Flutter low level audio plugin using SoLoud library with miniaudio backend and FFI. It provides player, basic capture from microphone, 3D audio and more.
| Linux | Windows | Android | MacOS | iOS | web |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 💙 | 💙 | 💙 | 💙 | 💙 | 😭 |
🌐 Supported on Linux, Windows, Mac, Android, and iOS
🎤 Player and capture audio from microphone (no recording)
🎶 3D audio with doppler effect
🎚️ Faders, oscillators and audio effects like echo, freeverb, robotizer, equalizer, bassboost
🎙️ Multiple voices, capable of playing different sounds simultaneously or even repeating the same sound multiple times on top of each other
💬 Includes a simple speech synthesizer
🔊 Supports various common formats such as 8, 16, and 32-bit WAVs, floating point WAVs, OGG, MP3, and FLAC
🎚️ Enables real-time retrieval of audio FFT and wave data
The flutter_soloud plugin utilizes a forked repository of SoLoud, where the miniaudio audio backend has been updated and is located in src/soloud/src/backend/miniaudio
For information regarding the SoLoud license, please refer to this link.
There are 5 examples: (to use microphone on MacOs or iOS you should add audio input permission in the example app)
The 1st is a simple use-case to show how to play a sound and how to activate the capture.
The 2nd aims to show a visualization of frequencies and wave data.
The file [Visualizer.dart] uses getAudioTexture2D to store new audio data into audioData on every tick.
The video below illustrates how the data is then converted to an image (the upper widget) and sent to the shader (the middle widget).
The bottom widgets use FFT data on the left and wave data represented with a row of yellow vertical containers with the height taken from audioData on the right.
The getAudioTexture2D returns an array of 512x256. Each row contains 256 Floats of FFT data and 256 Floats of wave data, making it possible to write a shader like a spectrogram (shader #8) or a 3D visualization (shader #9).
Shaders from 1 to 7 are using just 1 row of the audioData. Therefore, the texture generated to feed the shader should be 256x2 px. The 1st row represents the FFT data, and the 2nd represents the wave data.
Since many operations are required for each frame, the CPU and GPU can be under stress, leading to overheating of a mobile device.
It seems that sending an image (with setImageSampler()) to the shader is very expensive. You can observe this by disabling the shader widget.
soloud6.mp4
The 3rd example demonstrates how to manage sounds using their handles: every sound should be loaded before it can be played. Loading a sound can take some time and should not be done during gameplay, for instance, in a game. Once a sound is loaded, it can be played, and every instance of that same audio will be identified by its handle.
The example shows how you can have background music and play a fire sound multiple times.
soloud6-B.mp4
The 4th example shows how to enance audio with 3D capabilities. There is a circle where the listener is placed in the center and a moving siren audio is represented by a little circle which is automatically animated or can be moved by mouse gesture. The sound volume fades off at the circonference. There is also a doppler effect that can be turned off.
soloud8-3Daudio.mp4
The 5th example shows how to generete [SoundProps] key sounds. There is a handy tool method to generate the 12 key notes of a given octave. A widget to play them can be used with the touch or a keyboard. Different types of waveforms can be chosen including square,saw,sin,triangle,bounce,jaws,humps,fSquare and fSaw.
There are also simple knobs to adjust faders and oscillators. Other knobs to add/remove audio effects.
soloud9-waveform-B.mp4
First of all, AudioIsolate must be initialized:
Future<bool> start() async{
final value = SoLoud().startIsolate();
if (value == PlayerErrors.noError) {
debugPrint('isolate started');
return true;
} else {
debugPrint('isolate starting error: $value');
return false;
}
}
When succesfully started a sound can be loaded:
Future<SoundProps?> loadSound(String completeFileName) {
final load = await SoLoud().loadFile(completeFileName);
if (load.error != PlayerErrors.noError) return null;
return load.sound;
}
There are 3 convenient methods that can be used instead in the [SoloudLoadingTool] class:
Future<SoundProps?> loadFromAssets(String path)Future<SoundProps?> loadFromFile(String path)Future<SoundProps?> loadFromUrl(String url)
The [SoundProps] class:
class SoundProps {
SoundProps(this.soundHash);
// the [hash] returned by [loadFile]
final int soundHash;
/// handles of this sound. Multiple instances of this sound can be
/// played, each with their unique handle
List<int> handle = [];
/// the user can listed ie when a sound ends or key events (TODO)
StreamController<StreamSoundEvent> soundEvents = StreamController.broadcast();
}
soundHash and handle list are then used to call many methods in the AudioIsolate() class.
