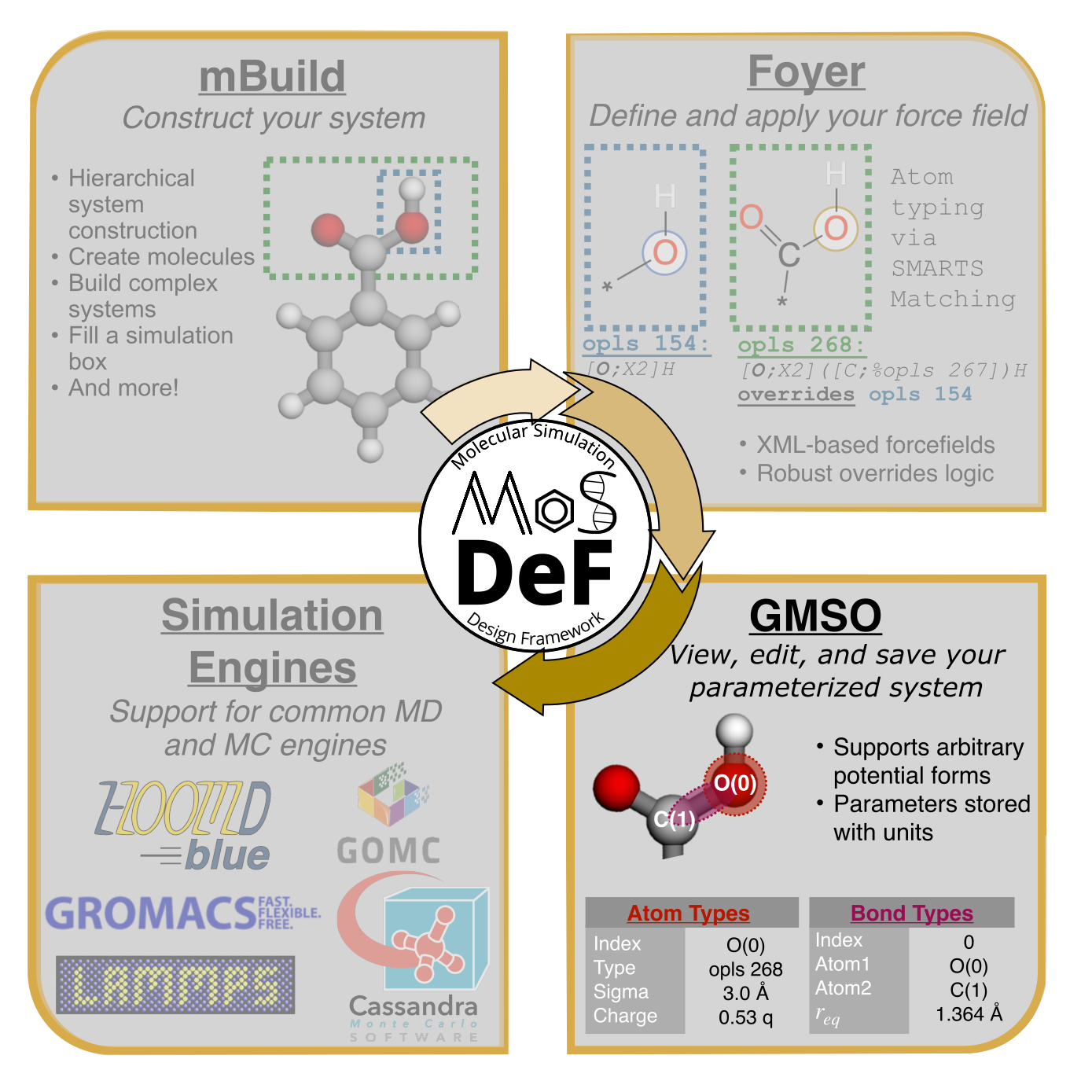
GMSOis a flexible storage of chemical topology for molecular simulation.
With a few lines of GMSO code, together with mBuild and foyer, users can rapidly prototype arbitrary parameterized chemical systems and generate data files for a wide variety of simulation engines.
