This document explains basic usage of Swift for TensorFlow, including:
- How to run the Swift REPL
- How to use the Swift interpreter and compiler
- How to use Swift for TensorFlow with Xcode (Mac only)
You must have a working toolchain for Swift for TensorFlow (swift, swiftc, etc) before proceeding with these instructions. If not, please install Swift for TensorFlow or build from source before proceeding.
To see example models written using Swift for TensorFlow, go to tensorflow/swift-models.
Note: Swift for TensorFlow is an early stage research project. It has been released to enable open source development and is not yet ready for general use by machine learning developers.
An easy way to experiment with Swift is the Read Eval Print Loop, or REPL. To try it, open your terminal application and run the following:
- Mac:
swift - Ubuntu:
swift -I/<path-to-toolchain>/usr/lib/swift/clang/include- This is a necessary workaround for SR-5524, a bug causing modulemap imports to fail in the REPL.
You should see a prompt, similar to the following:
Welcome to Swift version 4.2-dev (LLVM 04bdb56f3d, Clang b44dbbdf44). Type :help for assistance.
1>
You can type Swift statements and the REPL will execute them immediately. Results are formatted nicely:
1> import TensorFlow
2> var x = Tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
x: TensorFlow.Tensor<Double> = [[1.0, 2.0], [3.0, 4.0]]
3> x + x
$R0: TensorFlow.Tensor<Double> = [[2.0, 4.0], [6.0, 8.0]]
4> for _ in 0..<3 {
5. x += x
6. }
7> x
$R1: TensorFlow.Tensor<Double> = [[8.0, 16.0], [24.0, 32.0]]
8> x[0] + x[1]
$R2: TensorFlow.Tensor<Double> = [32.0, 48.0]
With the Swift interpreter, you can use Swift like a scripting language. Create a file called inference.swift with your favorite text editor and paste the following:
import TensorFlow
struct MLPClassifier {
var w1 = Tensor<Float>(shape: [2, 4], repeating: 0.1)
var w2 = Tensor<Float>(shape: [4, 1], scalars: [0.4, -0.5, -0.5, 0.4])
var b1 = Tensor<Float>([0.2, -0.3, -0.3, 0.2])
var b2 = Tensor<Float>([[0.4]])
func prediction(for x: Tensor<Float>) -> Tensor<Float> {
// The ⊗ operator performs matrix multiplication.
let o1 = tanh(x ⊗ w1 + b1)
return tanh(o1 ⊗ w2 + b2)
}
}
let input = Tensor<Float>([[0.2, 0.8]])
let classifier = MLPClassifier()
let prediction = classifier.prediction(for: input)
print(prediction)Save inference.swift and navigate to its containing directory in the terminal. Then, run swift -O inference.swift. You should see something like:
$ swift -O inference.swift
[[0.680704]]
Note: the -O flag enables Swift to run with optimizations. This is currently required for some programs that use the TensorFlow module to run properly. This will become unnecessary when the compiler implementation is completed.
The Swift interpreter ran your program and printed the classifier's prediction, as expected.
Extra: If your operating system supports multi-argument shebang lines, you can turn inference.swift into a directly-invokable script by adding the following line at the top of inference.swift:
- Mac:
#!/usr/bin/env swift -O - Ubuntu 16.04:
#!swift -O
Next, add executable permissions to inference.swift:
chmod +x inference.swift
You can now run inference.swift using ./inference.swift:
$ ./inference.swift
[[0.680704]]
If you get an error from running ./inference.swift directly but not from swift -O inference.swift, it’s likely because your operating system doesn’t support multi-argument shebang lines.
With the Swift compiler, you can compile Swift programs into executable binaries. To try it, run the following:
- Ubuntu:
swiftc inference.swift - Mac:
swiftc -O -sdk `xcrun --show-sdk-path` inference.swift
swiftc should produce an executable in the current directory called inference. Run it to see the same result:
$ ./inference
[[0.680704]]
This was a simple demonstration of Swift for TensorFlow. To see example models written using Swift for TensorFlow, go to tensorflow/swift-models.
