Each dialog in Bot Framework Composer includes a set of triggers (event handlers) that contain instructions for how the bot will respond to inputs received when the dialog is active. There are several different types of event handlers available in the Composer menu. They all work in a similar manner and can be interchanged in some cases. In this article, we will walk you through how to define each type of trigger. If you are not familiar with events and triggers in Composer, please read the events and triggers concept article.
The table below lists the five different types of triggers provided in BF Composer and their descriptions.
| Trigger Type | Description |
|---|---|
Handle an Intent |
Trigger an action when an Intent is recognized (and optionally entities) |
Handle Unknown Intent |
Trigger an action when no intent is recognized |
Handle a Dialog Event |
Trigger an action when a dialog event such as BeginDialog is fired |
Handle an Event: Activity |
Trigger an action to take when an activity event such as Handle ConversationUpdate is fired |
Handle a custom event |
Handle a pre-defined custom event such as Emit a custom event action. |
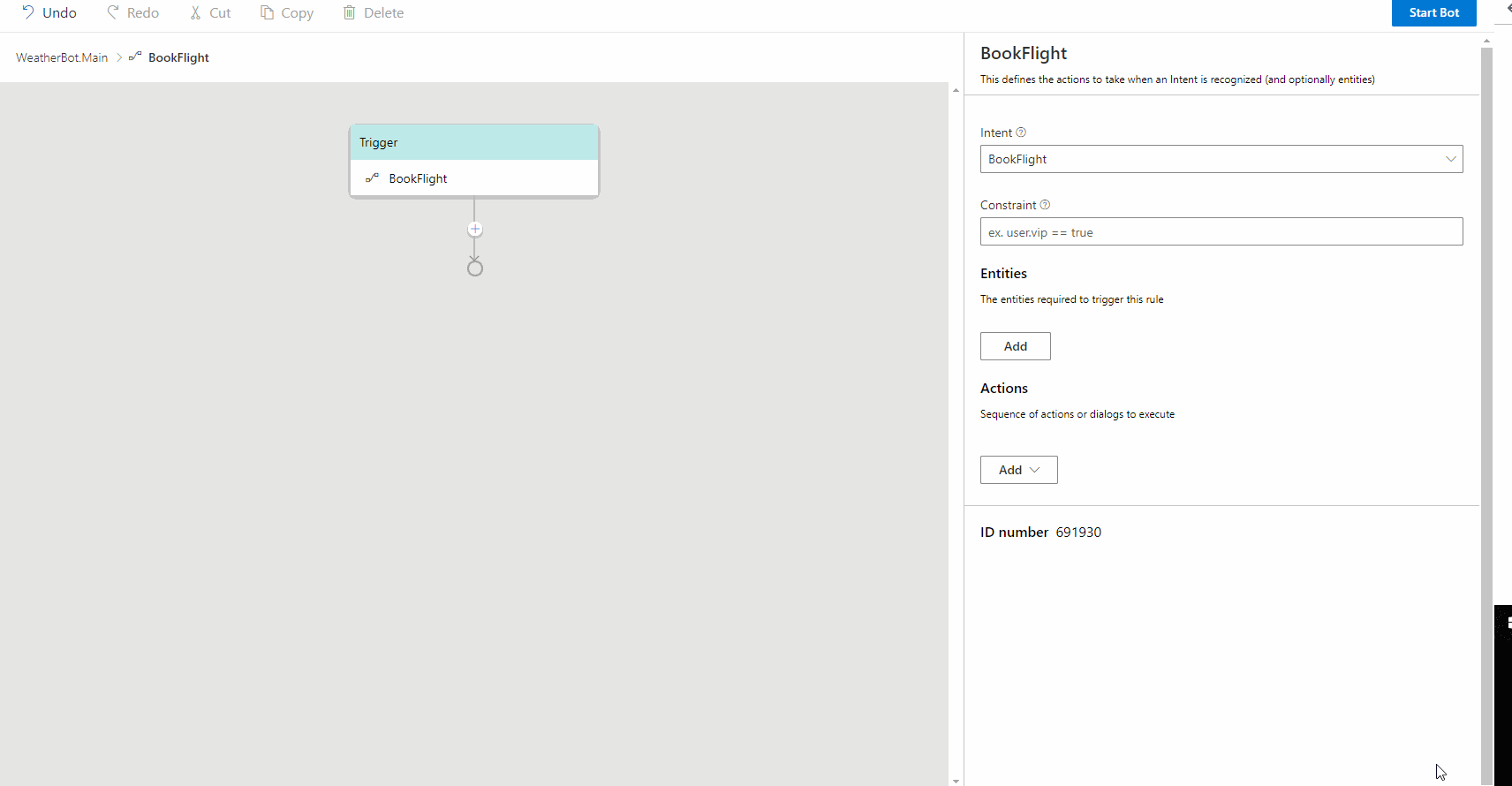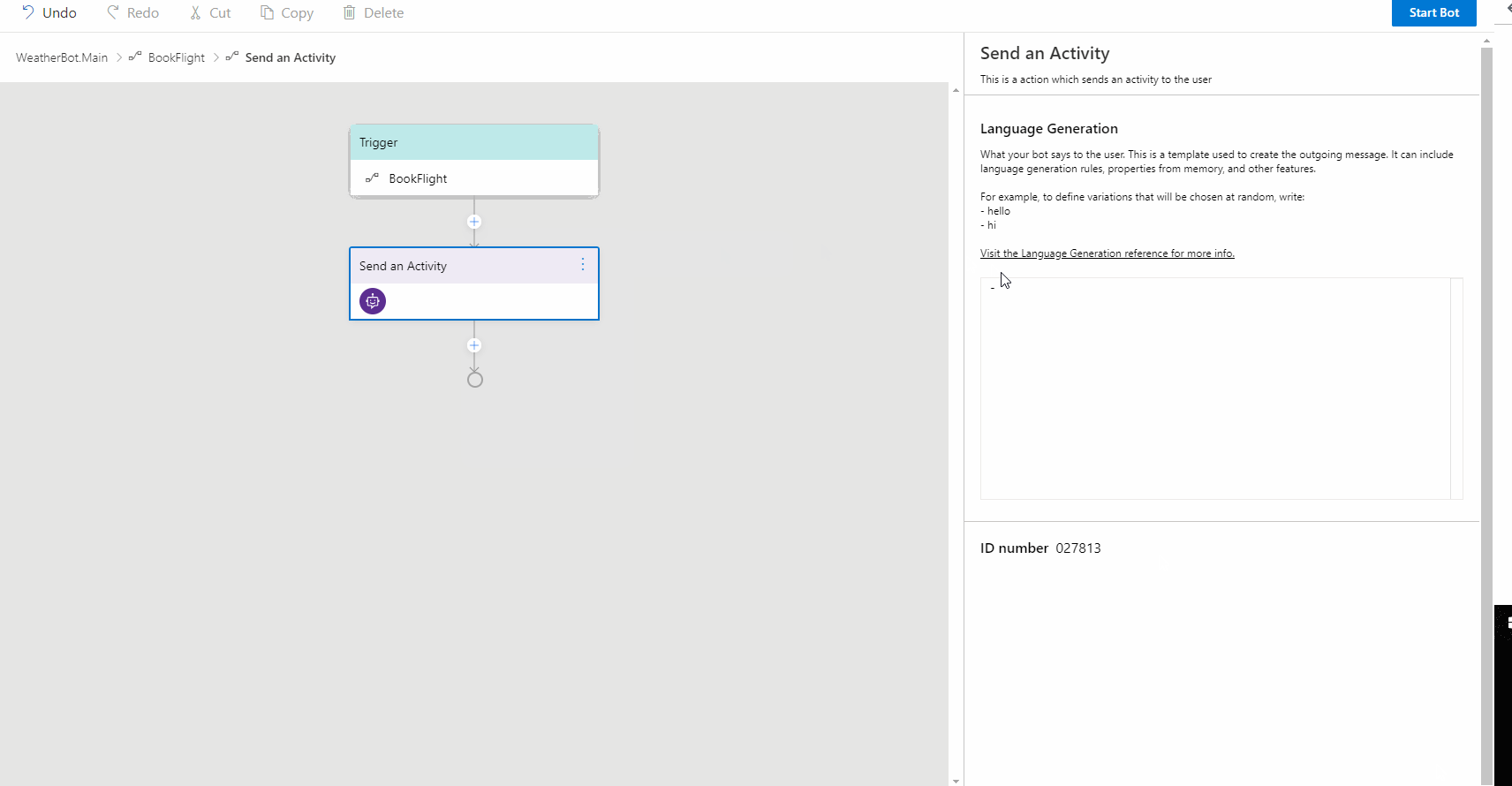