| title | description | author | ms.author | ms.date | ms.service | ms.subservice | ms.topic | ms.custom |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Quickstart: Azure Blob Storage library v12 - .NET |
In this quickstart, you will learn how to use the Azure Blob Storage client library version 12 for .NET to create a container and a blob in Blob (object) storage. Next, you learn how to download the blob to your local computer, and how to list all of the blobs in a container. |
twooley |
twooley |
03/03/2021 |
storage |
blobs |
quickstart |
devx-track-csharp |
Get started with the Azure Blob Storage client library v12 for .NET. Azure Blob Storage is Microsoft's object storage solution for the cloud. Follow steps to install the package and try out example code for basic tasks. Blob storage is optimized for storing massive amounts of unstructured data.
Use the Azure Blob Storage client library v12 for .NET to:
- Create a container
- Upload a blob to Azure Storage
- List all of the blobs in a container
- Download the blob to your local computer
- Delete a container
Additional resources:
[!INCLUDE storage-multi-protocol-access-preview]
- Azure subscription - create one for free
- Azure storage account - create a storage account
- Current .NET Core SDK for your operating system. Be sure to get the SDK and not the runtime.
This section walks you through preparing a project to work with the Azure Blob Storage client library v12 for .NET.
Create a .NET Core application named BlobQuickstartV12.
-
In a console window (such as cmd, PowerShell, or Bash), use the
dotnet newcommand to create a new console app with the name BlobQuickstartV12. This command creates a simple "Hello World" C# project with a single source file: Program.cs.dotnet new console -n BlobQuickstartV12 -
Switch to the newly created BlobQuickstartV12 directory.
cd BlobQuickstartV12 -
In side the BlobQuickstartV12 directory, create another directory called data. This is where the blob data files will be created and stored.
mkdir data
While still in the application directory, install the Azure Blob Storage client library for .NET package by using the dotnet add package command.
dotnet add package Azure.Storage.BlobsFrom the project directory:
-
Open the Program.cs file in your editor.
-
Remove the
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");statement. -
Add
usingdirectives. -
Update the
Mainmethod declaration to support async.Here's the code:
:::code language="csharp" source="~/azure-storage-snippets/blobs/quickstarts/dotnet/BlobQuickstartV12/app_framework.cs":::
[!INCLUDE storage-quickstart-credentials-include]
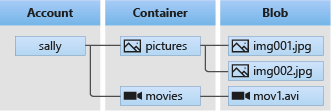
Azure Blob Storage is optimized for storing massive amounts of unstructured data. Unstructured data is data that does not adhere to a particular data model or definition, such as text or binary data. Blob storage offers three types of resources:
- The storage account
- A container in the storage account
- A blob in the container
The following diagram shows the relationship between these resources.
Use the following .NET classes to interact with these resources:
- BlobServiceClient: The
BlobServiceClientclass allows you to manipulate Azure Storage resources and blob containers. - BlobContainerClient: The
BlobContainerClientclass allows you to manipulate Azure Storage containers and their blobs. - BlobClient: The
BlobClientclass allows you to manipulate Azure Storage blobs.
These example code snippets show you how to perform the following with the Azure Blob Storage client library for .NET:
- Get the connection string
- Create a container
- Upload blobs to a container
- List the blobs in a container
- Download blobs
- Delete a container
The code below retrieves the connection string for the storage account from the environment variable created in the Configure your storage connection string section.
Add this code inside the Main method:
:::code language="csharp" source="~/azure-storage-snippets/blobs/quickstarts/dotnet/BlobQuickstartV12/Program.cs" id="Snippet_ConnectionString":::
Decide on a name for the new container. The code below appends a GUID value to the container name to ensure that it is unique.
Important
Container names must be lowercase. For more information about naming containers and blobs, see Naming and Referencing Containers, Blobs, and Metadata.
Create an instance of the BlobServiceClient class. Then, call the CreateBlobContainerAsync method to create the container in your storage account.
Add this code to the end of the Main method:
:::code language="csharp" source="~/azure-storage-snippets/blobs/quickstarts/dotnet/BlobQuickstartV12/Program.cs" id="Snippet_CreateContainer":::
The following code snippet:
- Creates a text file in the local data directory.
- Gets a reference to a BlobClient object by calling the GetBlobClient method on the container from the Create a container section.
- Uploads the local text file to the blob by calling the UploadAsync method. This method creates the blob if it doesn't already exist, and overwrites it if it does.
Add this code to the end of the Main method:
:::code language="csharp" source="~/azure-storage-snippets/blobs/quickstarts/dotnet/BlobQuickstartV12/Program.cs" id="Snippet_UploadBlobs":::
List the blobs in the container by calling the GetBlobsAsync method. In this case, only one blob has been added to the container, so the listing operation returns just that one blob.
Add this code to the end of the Main method:
:::code language="csharp" source="~/azure-storage-snippets/blobs/quickstarts/dotnet/BlobQuickstartV12/Program.cs" id="Snippet_ListBlobs":::
Download the previously created blob by calling the DownloadToAsync method. The example code adds a suffix of "DOWNLOADED" to the file name so that you can see both files in local file system.
Add this code to the end of the Main method:
:::code language="csharp" source="~/azure-storage-snippets/blobs/quickstarts/dotnet/BlobQuickstartV12/Program.cs" id="Snippet_DownloadBlobs":::
The following code cleans up the resources the app created by deleting the entire container by using DeleteAsync. It also deletes the local files created by the app.
The app pauses for user input by calling Console.ReadLine before it deletes the blob, container, and local files. This is a good chance to verify that the resources were actually created correctly, before they are deleted.
Add this code to the end of the Main method:
:::code language="csharp" source="~/azure-storage-snippets/blobs/quickstarts/dotnet/BlobQuickstartV12/Program.cs" id="Snippet_DeleteContainer":::
This app creates a test file in your local data folder and uploads it to Blob storage. The example then lists the blobs in the container and downloads the file with a new name so that you can compare the old and new files.
Navigate to your application directory, then build and run the application.
dotnet builddotnet runThe output of the app is similar to the following example:
Azure Blob Storage v12 - .NET quickstart sample
Uploading to Blob storage as blob:
https://mystorageacct.blob.core.windows.net/quickstartblobs60c70d78-8d93-43ae-954d-8322058cfd64/quickstart2fe6c5b4-7918-46cb-96f4-8c4c5cb2fd31.txt
Listing blobs...
quickstart2fe6c5b4-7918-46cb-96f4-8c4c5cb2fd31.txt
Downloading blob to
./data/quickstart2fe6c5b4-7918-46cb-96f4-8c4c5cb2fd31DOWNLOADED.txt
Press any key to begin clean up
Deleting blob container...
Deleting the local source and downloaded files...
Done
Before you begin the clean up process, check your data folder for the two files. You can open them and observe that they are identical.
After you've verified the files, press the Enter key to delete the test files and finish the demo.
In this quickstart, you learned how to upload, download, and list blobs using .NET.
To see Blob storage sample apps, continue to:
[!div class="nextstepaction"] Azure Blob Storage SDK v12 .NET samples
- For tutorials, samples, quick starts and other documentation, visit Azure for .NET and .NET Core developers.
- To learn more about .NET Core, see Get started with .NET in 10 minutes.