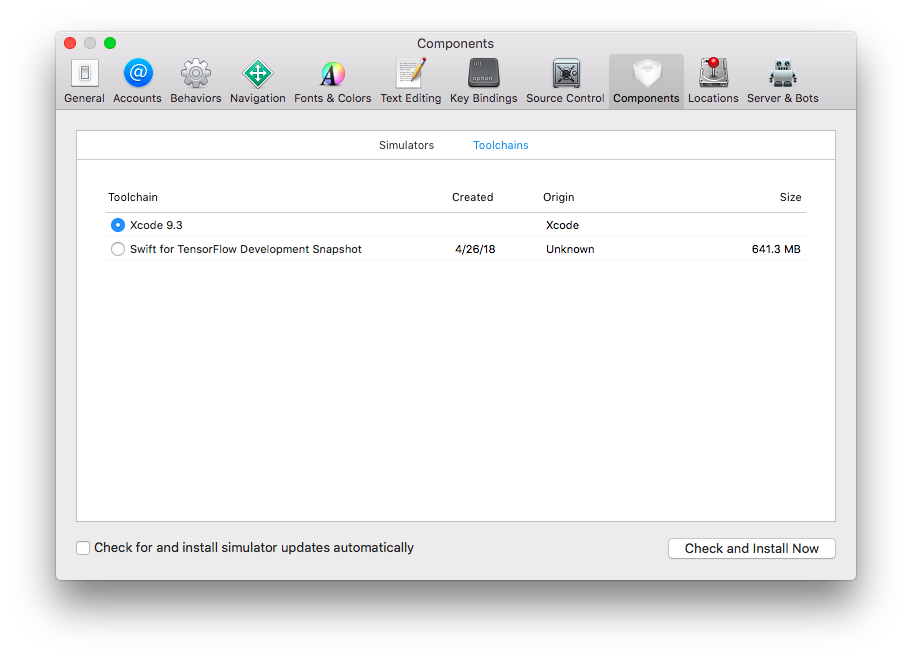
To use Swift for TensorFlow with Xcode, you must have installed a toolchain from this page.
- Open Xcode’s
Preferences, navigate toComponents > Toolchains, and select the installed Swift for TensorFlow toolchain. The name of the toolchain should start with "Swift for TensorFlow Development Snapshot".
-
In the menu bar, select
File > New > Playground.... -
Then, select
macOSandBlankand hitNext. -
Choose a location for the Playground file and hit
Create. Xcode should open your new Playground. -
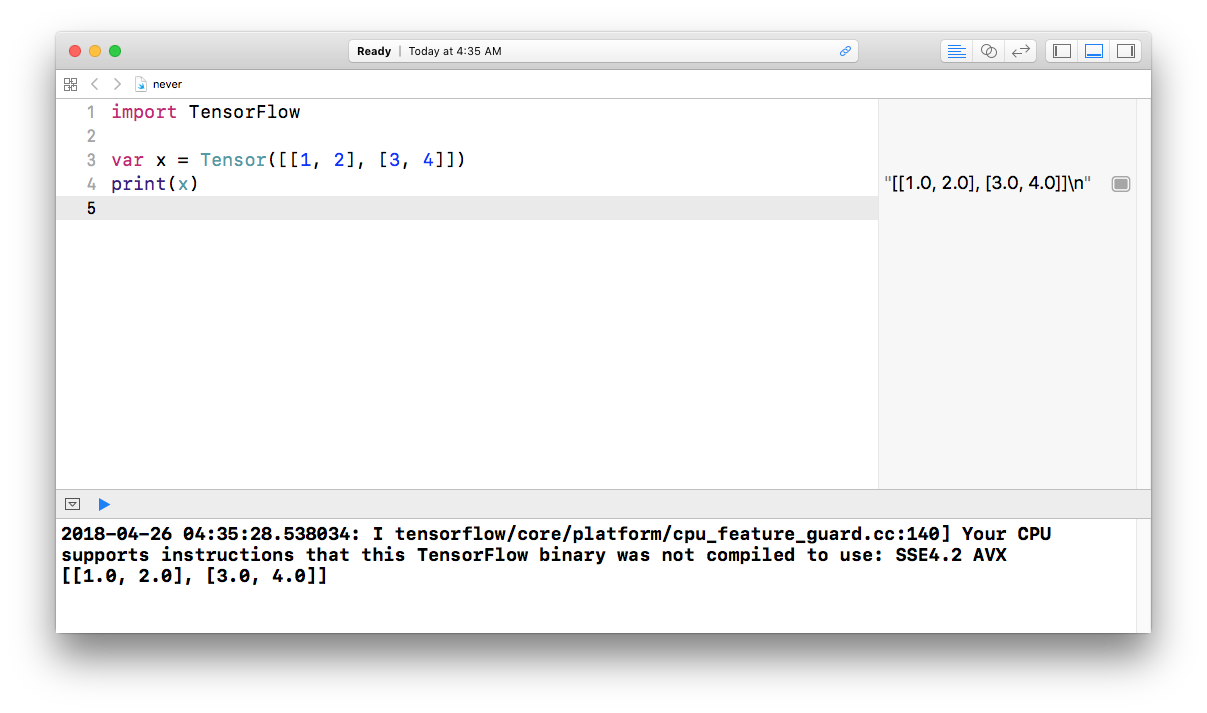
In the Playground, let’s try importing TensorFlow! Paste the following code:
import TensorFlow
let x = Tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
print(x)- After a moment, the Playground should finish running and print the result in the display at the bottom.
Note: Xcode Playgrounds are a great interactive environment for prototyping code, but they often hang or crash. If that happens, try restarting Xcode. There are some documented bugs regarding Swift for TensorFlow and Playgrounds. If you discover a new bug, please file an issue.