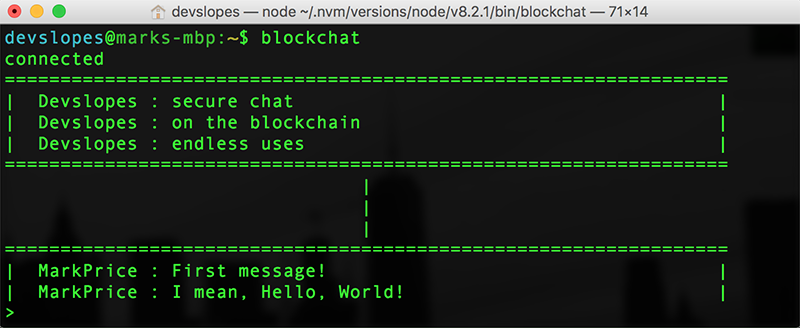
To join a bunch of developer nerds in a global chat simply:
- Install node 8.2+ or use
nvm use 8.2 - Run
npm install blockchat -g - Run
blockchat - Chat
To understand how all this works:
- Look at the source code
- Create your own blockchain following the steps below. Experiment with the code!
This blockchain app uses LotionJS - which is really the world's first Javascript interface for blockchain development. Lotion uses Tendermint for p2p, security, consensus and more.
Lotion & Tendermint use Proof of Stake for consensus (which means no miner nodes needed!).
Get $15 FREE credit for Digital Ocean hosting. Use this code on the billing page: DODEVSLOPES15
You will need hosting if you are to launch your own blockchain.
Fork this repo onto your own Github.
First you will need to create a private/public key pair for each Validator you will have on the blockchain. 3 Validator Lotion nodes will do the trick.
- In
chat-node.jssetdevMode: truein the Lotion Options. This will wipe all blockchain data each time the app is run.
let opts = {
devMode: true,
initialState: {
messages: [
{ sender: 'Devslopes', message: 'secure chat' },
{ sender: 'Devslopes', message: 'on the blockchain' },
{ sender: 'Devslopes', message: 'endless uses' }
]
}
}
- From the terminal run
node chat-node.jsyou will see output similar to this (with different values):
{
tendermintPort: 44965,
abciPort: 42071,
txServerPort: 3000,
GCI: '21abc89268e03ce032f0c6ff29bb387da1e2682976934a0bb5d0d42bb55dcd6c',
p2pPort: 43845,
lotionPath: '/.lotion/networks/7fff170ea744955c7055dc540d3f68431fd7d2b50b3ca9729c2b2be00a03046e173989453',
genesisPath: '/.lotion/networks/7fff170ea744955c7055dc540d3f68431fd7d2b50b3ca9729c2b2be00a03046e173989453/genesis.json',
lite: false
}
- Copy the
genesis.jsonfile from the path above and paste it in the home directory of this repo. iemv ~/.lotion/networks/7fff170ea744955c7055dc540d3f68431fd7d2b50b3ca9729c2b2be00a03046e173989453/genesis.json ./
Now you have a genesis file for your app. But it only has one validator in it.
- Next copy the validator file in the same way to this directory but rename it with a 1 ie
mv ~/.lotion/networks/7fff170ea744955c7055dc540d3f68431fd7d2b50b3ca9729c2b2be00a03046e173989453/priv_validator.json ./priv_validator1.json
We need to copy the priv_validator to our repo so we can add these to the genesis as well as use them for our validator servers. Eventually we will delete them from this repo.
-
Run
node chat-node.jsto generate a new genesis andpriv-validator.json- this time we don't want the new genesis file. But we DO want thepriv_validator.json- so copy it from the new app path like we did before and this time name itpriv_validator2.json -
Run
node chat-node.jsagain and repeat the process to createpriv_validator3.json
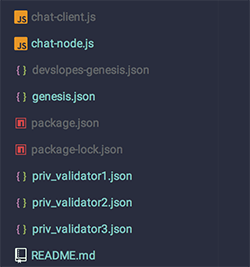
If you did these steps correctly your project folder now looks similar to this:
- Grab the public key data from each validator json file and put it in the
genesis.jsonfile in thevalidatorsarray. It might look similar to:
{
"app_hash": "7fff170ea744955c7055dc540d3f68431fd7d2b50b3ca9729c2b2be00a03046e173989453",
"chain_id": "mycoolblockchainapp",
"genesis_time": "0001-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"validators": [
{
"name": "",
"power": 10,
"pub_key": {
"data": "C2BFD789B00FC0D42A4FC53EF31AB324912E262D51C4044161A3200D10FDD1F6",
"type": "ed25519"
}
},
{
"name": "",
"power": 10,
"pub_key": {
"data": "A2BFR789B00FC0D42A4FC53EF31AB324912E362D51C4044161A3200D10FDD1F6",
"type": "ed25519"
}
},
{
"name": "",
"power": 10,
"pub_key": {
"data": "L1BFD789B00FC0D42A4FC53EF31AB324812E262D51C4044161A3200D10FDD1F6",
"type": "ed25519"
}
}
]
}
-
Now that we have private keys for 3 nodes/machines, and we have our genesis file, we have everything we need to start a blockchain network in a realistic scenario.
-
Make sure the code is bringing in the genesis file in the
chat-node.js
let genesis = require.resolve('./genesis.json');
This tells lotion who our validators are and information about our app.
- You will need a hosting service like
AWSorDigital Oceanthat can run the Lotion app with all the proper ports/etc. I recommend Digital Ocean.
Create a new Droplet (and don't forget to use the free credits above). I usually choose a One Click App and pick Docker - you should just make sure it has Node on it.
Add your SSH keys to Digital Ocean or create a root password. If you need help with that see here.
- SSH into your new Digital Ocean Droplet. Clone this repository: https://github.com/devslopes/blockchat.git
By default Digital Ocean exposes all ports. If you have any issues, just make sure that ports 46656 and 46657 are exposed to the outside world.
-
Copy the data from one of your
priv_validator.jsonfiles into the the repo you just clone in a file namedpriv_validator.json. Again make sure this file is never added to version control. -
Run your chat-node via
node chat-node.js. If you are creating 3 validators (or more) this will look frozen like it isn't doing anything. That is because 2/3 of all validators must be online before it starts writing blocks. Once your other validators are online you would see output in the console here. Also note that you need a node process manager so the app can run all the time. I recommend pm2.
Once installed you can do something like pm2 start node-chat.js --name blockchat
-
Create two more droplets on Digital Ocean OR figure out how to work with Docker, or Docker Swarm (it isn't overly easy - but can save you money) so you can have 3 containers in the same droplet. Clone repos on those machines and add the associated private keys in the
priv_validator.jsonfiles -
Once at least 2/3 of the validators listed in
genesis.jsonare online your blockchain validator nodes will start writing blocks (and logging output)
There are a handful of things that could go wrong. Here are a few to account for:
- Don't screw up your private keys and genesis.json - each validator must have a unique private key, and then must provide the public key and that key must be in the genesis.json - if you accidentally put two of the same public key in the genesis or if a key exists in genesis that is not in a private key on the server things wont work
- If you ever change ANYTHING in genesis.json the app can break. If changes need to be made to genesis.json after your validators are live, just make sure that your validators update the source code asap.
- Try not to use GCI to connect to a blockchain - they change often. If connecting as a light client insert the peers and the genesis instead
- It's best to test with ONE validator first, then add more - that way you can solve problems along the way.
- When developing, do so with
devMode: trueso it deletes the blockchain data each run - otherwise you'll have bugs while making so many changes to the blockchain