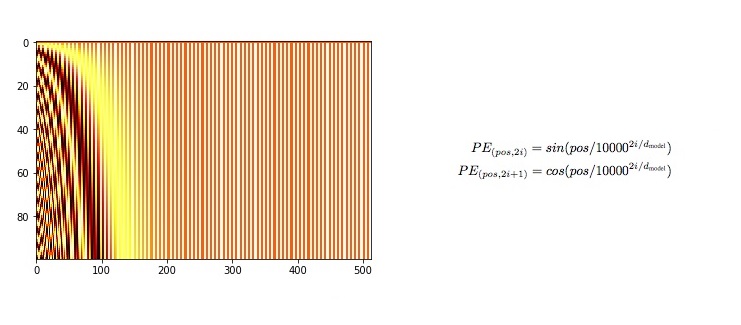
class PositionalEncoding(nn.Module):
"""
compute sinusoid encoding.
"""
def __init__(self, d_model, max_len, device):
"""
constructor of sinusoid encoding class
:param d_model: dimension of model
:param max_len: max sequence length
:param device: hardware device setting
"""
super(PositionalEncoding, self).__init__()
# same size with input matrix (for adding with input matrix)
self.encoding = torch.zeros(max_len, d_model, device=device)
self.encoding.requires_grad = False # we don't need to compute gradient
pos = torch.arange(0, max_len, device=device)
pos = pos.float().unsqueeze(dim=1)
# 1D => 2D unsqueeze to represent word's position
_2i = torch.arange(0, d_model, step=2, device=device).float()
# 'i' means index of d_model (e.g. embedding size = 50, 'i' = [0,50])
# "step=2" means 'i' multiplied with two (same with 2 * i)
self.encoding[:, 0::2] = torch.sin(pos / (10000 ** (_2i / d_model)))
self.encoding[:, 1::2] = torch.cos(pos / (10000 ** (_2i / d_model)))
# compute positional encoding to consider positional information of words
def forward(self, x):
# self.encoding
# [max_len = 512, d_model = 512]
batch_size, seq_len = x.size()
# [batch_size = 128, seq_len = 30]
return self.encoding[:seq_len, :]
# [seq_len = 30, d_model = 512]
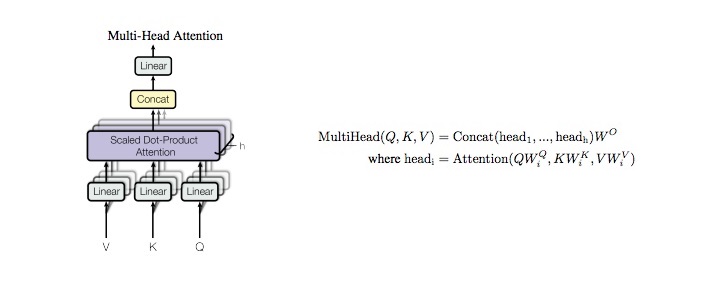
# it will add with tok_emb : [128, 30, 512] class MultiHeadAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, n_head):
super(MultiHeadAttention, self).__init__()
self.n_head = n_head
self.attention = ScaleDotProductAttention()
self.w_q = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model)
self.w_k = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model)
self.w_v = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model)
self.w_concat = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model)
def forward(self, q, k, v, mask=None):
# 1. dot product with weight matrices
q, k, v = self.w_q(q), self.w_k(k), self.w_v(v)
# 2. split tensor by number of heads
q, k, v = self.split(q), self.split(k), self.split(v)
# 3. do scale dot product to compute similarity
out, attention = self.attention(q, k, v, mask=mask)
# 4. concat and pass to linear layer
out = self.concat(out)
out = self.w_concat(out)
# 5. visualize attention map
# TODO : we should implement visualization
return out
def split(self, tensor):
"""
split tensor by number of head
:param tensor: [batch_size, length, d_model]
:return: [batch_size, head, length, d_tensor]
"""
batch_size, length, d_model = tensor.size()
d_tensor = d_model // self.n_head
tensor = tensor.view(batch_size, length, self.n_head, d_tensor).transpose(1, 2)
# it is similar with group convolution (split by number of heads)
return tensor
def concat(self, tensor):
"""
inverse function of self.split(tensor : torch.Tensor)
:param tensor: [batch_size, head, length, d_tensor]
:return: [batch_size, length, d_model]
"""
batch_size, head, length, d_tensor = tensor.size()
d_model = head * d_tensor
tensor = tensor.transpose(1, 2).contiguous().view(batch_size, length, d_model)
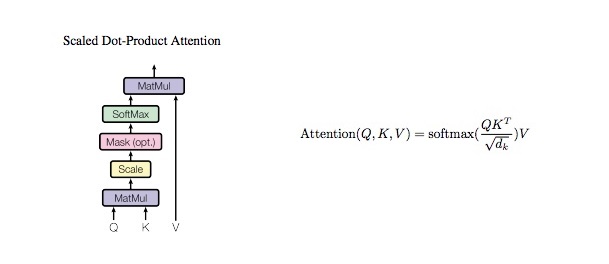
