| title | description | services | author | ms.author | ms.reviewer | ms.service | ms.custom | ms.topic | ms.date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Tutorial: Analyze Apache Spark data using Power BI in Azure HDInsight |
Use Microsoft Power BI to visualize Apache Spark data stored HDInsight clusters |
hdinsight |
hrasheed-msft |
hrasheed |
jasonh |
hdinsight |
hdinsightactive,mvc |
tutorial |
05/07/2018 |
Learn how to use Microsoft Power BI to visualize data in an Apache Spark cluster in Azure HDInsight.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
[!div class="checklist"]
- Visualize Spark data using Power BI
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin.
- Complete the article Tutorial: Load data and run queries on an Apache Spark cluster in Azure HDInsight.
- Power BI: Power BI Desktop and Power BI trial subscription (optional).
The Jupyter Notebook that you created in the previous tutorial includes code to create an hvac table. This table is based on the CSV file available on all HDInsight Spark clusters at \HdiSamples\HdiSamples\SensorSampleData\hvac\hvac.csv. Use the following procedure to verify the data.
-
From the Jupyter notebook, paste the following code, and then press SHIFT + ENTER. The code verifies the existence of the tables.
%%sql SHOW TABLESThe output looks like:
If you closed the notebook before starting this tutorial,
hvactemptableis cleaned up, so it's not included in the output. Only Hive tables that are stored in the metastore (indicated by False under the isTemporary column) can be accessed from the BI tools. In this tutorial, you connect to the hvac table that you created. -
Paste the following code in an empty cell, and then press SHIFT + ENTER. The code verifies the data in the table.
%%sql SELECT * FROM hvac LIMIT 10The output looks like:
-
From the File menu on the notebook, click Close and Halt. Shut down the notebook to release the resources.
In this section, you use Power BI to create visualizations, reports, and dashboards from the Spark cluster data.
The first steps in working with Spark are to connect to the cluster in Power BI Desktop, load data from the cluster, and create a basic visualization based on that data.
Note
The connector demonstrated in this article is currently in preview. Provide any feedback you have through the Power BI Community site or Power BI Ideas.
-
Open Power BI Desktop.
-
From the Home tab, click Get Data, then More.
-
Enter
Sparkin the search box, select Azure HDInsight Spark, and then click Connect. -
Enter your cluster URL (in the form
mysparkcluster.azurehdinsight.net), select DirectQuery, and then click OK.You can use either data connectivity mode with Spark. If you use DirectQuery, changes are reflected in reports without refreshing the entire dataset. If you import data, you must refresh the data set to see changes. For more information on how and when to use DirectQuery, see Using DirectQuery in Power BI.
-
Enter the HDInsight login account information, then click Connect. The default account name is admin.
-
Select the
hvactable, wait to see a preview of the data, and then click Load.Power BI Desktop has the information it needs to connect to the Spark cluster and load data from the
hvactable. The table and its columns are displayed in the Fields pane. See the following screenshot: -
Visualize the variance between target temperature and actual temperature for each building:
-
In the VISUALIZATIONS pane, select Area Chart.
-
Drag the BuildingID field to Axis, and drag the ActualTemp and TargetTemp fields to Value.
The diagram looks like:
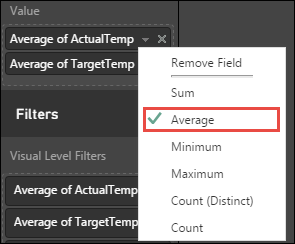
By default the visualization shows the sum for ActualTemp and TargetTemp. Click the down arrow next to ActualTemp and TragetTemp in the Visualizations pane, you can see Sum is selected.
-
Click the down arrows next to ActualTemp and TragetTemp in the Visualizations pane, select Average to get an average of actual and target temperatures for each building.
Your data visualization shall be similar to the one in the screenshot. Move your cursor over the visualization to get tool tips with relevant data.
-
-
Click File then Save, and enter the name
BuildingTemperature.pbixfor the file.
The Power BI service allows you to share reports and dashboards across your organization. In this section, you first publish the dataset and the report. Then, you pin the report to a dashboard. Dashboards are typically used to focus on a subset of data in a report; you have only one visualization in your report, but it's still useful to go through the steps.
-
Open Power BI Desktop.
-
From the Home tab, click Publish.
-
Select a workspace to publish your dataset and report to, then click Select. In the following image, the default My Workspace is selected.
-
After the publishing is succeeded, click Open 'BuildingTemperature.pbix' in Power BI.
-
In the Power BI service, click Enter credentials.
-
Click Edit credentials.
-
Enter the HDInsight login account information, and then click Sign in. The default account name is admin.
-
In the left pane, go to Workspaces > My Workspace > REPORTS, then click BuildingTemperature.
You should also see BuildingTemperature listed under DATASETS in the left pane.
The visual you created in Power BI Desktop is now available in the Power BI service.
-
Hover your cursor over the visualization, and then click the pin icon on the upper right corner.
-
Select "New dashboard", enter the name
Building temperature, then click Pin. -
In the report, click Go to dashboard.
Your visual is pinned to the dashboard - you can add other visuals to the report and pin them to the same dashboard. For more information about reports and dashboards, see Reports in Power BI and Dashboards in Power BI.
In this tutorial, you learned how to:
- Visualize Apache Spark data using Power BI.
Advance to the next article to see how the data you registered in Spark can be pulled into a BI analytics tool such as Power BI.
[!div class="nextstepaction"] Run an Apache Spark streaming job