The tokenfactory module allows any account to create a new token with
the name factory/{creator address}/{subdenom}. Because tokens are
namespaced by creator address, this allows token minting to be
permissionless, due to not needing to resolve name collisions. A single
account can create multiple denoms, by providing a unique subdenom for each
created denom. Once a denom is created, the original creator is given
"admin" privileges over the asset. This allows them to:
- Mint their denom to any account
- Burn their denom from any account
- Create a transfer of their denom between any two accounts
- Change the admin. In the future, more admin capabilities may be added. Admins
can choose to share admin privileges with other accounts using the authz
module. The
ChangeAdminfunctionality, allows changing the master admin account, or even setting it to"", meaning no account has admin privileges of the asset.
In our fork of cosmos-sdk, we have added two hooks: TrackBeforeSend and BlockBeforeSend.
The APIs for TrackBeforeSend and BlockBeforeSend are as follows:
TrackBeforeSend(ctx sdk.Context, from, to sdk.AccAddress, amount sdk.Coins)
BlockBeforeSend(ctx sdk.Context, from, to sdk.AccAddress, amount sdk.Coins) error Note that both hooks take the same arguments, but BlockBeforeSend returns and triggers an error, while TrackBeforeSend does not. That is, any error triggered by the BlockBeforeSend hook implementation would cancel the state transition and, consequently, the send itself, while any error omitted from TrackBeforeSend would be gracefully silenced.
TrackBeforeSend and BlockBeforeSend are both triggered before any send action occurs, specifically before we call sendCoins, the internal API for transferring coins.
func (k BaseSendKeeper) SendCoins(ctx sdk.Context, fromAddr sdk.AccAddress, toAddr sdk.AccAddress, amt sdk.Coins) error {
// BlockBeforeSend hook should always be called before the TrackBeforeSend hook.
err := k.BlockBeforeSend(ctx, fromAddr, toAddr, amt)
if err != nil {
return err
}
return k.sendCoins(ctx, fromAddr, toAddr, amt)
}Note that for Module to Module send, the BlockBeforeSend hooks are not triggered, as we do not want to block module-to-module sends in any case.
Please see PR421 for more implementation details.
Due to the difference two hooks mentioned above, TrackBeforeSend is useful for cases when a contract needs to track specific send actions of the token factory denom, whilst BlockBeforeSend would be more useful for situations when we want to block specific sends using contracts.
Each Token Factory denom allows the registration of one contract address. This contract is sudo-called every time the aforementioned bank hooks are activated.
Contracts are able to integrate with these hooks by implementing BlockBeforeSend and TrackBeforeSend message as the following example:
#[entry_point]
pub fn sudo(deps: DepsMut, env: Env, msg: SudoMsg) -> StdResult<Response> {
match &msg{
SudoMsg::BlockBeforeSend { from, to, amount} => {
Ok(Response::new().add_attributes(vec![
("hook", "block"),
("from", from),
("to", to),
("amount", &amount.to_string())
]))
},
SudoMsg::TrackBeforeSend { from, to, amount} => {
Ok(Response::new().add_attributes(vec![
("hook", "track"),
("from", from),
("to", to),
("amount", &amount.to_string())
]))
}
}
}Note that since TrackBeforeSend hook can also be triggered upon module to module send (which is not gas metered), we internally gas meter TrackBeforeSend with a gas limit of 100_000.