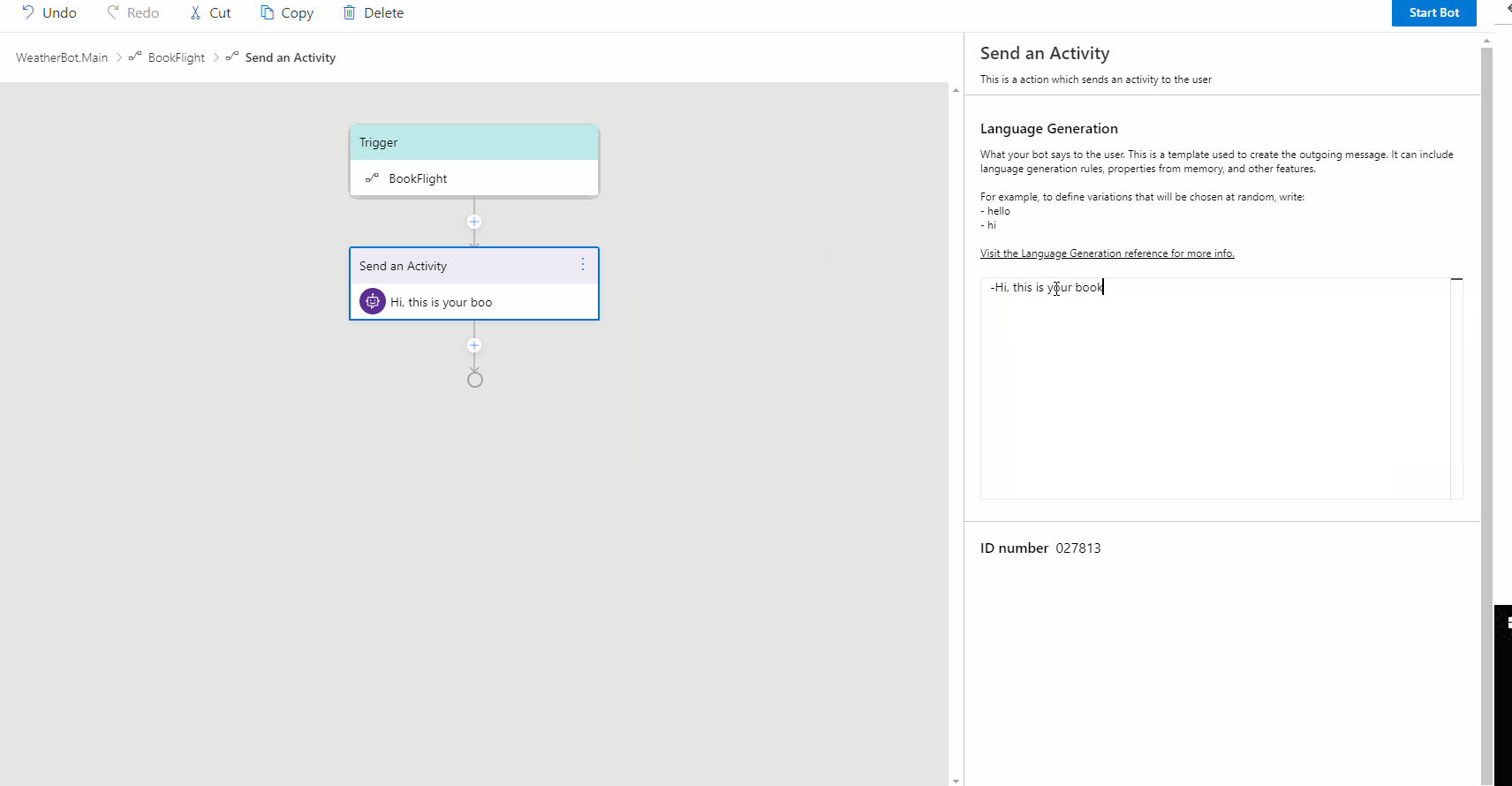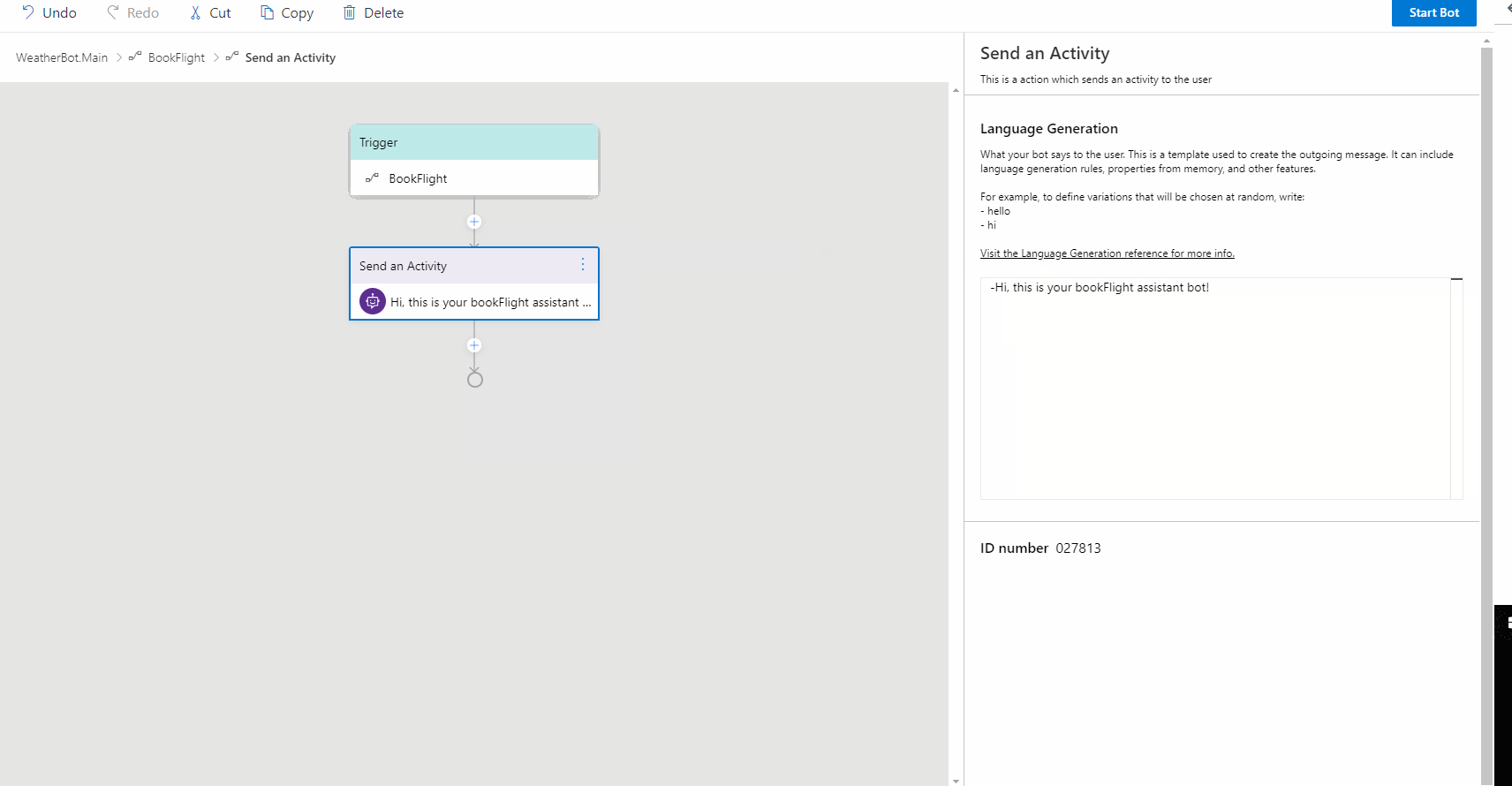
Handle an Intent defines the actions to take when an Intent is recognized (and optionally entities). Before defining a Handle an Intent trigger you need to select a recognizer type and define intents in your selected dialog:
On the right side of the dialog menu, select a recognizer type from the drop down menu. LUIS is the default recognizer type.
