- 📔Day 1
- Introduction
- Requirements
- Setup
- Adding JavaScript to a web page
- Introduction to Data types
- Comments
- Variables
- 💻 Day 1: Exercises
- 📔 Day 2
- Data types
- Numbers
- Strings
Congratulations for deciding to participate in a 30 days of JavaScript programming challenge . In this challenge you will learn everything you need to be a JavaScript programmer and in general the whole concepts of programming. In the end of the challenge you will get a 30DaysOfJavaScript programming challenge certificate. Join the telegram group.
A 30DaysOfJavaScript challenge is a guide for both beginners and advanced JavaScript developers. Welcome to JavaScript. I enjoy using and teaching JavaScript and I hope you will do so. JavaScript is the language of the browser.
In this step by step tutorial, you will learn JavaScript, the most popular programming language in the history of mankind. You use JavaScript to add interactivity to websites, to develop mobile apps, desktop applications, games and nowadays JavaScript can be used for machine learning and AI. JavaScript (JS) has increased in popularity in recent years and has been the leading programming language for four consecutive years and is the most used programming language on Github.
No prior knowledge of programming is required to follow this challenge. You need only:
- Motivation
- Computer
- Internet
- Browser
- Code Editor
I believe you have the motivation and a strong desire to be a developer, computer and internet. If you have those you have everything.
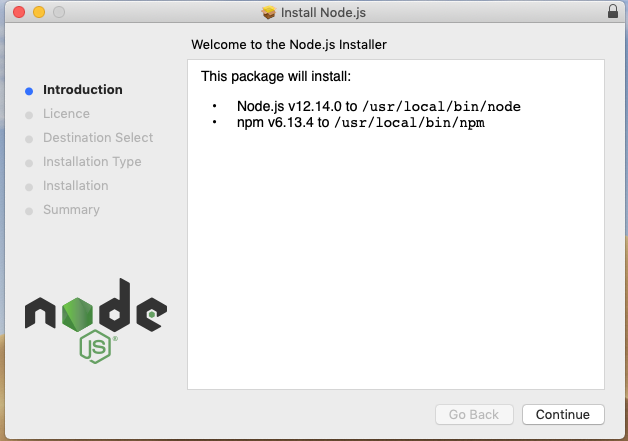
You may not need it right now but you may need it for later. Install node.js.
After downloading double click and install
We can check if node is installed in our local machine by opening our device terminal or command prompt.
asabeneh $ node -v
v12.14.0I am using node version 12.14.0 which is the recommended version of node.
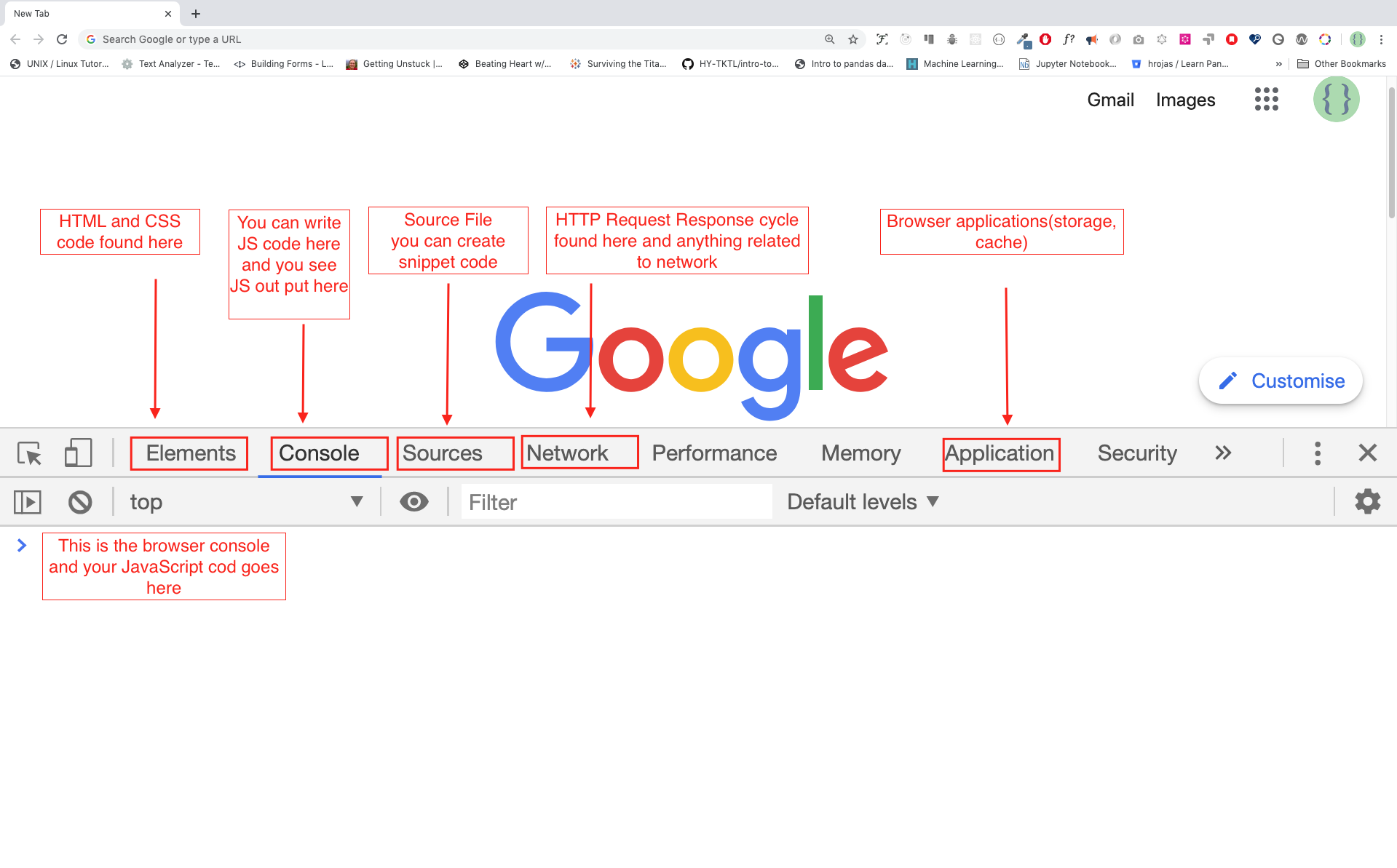
There are many browsers out there but I strongly recommend Google Chrome.
Install google chrome if you do not have one yet. We can write small JavaScript code on the browser console but we do not use the browser console to develop applications.
You can open the google chrome either by clicking three dots at the top right corner of chrome browser or using a shortcut. I prefer using shortcuts.
To open chrome console using short cut.