warning: when you call a load* method, in return you will get a SoundProps. This is the reference to the sound which is used by SoLoud and need to be disposed when is no more needed. When you play a SoundsProps, intstead a new handle, to identify the new playing instance, is created and added to SoundProps.handle list. This let you play the sound as many times you want without calling a load* method again which can be laggy. To dispose a sound call you should call Soloud().disposeSound or Soloud().disposeAllSounds
Start the capture
SoLoud().initCapture();
SoLoud().startCapture();
now it's possible to get audio data. When the mic is no more needed, it can be stopped:
SoLoud().stopCapture();
With the audio data it will be simple to do something like in the 1st example:
soloud7-capture.mp4
The AudioIsolate instance has the duty of receiving commands and sending them to a separate Isolate, while returning the results to the main UI isolate.
| Function | Returns | Params | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| startIsolate | PlayerErrors | - | Start the audio isolate and listen for messages coming from it. |
| stopIsolate | bool | - | Stop the loop, stop the engine, and kill the isolate. Must be called when there is no more need for the player or when closing the app. |
| isIsolateRunning | bool | - | Return true if the audio isolate is running. |
| initEngine | PlayerErrors | - | Initialize the audio engine. Defaults are: Sample rate 44100, buffer 2048, and Miniaudio audio backend. |
| dispose | - | - | Stop the audio engine. |
| loadFile | ({PlayerErrors error, SoundProps? sound}) | String fileName, LoadMode mode = LoadMode.memory |
Load a new sound to be played once or multiple times later. If mode = LoadMode.disk, seek will have lags with MP3s. |
| play | ({PlayerErrors error, SoundProps sound, int newHandle}) | int soundHash, {double volume = 1,double pan = 0,bool paused = false,} |
Play an already loaded sound identified by [sound]. |
| speechText | ({PlayerErrors error, SoundProps sound}) | String textToSpeech |
Speech from the given text. |
| pauseSwitch | PlayerErrors | int handle |
Pause or unpause an already loaded sound identified by [handle]. |
| getPause | ({PlayerErrors error, bool pause}) | int handle |
Get the pause state of the sound identified by [handle]. |
| setRelativePlaySpeed | PlayerErrors | int handle, double speed |
Set a sound's relative play speed. |
| getRelativePlaySpeed | ({PlayerErrors error, double speed}) | int handle |
Return the current play speed. |
| stop | PlayerErrors | int handle |
Stop an already loaded sound identified by [handle] and clear it. |
| disposeSound | PlayerErrors | int handle |
Stop ALL handles of the already loaded sound identified by [soundHash] and dispose it. |
| getLooping | ({PlayerErrors error, bool isLooping}) | - | Query whether a sound is set to loop. |
| setLooping | - | int handle, bool enable |
This function can be used to set a sample to play on repeat, instead of just playing once. |
| getLoopPoint | ({PlayerErrors error, double time}) | - | Get sound loop point value. |
| setLoopPoint | PlayerErrors | SoundHandle handle, double time |
Set sound loop point value. |
| getLength | ({PlayerErrors error, double length}) | int soundHash |
Get the sound length in seconds. |
| seek | PlayerErrors | int handle, double time |
Seek playing in seconds. WARNING: when loading an MP3 file with mode = LoadMode.disk, the seek is laggy. This should not happens with FLACs, OGGs and WAVs. |
| getPosition | ({PlayerErrors error, double position}) | int handle |
Get the current sound position in seconds. |
| getVolume | ({PlayerErrors error, double volume}) | int handle |
Get current [handle] volume. |
| setVolume | ({PlayerErrors error, double volume}) | int handle, double volume |
set [handle] volume. |
| getIsValidVoiceHandle | ({PlayerErrors error, bool isValid}) | int handle |
Check if a handle is still valid. |
| setVisualizationEnabled | - | bool enabled |
Enable or disable getting data from getFft, getWave, getAudioTexture*. |
| getVisualizationEnabled | ({PlayerErrors error, bool isEnabled}) | - | Get the state of visualization flag. |
| getFft | - | Pointer<Float> fft |
Returns a 256 float array containing FFT data. |
| getWave | - | Pointer<Float> wave |
Returns a 256 float array containing wave data (magnitudes). |
| getAudioTexture | - | Pointer<Float> samples |
Returns in samples a 512 float array.- The first 256 floats represent the FFT frequencies data [>=0.0]. - The other 256 floats represent the wave data (amplitude) [-1.0~1.0]. |
| getAudioTexture2D | - | Pointer<Pointer<Float>> samples |
