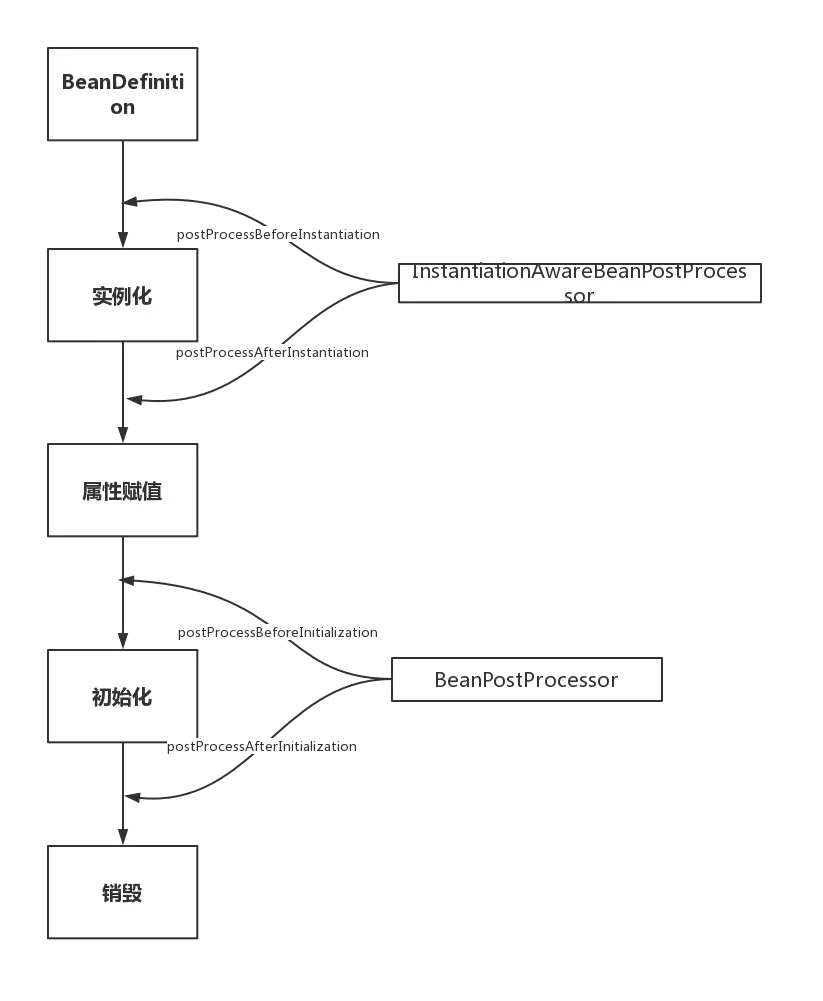
-
实例化 Instantiation
-
属性赋值 Populate
-
BeanNameAware
-
BeanFactoryAware, ApplicationContextAware
-
BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization
-
InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
-
@PostConstruct
-
初始化 Initialization
-
BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization
-
DisposableBean
-
@PreDestroy
-
销毁 Destruction
ConfigurableApplicationContext#close()((AbstractApplicationContext)context).registerShutdownHook();此代码将注册 jvm系统钩子Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(...)
主线生命周期参考源码
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
doCreateBean
createBean
在 xml 配置中这两个注解分别对应 init-method, destory-method
Constructor > @Autowired > @PostConstruct
具体参考 Spring Bean 生命周期 源码参考部分
@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED)
- REQUIRED : 如果有事务则加入事务,如果没有事务,则创建一个新的(默认值)
- NOT_SUPPORTED : Spring不为当前方法开启事务,相当于没有事务
- REQUIRES_NEW : 不管是否存在事务,都创建一个新的事务,原来的方法挂起,新的方法执行完毕后,继续执行老的事务
- MANDATORY : 必须在一个已有的事务中执行,否则报错
- NEVER : 必须在一个没有的事务中执行,否则报错
- SUPPORTS : 如果其他bean调用这个方法时,其他bean声明了事务,则就用这个事务,如果没有声明事务,那就不用事务
- NESTED : 如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行。如果当前没有事务,则执行与REQUIRED类似的操作
@Transactional(isolation=Isolation.DEFAULT)
- ISOLOCATION_DEFAULT: 数据库默认级别。 ORACLE(读已提交) MySQL(可重复读)
- ISOLOCATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED: 允许读取未提交的读, 可能导致脏读,不可重复读,幻读
- ISOLOCATION_READ_COMMITTED: 允许读取已提交的读,可能导致不可重复读,幻读
- ISOLOCATION_REPEATABLE_READ : 不能能更新另一个事务修改单尚未提交(回滚)的数据,可能引起幻读
- ISOLOCATION_SERIALIZABLE: 序列执行效率低
@Service
@Scope(ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON)
public class MilestoneServiceImpl implements MilestoneService {
}-
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory#SCOPE_PROTOTYPE
唯一bean实例,Spring中的bean默认都是单例的。
-
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory#SCOPE_SINGLETON
每次请求都会创建一个新的bean实例。
-
org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext#SCOPE_REQUEST
每一次HTTP请求都会产生一个新的bean,该bean仅在当前HTTP request内有效
-
org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext#SCOPE_SESSION
每一次HTTP请求都会产生一个新的bean,该bean仅在当前HTTP session内有效。
默认单例情况下,有可能发生线程安全问题。当多个线程操作同一个对象的时候,对这个对象的非静态成员变量的写操作会存在线程安全问题。
- 在bean对象中尽量避免定义可变的成员变量
- 使用 ThreadLocal。Spring 源码中多种上下文都是这么使用的
- 工厂设计模式:Spring使用工厂模式通过BeanFactory和ApplicationContext创建bean对象。
- 代理设计模式:Spring AOP功能的实现。
- 单例设计模式:Spring中的bean默认都是单例的。
- 模板方法模式:Spring Security中的AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider#authenticate
- 包装器设计模式:我们的项目需要连接多个数据库,而且不同的客户在每次访问中根据需要会去访问不同的数据库。这种模式让我们可以根据客户的需求能够动态切换不同的数据源。
- 观察者模式:定义对象间的一种一对多的依赖关系,当一个对象的状态发生改变时,所有依赖于它的对象都得到通知并被自动更新。spring中Observer模式常用的地方是listener的实现。如ApplicationListener。
- 适配器模式:Spring AOP的增强或通知(Advice)使用到了适配器模式、Spring MVC中也是用到了适配器模式适配Controller。
循环依赖:类A 依赖 类B ,类B 又依赖 类A
关闭循环依赖:
@Component
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
((AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory) beanFactory).setAllowCircularReferences(false);
}
}无法解决的循环依赖
一般可以处理 setter 注入或 属性 @Autowired
无法处理构造器注入 和 @Scope(ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE)
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.java
// 一级缓存:缓存已经初始化完成,可以暴露的 bean 对象,已经完成初始化,属性设置