Mac
Command+Option+I
Windows:
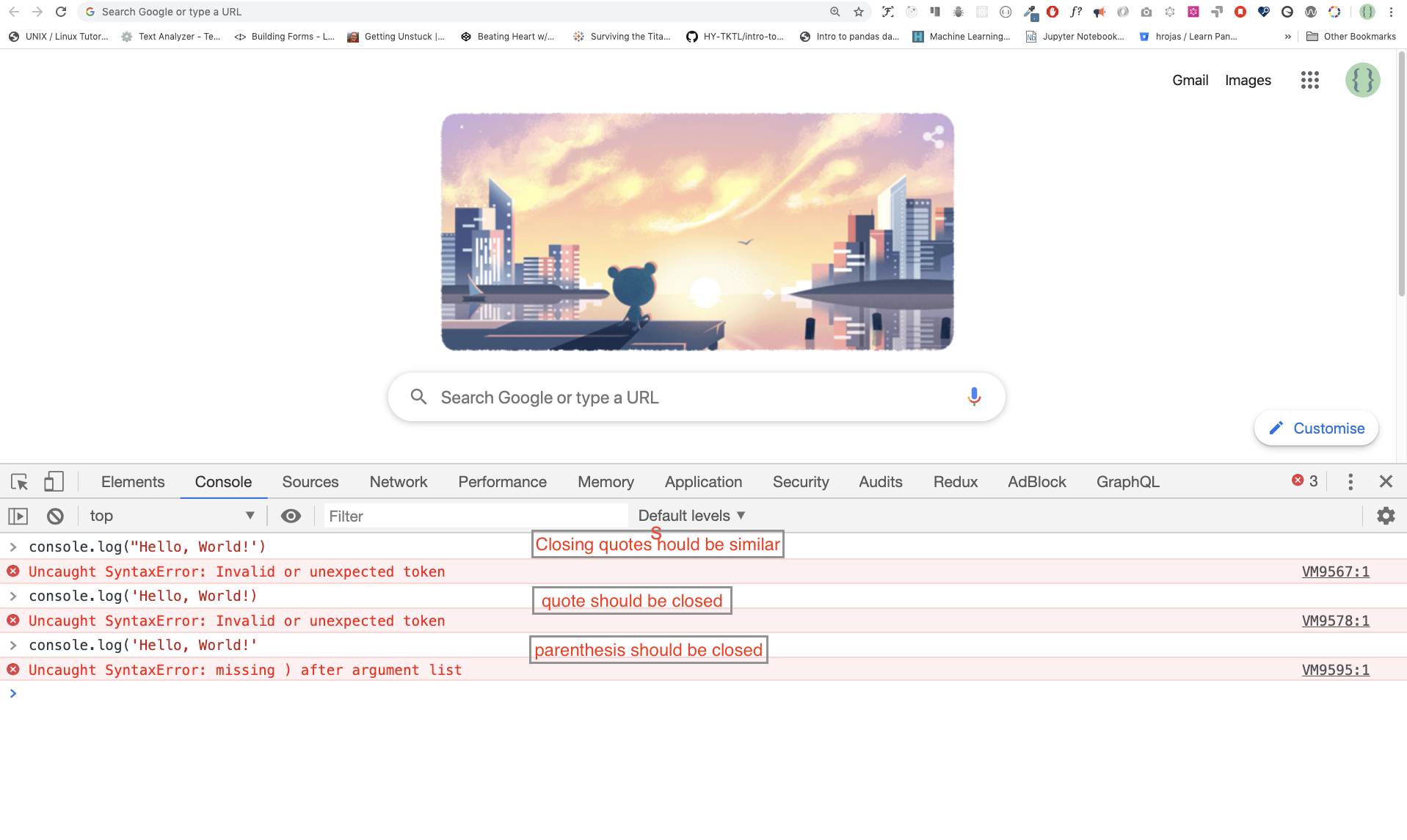
Ctl+Shift+IAfter you open the google chrome console try to explore the marked buttons. We will spend most of the time on the Console part. The Console is the place where your JavaScript code goes. The google console V8 engine change your JavaScript code to machine code. Let us write a JavaScript code on google chrome console:
We can write any JavaScript code on google console or any browser console but for this challenge we only focus on google chrome console. Open the console using:
Mac
Command+Option+I
Windows:
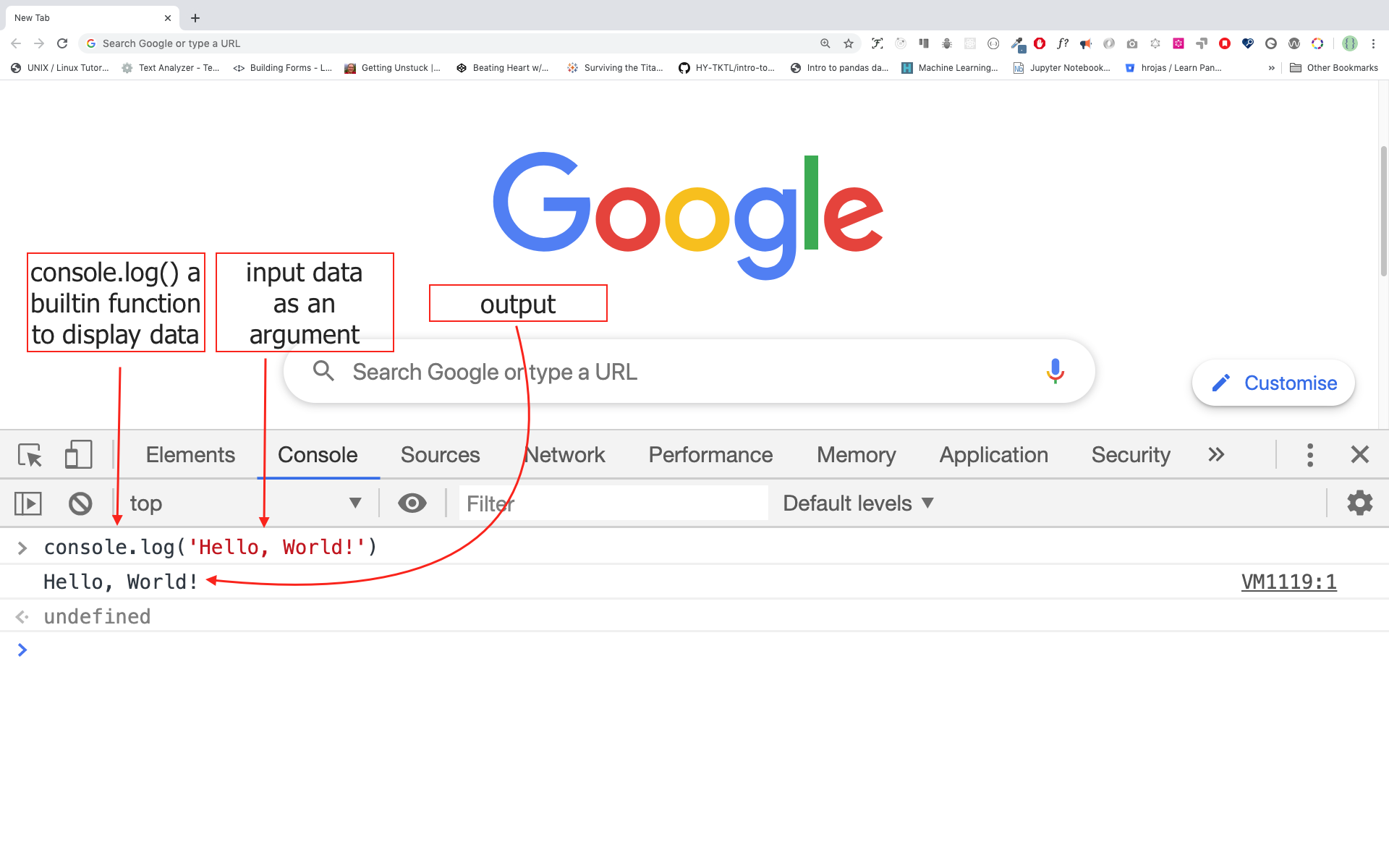
Ctl+Shift+ITo write our first JavaScript code we used a builtin function console.log(). We passed an argument as an input data and the function display the output. We passed 'Hello, World' as input data or argument in the console.log() function.
console.log('Hello, World!')The console.log(param1, param2, param3), can take multiple arguments.
