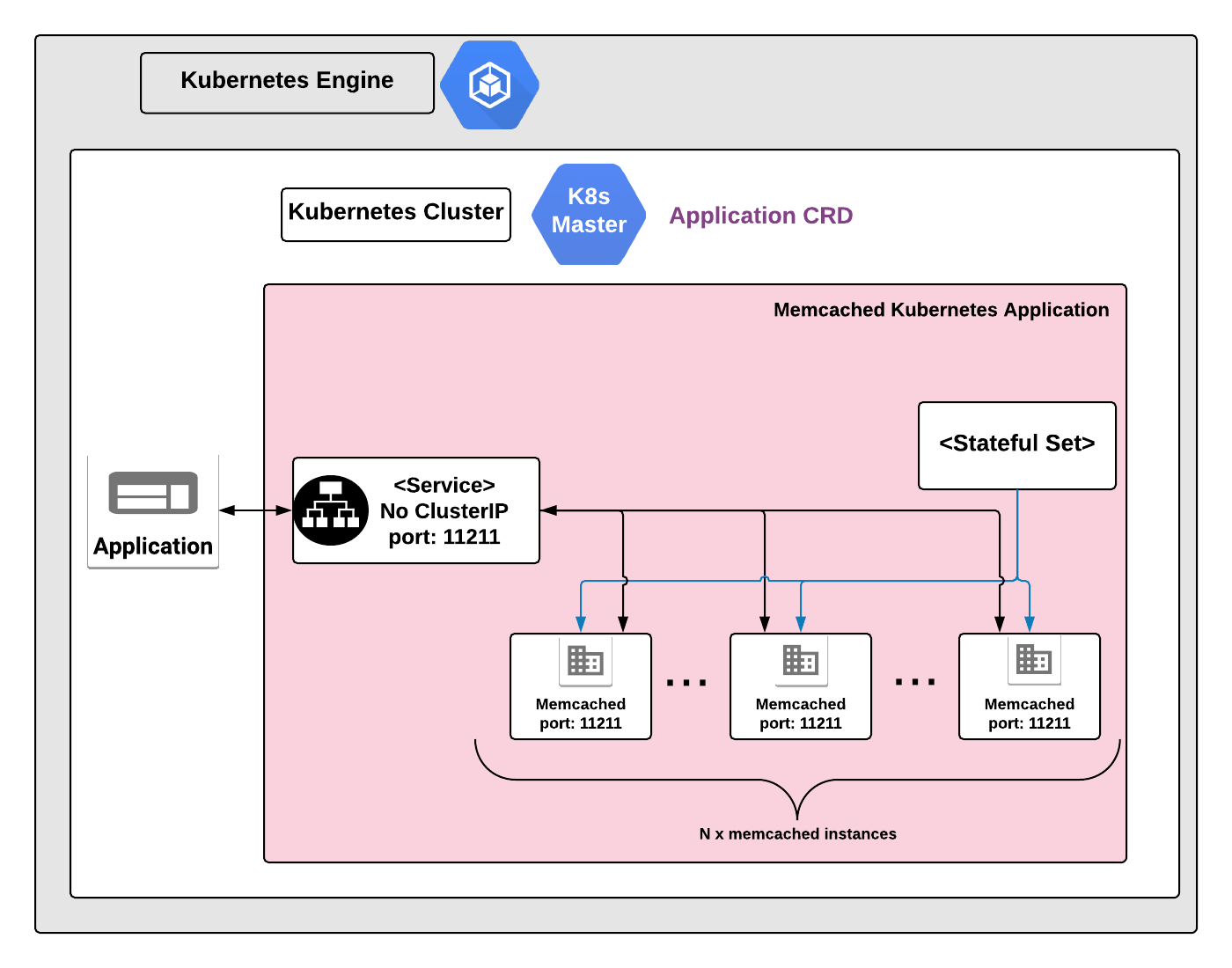
Memcached is an open source in-memory key-value store. The key features of this application include high performance and ease of distribution. While Memcached is intended to be used with dynamic web applications, it can be used as a caching system for a number of databases.
To learn more about Memcached, visit the Memcached website.
Popular open stacks on Kubernetes packaged by Google.
A Kubernetes StatefulSet manages all the Memcached Pods in ths application. Each Pod runs a single instance of Memcached, which listens on the TCP port 11211.
This application is set up as an internal cache, and so is not exposed to external traffic. The Memcached Service also doesn't have a service IP address, to prevent the discovery of the Pod IP addresses. Typically, Memcached clients discover the IP addresses of Memcached on their own, and implement a mechanism to query and distribute their requests to the pool of Memcached instances.
