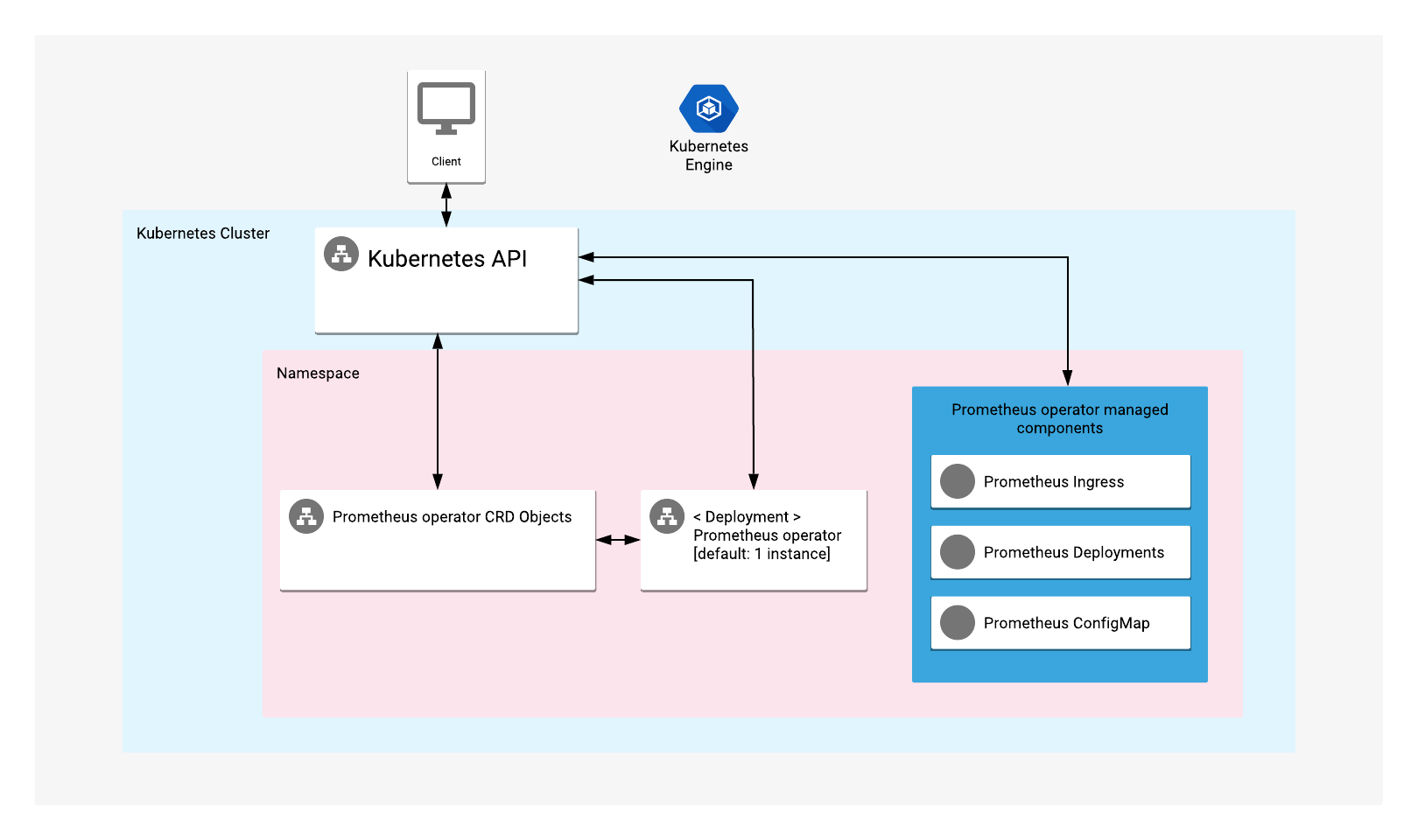
Prometheus Operator is a management tool for installing and operating instances of Prometheus, a monitoring and alerting toolkit.
For more information, visit the Prometheus official website.
Popular open stacks on Kubernetes, packaged by Google.
The app offers a Prometheus Operator deployment on a Kubernetes cluster.
Get up and running with a few clicks! Install this Prometheus operator app to a Google Kubernetes Engine cluster using Google Cloud Marketplace. Follow the on-screen instructions.
You'll need the following tools in your development environment. If you are
using Cloud Shell, then gcloud, kubectl, Docker, and Git are installed in your
environment by default.
Configure gcloud as a Docker credential helper:
gcloud auth configure-dockerCreate a new cluster from the command-line:
export CLUSTER=prometheus-operator-cluster
export ZONE=us-west1-a
gcloud container clusters create "${CLUSTER}" --zone "${ZONE}"Configure kubectl to connect to the new cluster.
gcloud container clusters get-credentials "${CLUSTER}" --zone "${ZONE}"Clone this repo and its associated tools repo:
git clone --recursive https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/click-to-deploy.gitAn Application resource is a collection of individual Kubernetes components, such as Services, Deployments, and so on, that you can manage as a group.
To set up your cluster to understand Application resources, run the following command:
kubectl apply -f "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/marketplace-k8s-app-tools/master/crd/app-crd.yaml"You need to run this command once.
The Application resource is defined by the Kubernetes SIG-apps community. The source code can be found on github.com/kubernetes-sigs/application.
