- Download and install Kublr Control Plane documentation
- Create new Kubernetes cluster using Kublr Control Plane.
When the cluster is up and running,
- Download the kubeconfig file.
- Set the
KUBECONFIGenvironment variableexport KUBECONFIG=$(pwd)/kubeconfig.
The Kublr Demo/Installer is a simple and convenient demo version of Kublr running in Docker that allows you deploy Kubernetes clusters. You can also install a non-production licensed version of the full Kublr Platform from the Kublr Demo/Installer.
By downloading and using the Kublr Demo/Installer and Kublr, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
Linux:
sudo docker run --name kublr -d --restart=unless-stopped -p 9080:9080 kublr/kublr:1.21.2
Windows:
docker run --name kublr -d --restart=unless-stopped -p 9080:9080 kublr/kublr:1.21.2
The Kublr Demo/Installer is a lightweight platform that allows you to run a demo or limited functionality, dockerized Kublr version. You can use it to:
- Manage a standalone Kubernetes cluster;
- Manage the full feature Kublr Platform;
The Kublr Demo/Installer stores all data about the clusters inside the Docker container. Therefore, if you delete the Docker container, you will lose all cluster and Kublr platform related data — though you won't lose the cluster and platform itself. The Kublr team recommends using the Kublr Demo/Installer to verify that a Kubernetes cluster can be created in your environment. So, test it before deploying a full and more permanent Kublr Platform in the cloud or on-premise.
- Download and install Docker
- 64-bit operating system to run the Kublr Demo/Installer
- To deploy a Kubernetes cluster or the full Kublr Platform, you’ll need an AWS, Azure, GCP account or an on-premise environment.
Open a terminal and launch following command:
sudo docker run --name kublr -d --restart=unless-stopped -p HOST_PORT:9080 -e KUBLR_HOST=HOST_IP:HOST_PORT kublr/kublr:1.21.2
Note Hereinafter, "sudo" is Linux specific - omit it to get command for Windows.
- HOST_PORT is a port available both on you workstation for the browser and available outside, from the network;
Here's a Kublr Demo/Installer launch command example:
sudo docker run --name kublr -d --restart=unless-stopped -p 9080:9080 kublr/kublr:1.21.2
The Kublr UI will be available on https://localhost:9080 (admin/kublrbox)
Note There can be a different address depending on your environment. Read carefully for the Kublr in Docker start notification text, as it may contain information about the access adress.
If you are going to set up a bare metal cluster on the Kublr platform, please add this additional parameter KUBLR_HOST, where the HOST_IP is available for cluster nodes:
sudo docker run --name kublr -d --restart=unless-stopped -p HOST_PORT:9080 -e KUBLR_HOST=HOST_IP:HOST_PORT kublr/kublr:1.21.2
If you have already started the Kublr Demo/Installer without the option KUBLR_HOST or your IP address has been changed (for example to switch networks), please use this command to correct the KUBLR_HOST:
docker exec -i kublr /bin/bash -c 'echo "KUBLR_HOST=HOST_IP:HOST_PORT" > /ip.external'; docker restart kublr
In order to run the Kublr Demo/Installer in an air-gapped environment, please request the launch command via [email](mailto:[email protected]?subject=AirGap Kublr Demo/Installer running command request) or use this contact us form.
By default, the Kublr UI, Keycloak UI, and API will be available on the exposed port 9080. After downloading the Docker image, it will take less than a minute for Kublr to start and be viewable.
- The Kublr UI is available on HTTP: https://localhost:9080, use admin/kublrbox for login to Kublr UI;
- Keycloak is available on HTTP: https://localhost:9080/auth, use admin/admin to manage Keycloack;
If you use KUBLR_HOST to define the public IP address and public port number of the host running Kublr (e.g. 192.168.99.234:9981), run this command:
sudo docker run --name kublr -d --restart=unless-stopped -p HOST_PORT:9080 -e KUBLR_HOST=HOST_IP:HOST_PORT kublr/kublr:1.21.2
Navigate to the following URLs:
- https://HOST_IP:HOST_PORT - Kublr UI (admin/kublrbox);
- https://HOST_IP:HOST_PORT/auth - Keycloack (admin/admin);
On first logon into Kublr, you will be prompted to complete your profile. Set your first and last names and valid business email address.
