CodeChecker is a static analysis infrastructure built on the LLVM/Clang
Static Analyzer toolchain, alternative tool
for scan-build in a Linux
or macOS (OS X) development environment.
- WEB GUI User Guide
- Table of Contents
- Products
- Runs and history events
- Reports
- Report details
- Statistics
The product system allows a single CodeChecker server to serve multiple
separate result databases, named products, under the same IP address and
authentication domain. Each product can be configured to use a separate
database and the access control can be configured separately for each product
by product administrators.
Most of the time a product represents a single GIT repository. For example we can create separate CodeChecker products for postgresql, curl, bitcoin or openssl repositories.
Note: comparison and statistics features can be used inside one product and not between multiple products.
In the product list table you can see the following information:
Product name: display name of the product.Confidentiality classification: The confidentiality category this product belongs to.Description: short description of the product.Administrator names: product admins have the right to allow access for individual people or LDAP groups.Number of runs: number of runs in the product.Latest store to the product: date of the latest run storage.Run store in progress: show run names if a storage is in progress.Action buttons(only for ADMINS): action buttons to edit and remove products.
Note: if you don't have permission for a product and you see the following message, ask permission from a product admin:
Click to the NEW PRODUCT button above the product list table, then fill the
form presented. The values that need to be filled here are the same as the
arguments for CodeChecker cmd products add.
NOTE: only users with Super Users access can add a new product.
If the product creation is successful, the window will disappear and the product will appear in the product list.
Review status change can be disabled on the WEB UI to force programmers to use inline source code comments. This can be configured on the product editing window by administrators of a product.
The confidentiality level of the product can be set here. There are three options:
- Confidential classified
- Internal classified
- Open classified
Editing a product configuration is done through the pencil icon which can be found in the latest Actions column of the product list table.
Products can be deleted by clicking on the red trash bin in the Actions column of the product list table. This way the product is only unmounted from the server (losing access control data and connection), but no analysis results are deleted. Database needs to be deleted separately.
- Server-wide permissions can be edited by clicking EDIT GLOBAL PERMISSION
button above the product list page. Only users with
Super Usersaccess can edit global permissions. - Product-level permissions can be edited by clicking the edit icon (blue pencil) for the product you want to configure the permissions.
The two lists show the users and groups known to the system - if a tick is present in its row, the given user or group has the permission directly granted. (Users who only have a certain permission through permission inheritance are not shown with a tick.)