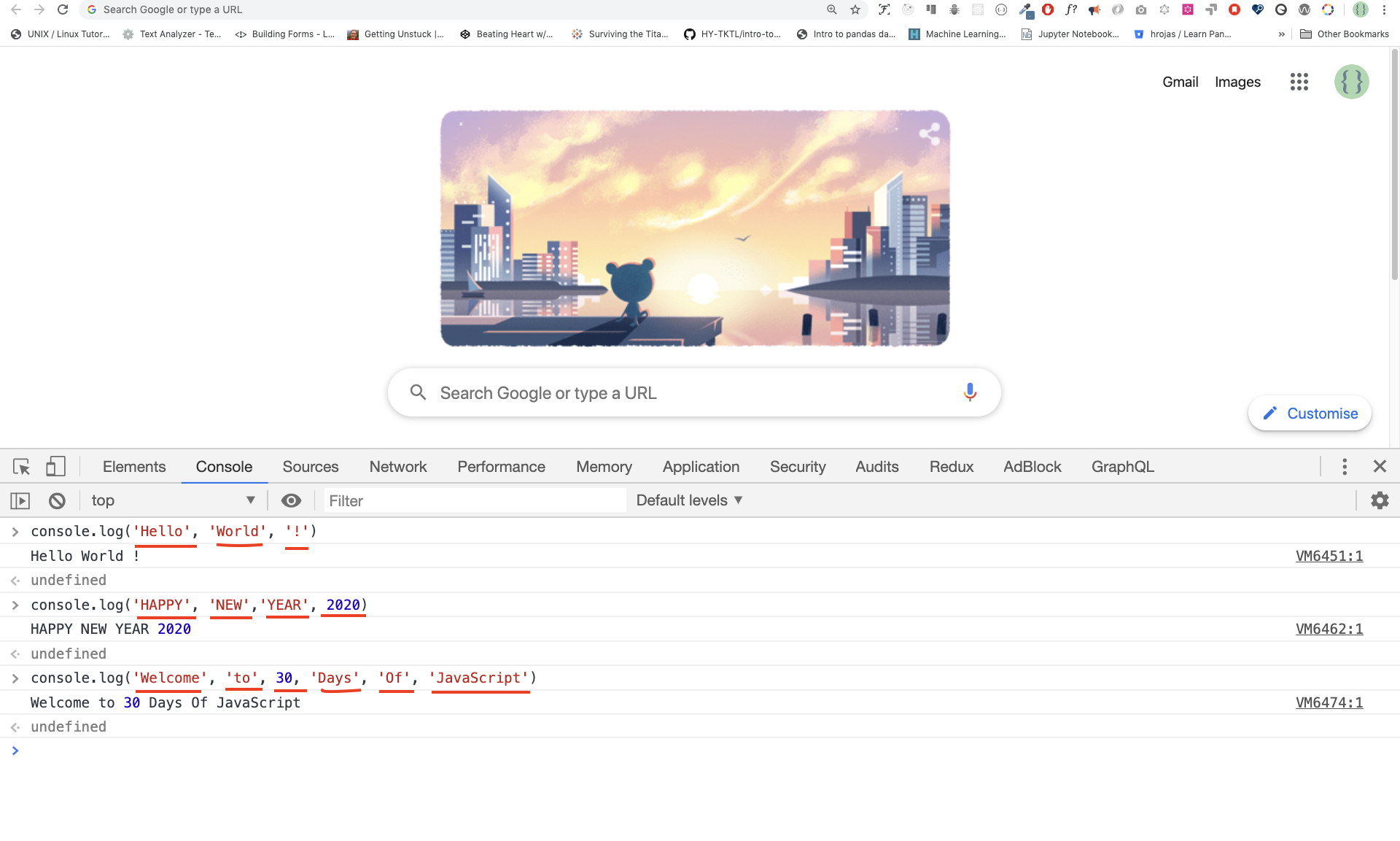
console.log('Hello', 'World', '!')
console.log('HAPPY', 'NEW', 'YEAR', 2020)
console.log('Welcome', 'to', 30, 'Days', 'Of', 'JavaScript')As you can see from the above snippet code, console.log() can take multiple arguments.
Congratulations! You wrote your first JavaScript code using console.log().
We add comment to our code. Comment is very important to make code more readable and to leave remark in our code. JavaScript does not execute comment part of our code. Any text starts with // in JavaScript is a comment or any thing enclose like this /* */ is a comment.
Example: Single Line Comment
// This is the first comment
// This is the second comment
// I am a single line comment
Example: Multiline Comment
/* This is a multiline comment multiline comment take multiple lines. JavaScript is the language the langauge of the web. */
JavaScript is a programming language and it has its own syntax like other languages. If we do not write a syntax which JavaScript understands it will raise different kind of errors. We will see different kind of JavaScript errors later but for now let us see syntax error.
I made a deliberate mistake the console raise a syntax error. Actually, the syntax is very informative. It tell what kind of mistake we made and we can fix the by reading error feedback. The process of identifying and removing errors from a program is called debugging. Let us fix the errors:
console.log("Hello, World!")
console.log('Hello, World!')So far, we saw how to display text using a console.log(). If we are printing text or string using console.log(), the text has to be under single, double or back tick. Example:
console.log("Hello, World!")
console.log('Hello, World!')
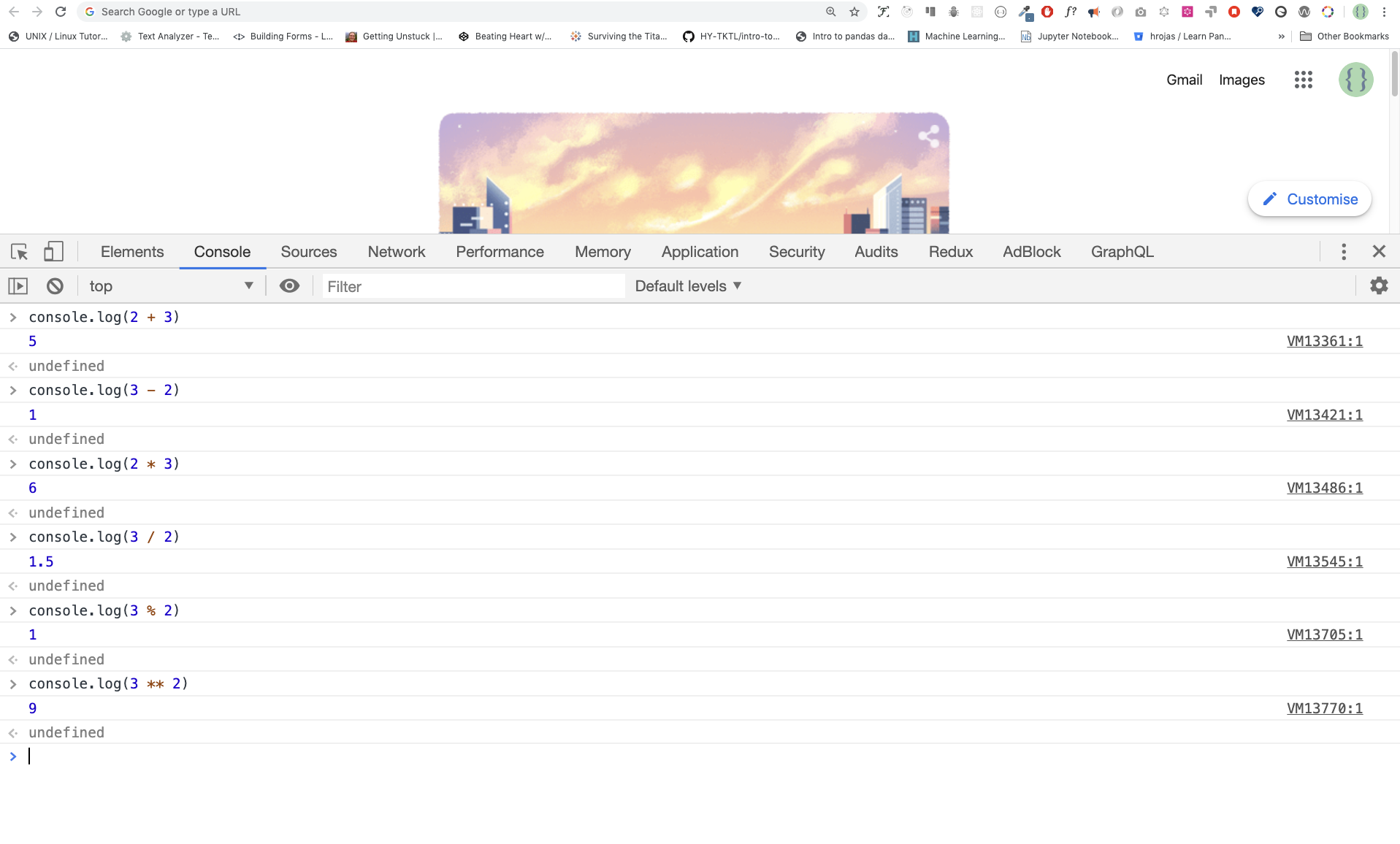
console.log(`Hello, World!`)Now, let us practice more writing JavaScript code using console.log() on google chrome console for number data types. In addition to text, we can also do mathematical calculations using JavaScript. Let us do the following simple calculations
console.log(2 + 3) // Addition
console.log(3 - 2) // Subtraction
console.log(2 * 3) // Multiplication
console.log(3 / 2) // Division
console.log(3 % 2) // Modulus - finding remainder
console.log(3 ** 2) // ExponentialWe can write code on the browser console but it won't be for a big project. In real work environment, developers use different code editors to write codes. In this 30 days python JavaScript challenge we will use visual studio code.
Visual studio code is a very popular open source text editor and I would recommend to download visual studio code, but if you are in favor of other editors, feel free to follow with what you have.