After you select the recognizer type, you can define intent(s) with corresponding utterances in the language understanding editor using the .lu file format. If you are not familiar with language understanding in Composer, please read the language understanding concept article.
After the recognizer is selected and the intents are defined, you can follow the steps to create a Handle an Intent trigger and configure the trigger with pre-defined intents.
On the left side of the Composer menu, click New Trigger and then select Handle an Intent from the drop-down menu. Select the intent you want to handle and click submit.
Under the Handle an Intent trigger node, click the "+" sign to add the action node(s) you want to include. For example, you can click Send Messages and then Send an Activity to send a message authored in LG file format. If you are not familiar with language generation in Composer, please read the language generation concept article.
Handle Unknown Intent defines the actions to take when an intent is not recognized. Unlike Handle an Intent trigger, you do not need to define any intents before defining the Handle Unknown Intent trigger. Please note that an "Unknown Intent" will defer to any specific intent that fires in a parent dialog.
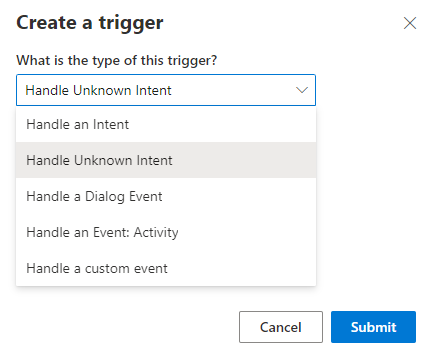
To define a Handle Unknown Intent trigger, follow the steps:
On the left side of the Composer menu, click New Trigger and select Handle Unknown Intent from the drop-down menu. Click submit.
Under the Handle Unknown Intent trigger, click the "+" sign to add the action node(s) you want to include. For example, you can click Send Messages and then Send an Activity to send a message authored in LG file format.
Define the actions to take when a dialog event such as BeginDialog is fired. Most dialogs will include an event handler configured to respond to the BeginDialog event, which fires when the dialog begins and allows the bot to respond immediately. Follow the steps below to define a Handle a Dialog Event trigger and add BeginDialog activity to the trigger.
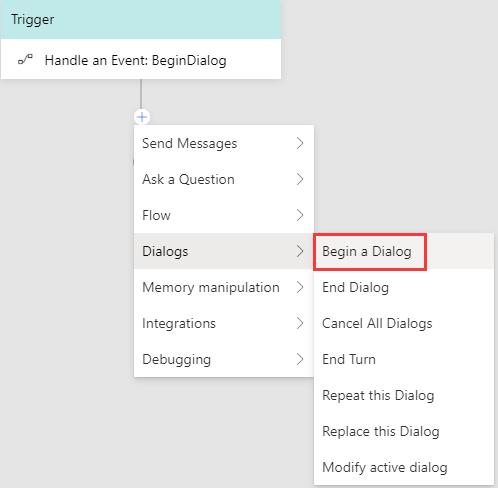
On the left side of the Composer menu, click New Trigger and then select Handle a Dialog Event from the drop-down menu. Select the dialog event you want to handle and click submit. For example, let's choose Handle a Dialog Event: BeginDialog.
Under the Handle a Dialog Event trigger, click the "+" sign to add the action node(s) you want to include. For example, let's select Begin a Dialog activity to begin a dialog.
Configure a dialog to theBegin a Dialog activity.
Handle an Event: Activity is a type of trigger used to handle activity events such as your bot receiving a ConversationUpdate Activity. The following steps show how to define a Handle an Event: Activity trigger to handle a ConversationUpdate activity in a dialog to send a "welcome" message.
On the navigation pane on the left side, select Main dialog. Click New Trigger and select Handle an Event: Activity from the drop-down menu. Select Handle ConversationUpdate activity and then click submit.
In the Handle ConversationUpdate trigger node, click the "+" sign to add the action node you want to include. For example, let's click Send Messages and then Send an Activity to send a welcome message. You can define response messages following the .LG file format in the language generation editor.
Handle a custom event is a type of trigger to handle a custom event such as Emit a custom event action. Bots can emit user-defined events using the "Emit a custom event" action which will trigger this handler. So when you define an Emit a custom event action, you need to define a Handle a custom event trigger to handle the pre-defined event. Here are the steps to define a Handle a Custom Event trigger.