Only the permissions you have rights to manage are shown.
You can edit multiple permissions opening the window only once. Simply tick or untick the users/groups you want to give the permission to or revoke from them. Clicking SAVE will save the changes to the database.
There is an option to set a global notification text, that will show on top of every page below the header bar.
You can edit this alert on the products page with EDIT ANNOUNCEMENT button,
but Super User permissions are necessary.
You can remove the current notification by saving an empty text.
A run represents subsequent analysis activities for the same source code with the same analysis settings (checker configurations). We are storing analysis results to a run within a product:
CodeChecker store \
--name master_xerces \
--url https://my.codechecker.server.com/xerces
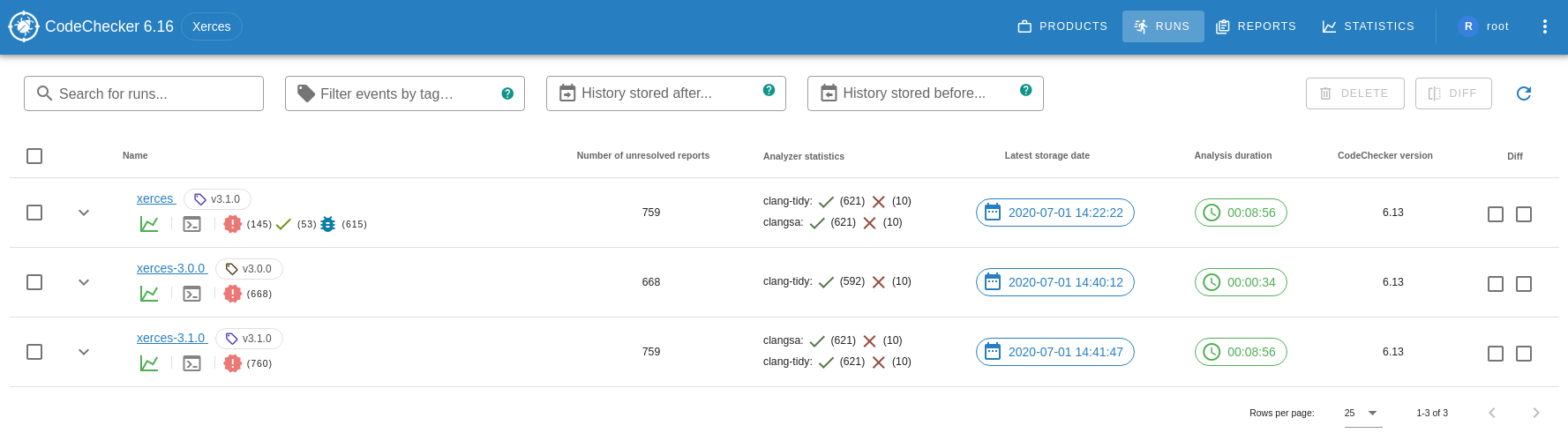
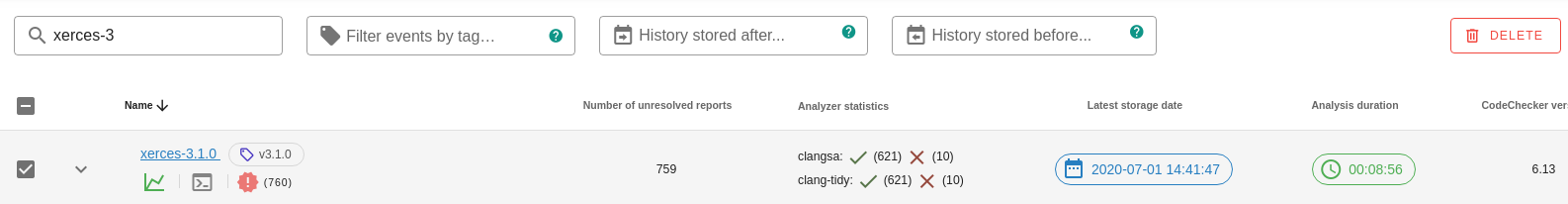
./reportsThis page contains the analysis runs available on the server under the selected product.
Each run has the following fields/columns:
Delete: in the first column of the run list table you can select multiple runs which will be removed by clicking on the DELETE button. For more information see.Unique namewhich identifies a run. If an already existing run name is used during the storage, the run will be updated: a new history event will be created for the run and the detection status will be changed for each report.Version tag(optional): a unique identifier for this individual store of results in the run's history.Description(optional): a custom textual description to be shown alongside the run. You can find more information how to see the description here.Check commandwhich was used to analyze your project. You can find more information how to see the check command here.Detection status counts: show the number of reports distributed by detection statuses.
Number of unresolved reports: number of non unique reports excluding Resolved, False positive and Intentional reports.Analyzer statistics: information about the analysis. You can find more information how to see the analysis statistics here.Latest storage date: latest storage/update date of the run.Analysis duration: the length of the analysis.CodeChecker versionwhich was used during the analysis.Diff: in this column you can select two runs (baseline and compared to) which will be compared to each other by click on the DIFF button. For more information see.
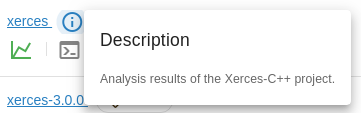
Description is a custom textual description to be shown alongside the run and
given by the CodeChecker store command:
CodeChecker store \
--name xerces \
--description "Analysis results of the Xerces-C++ project." \
--url https://my.codechecker.server.com/xerces \
./reportsClick on the [i] button beside the run name to show the description.
Check/Analyze command is the command which was used to analyze your project:
CodeChecker analyze \
-o ./reports \
-e sensitive \
./compilation_database.jsonClick on the console button under the run name to show the check command.