Return a floats matrix of 256x512. Every row is composed of 256 FFT values plus 256 wave data. Every time is called, a new row is stored in the first row and all the previous rows are shifted up (the last will be lost). |
| setFftSmoothing | - | double smooth |
Smooth FFT data. When new data is read and the values are decreasing, the new value will be decreased with an amplitude between the old and the new value. This will result in a less shaky visualization. 0 = no smooth 1 = full smooth The new value is calculated with: newFreq = smooth * oldFreq + (1 - smooth) * newFreq |
| Function | Returns | Params | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| loadWaveform | ({PlayerErrors error, SoundProps? sound}) | WaveForm waveformbool superWavedouble scaledouble detune |
Load a new sound to be played. |
| setWaveform | PlayerErrors | SoundProps soundWaveForm newWaveform |
Set a new waveform for the [sound]. |
| setWaveformScale | PlayerErrors | SoundProps sounddouble newScale |
Set a new scale for the [sound] (only if [superWave] is true). |
| setWaveformDetune | PlayerErrors | SoundProps sounddouble newDetune |
Set a new detune for the [sound] (only if [superWave] is true). |
| setWaveformFreq | PlayerErrors | SoundProps sounddouble newFreq |
Set a new frequency for the [sound]. |
| setWaveformSuperWave | PlayerErrors | SoundProps soundbool superwave |
Set to compute superwave for the [sound]. |
enum WaveForm
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| square | Raw, harsh square wave |
| saw | Raw, harsh saw wave |
| sin | Sine wave |
| triangle | Triangle wave |
| bounce | Bounce, i.e, abs(sin()) |
| jaws | Quater sine wave, rest of period quiet |
| humps | Half sine wave, rest of period quiet |
| fSquare | "Fourier" square wave; less noisy |
| fSaw | "Fourier" saw wave; less noisy |
These methods add audio effects to sounds. Faders and oscillators are binded to sound handles, so they need [SoundProps.handle] as first parameter. Audio FXs like echo, freeverb, bassboost etc, are working on the output, so they can set anytime while playing something.
| Function | Returns | Params | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| fadeGlobalVolume | PlayerErrors error | double to,double time |
Smoothly change the global volume over specified time. |
| fadeVolume | PlayerErrors error | int handle,double to,double time |
Smoothly change a channel's volume over specified time. |
| fadePan | PlayerErrors error | int handle,double to,double time |
Smoothly change a channel's pan setting over specified time. |
| fadeRelativePlaySpeed | PlayerErrors error | int handle,double to,double time |
Smoothly change a channel's relative play speed over specified time. |
| schedulePause | PlayerErrors error | int handle,double time |
After specified time, pause the channel. |
| scheduleStop | PlayerErrors error | int handle,double time |
After specified time, stop the channel. |
| oscillateVolume | PlayerErrors error | int handle,double from,double to,double time |
Smoothly change a channel's pan setting over specified time. |
| oscillatePan | PlayerErrors error | int handle,double from,double to,double time |
Set fader to oscillate the panning at specified frequency. |
| oscillateRelativePlaySpeed | PlayerErrors error | int handle,double from,double to,double time |
Set fader to oscillate the relative play speed at specified frequency. |
| oscillateGlobalVolume | PlayerErrors error | double from,double to,double time |
Set fader to oscillate the global volume at specified frequency. |
| isFilterActive | ({PlayerErrors error, int index}) | FilterType filterType |
Check if the given filter is active or not. |
| getFilterParamNames | ({PlayerErrors error, List names}) | FilterType filterType |
Get parameters names of the given filter. |
| addGlobalFilter | PlayerErrors | FilterType filterType |
Add the filter [filterType]. |
| removeGlobalFilter | PlayerErrors | FilterType filterType |
Remove the filter [filterType]. |
| setFxParams | PlayerErrors | FilterType filterType,int attributeId,double value |
Set the effect parameter with id [attributeId] of [filterType] with [value] value. |
| getFxParams | PlayerErrors | FilterType filterType,int attributeId |
Get the effect parameter with id [attributeId] of [filterType]. |
enum FilterType
| Name |
|---|
| biquadResonantFilter |
| eqFilter |
| echoFilter |
| lofiFilter |
| flangerFilter |
| bassboostFilter |
| waveShaperFilter |
| robotizeFilter |
| freeverbFilter |
There are also conveninet const to easily access effect parameter like filter name, param names, mins values, max values and defaults:
fxEq, fxEcho, fxLofi, fxFlanger, fxBassboost, fxWaveShaper, fxRobotize, fxFreeverb.