In your bot's authoring canvas, select the trigger you want to define an Emit a custom event action. For example, we select the Handle ConversationUpdate trigger and we want to define a Emit a custom event action after the Send a response action. Click on the "+" sign after the Send a responseaction node, select Access external resources and then click Emit a custom event action.
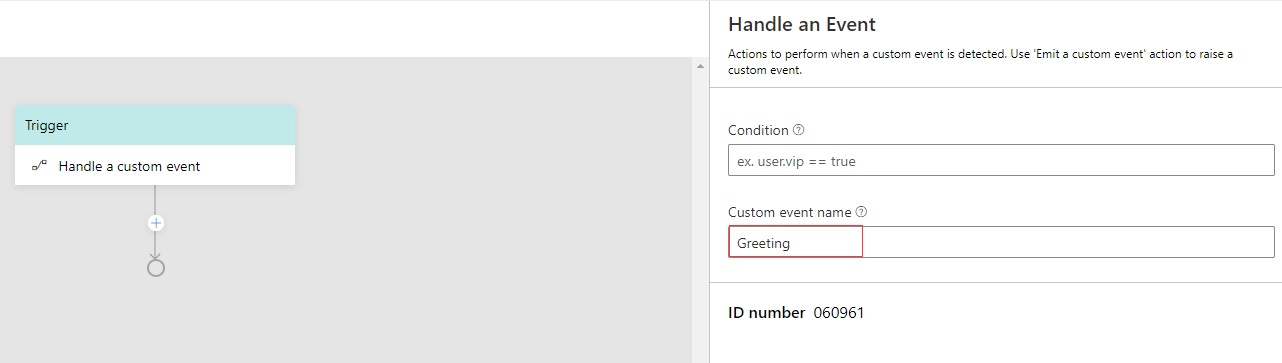
On the property editor on the right side, you may define some properties of this event. Let's give this event a name such as "Greeting", set event values in the Event value section if necessary and check Bubble event. When Bubble eventis checked this event will be passed on to the parent dialogs to look for handlers to handle it.