To learn more, get started, or contribute, check out our Documentation.
This is an example using mBuild and Foyer to build a GMSO topology and write out to LAMMPS.
import foyer
import forcefield_utilities as ffutils
from mbuild.lib.molecules import Ethane
from gmso.external.convert_mbuild import from_mbuild
from gmso.parameterization import apply
from gmso.formats.lammpsdata import write_lammpsdata
# Start with a mBuild compound
mb_ethane = Ethane()
oplsaa = ffutils.FoyerFFs().load('oplsaa').to_gmso_ff()
# atomtype the system with foyer, and convert the resulting structure to a topology
gmso_ethane = from_mbuild(mb_ethane)
apply(top=gmso_ethane,
forcefields=oplsaa,
identify_connections=True)
# Write out lammps datafile
write_lammpsdata(gmso_ethane, filename='ethane.lammps', atom_style='full')GMSO is designed to be a general and flexible representation of chemical topolgies for molecular simulation.
With an emphasis on assuming as little as possible about the chemical system, model, or engine, GMSO can enable support for a variety of systems.
GMSO is a part of the MoSDeF (Molecular Simulation and Design Framework) ecosystem, and is intended to be the backend replacement for the foyer package.
Libraries in the MoSDeF ecosystem are designed to provide utilities neccessary to streamline
a researcher's simulation workflow. When setting up simulation studies,
we also recommend users to follow the TRUE
(Transparent, Reproducible, Usable-by-others, and Extensible) standard, which is a set of common
practices meant to improve the reproducibility of computational simulation research.
GMSO's goal is to provide a flexible backend framework to store topological information of a chemical system in a reproducible fashion.
Topology in this case is defined as the information needed to initialize a molecular simulation.
Depending on the type of simulation performed, this ranges from:
- particle positions
- particle connectivity
- box information
- forcefield data
- functional forms defined as
sympyexpressions - parameters with defined units
- partial charges
- tabulated data
- etc.
- functional forms defined as
- Other optional data
- particle mass
- elemental data
- etc.
With these driving goals for GMSO, the following features are enabled:
-
Supporting a variety of models in the molecular simulation/computational chemistry community_: No assumptions are made about an interaction site representing an atom or bead, instead these can be atomistic, united-atom/coarse-grained, polarizable, and other models!
-
Greater flexibility for exotic potentials: The
AtomType(and analogue classes for intramolecular interactions) usessympyto store any potential that can be represented by a mathematical expression. -
Adaptable for new engines: by not being designed for compatibility with any particular molecular simulation engine or ecosystem, it becomes more tractable for developers in the community to add glue for engines that are not currently supported.
-
Compatibility with existing community tools: No single molecular simulation tool will ever be a silver bullet, so
GMSOincludes functions to convert between various file formats and libraries. These can be used in their own right to convert between objects in-memory and also to support conversion to file formats not natively supported at any given time. Currently supported conversions include: -
Native support for reading and writing many common file formats: We natively have support for:
XYZGROTOPLAMMPSDATA- indirect support, through other libraries, for many more!
For full, detailed instructions, refer to the documentation for installation
GMSO is available on conda and can be installed as:
conda install -c conda-forge gmsoDependencies of GMSO are listed in the files environment.yml (lightweight environment specification containing minimal dependencies) and environment-dev.yml (comprehensive environment specification including optional and testing packages for developers).
The gmso or gmso-dev conda environments can be created with
git clone https://github.com/mosdef-hub/gmso.git
cd gmso
# for gmso conda environment
conda env create -f environment.yml
conda activate gmso
# for gmso-dev
conda env create -f environment-dev.yml
conda activate gmso-dev
# install a non-editable version of gmso
pip install .
Once all dependencies have been installed and the conda environment has been created, the GMSO itself can be installed.
cd gmso
conda activate gmso-dev # or gmso depending on your installation
pip install -e .
The full documentation can be found at gmso.mosdef.org.