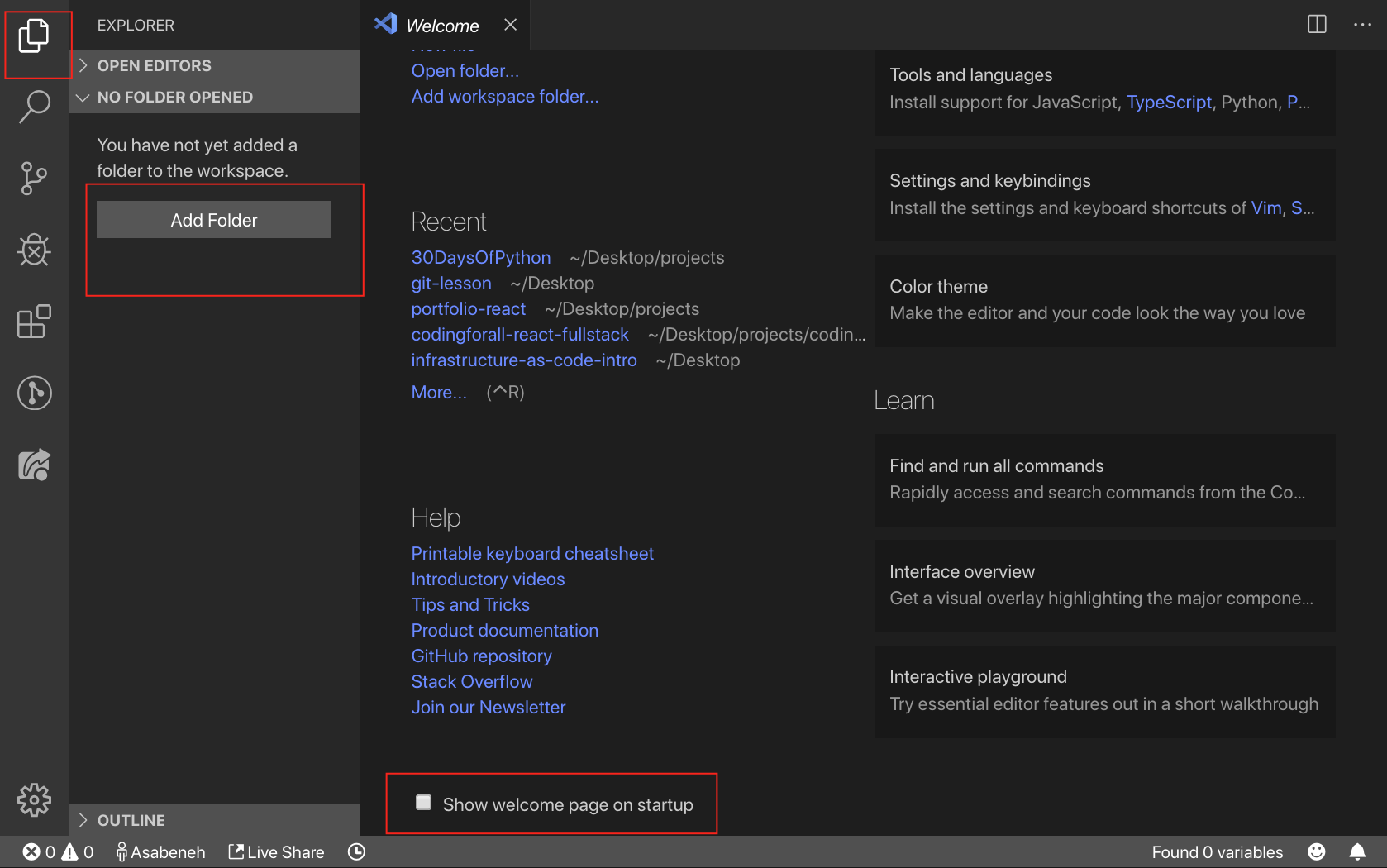
If you installed visual studio code, let us start using it.
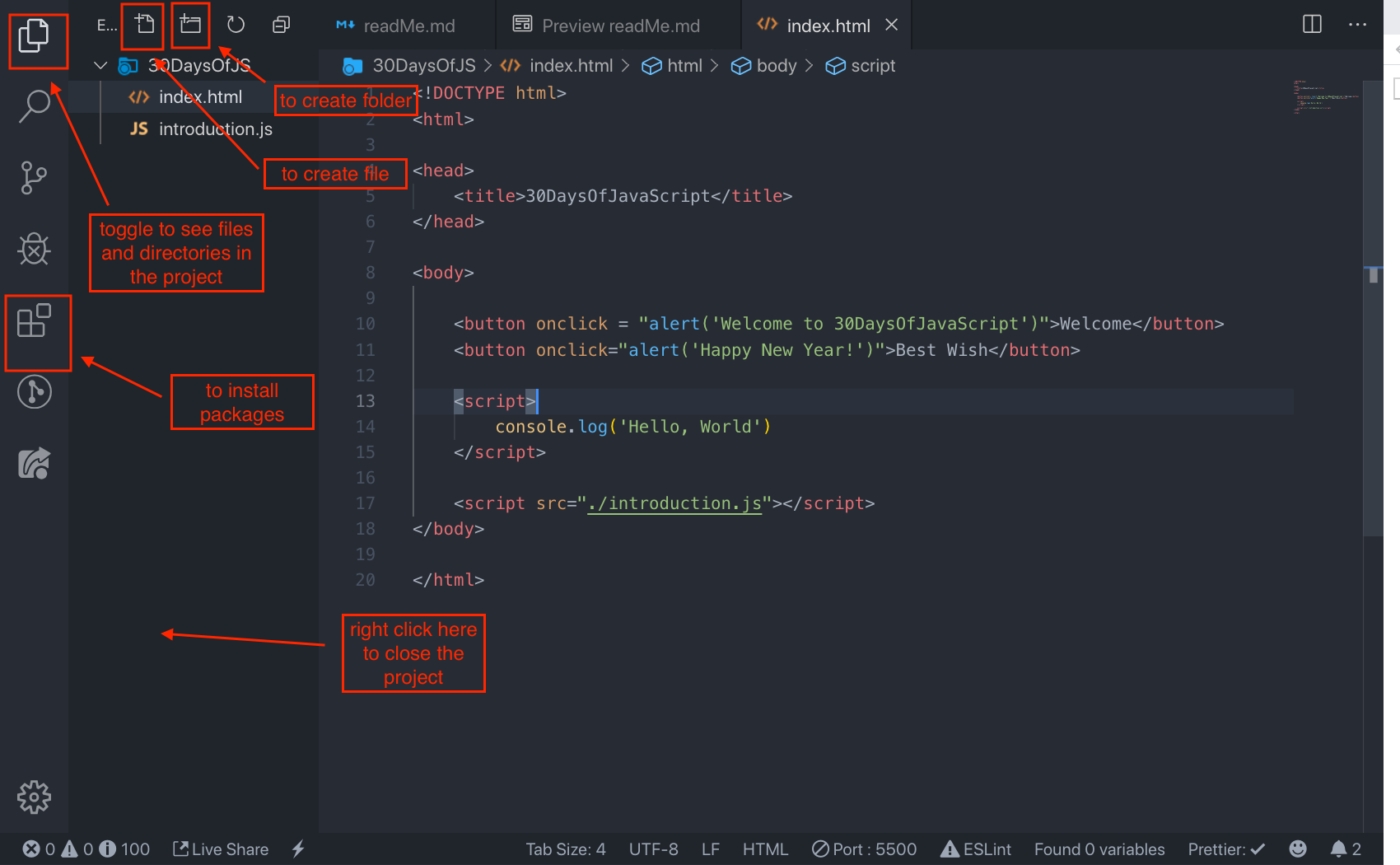
Open the visual studio code by double clicking the visual studio icon. When you open it you will get this kind of interface. Try to interact with the labelled icons.
JavaScript can be added to a web page in three ways:
- Inline script
- Internal script
- External script
- Multiple External scripts
The following sections show different ways of adding JavaScript code to your web page.