| Function | Returns | Params | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| play3d | int handle |
int soundHash, double posX, double posY, double posZ,{ double velX = 0,double velY = 0,double velZ = 0,double volume = 1,bool paused = false} |
play3d() is the 3d version of the play() call. Returns the handle of the sound, 0 if error |
| set3dSoundSpeed | - | double speed |
Since SoLoud has no knowledge of the scale of your coordinates, you may need to adjust the speed of sound for these effects to work correctly. The default value is 343, which assumes that your world coordinates are in meters (where 1 unit is 1 meter), and that the environment is dry air at around 20 degrees Celsius. |
| get3dSoundSpeed | double |
- | Get the sound speed. |
| set3dListenerParameters | - | double posX,double posY,double posZ,double atX,double atY,double atZ,double upX,double upY,double upZ,double velocityX,double velocityY,double velocityZ |
You can set the position, at-vector, up-vector and velocity parameters of the 3d audio listener with one call. |
| set3dListenerPosition | - | double posX,double posY,double posZ |
Get the sound speed. |
| set3dListenerAt | - | double atX,double atY,double atZ |
You can set the "at" vector parameter of the 3d audio listener. |
| set3dListenerUp | - | double upX,double upY,double upZ |
You can set the "up" vector parameter of the 3d audio listener. |
| set3dListenerVelocity | - | double velocityX,double velocityY,double velocityZ |
You can set the listener's velocity vector parameter. |
| set3dSourceParameters | - | int handle,double posX,double posY,double posZ,double velocityX,double velocityY,double velocityZ |
You can set the position and velocity parameters of a live 3d audio source with one call. |
| set3dSourcePosition | - | int handle,double posX,double posY,double posZ |
You can set the position parameters of a live 3d audio source. |
| set3dSourceVelocity | - | int handle,double velocityX,double velocityY,double velocityZ |
You can set the velocity parameters of a live 3d audio source. |
| set3dSourceMinMaxDistance | - | int handle,double minDistance,double maxDistance |
You can set the minimum and maximum distance parameters of a live 3d audio source. |
| set3dSourceAttenuation | - | int handle,int attenuationModel,double attenuationRolloffFactor |
You can change the attenuation model and rolloff factor parameters of a live 3d audio source. See https://solhsa.com/soloud/concepts3d.html |
| set3dSourceDopplerFactor | - | int handle,double dopplerFactor |
You can change the doppler factor of a live 3d audio source. See https://solhsa.com/soloud/concepts3d.html |
The PlayerErrors enum:
| name | description |
|---|---|
| noError | No error |
| invalidParameter | Some parameter is invalid |
| fileNotFound | File not found |
| fileLoadFailed | File found, but could not be loaded |
| dllNotFound | DLL not found, or wrong DLL |
| outOfMemory | Out of memory |
| notImplemented | Feature not implemented |
| unknownError | Other error |
| backendNotInited | Player not initialized |
| nullPointer | null pointer. Could happens when passing a non initialized pointer (with calloc()) to retrieve FFT or wave data |
| soundHashNotFound | The sound with specified hash is not found |
| fileAlreadyLoaded | The sound file has already been loaded |
| isolateAlreadyStarted | Audio isolate already started |
| isolateNotStarted | Audio isolate not yet started |
| engineNotInited | Engine not yet started |
AudioIsolate() has a StreamController which can be used, for now, only to know when a sound handle reached the end:
StreamSubscription<StreamSoundEvent>? _subscription;
void listedToEndPlaying(SoundProps sound) {
_subscription = sound!.soundEvents.stream.listen(
(event) {
/// Here the [event.handle] of [sound] has naturally finished
/// and [sound.handle] doesn't contains [envent.handle] anymore.
