There are two cases to use multi-heap.
- continuous physical RAM but want to split regions
- separated physical RAMs but want to use for heap
To enable multi-heap, please find three steps as shown below:
In menuconfig, Set CONFIG_MM_REGIONS value which shows how many regions are.
Memory Management -> Number of memory regions -> change a number over 2
In menuconfig, Set CONFIG_MM_NHEAPS value which indicates how many heaps are.
Memory Management -> Number of heaps -> change a number over 2
For a detailed description of REGION and HEAP, please refer to Terms for REGION and HEAP
In menuconfig, set start addresses, CONFIG_RAM_REGIONx_START with hexa values, set sizes, CONFIG_RAM_REGIONx_SIZE with decimal values(in bytes) of new heap, and set indexes, CONFIG_RAM_REGIONx_HEAP_INDEX with decimal values of new heap. CONFIG_RAM_REGIONx_HEAP_INDEX can be start from 0.
Hardware Configuration -> Chip Selection -> List of start address for RAM region -> set values
Hardware Configuration -> Chip Selection -> List of size for RAM region -> set values
Hardware Configuration -> Chip Selection -> List of heap index for RAM region -> set values
Each region is separated by ',' and all config should be in " " as shown below example:
"0x02000000,0x04000000,0x07000000"
"100,400,200"
"0,1,0"
Based on above configurations, up_addregion() function sets new regions automatically.
To use multi-heap, please find a link as shown below:
Supported APIs
If there are three physical RAMs, and want to use them as four heaps like below.

In this case, CONFIG_MM_REGIONS should be set to 6, and CONFIG_MM_NHEAPS should be set to 4.
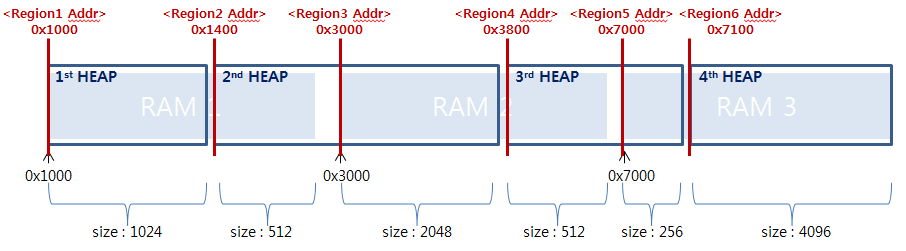
CONFIG_MM_REGIONS=6
CONFIG_MM_NHEAPS=4
CONFIG_RAM_REGIONx_START="0x1000,0x1400,0x3000,0x3800,0x7000,0x7100"
CONFIG_RAM_REGIONx_SIZE="1024,512,2048,512,256,4096"
CONFIG_RAM_REGIONx_HEAP_INDEX="0,1,1,2,2,3"
A header file mm.h provides following APIs which support to allocate memory for a specific heap as shown below:
void *malloc_at(int heap_index, size_t size);
void *calloc_at(int heap_index, size_t n, size_t elem_size);
void *memalign_at(int heap_index, size_t alignment, size_t size);
void *realloc_at(int heap_index, void *oldmem, size_t size);
void *zalloc_at(int heap_index, size_t size);
The difference between Xalloc and Xalloc_at is like below :
Xalloc_at tries to allocate memory for a specific heap which passed by api argument. If there is no enough space to allocate, it will return NULL.
Xalloc tries to allocate memory for base heap which heap index is 0. If there is no enough space to allocate, it will try to allocate in order from the next index for whole heaps.