The "valid business email address" means that your email at most public domains (like "[email protected]", "...@ÿahoo.com" etc.) will not be accepted - instead you should use your organization or other private domain.
For instructions on deploying cluster on other supported cloud platforms or baremetal, see Documentation.
- Log into Kublr using your credentials.
- On the left menu, click Credentials.
- Click Add Credentials.
- Set Credentials Type to "AWS Credentials".
- Enter Credentials Name.
- Enter Access Key from AWS Management Console / IAM (see above).
- Enter Secret Key from AWS Management Console / IAM (see above).
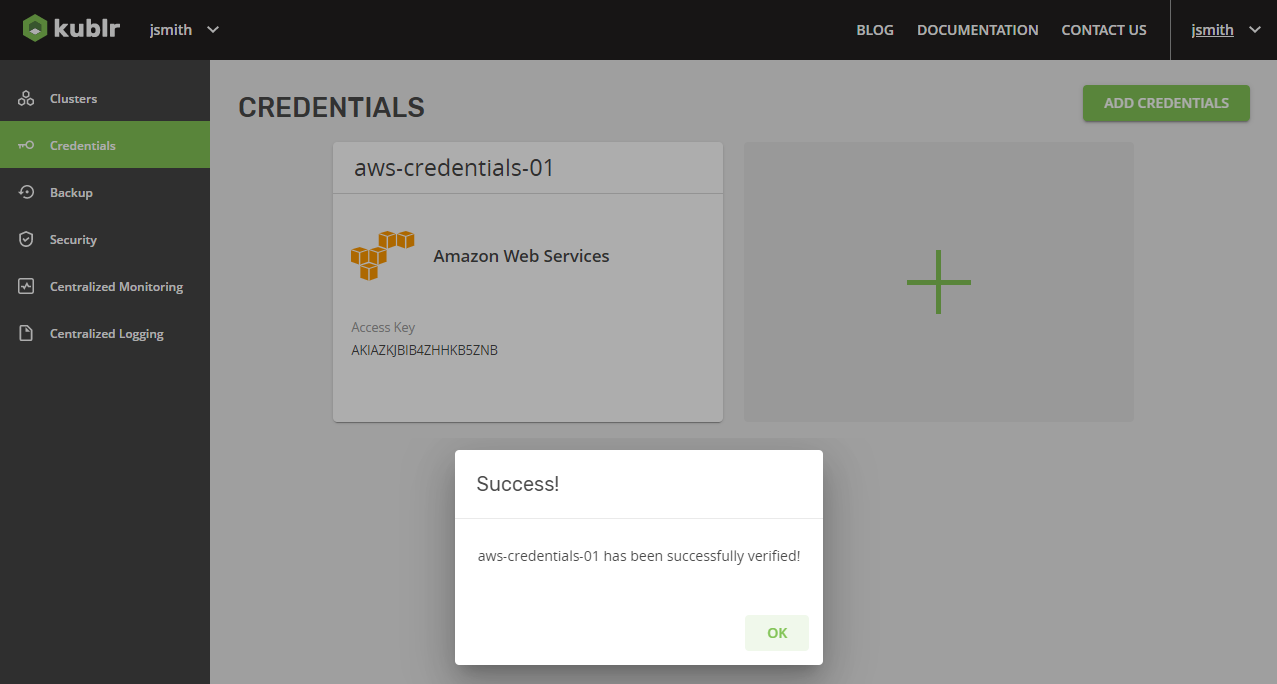
- Click Save Credentials. The "Credentials have been successfully created" popup will be displayed.
- To verify if credentials are valid and ready to be used, mouse over the created credentials and click the displayed Test button.
Verification success popup will be displayed.
- Click Ok.