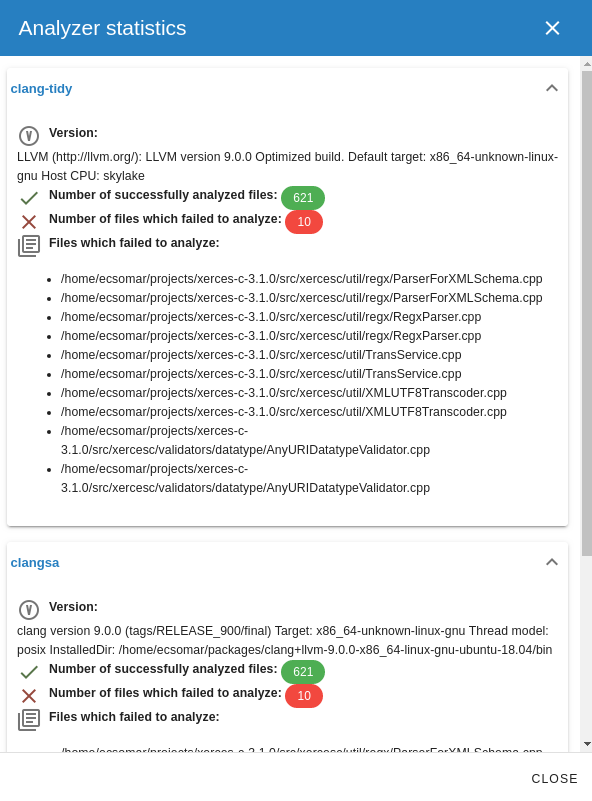
Analyzer statistics show the following information for each analyzer (Clang Static Analyzer, Clang Tidy):
- Analyzer version.
- Number of successfully analyzed files.
- Number of files which failed to analyze.
- List of files which failed to analyze.
Click on the Analyzer statistics column to show analyzer statistics for a
run.

Note that analysis failure may come with incomplete results. Possible reasons of analysis failure are gcc/clang incompatibility (thus compilation error), analyzer runtime crash, etc.
You can filter runs by run name using the input box above the run list table. The filter is case insensitive and does a substring matching. If we start typing some phrase in this input box, the list are being filtered automatically.
NOTE:
- other filters in beside the run name filter can be used to filter run history events.
- filters will be saved in the URL query parameter list.
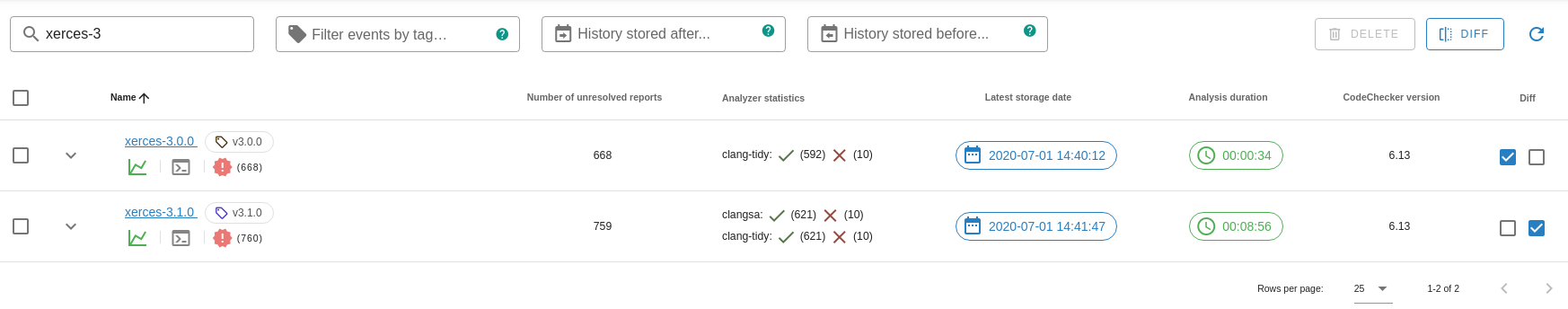
Calculates the difference between two analyses of the project, showing which reports have been fixed and which are newly introduced.
To compare analysis results you have to do the following:
- select BASELINE* runs with the first checkbox in the Diff column of the run list table.
- select COMPARE TO* runs with the second checkbox in the Diff column of the run list table.
- click on the
Diffbutton above the run list table.
It is possible to change the order of the runs by clicking on a cell at the header of the run list table. For example, you can sort the run list by the storage date or the run name.
You can delete multiple runs by selecting them with the checkboxes in the first
column of the run list table and clicking on the DELETE button above the run
list table. It will remove the run and all related data from the database.
IMPORTANT: be careful when you delete a run because this operation can not be undone.
On every run storage event a history event is created for the run. You can
see the history events for a run if you click to the expand arrow (v icon)
beside the run name column.