return tensorclass ScaleDotProductAttention(nn.Module):
"""
compute scale dot product attention
Query : given sentence that we focused on (decoder)
Key : every sentence to check relationship with Qeury(encoder)
Value : every sentence same with Key (encoder)
"""
def __init__(self):
super(ScaleDotProductAttention, self).__init__()
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
def forward(self, q, k, v, mask=None, e=1e-12):
# input is 4 dimension tensor
# [batch_size, head, length, d_tensor]
batch_size, head, length, d_tensor = k.size()
# 1. dot product Query with Key^T to compute similarity
k_t = k.transpose(2, 3) # transpose
score = (q @ k_t) / math.sqrt(d_tensor) # scaled dot product
# 2. apply masking (opt)
if mask is not None:
score = score.masked_fill(mask == 0, -10000)
# 3. pass them softmax to make [0, 1] range
score = self.softmax(score)
# 4. multiply with Value
v = score @ v
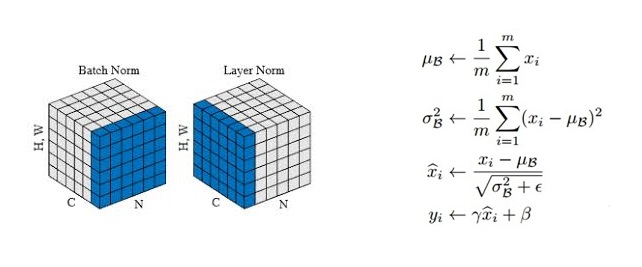
return v, scoreclass LayerNorm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, eps=1e-12):
super(LayerNorm, self).__init__()
self.gamma = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(d_model))
self.beta = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(d_model))
self.eps = eps
def forward(self, x):
mean = x.mean(-1, keepdim=True)
var = x.var(-1, unbiased=False, keepdim=True)
# '-1' means last dimension.
out = (x - mean) / torch.sqrt(var + self.eps)
out = self.gamma * out + self.beta
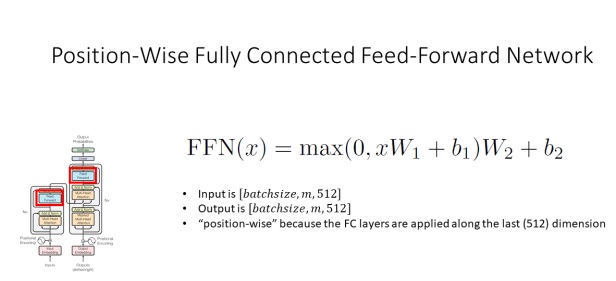
return outclass PositionwiseFeedForward(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, hidden, drop_prob=0.1):
super(PositionwiseFeedForward, self).__init__()
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(d_model, hidden)
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(hidden, d_model)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=drop_prob)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.linear1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.linear2(x)
return xclass EncoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, ffn_hidden, n_head, drop_prob):
super(EncoderLayer, self).__init__()
self.attention = MultiHeadAttention(d_model=d_model, n_head=n_head)
self.norm1 = LayerNorm(d_model=d_model)
self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout(p=drop_prob)
self.ffn = PositionwiseFeedForward(d_model=d_model, hidden=ffn_hidden, drop_prob=drop_prob)
self.norm2 = LayerNorm(d_model=d_model)
self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout(p=drop_prob)
def forward(self, x, src_mask):
# 1. compute self attention
_x = x
x = self.attention(q=x, k=x, v=x, mask=src_mask)
# 2. add and norm
x = self.dropout1(x)
x = self.norm1(x + _x)
# 3. positionwise feed forward network
_x = x
x = self.ffn(x)
# 4. add and norm
x = self.dropout2(x)
x = self.norm2(x + _x)
return xclass Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, enc_voc_size, max_len, d_model, ffn_hidden, n_head, n_layers, drop_prob, device):
super().__init__()
self.emb = TransformerEmbedding(d_model=d_model,
max_len=max_len,
vocab_size=enc_voc_size,
drop_prob=drop_prob,
device=device)