/// Not passing here when calling [SoLoud().stop()]
/// or [SoLoud().disposeSound()]
},
);
}
it has also a StreamController to monitor when the engine starts or stops:
SoLoud().audioEvent.stream.listen(
(event) {
/// event is of [AudioEvent] enum type:
/// [AudioEvent.isolateStarted] the player is started and sounds can be played
/// [AudioEvent.isolateStopped] player stopped
/// [captureStarted] microphone is active and audio data can be read
/// [captureStopped] microphone stopped
},
);
| Function | Returns | Params | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| listCaptureDevices | CaptureDevice | - | List available input devices. Useful on desktop to choose which input device to use. |
| initCapture | CaptureErrors | - | Initialize input device with [deviceID] Return [CaptureErrors.captureNoError] if no error. |
| isCaptureInitialized | bool | - | Get the status of the device. |
| isCaptureStarted | bool | - | Returns true if the device is capturing audio. |
| stopCapture | CaptureErrors | - | Stop and deinit capture device. |
| startCapture | CaptureErrors | - | Start capturing audio data. |
| getCaptureAudioTexture2D | CaptureErrors | - | Return a floats matrix of 256x512 Every row are composed of 256 FFT values plus 256 of wave data. Every time is called, a new row is stored in the first row and all the previous rows are shifted up (the last one will be lost). |
| setCaptureFftSmoothing | CaptureErrors | double smooth |
Smooth FFT data. When new data is read and the values are decreasing, the new value will be decreased with an amplitude between the old and the new value. This will resul on a less shaky visualization. [smooth] must be in the [0.0 ~ 1.0] range. 0 = no smooth 1 = full smooth the new value is calculated with: newFreq = smooth * oldFreq + (1 - smooth) * newFreq |
The flutter_soloud package logs everything
(from severe warnings to fine debug messages) using the standard
logging package.
See the example's lib/main.dart to see how to capture these logs.
For example:
import 'dart:developer' as dev;
void main() {
// Cut-off for messages. (Lower levels than INFO will be discarded.)
Logger.root.level = Level.FINE;
Logger.root.onRecord.listen((record) {
// Forward logs to the console.
dev.log(
record.message,
time: record.time,
level: record.level.value,
name: record.loggerName,
zone: record.zone,
error: record.error,
stackTrace: record.stackTrace,
);
// TODO: if needed, forward to Sentry.io, Crashlytics, etc.
});
runApp(const MyApp());
}If you don't set up a listener like the one above, there will be no logging from the package.
See the logging package's documentation
to learn more about its functionality.
To use native code, bindings from Dart to C/C++ are needed. To avoid writing these manually, they are generated from the header file (src/ffi_gen_tmp.h) using package:ffigen and temporarily stored in lib/flutter_soloud_FFIGEN.dart. You can generate the bindings by running dart run ffigen.
Since I needed to modify the generated .dart file, I followed this flow:
- Copy the function declarations to be generated into
src/ffi_gen_tmp.h. - The file
lib/flutter_soloud_FFIGEN.dartwill be generated. - Copy the relevant code for the new functions from
lib/flutter_soloud_FFIGEN.dartintolib/flutter_soloud_bindings_ffi.dart.
Additionally, I have forked the SoLoud repository and made modifications to include the latest Miniaudio audio backend. This backend is in the [new_miniaudio] branch of my fork and is set as the default.
This plugin uses the following structure:
-
lib: Contains the Dart code that defines the API of the plugin relative to all platforms. -
src: Contains the native source code. Linux, Android and Windows have their own CmakeFile.txt file in their own subdir to build the code into a dynamic library. -
src/soloud: contains the SoLoud sources of my fork
I have provided the necessary settings in the .vscode directory for debugging native C++ code on both Linux and Windows. To debug on Android, please use Android Studio and open the project located in the example/android directory. However, I am not familiar with the process of debugging native code on Mac and iOS.