You will see the following information for each history event:
Storage datewhen the run was stored to the server.User namewho performed theCodeChecker storeoperation.Show statisticsbutton which can be used to show the statistics for this history event.Check commandwhich was used to analyze your project. You can click to the console style button (>_icon) to see the actual check command of the history event.CodeChecker versionwhich was used during the analysis.Analyzer statistics: information about the analysis. You can click to this section to see the details.
Calculates difference between two analyses of the same run storage, showing which reports have been fixed and which are newly introduced.
To compare analysis history events you have to do the following:
- select BASELINE* runs with the first checkbox in the Diff column of the run list table for a history event.
- select COMPARE TO* runs with the second checkbox in the Diff column of the run list table for a history event.
- click on the
Diffbutton above the run list table.
You can filter run history events with the tag name and storage date input boxes above the run list table.
Note: the filters will be saved in the URL query parameter list.
If you select a run at the list of runs view, you get to this page. This page lists the analysis result for the given run.
Every report has the following fields:
Unique report identifier(repot hash). You can find more information how these hashes are generated here.File path: file path where the report is found.Line and column numbersof the report where the bug is.Checker namewhich found the report during the analysis.Checker message: description about the report.Analyzer namewhich found the problem during the analysis.SeverityBug path length: length of the bug path. Reports with longer bug path are more difficult to understand.Latest review statusLatest detection status. This column is visible only when uniqueing is disabled.Detection date: the storage date when the report was stored to the server for the first time. This field is visible only when you hover your mouse over the Detection status icon.Fix date: storage date when the report is dissapeared from a run update. This field is visible only when you hover your mouse over the Detection status icon.
Reports can be assigned a review status of the following values:
- Unreviewed (default): Nobody has seen this report.
- Confirmed: This is really a bug.
- False positive: This is not a bug. Before marking a bug false positive you should read the false positive how to.
- Intentional: This report is a bug but we don't want to fix it.
Review status can be set on the GUI or by using source code comments (codechecker_false_positive, codechecker_confirmed, etc.)
Review status set in source comments are applied on the individual report instances, while review status set in the GUI are added as Review Status Rules connected to report hashes.
So when you chang the review status of a report in the GUI, it will change the review status in all reports with the same hash in all runs. Reports stored in the future with the same hash will also get the same review status.
So once you set the review status in the GUI, there is no need to set the same review status again in other runs.
Note: source code comment is stronger and can overwrite the value in the database.
Review status values added in the WEB GUI are stored as Review Status Rules
and can be managed in the Configuration/ReviewStatusRules tab.

The detection status is the state of a bug report in a run.
- The detection status of a report is connected to the report ID. It means that every report has a separate detection status.
- It will be calculated automatically by the server on run storage events based on the reports in the last storage and the current storage.
- Changing the review status by using source code comments will not affect the detection status change.
When storing the results of a run from scratch then each report has detection status New. When the reports stored again with the same run name then the detection status can change to one of the following options:
- Resolved: when the bug report can't be found after the subsequent storage.
- Unresolved: when the bug report is still among the results after the subsequent storage.
- Reopened: when a resolved bug appears again.
- Off: were reported by a checker that is switched off during the last analysis which results were stored.
- Unavailable: were reported by a checker that does not exists anymore because it was removed or renamed.
The diagram below shows the detection status transition which may happen when storing results to the server. For example if the detection status of a report in the database is New the server will change it to Unresolved, Resolved, Off or Unavailable based on the conditions above.
