| title | description | services | author | ms.author | ms.reviewer | ms.service | ms.topic | ms.date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Quickstart: Create an Azure Data Explorer cluster and database |
In this quickstart, you learn how to create an Azure Data Explorer cluster and database, and ingest (load) data. |
data-explorer |
orspod |
v-orspod |
mblythe |
data-explorer |
quickstart |
09/24/2018 |
Azure Data Explorer is a fast and highly scalable data exploration service for log and telemetry data. To use Azure Data Explorer, you first create a cluster, and create one or more databases in that cluster. Then you ingest (load) data into a database so that you can run queries against it. In this quickstart, you create a cluster and a database. In subsequent articles, we show you how to ingest data.
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free Azure account before you begin.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
You create an Azure Data Explorer cluster in an Azure resource group, with a defined set of compute and storage resources.
-
Select the Create a resource button (+) in the upper-left corner of the portal.
-
Search for Azure Data Explorer.
-
Under Azure Data Explorer, at the bottom of the screen, select Create.
-
Enter a unique name for your cluster, select your subscription, and create a resource group named test-resource-group.
-
Fill out the form with the following information.
Setting Suggested value Field description Cluster name A unique cluster name Choose a unique name that identifies your cluster. For example, mytestcluster. The domain name [region].kusto.windows.net is appended to the cluster name you provide. The name can contain only lowercase letters and numbers. It must contain from 3 to 22 characters. Subscription Your subscription Select the Azure subscription that you want to use for your cluster. Resource group test-resource-group Create a new resource group. Location West US Select West US for this quickstart. For a production system, select the region that best meets your needs. Compute specifications D13_v2 Select the lowest price specification for this quickstart. For a production system, select the specification that best meets your needs. -
Select Create to provision the cluster. Provisioning typically takes about ten minutes. Select Notifications on the toolbar to monitor the provisioning process.
-
When the process is complete, select Notifications, then Go to resource.
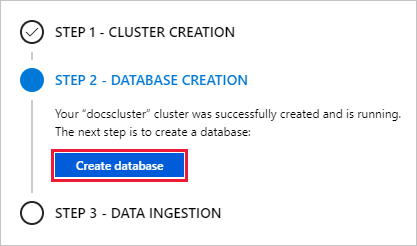
You're now ready for the second step in the process: database creation.
-
On the Overview tab, select Create database.
-
Fill out the form with the following information.
Setting Suggested value Field description Database name TestDatabase The database name must be unique within the cluster. Retention period 3650 The time span for which it's guaranteed that the data is kept available to query. The time span is measured from the time that data is ingested. Cache period 31 The time span for which to keep frequently-queried data available in SSD storage or RAM, rather than in longer-term storage. -
Select Save to create the database. Creation typically takes less than a minute. When the process is complete, you're back on the cluster Overview tab.
Now that you have a cluster and database, you can run queries and commands. You don't have any data in the database yet, but you can still see how the tools work.
-
Under your cluster, select Query.
-
Paste the following command into the query window:
.show databases, then select Run.The result set shows TestDatabase, the only database in the cluster.
-
Paste the following command into the query window:
.show tables, then select that command in the window. Select Run.This command returns an empty result set because you don't have any tables yet. You add a table in the next article in this series.
You can stop and restart a cluster depending on business needs.
-
To stop the cluster, at the top of the Overview tab, select Stop.
When the cluster is stopped, data is not available for queries, and you can't ingest new data.
-
To restart the cluster, at the top of the Overview tab, select Start.
When the cluster is restarted, it takes about ten minutes for it to become available (like when it was originally provisioned). It takes additional time for data to load into the hot cache.
If you plan to follow our other quickstarts and tutorials, keep the resources you created. If not, clean up test-resource-group, to avoid incurring costs.
-
In the Azure portal, select Resource groups on the far left, and then select the resource group you created.
-
Under test-resource-group, select Delete resource group.
-
In the new window, type the name of the resource group to delete (test-resource-group), and then select Delete.
[!div class="nextstepaction"] Quickstart: Ingest data from Event Hub into Azure Data Explorer