Get up and running with a few clicks! Install this Memcached app to a Google Kubernetes Engine cluster using Google Cloud Marketplace. Follow the on-screen instructions.
You can use Google Cloud Shell or a local workstation to complete the following steps.
You'll need the following tools in your development environment. If you are
using Cloud Shell, gcloud, kubectl, Docker, and Git are installed in your
environment by default.
Configure gcloud as a Docker credential helper:
gcloud auth configure-dockerCreate a new cluster from the command line.
export CLUSTER=memcached-cluster
export ZONE=us-west1-a
gcloud container clusters create "$CLUSTER" --zone "$ZONE"Configure kubectl to connect to the new cluster.
gcloud container clusters get-credentials "$CLUSTER" --zone "$ZONE"Clone this repo and the associated tools repo.
git clone --recursive https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/click-to-deploy.gitAn Application resource is a collection of individual Kubernetes components, such as Services, Deployments, and so on, that you can manage as a group.
To set up your cluster to understand Application resources, run the following command:
kubectl apply -f "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/marketplace-k8s-app-tools/master/crd/app-crd.yaml"You need to run this command once.
The Application resource is defined by the Kubernetes SIG-apps community. The source code can be found on github.com/kubernetes-sigs/application.
Navigate to the memcached directory:
cd click-to-deploy/k8s/memcachedChoose an instance name and namespace for the app. You typically use namespaces if you have many users spread across multiple teams or projects.
export APP_INSTANCE_NAME=memcached-1
export NAMESPACE=defaultSet the number of replicas:
export REPLICAS=3Enable Stackdriver Metrics Exporter:
NOTE: Your GCP project must have Stackdriver enabled. If you are using a non-GCP cluster, you cannot export metrics to Stackdriver.
By default, application does not export metrics to Stackdriver. To enable this
option, change the value to true.
export METRICS_EXPORTER_ENABLED=falseSet up the image tag:
It is advised to use stable image reference which you can find on Marketplace Container Registry. Example:
export TAG="1.5.22-20200311-091944"Alternatively you can use short tag which points to the latest image for selected version.
Warning: this tag is not stable and referenced image might change over time.
export TAG="1.5"Configure the container image:
export IMAGE_MEMCACHED="marketplace.gcr.io/google/memcached"
export IMAGE_METRICS_EXPORTER="marketplace.gcr.io/google/memcached/prometheus-to-sd:${TAG}"If you use a different namespace than default, run the command below to create
a new namespace:
kubectl create namespace "$NAMESPACE"Use helm template to expand the template. We recommend that you save the
expanded manifest file for future updates to the application.
helm template chart/memcached \
--name "$APP_INSTANCE_NAME" \
--namespace "$NAMESPACE" \
--set memcached.replicas="$REPLICAS" \
--set memcached.image.repo="$IMAGE_MEMCACHED" \
--set memcached.image.tag="$TAG" \
--set metrics.image="$IMAGE_METRICS_EXPORTER" \
--set metrics.exporter.enabled="$METRICS_EXPORTER_ENABLED" \
> "${APP_INSTANCE_NAME}_manifest.yaml"Use kubectl to apply the manifest to your Kubernetes cluster:
kubectl apply -f "${APP_INSTANCE_NAME}_manifest.yaml" --namespace "${NAMESPACE}"To get the GCP Console URL for your app, run the following command:
echo "https://console.cloud.google.com/kubernetes/application/${ZONE}/${CLUSTER}/${NAMESPACE}/${APP_INSTANCE_NAME}"To view your app, open the URL in your browser.
To use the app, you follow these high-level steps:
-
Get the external IP address for the Memcached cluster.
-
Configure your application to use the Memcached cluster as a cache. Typically, applications use specialized Memcached clients, such as pymemcache. The clients run a hashing algorithm to select a Memcached server for storing or retrieving cached data.
Your application can get information about Memcached instances using the
kubectl command, or programmatically.
To get the IP addresses of your Memcached instances using kubectl, run the
following command:
kubectl get pods -o wide -l app.kubernetes.io/name=$APP_INSTANCE_NAME --namespace "$NAMESPACE"To get the IP addresses of your Memcached instances from within the Kubernetes cluster (such as from a Memcached Pod) run the following command
nslookup $APP_INSTANCE_NAME-memcached-svc.$NAMESPACE.svc.cluster.localTo get the IP addresses of your Memcached instances using Python, you can use
the kubernetes module.