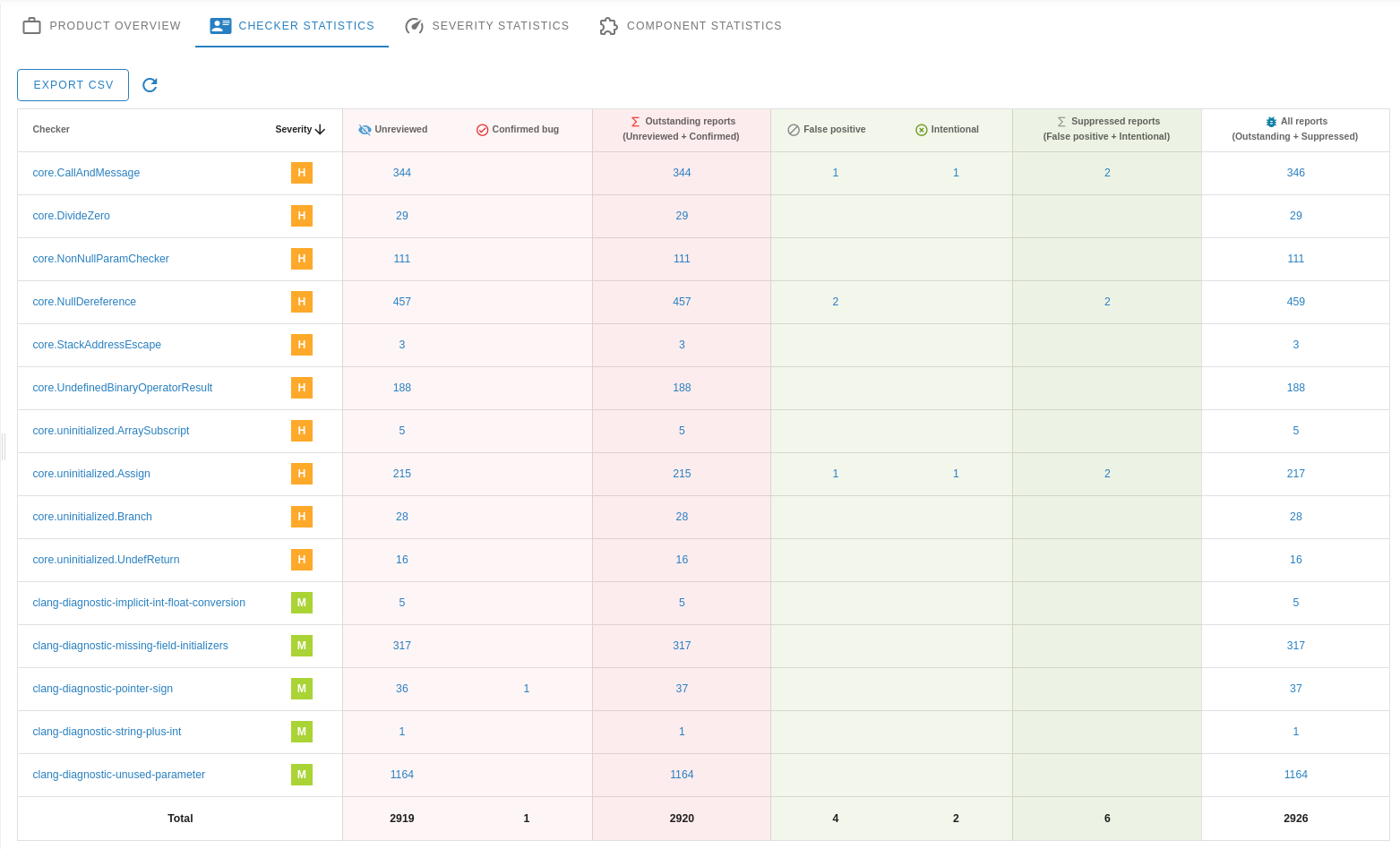
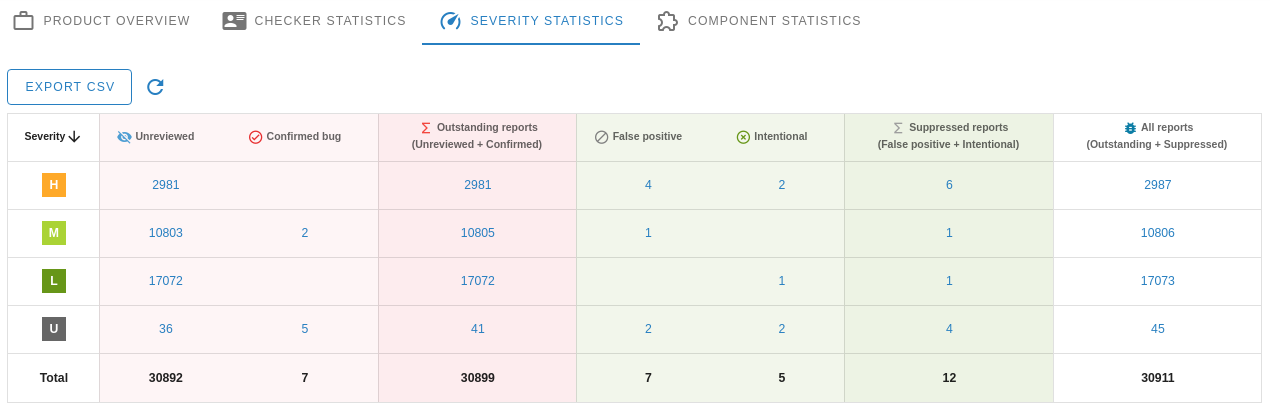
We are mapping checker names to different severity levels:
- Critical: clang-diagnostic-error (compilation error and the analysis was not successful).