Navigate to the prometheus-operator directory:
cd click-to-deploy/k8s/prometheus-operatorChoose an instance name and
namespace
for the app. In most cases, you can use the default namespace.
export APP_INSTANCE_NAME=prometheus-operator-1
export NAMESPACE=defaultSet up the image tag:
It is advised to use stable image reference which you can find on Marketplace Container Registry. Example:
export TAG="0.34.0-20200213-133013"Alternatively you can use short tag which points to the latest image for selected version.
Warning: this tag is not stable and referenced image might change over time.
export TAG="0.34"Configure the container image:
export IMAGE_OPERATOR="marketplace.gcr.io/google/prometheus-operator"If you plan to use a different namespace than the default, run the command below to create a new namespace:
kubectl create namespace "${NAMESPACE}"Define the environment variables:
export OPERATOR_SERVICE_ACCOUNT="${APP_INSTANCE_NAME}-prometheus-operator"Expand the manifest to create Service Accounts:
cat resources/service-accounts.yaml \
| envsubst '${APP_INSTANCE_NAME} \
${NAMESPACE} \
${OPERATOR_SERVICE_ACCOUNT}' \
> "${APP_INSTANCE_NAME}_sa_manifest.yaml"Create the accounts on the cluster with kubectl:
kubectl apply -f "${APP_INSTANCE_NAME}_sa_manifest.yaml" \
--namespace "${NAMESPACE}"Use helm template to expand the template. We recommend that you save the
expanded manifest file for future updates to the app.
helm template chart/prometheus-operator \
--name "${APP_INSTANCE_NAME}" \
--namespace "${NAMESPACE}" \
--set operator.image.repo="${IMAGE_OPERATOR}" \
--set operator.image.tag="${TAG}" \
--set deployerHelm.image="gcr.io/cloud-marketplace-tools/k8s/deployer_helm:0.8.0" \
--set operator.serviceAccountName="${OPERATOR_SERVICE_ACCOUNT}" \
> "${APP_INSTANCE_NAME}_manifest.yaml"Use kubectl to apply the manifest to your Kubernetes cluster:
kubectl apply -f "${APP_INSTANCE_NAME}_manifest.yaml" --namespace "${NAMESPACE}"To get the Cloud Console URL for your app, run the following command:
echo "https://console.cloud.google.com/kubernetes/application/${ZONE}/${CLUSTER}/${NAMESPACE}/${APP_INSTANCE_NAME}"To view the app, open the URL in your browser.
Clone this repo:
git clone --recursive https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/click-to-deploy.gitNavigate to the prometheus-operator directory:
cd click-to-deploy/k8s/prometheus-operator/resources/sampleRun the following command to deploy a Prometheus instance:
kubectl apply --namespace "${NAMESPACE}" -f \
01-prometheus-cluster-role.yaml,\
02-prometheus-service-account.yaml,\
03-prometheus-cluster-role-binding.yaml,\
04-kubelet-service-monitor.yaml,\
05-prometheus.yamlYou can find additional configuration options in the official Prometheus documentation.
The Prometheus query interface will be available at http://localhost:9090/.
Run the following command to start port forwarding:
kubectl --namespace "${NAMESPACE}" port-forward \
service/prometheus-operated 9090:9090Scaling is not supported for Prometheus Operator.
To back up Prometheus resources, use the following command:
export NAMESPACE=default
kubectl --namespace "${NAMESPACE}" get crd \
prometheuses.monitoring.coreos.com \
servicemonitors.monitoring.coreos.com \
podmonitors.monitoring.coreos.com \
alertmanagers.monitoring.coreos.com \
prometheusrules.monitoring.coreos.com \
--output=yaml > backup_file.yamlkubectl --namespace "${NAMESPACE}" apply -f backup_file.yamlThe Prometheus Operator deployment is configured to roll out updates automatically. To start an update, patch the deployment with a new image reference:
kubectl set image deployment ${APP_INSTANCE_NAME}-prometheus-operator --namespace ${NAMESPACE} \
"prometheus-operator=[NEW_OPERATOR_IMAGE_REFERENCE]"where [NEW_OPERATOR_IMAGE_REFERENCE] is the Docker image reference
of the new image that you want to use.
To check the status of Pods in the StatefulSet, and the progress of the new image, run the following command:
kubectl get pods --selector app.kubernetes.io/name=${APP_INSTANCE_NAME} \
--namespace ${NAMESPACE}-
In the Cloud Console, open Kubernetes Applications.
-
From the list of apps, click Prometheus.
-
On the Application Details page, click Delete.
Set your installation name and Kubernetes namespace:
export APP_INSTANCE_NAME=prometheus-operator-1
export NAMESPACE=defaultNOTE: We recommend that you use a kubectl version that is the same as the version of your cluster. Using the same versions of kubectl and the cluster helps to avoid unforeseen issues.
To delete the resources, use the expanded manifest file used for the installation.
Run kubectl on the expanded manifest file:
kubectl delete -f ${APP_INSTANCE_NAME}_manifest.yaml --namespace ${NAMESPACE}Otherwise, delete the resources by using types and a label:
kubectl delete application \
--namespace ${NAMESPACE} \
--selector app.kubernetes.io/name=${APP_INSTANCE_NAME}NOTE: This will only delete the
prometheus-operatorapp. Allprometheus-operator-managed resources will remain available.
Optionally, if you don't need the deployed app or the GKE cluster, use this command to delete the cluster:
gcloud container clusters delete "${CLUSTER}" --zone "${ZONE}"