self.layers = nn.ModuleList([EncoderLayer(d_model=d_model,
ffn_hidden=ffn_hidden,
n_head=n_head,
drop_prob=drop_prob)
for _ in range(n_layers)])
def forward(self, x, src_mask):
x = self.emb(x)
for layer in self.layers:
x = layer(x, src_mask)
return xclass DecoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, ffn_hidden, n_head, drop_prob):
super(DecoderLayer, self).__init__()
self.self_attention = MultiHeadAttention(d_model=d_model, n_head=n_head)
self.norm1 = LayerNorm(d_model=d_model)
self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout(p=drop_prob)
self.enc_dec_attention = MultiHeadAttention(d_model=d_model, n_head=n_head)
self.norm2 = LayerNorm(d_model=d_model)
self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout(p=drop_prob)
self.ffn = PositionwiseFeedForward(d_model=d_model, hidden=ffn_hidden, drop_prob=drop_prob)
self.norm3 = LayerNorm(d_model=d_model)
self.dropout3 = nn.Dropout(p=drop_prob)
def forward(self, dec, enc, trg_mask, src_mask):
# 1. compute self attention
_x = dec
x = self.self_attention(q=dec, k=dec, v=dec, mask=trg_mask)
# 2. add and norm
x = self.dropout1(x)
x = self.norm1(x + _x)
if enc is not None:
# 3. compute encoder - decoder attention
_x = x
x = self.enc_dec_attention(q=x, k=enc, v=enc, mask=src_mask)
# 4. add and norm
x = self.dropout2(x)
x = self.norm2(x + _x)
# 5. positionwise feed forward network
_x = x
x = self.ffn(x)
# 6. add and norm
x = self.dropout3(x)
x = self.norm3(x + _x)
return xclass Decoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dec_voc_size, max_len, d_model, ffn_hidden, n_head, n_layers, drop_prob, device):
super().__init__()
self.emb = TransformerEmbedding(d_model=d_model,
drop_prob=drop_prob,
max_len=max_len,
vocab_size=dec_voc_size,
device=device)
self.layers = nn.ModuleList([DecoderLayer(d_model=d_model,
ffn_hidden=ffn_hidden,
n_head=n_head,
drop_prob=drop_prob)
for _ in range(n_layers)])
self.linear = nn.Linear(d_model, dec_voc_size)
def forward(self, trg, src, trg_mask, src_mask):
trg = self.emb(trg)
for layer in self.layers:
trg = layer(trg, src, trg_mask, src_mask)
# pass to LM head
output = self.linear(trg)
return outputI use Multi30K Dataset to train and evaluate model
You can check detail of dataset here
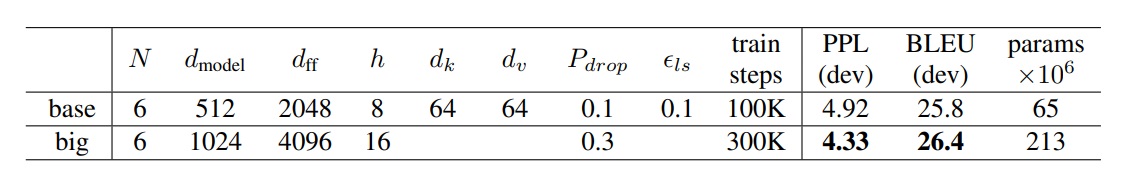
I follow original paper's parameter settings. (below)
- total parameters = 55,207,087
- model size = 215.7MB
- lr scheduling : ReduceLROnPlateau
- batch_size = 128
- max_len = 256
- d_model = 512
- n_layers = 6
- n_heads = 8
- ffn_hidden = 2048
- drop_prob = 0.1
- init_lr = 0.1
- factor = 0.9
- patience = 10
- warmup = 100
- adam_eps = 5e-9
- epoch = 1000
- clip = 1
- weight_decay = 5e-4
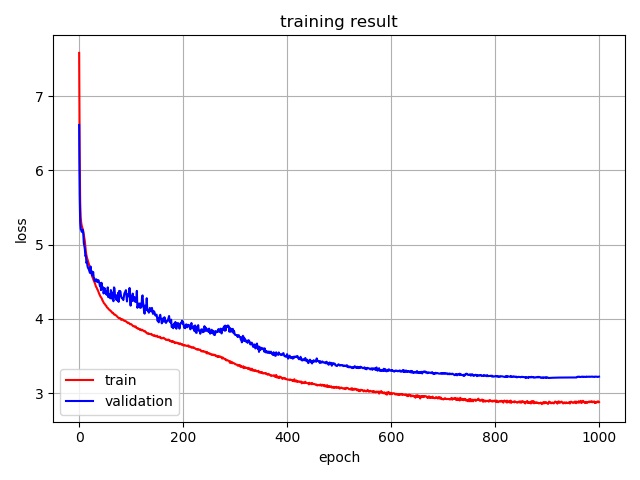
- Minimum Training Loss = 2.852672759656864
- Minimum Validation Loss = 3.2048025131225586
| Model | Dataset | BLEU Score |
|---|---|---|
| Original Paper's | WMT14 EN-DE | 25.8 |
| My Implementation | Multi30K EN-DE | 26.4 |
- Attention is All You Need, 2017 - Google
- The Illustrated Transformer - Jay Alammar
- Data & Optimization Code Reference - Bentrevett
Copyright 2019 Hyunwoong Ko.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.