- High: core.DivideZero, core.NullDereference, cplusplus.NewDelete, etc.
- Medium: unix.Malloc, core.uninitialized.Assign, etc.
- Low deadcode.DeadStores, misc-unused-parameters, etc.
- Style: modernize-raw-string-literal, modernize-use-auto, etc.
- Unspecified: android-cloexec-dup, etc.
When opening the Reports list view on the left sidebar you will see the following:
The following filter options are available:
Unique reports- You can uniqueing the reports by checking this. For more information click here.- Baseline
Run / Tag Filter- You can select one or more run names with tags. The result list is restricted on the findings in these runs/tags. By selecting a specific run in the runs view this field is filled by default. When runs are stored in update mode (i.e. on the same run name), then the specific runs can be tagged in order to be easier to identify them. By this field you can also select the reports found during a specific run event. For this you can use the cogwheel button beside each run after hovering on the run to specify a tag.Outstanding reports on a given date- Filter reports that were DETECTED BEFORE the given date and NOT FIXED BEFORE the given date.
- Compare to
Run / Tag Filter- Here you can select multiple runs / tags which you want to compare against the baseline filter set.Outstanding reports on a given date- Here you can select date which you want to compare against the baseline filter set.Diff type- Here you can set if you'd like to see the reports which appear only in the Baseline, Compare to or both.
File path: You can choose a set of files to restrict the list of bug reports.Checker name- If you are interested in specific type of bugs then here you can choose them.Severity- The nature of the reports is sorted in different severity levels. For example, a division by zero or a null pointer dereference is more serious than an unused variable. By this field you can select the reports on the given severity levels.Latest Review Status- You can select the reports with the given review status to check only False positive, Unreviewed, etc. reports.Latest Detection Status- You can select the reports with the given detection status to check only Unresolved, Resolved, etc. reports.Analyzer name- If you are interested in specific type of reports which were detected by an analyzer (Clang Tidy, CppCheck etc.) then here you can choose them.Source component- Here you can select multiple source components which are named collections of directories specified as directory filter.Checker message- The static analysis tools provide a message to indicate the reason of a specific bug. This message is also filterable.- Dates
Detection date- Filter reports that were detected between the given interval.Fix date- Filter reports that were fixed between the given interval.
Report hash- Every report has a unique (hash) identifier called Report Identifier which can be filtered by using this input box.Bug path length- A bug path length interval can restrict the list of displayed bug reports. In these fields you can choose the minimum and maximum values of bug path length.
Every filter is collapsed by default to save more space in the UI. To expand
the filter and see the selected filter items you can click on the down arrow
(v icon) beside each filter name.
Every report has a detection date and a fix date.
Detection date: the storage date when the report was stored to the server for the first time.Fix date: storage date when the report is dissapeared from a run update.
Available date filters:
Detection date: get results which were detected between the given dates.Fix date: get results which were fixed between the given dates.Outstanding reports on a given date: get results which were DETECTED BEFORE the given date and NOT FIXED BEFORE the given date.
At Run / Tag filter, File path, Checker message and Report hash filters
you can filter the results by using the * quantifiers which matches any
number of characters (zero or more). So if you have for example run_1_a_name,
run_2_b_name, run_2_c_name, run_3_d_name then run_2* will select
run_2_b_name and run_2_c_name.
When you select a filter option on any field then a number indicates on the right side of the option the number of reports which belong to that specific option. If the report count could not be determined this value will be N/A.
Filtered reports can be removed by clicking on the REMOVE FILTERED REPORS button at the bottom of the filter bar.
!!!WARNING!!!: once you have removed filtered reports it can not be undone. Please make sure that you want to remove all filtered results before clicking on this button.
Filter options can be cleared separately by clicking on the trash icon beside a filter or all filters can be cleared by using CLEAR ALL FILTERS button at the top of the filter bar.
At the top of the filter panel there is a Unique reports checkbox. This
narrows the report list to unique bug (group findings that have the same
Report Identifier (report hash) within or across multiple runs).
The same bug may appear several times if it is found on different control
paths, i.e. through different function calls or in multiple runs. By checking
Unique reports a report appears only once even if it is found on several
paths.