When debugging the package using the example/ app, you might want to change
the logging level to something more granular. For example, in main():
// Capture even the finest log messages.
Logger.root.level = Level.ALL;One thing that's missing (as of March 2024) is logging
from inside the audio isolate.
We'd have to send logs to the main isolate through an event,
which might be too expensive and brittle.
Feel free to use debugPrint in audio_isolate.dart
when working on the package.
Just make sure to delete those calls before submitting pull requests.
We don't want to pollute developers' console outputs.
If you encounter any glitches, they might be caused by PulseAudio. To troubleshoot this issue, you can try disabling PulseAudio within the linux/src.cmake file. Look for the line add_definitions(-DMA_NO_PULSEAUDIO) and uncomment it (now it is the default behavior).
The default audio backend is miniaudio, which will automatically select the appropriate audio backend based on your Android version:
- AAudio with Android 8.0 and newer.
- OpenSL|ES for older Android versions.
For Windows users, SoLoud utilizes Openmpt through a DLL, which can be obtained from https://lib.openmpt.org/. If you wish to use this feature, install the DLL and enable it by modifying the first line in windows/src.cmake.
Openmpt functions as a module-playing engine, capable of replaying a wide variety of multichannel music formats (669, amf, ams, dbm, digi, dmf, dsm, far, gdm, ice, imf, it, itp, j2b, m15, mdl, med, mid, mo3, mod, mptm, mt2, mtm, okt, plm, psm, ptm, s3m, stm, ult, umx, wow, xm). Additionally, it can load wav files and may offer better support for wav files compared to the stand-alone wav audio source.
On the simulator, the Impeller engine doesn't work (20 Lug 2023). To disable it, run the following command:
flutter run --no-enable-impeller
Unfortunately, I don't have a real device to test it.
I put in a lot of effort to make this to work on the web! :(
I have successfully compiled the sources with Emscripten. Inside the web directory, there's a script to automate the compiling process using the CmakeLists.txt file. This will generate libflutter_soloud_web_plugin.wasm and libflutter_soloud_web_plugin.bc.
Initially, I tried using the wasm_interop plugin, but encountered errors while loading and initializing the Module.
Then, I attempted using web_ffi, but it seems to have been discontinued because it only supports the old dart:ffi API 2.12.0, which cannot be used here.
Many things can still be done.
- Record from microphone to audio file.
- Since the
loadaudio file feature uses the memory to store all audio data (see #26) to have no lags when start playing (useful with game sounds), make it possible to useSoloud::wavStream - The FFT data doesn't match my expectations. Some work still needs to be done on Analyzer::calcFFT() in
src/analyzer.cpp.
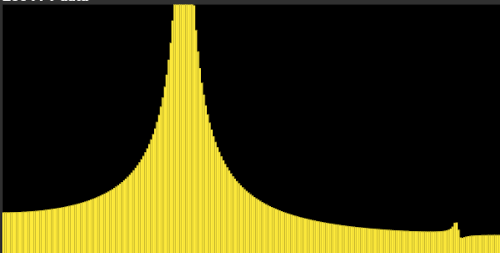 |
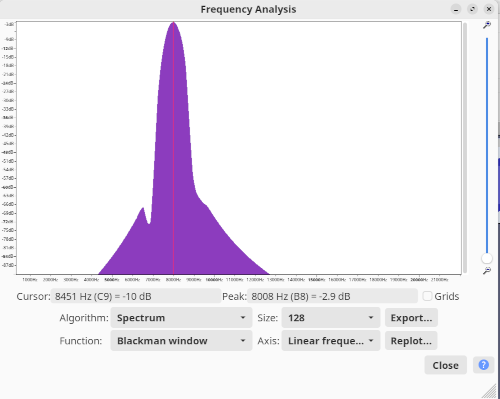 |
|---|---|
| flutter_soloud spectrum | audacity spectrum |
For now, only a small portion of the possibilities offered by SoLoud have been implemented. Look here.
- audio filter effects
- 3D audio ✅
- TED and SID soundchip simulator (Commodore 64/plus)
- noise and waveform generation ✅ and much more I think!