/** Cache of singleton objects: bean name to bean instance. */
private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
// 三级缓存:存储回调方法,可以调用回调方法 getObject 获取正在创建 bean 对象
/** Cache of singleton factories: bean name to ObjectFactory. */
private final Map<String, ObjectFactory<?>> singletonFactories = new HashMap<>(16);
// 二级缓存:缓存的是已经完成初始化但还没设置属性的 bean 对象,正在创建中
/** Cache of early singleton objects: bean name to bean instance. */
private final Map<String, Object> earlySingletonObjects = new HashMap<>(16);- 使用 context.getBean(A.class),旨在获取容器内的单例A
- 先从一级缓存 singletonObjects 中去获取。(如果获取到就直接return)
- 如果获取不到或者对象正在创建中(isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation()),那就再从二级缓存 earlySingletonObjects 中获取。(如果获取到就直接return)
- 如果还是获取不到,且允许 singletonFactories(allowEarlyReference=true)通过 getObject() 获取。就从三级缓存 singletonFactory.getObject() 获取。(如果获取到了就从 singletonFactories 中移除,并且放进 earlySingletonObjects 。其实也就是从三级缓存移动(是剪切、不是复制哦~)到了二级缓存)
- 显然初次获取A是不存在的,因此走A的创建之路
- 实例化A,放入三级缓存
- 初始化A,设置属性,发现有 @Autowired B类
- 依旧去三个缓存中查找,显然还是没有,走B的创建之路
- 实例化B,放入三级缓存
- 初始化B,设置属性,发现有 @Autowired A类
- 缓存中查找,在三级缓存中发现,获取完在三级缓存中删除,保存到二级缓存中
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}- B初始化成功,删除二级三级缓存,保存到一级中
protected void addSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
this.singletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
}
}- B实例已经成功返回了,因此最终A也初始化成功
- B持有的已经是初始化完成的A,A持有的也是初始化完成的B
关键源码位置,结合官网文档效果更好
- 授权端点
/oauth/authorize
org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.endpoint.AuthorizationEndpoint- 授权确认端点
/oauth/confirm_access
org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.endpoint.WhitelabelApprovalEndpoint客户端是否自动确认授权取决于 org.springframework.security.oauth2.providerClientDetails#isAutoApprove
- 授权失败端点
/oauth/error
org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.endpoint.WhitelabelErrorEndpoint- 自定义上面两个URL
org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configuration.AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfiguration#authorizationEndpoint
org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configurers.AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer#pathMapping- 获得令牌端点
/oauth/token
org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.endpoint.TokenEndpoint- 生产 Token
org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.token.AbstractTokenGranter返回 JWT具体算法和公钥,如果没有使用 KeyPair 直接用 SigningKey 将直接这个 SigningKey 这是很危险的
- 获得令牌签名(公钥)端点
/oauth/token_key
org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.endpoint.TokenKeyEndpoint- 验证解析令牌端点
/oauth/check_token
org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.endpoint.CheckTokenEndpoint官方文档介绍,主要考虑授权服务与资源服务分开的情况,RemoteTokenServices 它将允许资源服务器通过HTTP请求来解码令牌(也就是授权服务的 /oauth/check_token 端点)。如果你的资源服务没有太大的访问量的话,那么使用RemoteTokenServices 将会很方便(所有受保护的资源请求都将请求一次授权服务用以检验token值),或者你可以通过缓存来保存每一个token验证的结果
- 验证流程
org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.authentication.OAuth2AuthenticationProcessingFilter从 header(Bearer Token Header) 、query(access_token) 里获取 token 进行认证处理
- 默认处理
org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.error.DefaultWebResponseExceptionTranslator- Spring MVC 处理
@ExceptionHandlerHttpMessageConverters