As part of an on-going project, I need to find a way to map value of an arbitrary layer back to its previous layer. Initially, it is meant to apply on a general architecture, Fully Connected Neural Network (NN). However, reconducting a well-known experiment seems to be a more reasonble approach to me. Therefore, I choose Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), one of two popular variants of NN, to test on. To be precise, I would call it Deconvolutional Neural Network (DeCNN) for this is a CNN integrated with an additional reversed process.
At first sight, one could treat NN as a simplified version of biological neurons, which consists of active units and bridges connect them to transmit signal. Somehow, for a particular task, with a given sufficient amount of samples, the neurons could automatically extract essential pattern through learning process - interaction between set of neurons.
Formally, a NN is defined by layers: input layers, hidden layers, and output layers. Within each layer is a set of unjoined nodes (neurons). The different in naming based on the data a layer has to handle. Take input layer for example, it could be an image vectoried into 2-dimension vector in grayscale form or higher dimensions as in RGB. The output layer on the other hand, is a prediction of label to assign to input image. Conventionally, it is a probability distribution vector over all possible labels. Last but not least, the hidden layer is where all learning activities happen, which has no desirable explanations so far and usually considered as a black box. These layers connect to each other via weights (bridges), with each end is a node in layer.
[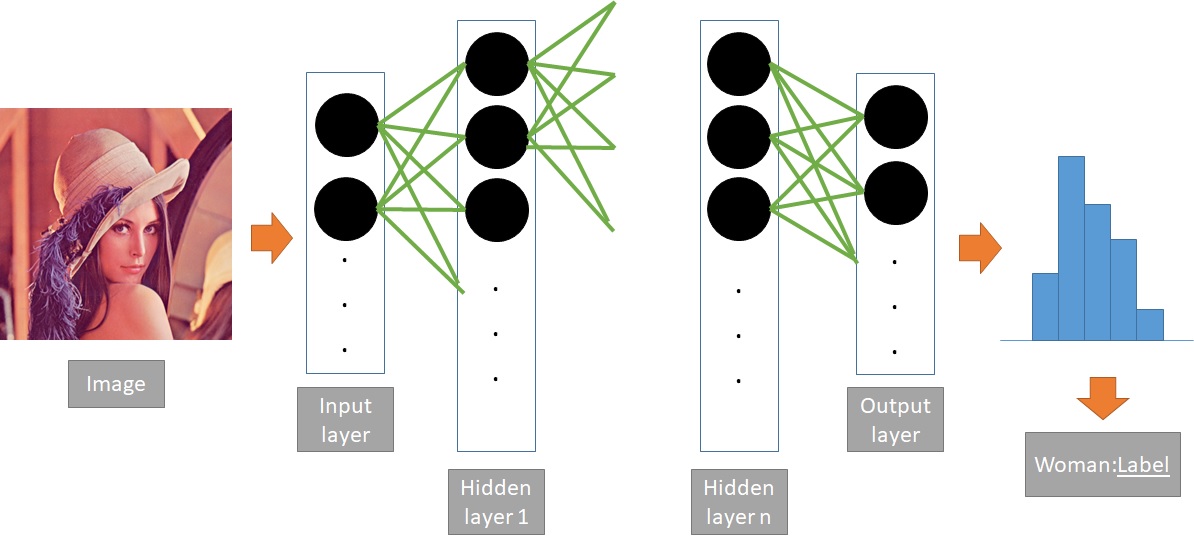 ]("General Architecture of Neural Network") ]("General Architecture of Neural Network") |
|---|
| General Architecture of Neural Network |
Despite the lack of understanding, one can turn NN into a strong classifier with Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD), an approximation method to minimize the number of mismatches between prediction and groundtruth. Thanks to this invention, most of the research nowadays mainly focus on modifying network's architecture or loss function. This algorithm consists of 2 phases: forward and backword. While forward phase spreads input value through the whole network until the output layer, backward phase calculates the loss in prediction and use it to accumulatively updates weights. It keeps iterating until a desired condition is met, for example number of loops or a specific threshold of loss. Note that most of all operations execute here are simply matrix multiplication (linear), for instance
and activation function (non-linear), such as
Take over the idea of NN, CNN contributes 2 things:
- address the problem of storing a vast amount of weights in the original model, replace with small size filters (or kernels).
- divide architecture into 2 sub-components: feature extraction and classifiers. Previously, features are cherry-picked before feeding into the NN, whereas now we could leave this job for CNN handles itself. This innovative idea entails two new operations on filters: convolution and pooling.
To put it p
tensorflow This report tensorflow not required
Though obvious. deconvo
Question:
- Matrix multiplication
Extension:
Feedback: [email protected]