Reports can be expanded to see all the reports with the same hash by using the
expand arrow (v icon) beside the report hash.
Note: detection status is not shown in this view and only the file name is shown because same report may have different detection statuses or can be found under different file paths.
In compare mode you can calculate the difference between multiple analyses of the project, showing which reports have been fixed and which are newly introduced or which can be found in all runs.
At the Baseline filter section you can select the run names / tags against which you want to check the difference.
At the Compare to filter section you can select the run names / tags which you want to compare against the Baseline runs and run tags.
You can also use the Outstanding report on a given date filter to compare
reports by dates.
By Diff type field it can be chosen whether reports Only in Baseline, Only in Compare to or Both in Baseline and Compare to should be shown. At each option the number of reports is displayed for the given category. Note, that the number of Both in Baseline and Compare to plus the number of Only in Compare to add up the number of Compare to, but this addition may not work for the number of Baseline reports. This behavior can be demonstrated by the following example. Suppose that two analyses are stored with the following reports. Some reports are occurring multiple times in a run. These can be made unique by Unique reports tick-box.
| Baseline | Compare to |
|---|---|
report_hash_1 |
|
report_hash_1 |
|
report_hash_2 |
report_hash_2 |
report_hash_2 |
report_hash_2 |
report_hash_2 |
report_hash_2 |
report_hash_2 |
|
report_hash_3 |
The multiplicity of comparison categories:
- Only in Baseline:
report_hash_1(2x) - Only in Compare to:
report_hash_3(1x) - Both in Baseline and Compare to:
report_hash_2(4x)
Note that report_hash_2 is displayed 4 times like in Compare to and not
3 times like in Baseline.
Source components are named collections of directory filters which can be used to filter run results (reports) by multiple file paths. Source components can be managed only by administrators after clicking on the pencil icon at the Source component filter.
A pop-up window will be opened where you can add, edit or remove existing source components.
Each line should begin with a + or a -, followed by a path glob pattern:
+: ONLY results from the matching file paths will be listed.-: results from the matching file paths will not be listed.
For more information see.
You can use cleanup plans to track progress of reports in your product. Clenup plans can be managed only by administrators after clicking on the pencil icon at the Cleanup plans filter.
A pop-up window will be opened where you can add, edit, close or remove existing cleanup plans.
You can assign multiple reports to a cleanup plan on the Reports view. For this you have to select at least one report by using check boxes on the first column of the report list table.
After reports are selected the Set cleanup plan above the reports table will be active and you can select a cleanup plan here by clicking on the cleanup plan name.
You can remove reports from a cleanup plan the same way by clicking on the cleanup plan name.
Notes:
- You can select all reports on the current page by using the checkbox in the first column of the header bar.
- If multiple reports are selected and at least one report can be found in a cleanup plan but not all of them, after clicking on the Set cleanup plan button beside the cleanup plan a minus sign (-) will be shown. Clicking on the cleanup plan name in this case will assign every selected report to the cleanup.
You can also assign current report to a cleanup plan on the Report detail
view:

Report Navigation Tree shows the found reports at the currently opened file. The reports are grouped by the severity level. You can navigate between them by clicking on a node in the tree.
Button Pane contains several items which help you to change or get some property of the currently opened report.
REPORT INFO button shows detailed information about the currently opened
report such as Report ID, Run name, Detection / Fix date etc.
SHOW DOCUMENTATION button shows the documentation of the actual checker which
identified the currently opened report.
Reports can be assigned a review status of Unreviewed, Confirmed, False positive, Intentional along with an optional comment on why this status was applied.
It can be changed on the GUI or by using source code comments (codechecker_false_positive, codechecker_confirmed, etc.)
We can change the review status on the GUI from the default Unreviewed option to something else in the report details view above the file view.
If you changed the review status, you can optionally explain the reason why
you changed it.

If somebody has already changed the review status from the default one, you can see extra information (who changed the review status, when and why) beside the review status selector by hovering on the message icon. This message icon is hidden by default if nobody has changed the review status.
Note: source code comments have priority over the value stored in the database.
Several reports may belong to a specific bug if the bug itself can be reached
on different control paths. With the Found in select option you can check
whether the selected report is available on a different path.
Some checkers are able to follow the execution path along the control flow of the program. If a bug appears on any of these paths, then CodeChecker is able to present the full path on which this so called symbolic execution reached the place of error. This path can be checked in this bug path view.