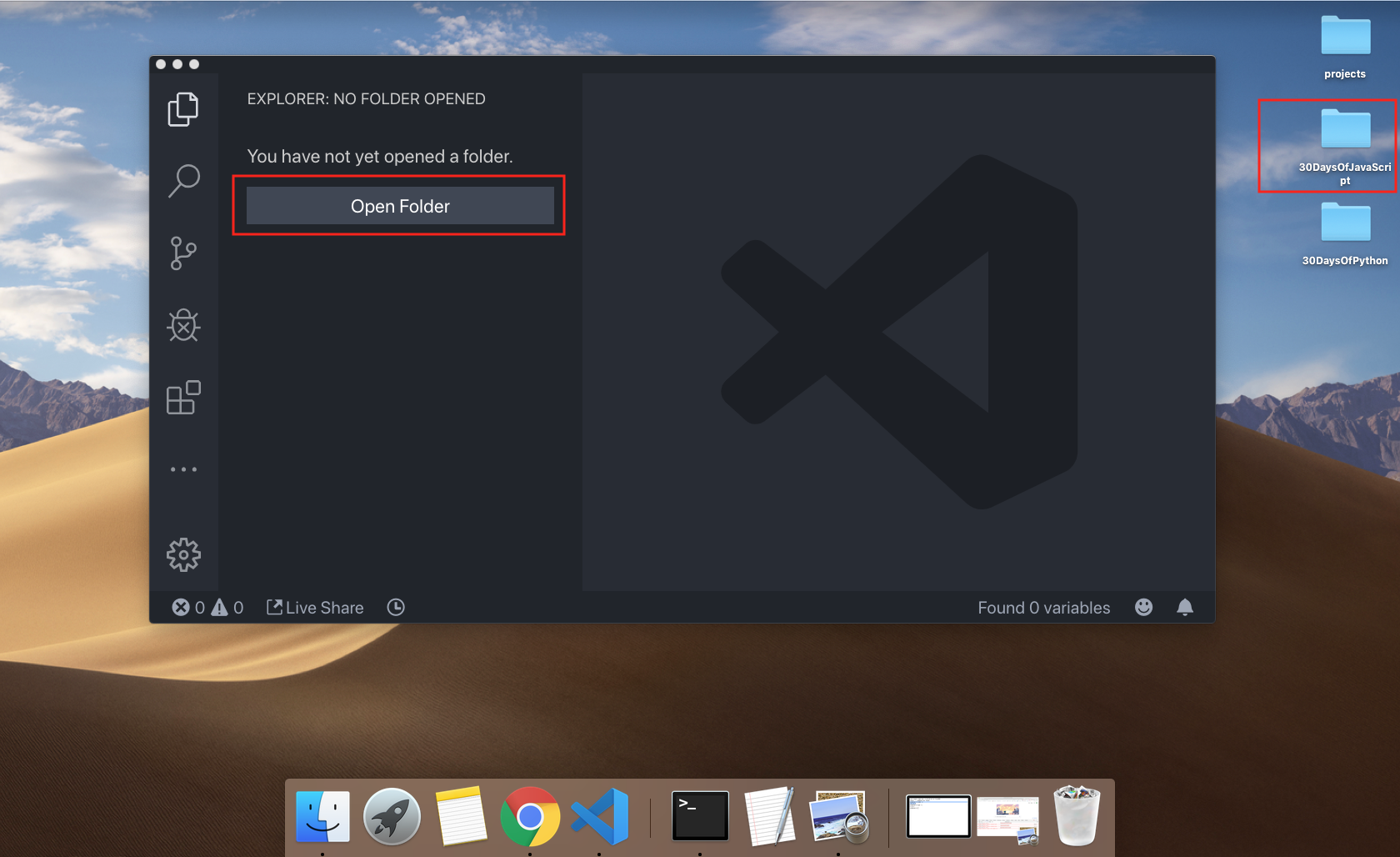
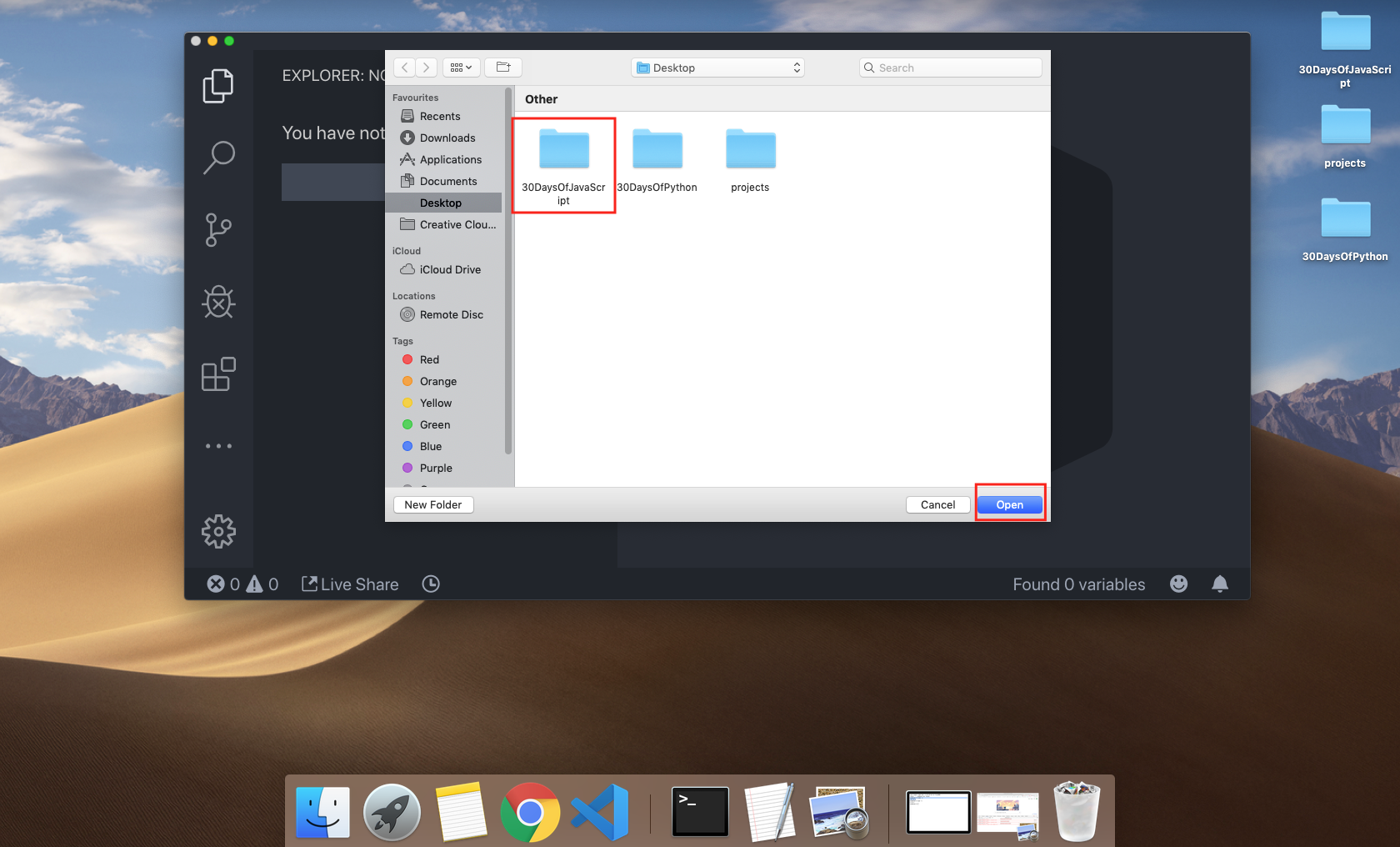
Create a folder on your desktop and call it 30DaysOfJS or in any location and create an index.html file in project folder. Then paste the following code and open it in a browser, either in Chrome.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>30DaysOfScript:Inline Script</title>
</head>
<body>
<button onclick="alert('Welcome to 30DaysOfJavaScript!');">Click Me</button>
</body>
</html>Now, you wrote your first inline script. We can create a pop up alert message using the build in alert() function.