To install the kubernetes module, run the following command:
pip install kubernetesUse the following sample Python code to get the IP addresses:
import os
# kubernetes module; install with `pip install kubernetes`
from kubernetes import client, config
# Load Kubernetes config
config.load_kube_config()
# Create a Kubernetes client
k8s_client = client.CoreV1Api()
# Get the list of all pods
pod_list = k8s_client.list_namespaced_pod("default")
# list all pods from the default namespace
for pod in pod_list.items:
print("%s\t%s\t%s" % (pod.metadata.name, pod.status.phase, pod.status.pod_ip))For more information on using the kubernetes module, see
https://github.com/kubernetes-client/python
You can use one of many Memcached clients to access your Memcached cluster, such
as pymemcache. For information on pymemcache, see
http://pymemcache.readthedocs.io/en/latest/getting_started.html.
Avoid exposing your Memcached service externally. Applications in the same Kubernetes cluster as the app can access your Memcached instances.
In this specific example, there is no encryption between applications and the Memcached instances, and no authentication/authorization schema is applied.
The application is configured to expose its metrics through Memcached Exporter in the Prometheus format. For more detailed information on setting up the plugin, see the Memcached Exporter documentation.
You can access the metrics at [POD_IP]:9150/metrics, where [POD_IP] is the
IP address read from the Kubernetes headless Service
$APP_INSTANCE_NAME-memcached-prometheus-svc.
Prometheus can be configured to automatically collect the application's metrics. Follow the steps in Configuring Prometheus.
You configure the metrics in the
scrape_configs section.
The deployment includes a
Prometheus to Stackdriver (prometheus-to-sd)
container. If you enabled the option to export metrics to Stackdriver, the
metrics are automatically exported to Stackdriver and visible in
Stackdriver Metrics Explorer.
The name of each metric starts with the application's name, which you define in
the APP_INSTANCE_NAME environment variable.
The exporting option might not be available for GKE on-prem clusters.
Note: Stackdriver has quotas for the number of custom metrics created in a single GCP project. If the quota is met, additional metrics might not show up in the Stackdriver Metrics Explorer.
You can remove existing metric descriptors using Stackdriver's REST API.
You can scale your Memcached service up or down by changing the number of replicas, using the following command:
kubectl scale statefulsets "$APP_INSTANCE_NAME-memcached" \
--namespace "$NAMESPACE" \
--replicas=[NEW_REPLICAS]Where [NEW_REPLICAS] is the new number.
If you want to use an updated image for the Memcached container, use the following steps:
-
In the Memcached StatefulSet, change the image that is used for the Pod template:
kubectl set image statefulset "$APP_INSTANCE_NAME-memcached" \ --namespace "$NAMESPACE" memcached=[NEW_IMAGE_REFERENCE]
where
[NEW_IMAGE_REFERENCE]is the updated image. -
To check the status of Pods in the StatefulSet, and the progress of the new image, run the following command:
kubectl get pods -l app.kubernetes.io/name=$APP_INSTANCE_NAME --namespace "$NAMESPACE"
-
To verify the image used by the Pods, run the following command:
kubectl get pods -l app.kubernetes.io/name=$APP_INSTANCE_NAME --namespace "$NAMESPACE" -o=jsonpath='{range .items[*]}{"\n"}{.metadata.name}{":\t"}{range .spec.containers[*]}{.image}{", "}{end}{end}' | sort
You can delete the Memcached application using the Google Cloud Platform Console, or using the command line.
-
In the GCP Console, open Kubernetes Applications.
-
From the list of applications, click Memcached.
-
On the Application Details page, click Delete.
-
Navigate to the
memcacheddirectory.cd click-to-deploy/k8s/memcached -
Expand the manifest template
Use
helm templateto expand the template.helm template chart/memcached \ --name "$APP_INSTANCE_NAME" \ --namespace "$NAMESPACE" \ --set memcached.replicas="$REPLICAS" \ --set memcached.image.repo="$IMAGE_MEMCACHED" \ --set memcached.image.tag="$TAG" \ --set metrics.image="$IMAGE_METRICS_EXPORTER" \ --set metrics.exporter.enabled="$METRICS_EXPORTER_ENABLED" \ > "${APP_INSTANCE_NAME}_manifest.yaml"
-
Run the
deletecommandkubectl delete -f ${APP_INSTANCE_NAME}_manifest.yaml --namespace $NAMESPACE
Optionally, if you don't need the deployed application or the GKE cluster, delete the cluster using this command:
gcloud container clusters delete "$CLUSTER" --zone "$ZONE"