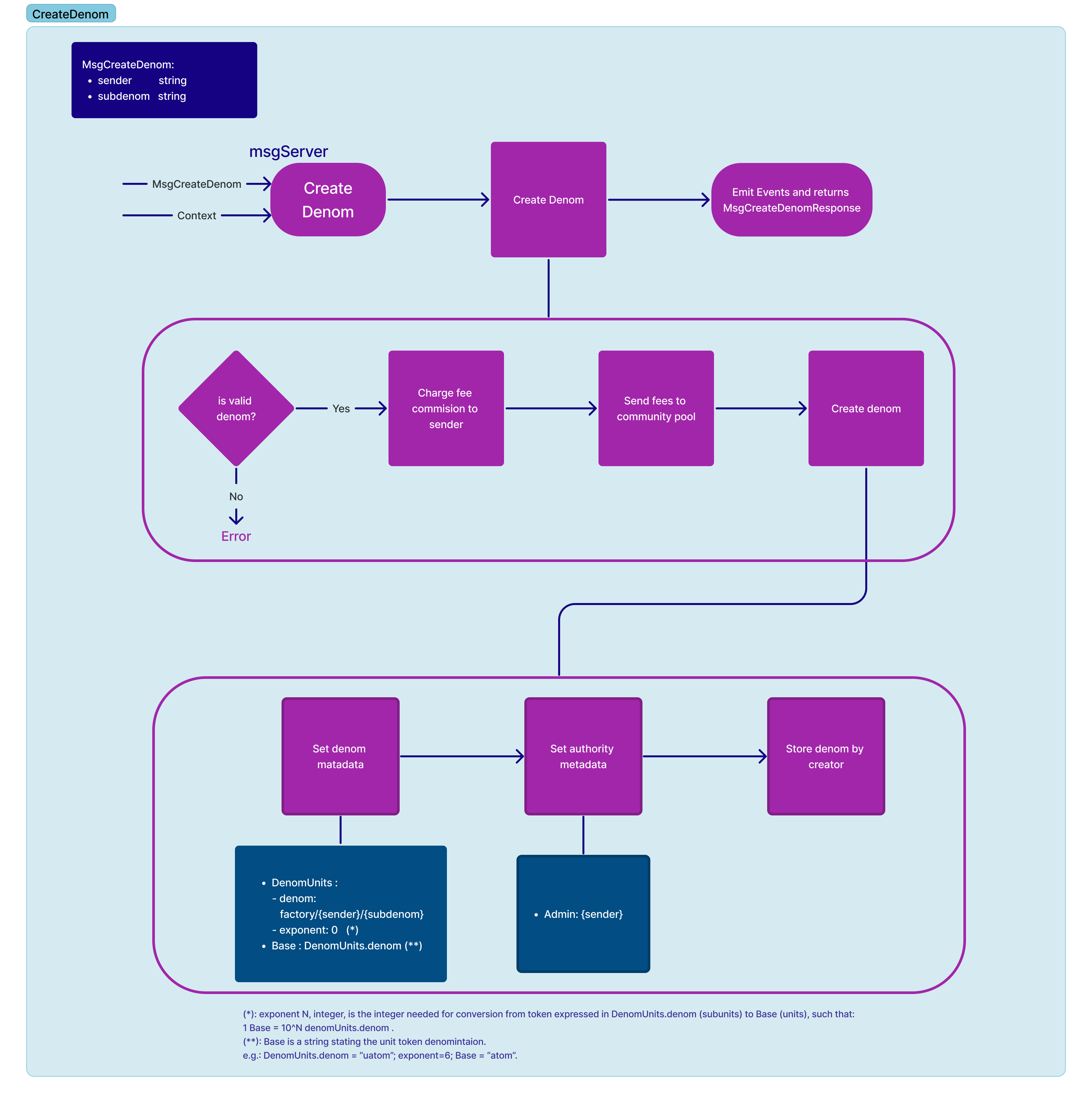
Creates a denom of factory/{creator address}/{subdenom} given the denom creator
address and the subdenom. Subdenoms can contain [a-zA-Z0-9./].
message MsgCreateDenom {
string sender = 1 [ (gogoproto.moretags) = "yaml:\"sender\"" ];
string subdenom = 2 [ (gogoproto.moretags) = "yaml:\"subdenom\"" ];
}State Modifications:
- Fund community pool with the denom creation fee from the creator address, set
in
Params. - Consume an amount of gas corresponding to the
DenomCreationGasConsumeparameter specified inParams. - Set
DenomMetaDatavia bank keeper. - Set
AuthorityMetadatafor the given denom to store the admin for the created denomfactory/{creator address}/{subdenom}. Admin is automatically set as the Msg sender. - Add denom to the
CreatorPrefixStore, where a state of denoms created per creator is kept.