Internal script can be written in the head or the body but it is preferred to put it on the body of the html document. First let us write on the head part of the page.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>30DaysOfScript:Internal Script</title>
<script>
console.log("Welcome to 30DaysOfJavaScript");
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
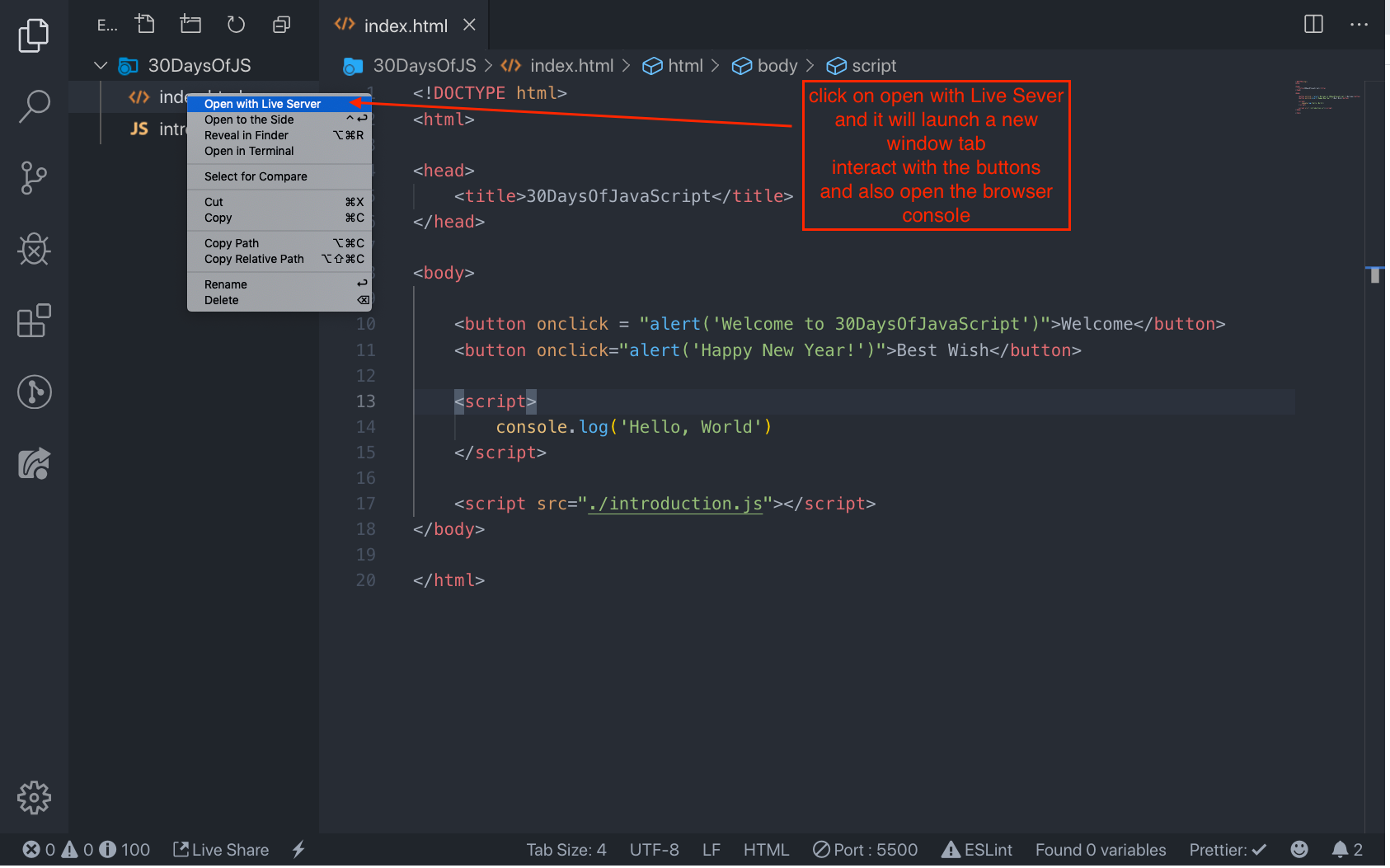
</html>This is how we write internal script most of the time. Writing the JavaScript code in the body section is the most preferred place. Open the browser console to see the out put from the console.log()
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>30DaysOfScript:Internal Script</title>
</head>
<body>
<button onclick="alert('Welcome to 30DaysOfJavaScript!');">Click Me</button>
<script>
console.log("Welcome to 30DaysOfJavaScript");
</script>
</body>
</html>Open the browser console to see the out put from the console.log()
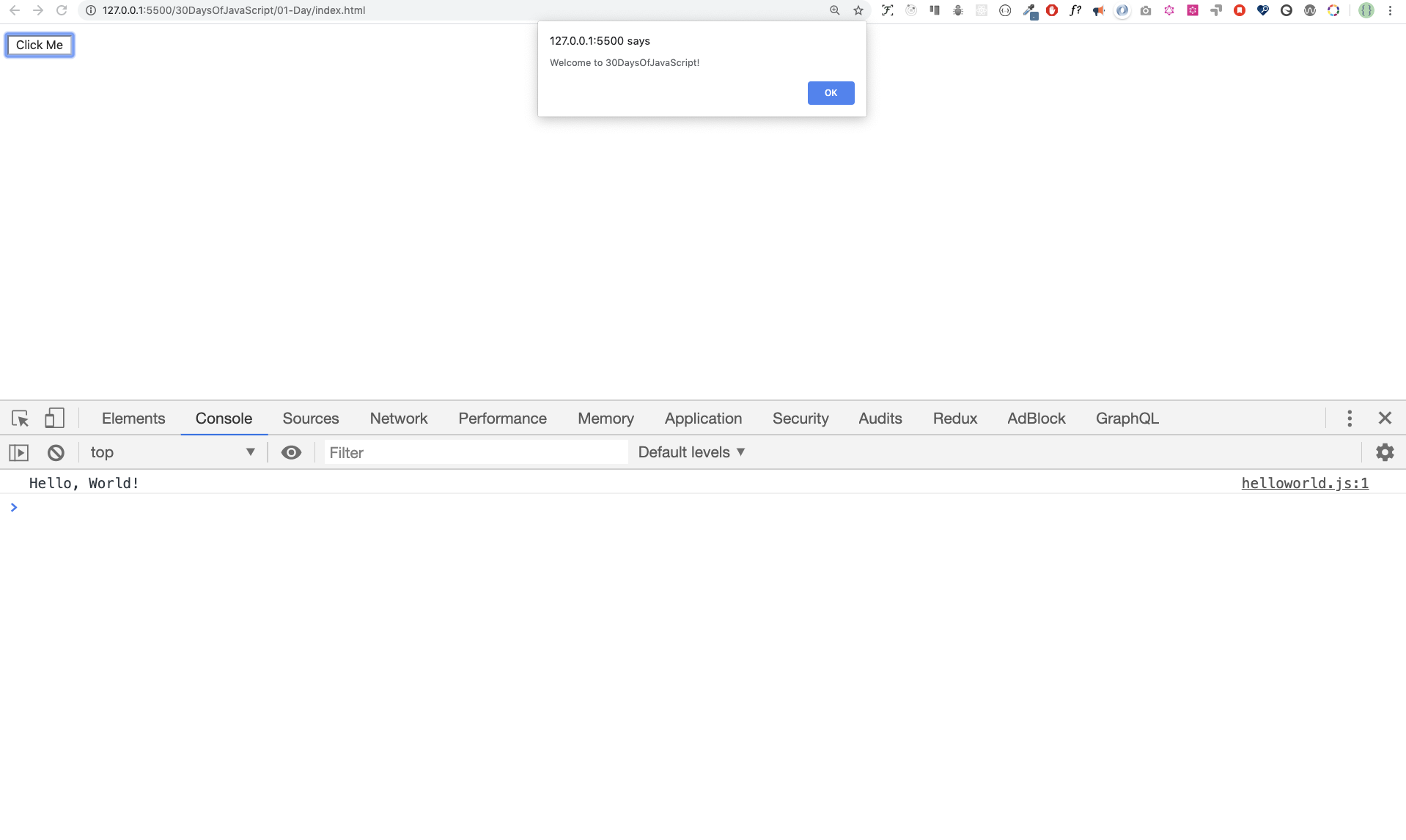
Similar to the internal script, the external script link can be on the header or body but it is preferred to put it in the body. First we should create an external JavaScript file with .js extension. Any JavaScript file ends with .js. Create a file introduction.js inside your project directory and write the following code and link this. js file at the bottom of the body
console.log('Welcome to 30DaysOfJavaScript')External script in the head
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>30DaysOfJavaScript:External script</title>
<script src="introduction.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</htmlExternal Script in the body
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>30DaysOfJavaScript:External script</title>
</head>
<body>
//it could be in the header or in the body
// Here is the recommended place to put the external script
<script src="introduction.js"></script>
</body>
</htmlOpen the browser console to see the out put from the console.log()
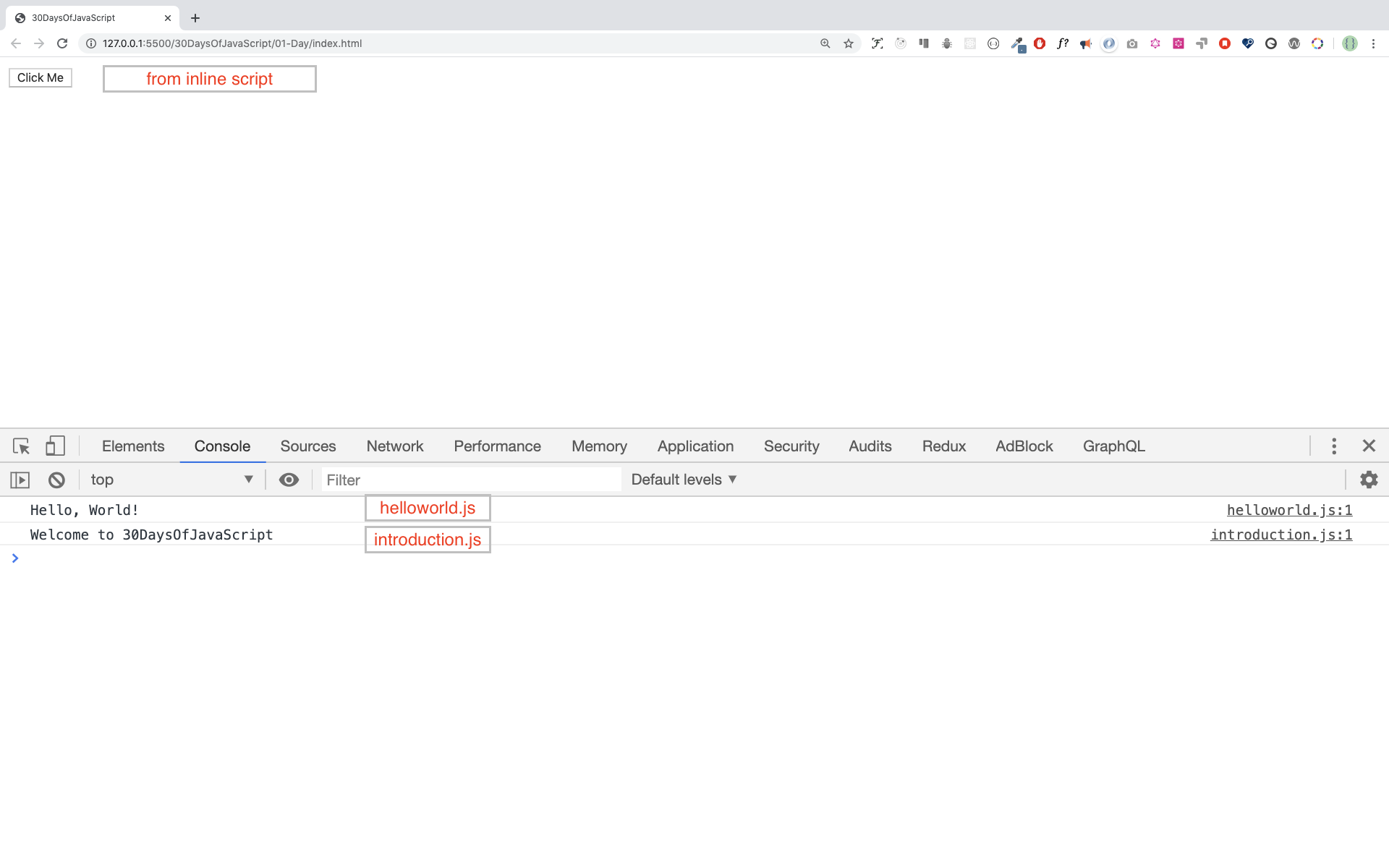
We can link multiple external JavaScript files to a web page. Create helloworld.js file inside 30DaysOfJS folder and write the following code
console.log('Hello, World!')<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Multiple External Scripts</title>
</head>
<body>
<script src ="./helloworld.js"></script>
<script src="./introduction.js"></script>
</body>
</htmlYour main.js file should be below all other scripts. Watch out your exercise needs to understand this line.
In JavaScript and also other programming languages there are different kinds of data types. The following are JavaScript primitive data types:String, Number, Boolean, undefined, Null and Symbol.
- Integer: Integer(negative, zero and positive) numbers
Example:
... -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3 ...
- Float: Decimal number
Example
... -3.5, -2.25, -1.0, 0.0, 1.1, 2.2, 3.5 ...