Now let's create a Handle a Custom Event trigger to handle the Emit a custom event we defined in the previous section. On the navigation pane on the left side, click on New Trigger in the dialog you want to create the trigger and select Handle a custom event from the drop-down menu. Click submit.
Now you have an empty Handle a Custom Event trigger in the authoring canvas. On the property editor on the left, fill in the name of you pre-defined event in the Custom event name section. In this case, we fill in the name "Greeting". Please be noted that the name in the Custom event name section should be exactly the same as the name you created for the pre-defined action.
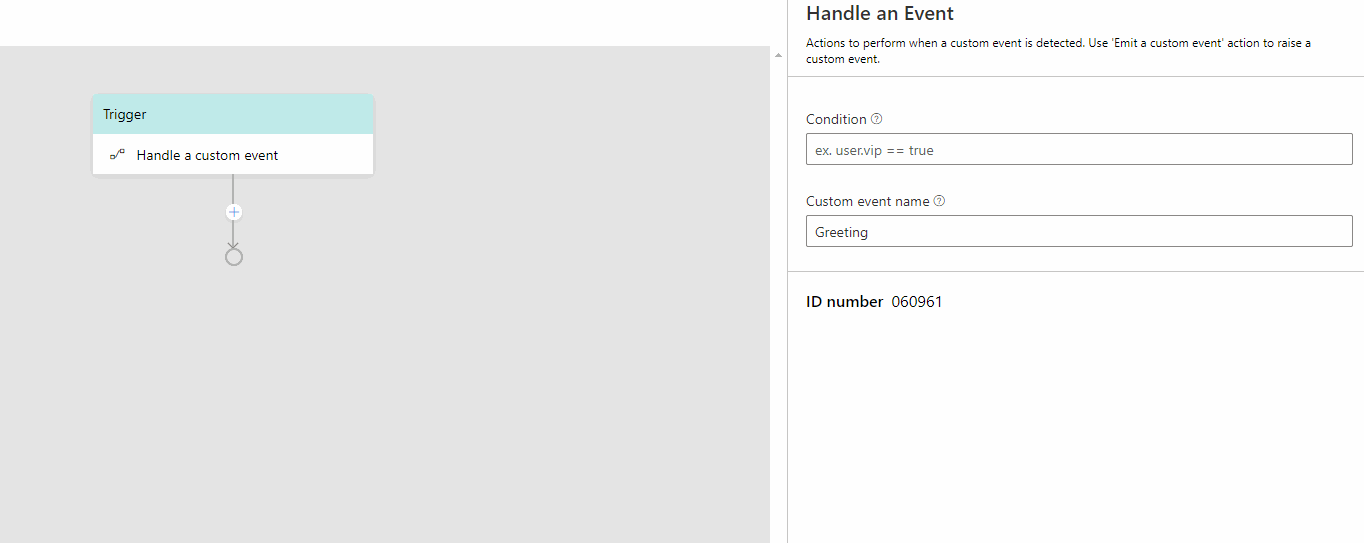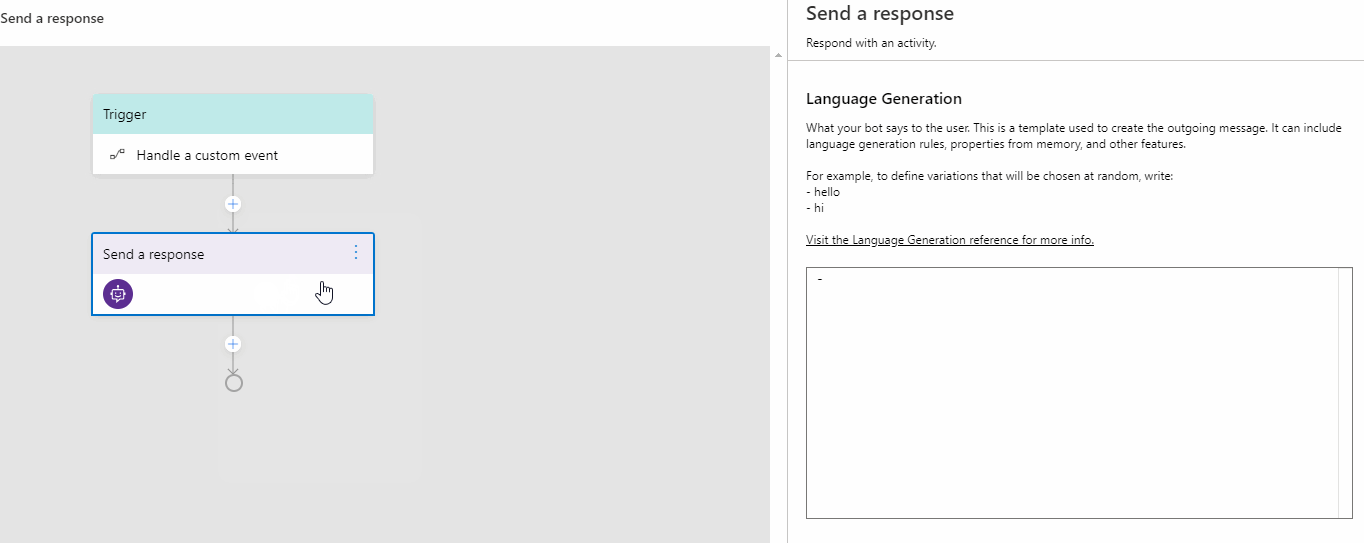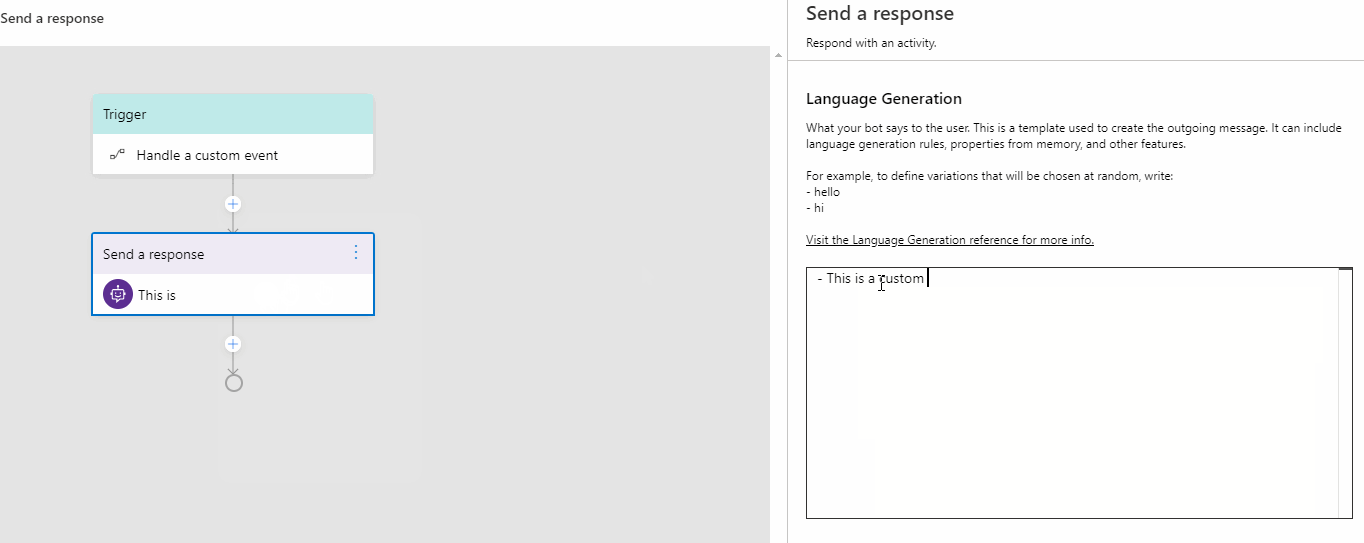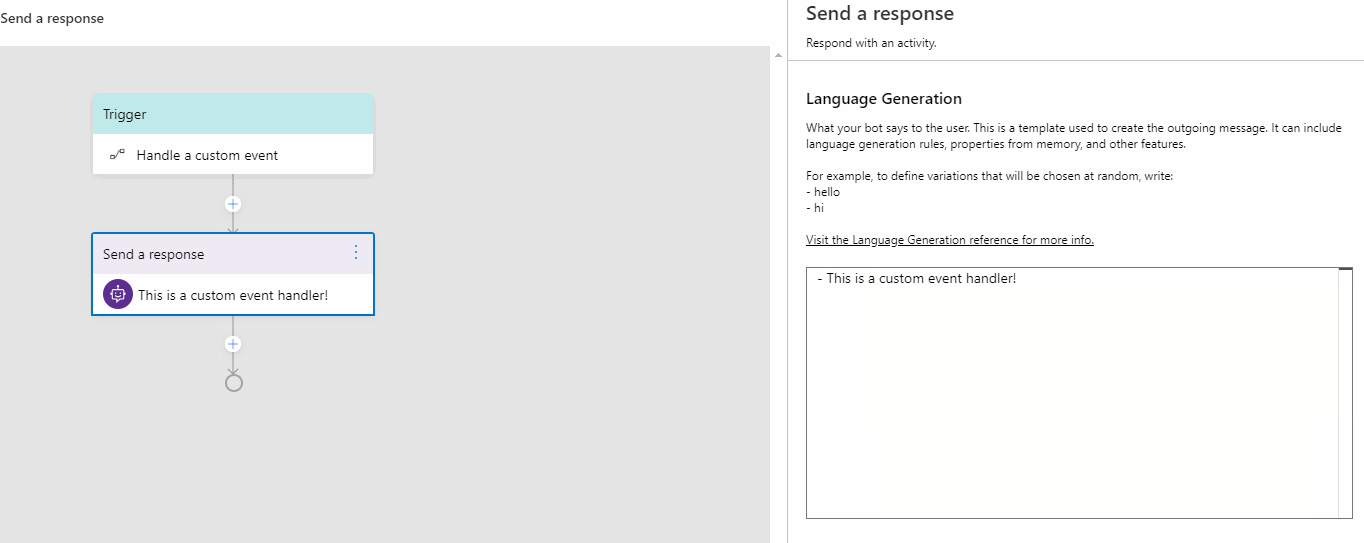
You can add any action to this trigger. Click the "+" sign under Handle a Custom Event and select Send a response action from the actions menu. Author your response for this action in the language generation inline editor as you want.
Now you have completed defining the Handle a Custom Event trigger. When the Emit a custom event is fired, the Handle a Custom Event trigger will be triggered and send the response you defined.