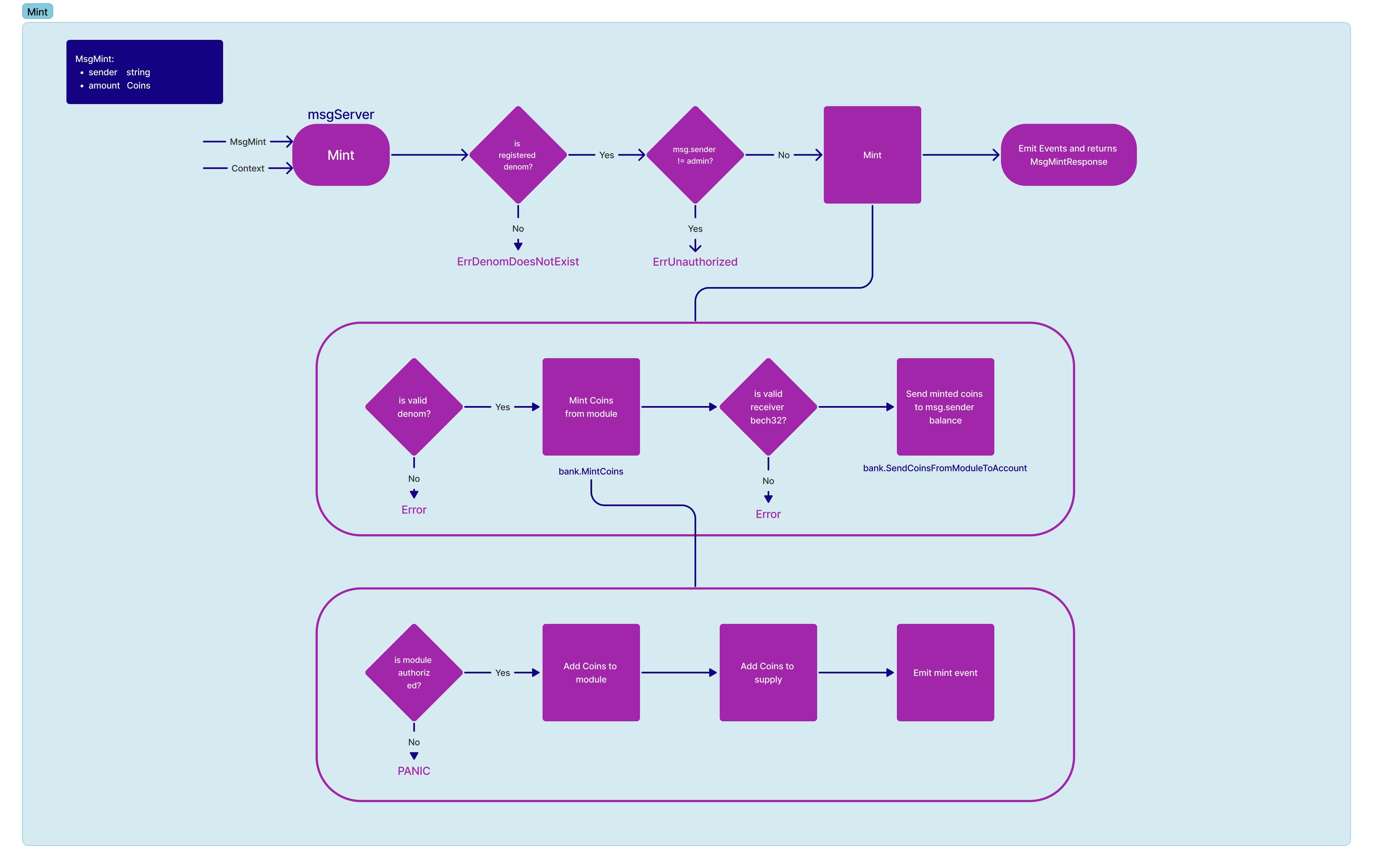
Minting of a specific denom is only allowed for the current admin. Note, the current admin is defaulted to the creator of the denom.
message MsgMint {
string sender = 1 [ (gogoproto.moretags) = "yaml:\"sender\"" ];
cosmos.base.v1beta1.Coin amount = 2 [
(gogoproto.moretags) = "yaml:\"amount\"",
(gogoproto.nullable) = false
];
}State Modifications:
- Safety check the following
- Check that the denom minting is created via