A collection of one or more characters under a single quote , double quote or back stick. Example:
'Asabeneh'
'Finland'
'JavaScript is a beautiful programming language'
"I love teaching"
'I hope you are enjoying the first day'
`We can also create a string using a back tick`Boolean value is either true or false. Any comparisons return a boolean value which is either true or false.
A boolean data type is either a True or False value.
Example:
true # if the light on ,the value is true
false # if the light off, the value is FalseIn JavaScript if we don't assign a value to a variable the value is undefined. In addition to that if a function is not returning anything it returns undefined.
let firstName;
console.log(firstName); //not defined, because it is not assigned to a value yetNull in JavaScript means an empty value.
To check the data type of a certain data type we use the typeof operator. See the following example.
console.log(typeof 'Asabeneh') // string
console.log(typeof 5) // number
console.log(typeof true ) // boolean
console.log(typeof null) // object type
console.log(typeof undefined) // undefinedCommenting in JavaScript is similar to other programming languages. Comments can help to make code more readable. There are two ways of commenting:
- Single line commenting
- Multiline commenting
// let firstName = 'Asabeneh'; single line comment
// let lastName = 'Yetayeh'; single line commentMultiline commenting:
/*
let location = 'Helsinki';
let age = 100;
let isMarried = true;
This is a Multiple line comment
*/Variables are containers of data. Variables store data in a memory location. When a variable is declared a memory location is reserved and when it is assigned to a value, the memory space will be filled with that data. To declare a variable we use, var, let or const keywords. I will talk about var, let and const in detail in other section(scope). For now, the above explanation is enough.
For a variable which changes at different time we use let but if the data doesn't change at all we use const. For example PI, country name, gravity do no change and we can use const.
A JavaScript variable name shouldn't begin with a number A JavaScript variable name does not allow special characters except dollar sign and underscore. A JavaScript variable name follows a camelCase convention. A JavaScript variable name shouldn't have space between words. The following are valid examples of JavaScript variables.
Valid variables in JavaScript:
firstName
lastName
country
city
capitalCity
age
isMarried
first_name
last_name
is_marreid
capital_city
num1
num_1
_num_1
$num1
year2020
year_2020Camel case or the first way of declaring is conventional in JavaScript. In this material, camelCase variables will be used.
Invalid variable:
first-name
1_num
num_#_1Let's declare variables with different data types. To declare a variable we need let or const keyword, the name of the variable, an equal sign (assignment operator) and a value.