Powered by Kublr, Vanilla Kubernetes Cluster does not include any advanced Kublr features, but is suitable for running workloads.
To add a new cluster:
-
On the left menu, click Clusters.
-
Click Add Cluster.
The Select Intallation Type dialog is displayed.
-
In the Select Intallation Type dialog, click Cluster.
-
In the ADD CLUSTER dialog, set Provider to "Amazon Web Services".
-
From the Credentials list, select previosly created AWS credentials.
-
Specify Cluster Name.
-
Set:
-
Scroll to the
Master Configurationsection. -
Specify the parameters of the master node(s) of your cluster as described below.
-
Select Instance Type from the list.
-
From the Masters list, select the number of master or management nodes in correspondence with the selected Instance Type.
-
From the Operating System list, select the host OS for virtual machines in the cluster.
-
Optionally, select Public SSH Key from the list.
-
Scroll to the
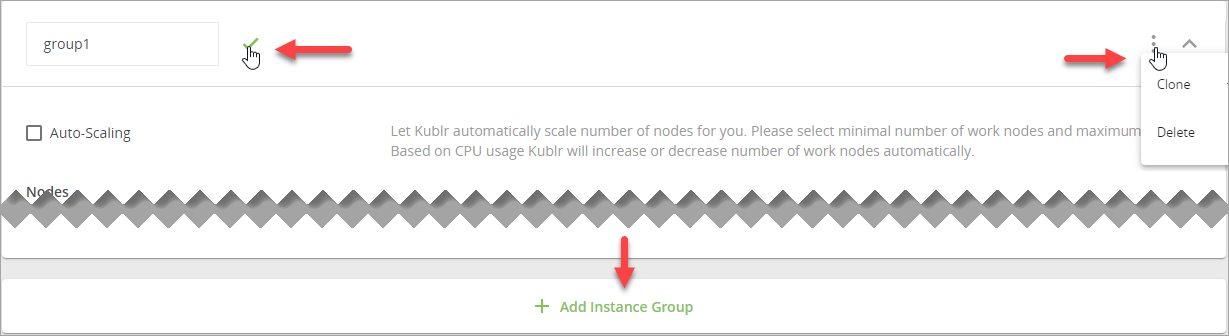
Instance Groupsection (default namegroup1). -
Specify the parameters of the work node(s) in your group as described below.
-
Select Instance Type from the list.
-
To select the number of work nodes in a group, do one of the following:
- In the Nodes field, set the number of work nodes.
- Select the Auto-Scaling option, and then set the Min Nodes and Max Nodes limitations.
-
From the Operating System list, select the host OS for virtual machines in the cluster.
-
If necessary, set your own name for the instance group.
Note You can also clone or delete the current instance group, or add another one.
-
Optionally, scroll to the
Featuressection. -
If necessary, add features to your cluster, specifying parameters under:
-
Customize the cluster spec. Press Customize Specification link. Editor dialog with full cluster spec in YAML format opens
- Navigate to .spec.master section.
- Find existing or add new subsection KublrAgentConfig
- Add a following YAML code:
kublrAgentConfig:
kublr:
kube_api_server_flag:
service_account_issuer: '--service-account-issuer=https://kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local'
-
At the bottom of the editor dialog, click Validate and Install.
A notification is displayed "Your cluster is being created. It might take a few minutes.".
-
In the notification window, click OK.
Your new cluster page is displayed on the Events tab showing the cluster creation progress.
After the cluster becomes ready, use Download Kube Config File link on Overview tab. This will download admin kubeconfig file which you can supply to sonobuoy, kubectl, helm and other tools to test and manage your cluster.
Download a sonobuoy binary release of the CLI, or build it yourself by running:
$ go get -u -v github.com/heptio/sonobuoy
$ sonobuoy run --mode=certified-conformanceThen the status commands $ sonobuoy status indicate that the execution is completed, you can download the results.
$ outfile=$(sonobuoy retrieve)untar the tarball, then add plugins/e2e/results/{e2e.log,junit_01.xml}
$ mkdir ./results; tar xzf $outfile -C ./results