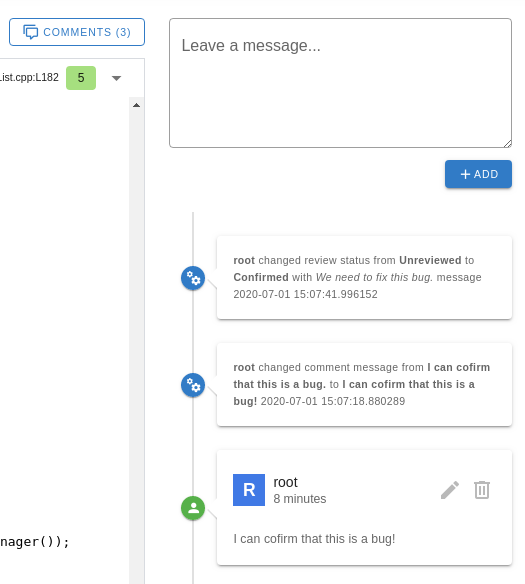
There are 2 types of comments:
user basedcomments.systemcomments.
You can add new user comments, edit () and delete () them.
The author of the comment will be the currently logged in user. If the user is not logged in, the author of the comment will be Anonymous.
System comments are automatically generated on the following events:
- on user comment update.
- on review status change.
System comments are cannot be removed.
Note: comments are connected to report hashes. This way the comments are shown for the same report found in multiple runs.
Multiple statistics are available inside the GUI:
- Product overview: overview of the quality status of the current product.
- Checker statistics: shows the number of reports grouped by checker names.
- Severity statistics: shows the number of reports grouped by severity levels.
- Component statistics: shows the number of reports grouped by source components.
This page shows an overview of the quality status of the current product.
It has the following sections:
- Number of NEW reports which were detected
today/yesterday/last 7 days/last 31 days. - Number of RESOLVED reports which were detected
today/yesterday/last 7 days/last 31 days. - Number of outstanding reports which are not fixed yet.
- Number of failed files in the current product. If you click to the number it will show you the list of failed files in a dialog.
- Number of checkers reporting faults.
- Number of outstanding reports chart per severity level. By default it will show statistics for the last 6 months. You can change it by using the input box in the top-right corner of this chart.
- Component statistics table grouped by severity levels. Each row can be expanded which will show a checker statistics for the actual component.
Shows the number of reports grouped by checker names.
Shows the number of reports grouped by severity levels.
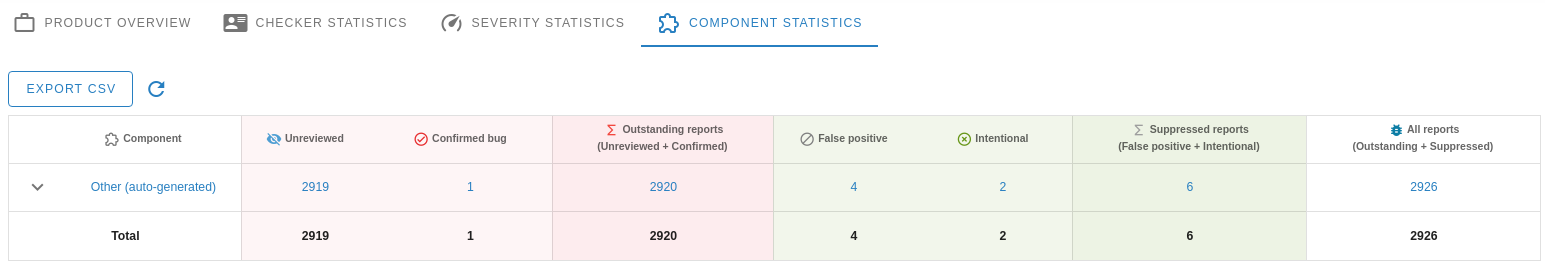
Shows the number of reports grouped by source components.
Each row can be expanded by using the ^ button beside the component name. It
will show a checker statistics table for the selected component.
We can get statistics only for specified runs, files, checker names etc. by using the filter bar.
For more information see
The same bug may appear several times if it is found on different execution paths, i.e. through different function calls. By checking Unique reports a report appears only once even if it is found on several paths.
By default uniqueing is enabled for statistics.
You can find more information how the report hashes are generated here.