tokenfactorymodule - Check that the sender of the message is the admin of the denom
- Check that the denom minting is created via
- Mint designated amount of tokens for the denom via
bankmodule
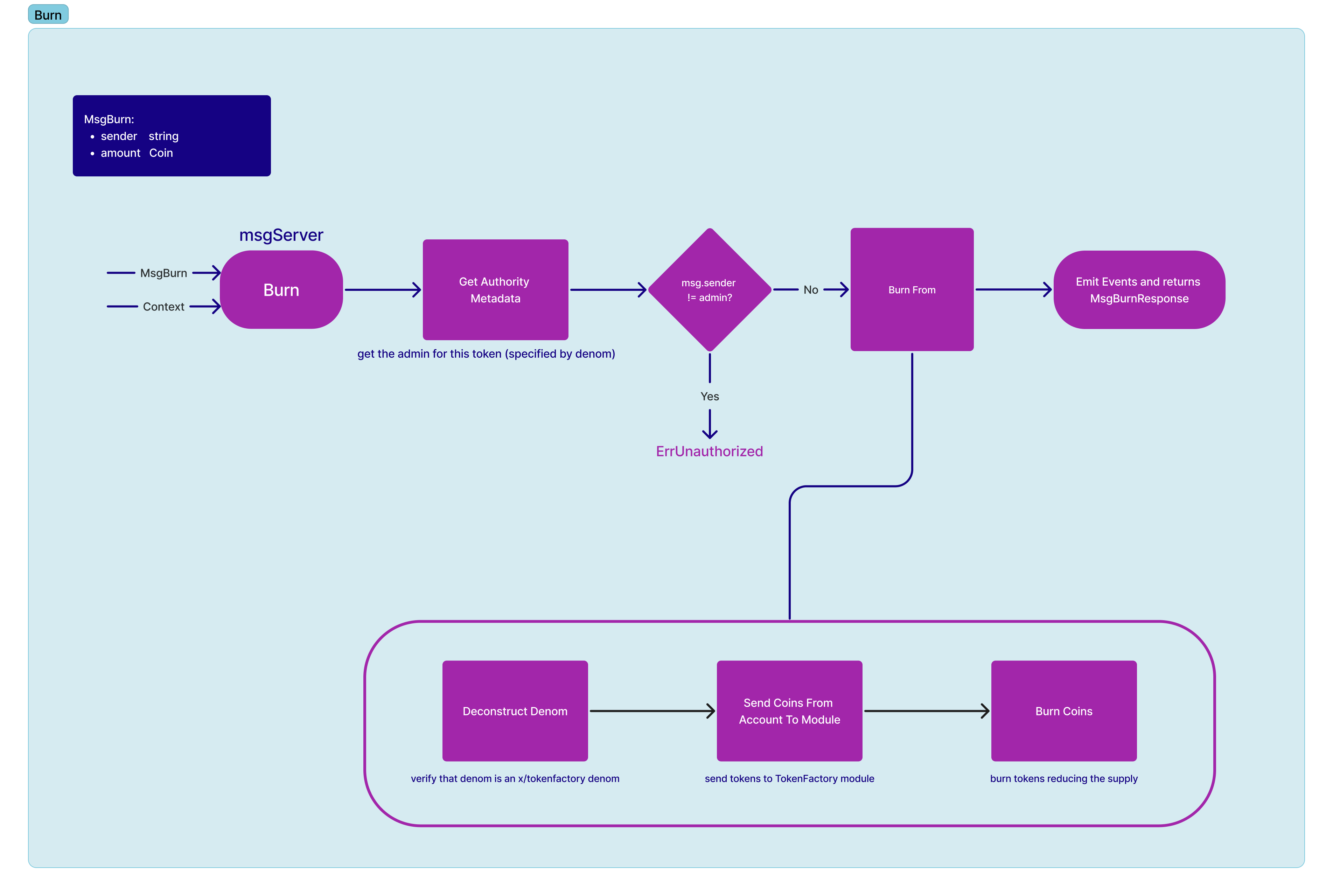
Burning of a specific denom is only allowed for the current admin. Note, the current admin is defaulted to the creator of the denom.
message MsgBurn {
string sender = 1 [ (gogoproto.moretags) = "yaml:\"sender\"" ];
cosmos.base.v1beta1.Coin amount = 2 [
(gogoproto.moretags) = "yaml:\"amount\"",
