A Circular Doubly Linked List is a linked data structure that consists of a set of sequentially linked records called nodes. Each node is connected to the next node and previous node via two link fields which refences the next node in sequence and previous node in sequence. Each node consists of a data/key.
This data structure is so called as it combines the features of both a circular linked list and a doubly linked list. As per doubly linked list characteristics - it consists of the previous node pointer that points to the previous node in the sequence. And similar to a circular linked list - the last node in the list points to the first node by next pointer and the first node points to the last node by the previous pointer.
Node traversal from any direction is possible and also jumping from head to last node or from last node to head is only one operation: head pointer previous is last node and the last node next pointer is head.
Hence in a Circular Doubly Linked List all nodes are connected to form a circle. There is no NULL at the end.
The head or starter pointer points to the beginning of the Circular Doubly Linked List.
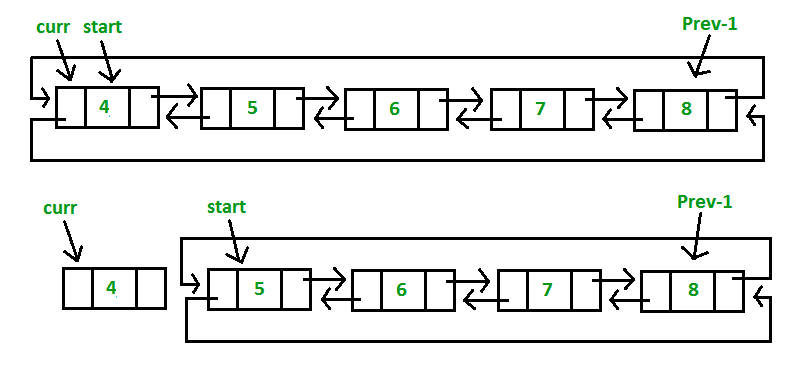
An example of a Circular Doubly Linked List:
In a prepend operation - a node is added to the beginning of the Circular Doubly Linked List. The newly added node becomes the head of the Circular Doubly Linked List. If the list is not an empty list - the appropriate next and previous pointers for the head, last node and the newly inserted node are updated. In an empty list - next, previous and head all point to the new node. The last node in the list is easily obtained using the previous pointer of the head or starter pointer.
In an append operation - a node is added to the end of the Circular Doubly Linked List. This new node after insertion points to the beginning of the Circular Doubly Linked List or the head. If the list is not an empty list - the appropriate next and previous pointers for the head, last node and the newly inserted node are updated. In an empty list - next, previous and head all point to the new node. The last node in the list is easily obtained using the previous pointer of the head or starter pointer.
If the Circular Doubly Linked List is empty - a node can be added via an append or prepend operation to create a new Circular Doubly Linked List with a single item.
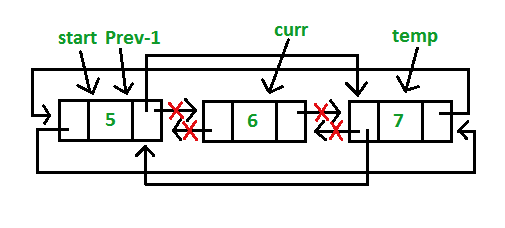
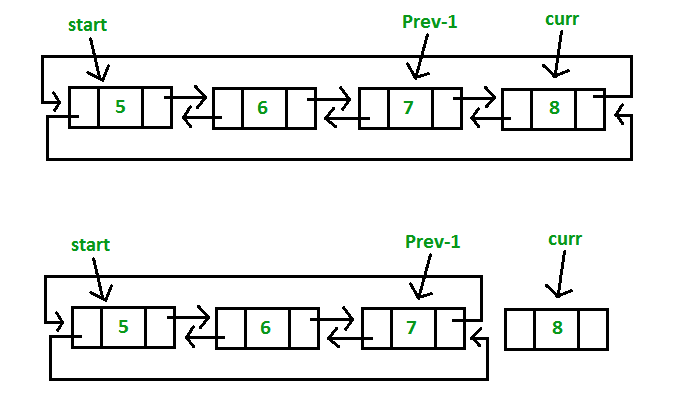
If the node after which the new key is to be inserted is the last node then an append operation is performed. If the node before which the new key is to be inserted is the first node then a prepend operation is performed.
Otherwise we the traverse the list and the new node is added after (or before) the given node. The previous and next pointers are updated appropriately.
The current node is set to NULL / None and no Circular Doubly Linked List remains.