Given a blacklist B containing unique integers from [0, N), write a function to return a uniform random integer from [0, N) which is NOT in B.
Optimize it such that it minimizes the call to system’s Math.random().
Note:
- 1 <= N <= 1000000000
- 0 <= B.length < min(100000, N)
- [0, N) does NOT include N. See interval notation.
Example 1:
Input:
["Solution","pick","pick","pick"]
[[1,[]],[],[],[]]
Output: [null,0,0,0]Example 2:
Input:
["Solution","pick","pick","pick"]
[[2,[]],[],[],[]]
Output: [null,1,1,1]Example 3:
Input:
["Solution","pick","pick","pick"]
[[3,[1]],[],[],[]]
Output: [null,0,0,2]Example 4:
Input:
["Solution","pick","pick","pick"]
[[4,[2]],[],[],[]]
Output: [null,1,3,1]Explanation of Input Syntax:
The input is two lists: the subroutines called and their arguments. Solution's constructor has two arguments, N and the blacklist B. pick has no arguments. Arguments are always wrapped with a list, even if there aren't any.
给一个数字 N,再给一个黑名单 B,要求在 [0,N) 区间内随机输出一个数字,这个是不在黑名单 B 中的任意一个数字。
这道题的 N 的范围特别大,最大是 10 亿。如果利用桶计数,开不出来这么大的数组。考虑到题目要求我们输出的数字是随机的,所以不需要存下所有的白名单的数字。
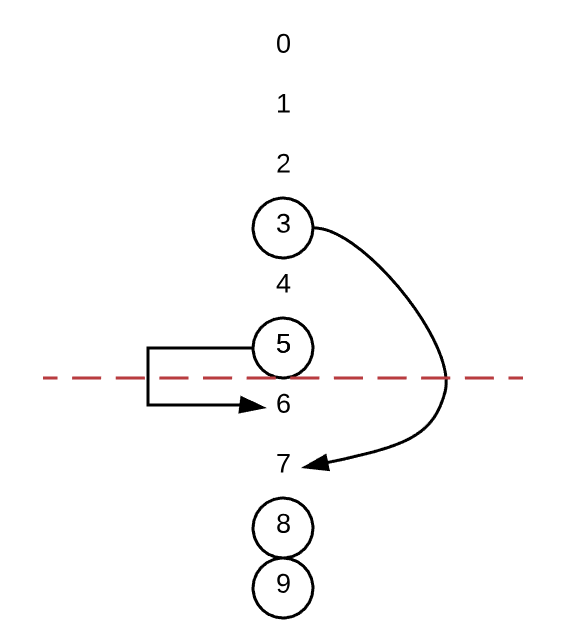
假设 N=10, blacklist=[3, 5, 8, 9]
这一题有点类似 hash 冲突的意思。如果随机访问一个数,这个数正好在黑名单之内,那么就 hash 冲突了,我们就把它映射到另外一个不在黑名单里面的数中。如上图,我们可以将 3,5 重新映射到 7,6 的位置。这样末尾开始的几个数要么是黑名单里面的数,要么就是映射的数字。
hash 表总长度应该为 M = N - len(backlist),然后在 M 的长度中扫描是否有在黑名单中的数,如果有,就代表 hash 冲突了。冲突就把这个数字映射到 (M,N) 这个区间范围内。为了提高效率,可以选择这个区间的头部或者尾部开始映射,我选择的是末尾开始映射。从 (M,N) 这个区间的末尾开始往前找,找黑名单不存在的数,找到了就把 [0,M] 区间内冲突的数字映射到这里来。最后 pick 的时候,只需要查看 map 中是否存在映射关系,如果存在就输出 map 中映射之后的值,如果没有就代表没有冲突,直接输出那个 index 即可。