(gogoproto.nullable) = false
];
}State Modifications:
- Safety check the following
- Check that the denom minting is created via
tokenfactorymodule - Check that the sender of the message is the admin of the denom
- Check that the denom minting is created via
- Burn designated amount of tokens for the denom via
bankmodule
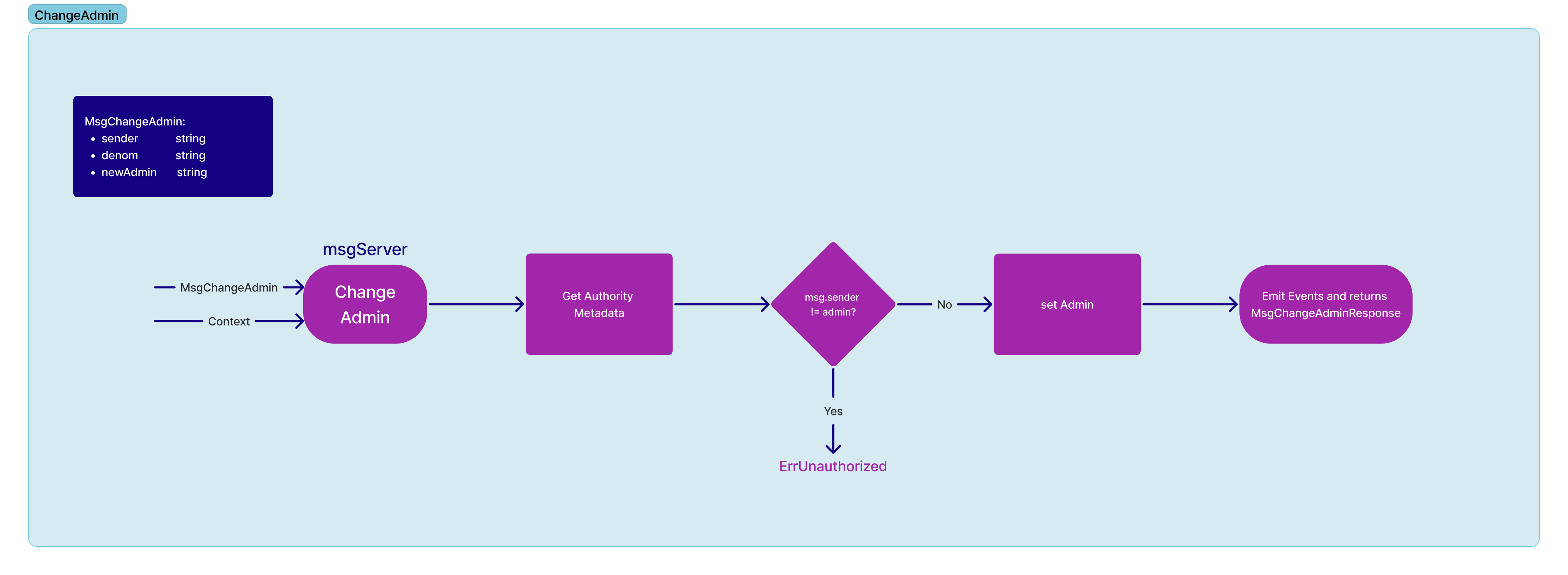
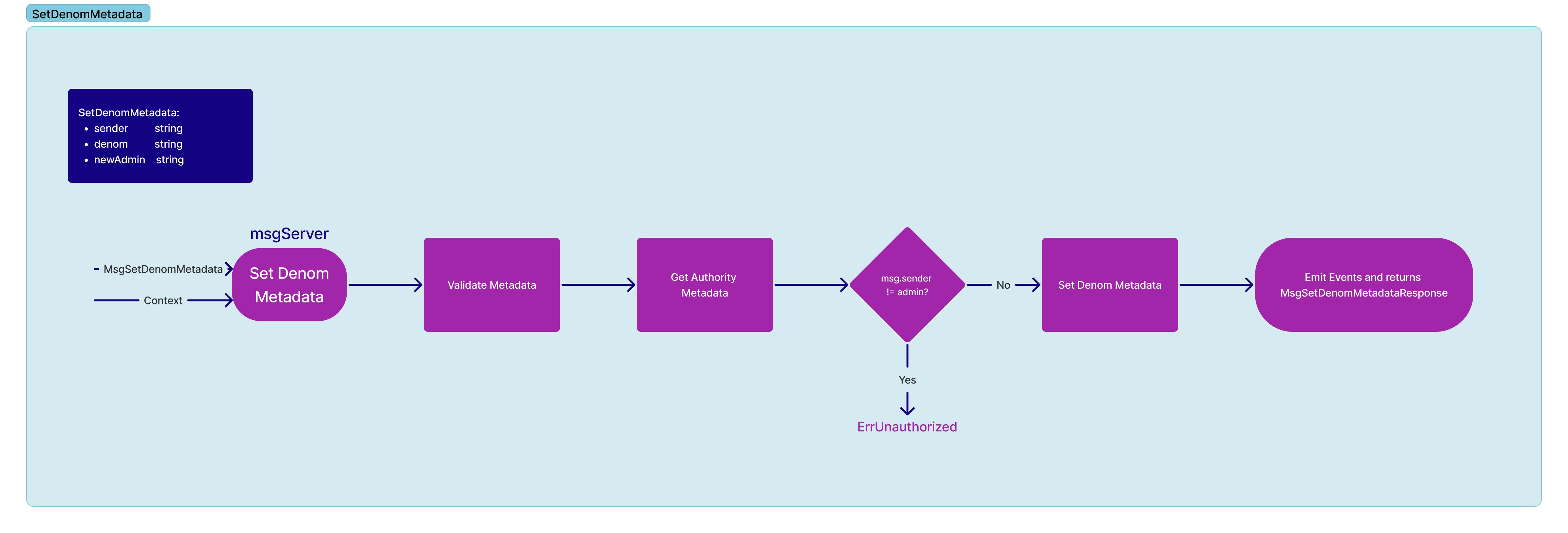
Change the admin of a denom. Note, this is only allowed to be called by the current admin of the denom.
message MsgChangeAdmin {
string sender = 1 [ (gogoproto.moretags) = "yaml:\"sender\"" ];
string denom = 2 [ (gogoproto.moretags) = "yaml:\"denom\"" ];
string newAdmin = 3 [ (gogoproto.moretags) = "yaml:\"new_admin\"" ];
}Setting of metadata for a specific denom is only allowed for the admin of the denom. It allows the overwriting of the denom metadata in the bank module.
message MsgChangeAdmin {
string sender = 1 [ (gogoproto.moretags) = "yaml:\"sender\"" ];
cosmos.bank.v1beta1.Metadata metadata = 2 [ (gogoproto.moretags) = "yaml:\"metadata\"", (gogoproto.nullable) = false ];
}State Modifications:
- Check that sender of the message is the admin of denom
- Modify
AuthorityMetadatastate entry to change the admin of the denom
The chain's bech32 prefix for addresses can be at most 16 characters long.
This comes from denoms having a 128 byte maximum length, enforced from the SDK, and us setting longest_subdenom to be 44 bytes.
A token factory token's denom is: factory/{creator address}/{subdenom}
Splitting up into sub-components, this has:
len(factory) = 72 * len("/") = 2len(longest_subdenom)len(creator_address) = len(bech32(longest_addr_length, chain_addr_prefix)).
Longest addr length at the moment is 32 bytes. Due to SDK error correction
settings, this means len(bech32(32, chain_addr_prefix)) = len(chain_addr_prefix) + 1 + 58.
Adding this all, we have a total length constraint of 128 = 7 + 2 + len(longest_subdenom) + len(longest_chain_addr_prefix) + 1 + 58.
Therefore len(longest_subdenom) + len(longest_chain_addr_prefix) = 128 - (7 + 2 + 1 + 58) = 60.
The choice between how we standardized the split these 60 bytes between maxes from longest_subdenom and longest_chain_addr_prefix is somewhat arbitrary. Considerations going into this:
- Per BIP-0173 the technically longest HRP for a 32 byte address ('data field') is 31 bytes. (Comes from encode(data) = 59 bytes, and max length = 90 bytes)
- subdenom should be at least 32 bytes so hashes can go into it
- longer subdenoms are very helpful for creating human readable denoms
- chain addresses should prefer being smaller. The longest HRP in cosmos to date is 11 bytes. (
persistence)
For explicitness, its currently set to len(longest_subdenom) = 44 and len(longest_chain_addr_prefix) = 16.
Please note, if the SDK increases the maximum length of a denom from 128 bytes, these caps should increase.
So please don't make code rely on these max lengths for parsing.
To create a new token, use the create-denom command from the tokenfactory module. The following example uses the address osmo1c584m4lq25h83yp6ag8hh4htjr92d954vklzja from mylocalwallet as the default admin for the new token.
To create a new token we can use the create-denom command.
osmosisd tx tokenfactory create-denom ufoo --keyring-backend=test --from mylocalwalletOnce a new token is created, it can be minted using the mint command in the tokenfactory module. Note that the complete tokenfactory address, in the format of factory/{creator address}/{subdenom}, must be used to mint the token.
osmosisd tx tokenfactory mint 100000000000factory/osmo1c584m4lq25h83yp6ag8hh4htjr92d954vklzja/ufoo --keyring-backend=test --from mylocalwalletTo view a token's metadata, use the denom-metadata command in the bank module. The following example queries the metadata for the token factory/osmo1c584m4lq25h83yp6ag8hh4htjr92d954vklzja/ufoo:
osmosisd query bank denom-metadata --denom factory/osmo1c584m4lq25h83yp6ag8hh4htjr92d954vklzja/ufooTo see a list of tokens created by a specific account, use the denoms-from-creator command in the tokenfactory module. The following example shows tokens created by the account osmo1c584m4lq25h83yp6ag8hh4htjr92d954vklzja:
osmosisd query tokenfactory denoms-from-creator osmo1c584m4lq25h83yp6ag8hh4htjr92d954vklzja