# Syntax
let nameOfVariable = value Examples: Variables
// Declaring different variables of different data types
let firstName = 'Asabeneh' // first name of a person
let lastName = 'Yetayeh' // last name of a person
let country = 'Finland' // country
let city = 'Helsinki' // capital city
let age = 100 // age in years
let isMarried = true
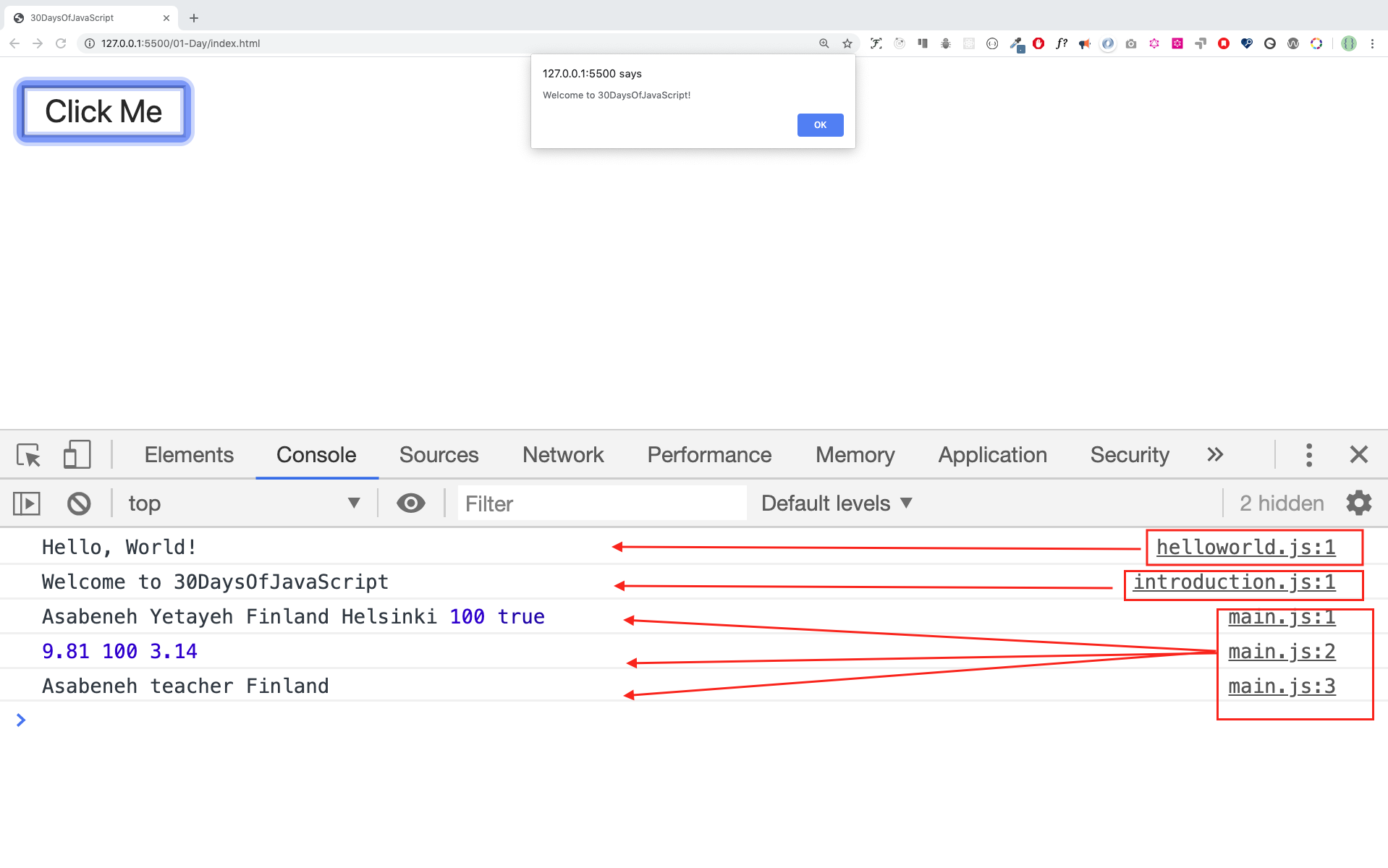
console.log(firstName, lastName, country, city, age, isMarried); //Asabeneh, Yetayeh, Finland, Helsinki, 100, True
// Declaring variables with number values
const gravity = 9.81; // earth gravity in m/s2
const boilingPoint = 100; // water boiling point, temperature in oC
const PI = 3.14; // geometrical constant
console.log(gravity, boilingPoint, PI); // 9.81, 100, 3.14
// Variables can also be declaring in one line separated by comma
let name = 'Asabeneh', //name of a person
job = 'teacher',
live = 'Finland';
console.log(name, job, live);When you run the files on 01-Day folder you should get this:
-
Write a single line comment which says, comments can make code readable
-
Write another single comment which says, welcome to 30DaysOfJavaScript
-
Write a multiline comment which says, comments can make code readable, easy to use and informative
-
Create a variable.js file and declare variables and assign string, boolean, undefined and null data types
-
Create datatypes.js file and use the JavaScript typeof operator to check different data types. Check the data type of each variables
-
Declare four variables without assigning values
-
Declare four variables with assigning values
-
Declare variables to store your first name, last name, marital status, country and age in multiple lines
-
Declare variables to store your first name, last name, marital status, country and age in a single line
-
Declare two variables myAge and yourAge and assign them initial values and log to browser console. Output:
I am 25 years old.
You are 30 years old.
In the previous section, we mentioned a little bit about data types. Data have data types. Data types describe the characteristics of data. Data types can be divided into
- Primitive data types
- Non-primitive data types(Object References)
Primitive data types in JavaScript includes:
- Numbers
- Strings
- Booleans
- Null
- Undefined
Non-primitive data types in JavaScript includes:
- Objects
- Functions
- Arrays
Now, let us see what exactly mean primitive and non-primitive data types. Primitive data types are immutable(non-modifiable) data types. Once a primitive data type is created we can not modify it. Example:
let word = 'JavaScript'If we try to modify the string stored in variable word JavaScript will raise an error. Any data type under single quote, double quote or back tick is a string data type.
word[0] = 'Y'This expression does not change the string stored in the variable word. So, we can say strings are not modifiable or immutable. Primitive data types are compared by its values. Let us compare different data values. See the example below:
let numOne = 3
let numTwo = 3
console.log(numOne == numTwo) // true
let js = 'JavaScript'
let py = 'Python'
console.log(js == py) //false
let lightOn = true
let lightOff = false
console.log(lightOn == lightOff) // falseNon-primitive data types are modifiable or mutable. We can modify the value of non-primitive data types after it gets created. Let us see by creating an array. Array is a list of data values in a square bracket. Array can contain the same or different data types. Arrays values are referenced by its index which starts at zero.
let nums = [1, 2, 3]
nums[0] = 10
console.log(nums) // [10, 2, 3]As you can see, an array which a non-primitive data type is a mutable. Non-primitive data types can not be compared by value. Even if two non-primitive data types have the same properties and values, they are not strictly equal.
let nums = [1, 2, 3]
let numbers = [1, 2, 3]
console.log(nums == numbers) // false
let userOne = {
name:'Asabeneh',
role:'teaching',
country:'Finland'
}
let userTwo = {
name:'Asabeneh',
role:'teaching',
country:'Finland'
}
console.log(userOne == userTwo)Rule of thumb, we do not compare non-primitive data types. Do not compare array, function or object. Non-primitive values are referred to as reference types because they are being compared by reference instead of value. Two objects are only strictly equal if they refer to the same underlying object.
let nums = [1, 2, 3]
let numbers = nums
console.log(nums == numbers) // true
let userOne = {
name:'Asabeneh',
role:'teaching',
country:'Finland'
}
let userTwo = userOne
console.log(userOne == userTwo) // trueIf you have hard time to understand the difference between primitive data types and non-primitive data types, you are not the only one. Calm down and just go to the next section and try to come back after some time. Now let us start the data types by number type.
Numbers are integers and decimal values which can do all the arithmetic operations Lets' see some examples of Numbers
let age = 35
const gravity = 9.81 //we use const for non-changing values, gravitational constant in m/s2
let mass = 72 // mass in Kilogram
const PI = 3.14 // pi a geometrical constant
//More Examples
const boilingPoint = 100 // temperature in oC, boiling point of water which is a constant
const bodyTemp = 37 // oC average human body temperature, which is a constant
console.log(age, gravity, mass, PI, boilingPoint, bodyTemp)In JavaScript the Math Object provides a lots of methods to work with numbers.
const PI = Math.PI
console.log(PI) // 3.141592653589793
console.log(Math.round(PI)) // 3; to round values to the nearest number
console.log(Math.round(9.81)) // 10
console.log(Math.floor(PI)) // 3; rounding down
console.log(Math.ceil(PI)) // 4; rounding up
console.log(Math.min(-5, 3, 20, 4,5, 10)) // -5, returns the minimum value
console.log(Math.max(-5, 3, 20, 4,5, 10)) // 20, returns the maximum value
const randNum = Math.random() // creates random number between 0 to 0.999999
console.log(randNum)
// Let create random number between 0 to 10
const num = Math.floor(Math.random () * 11) // creates random number between 0 and 10
console.log(num)
//Absolute value
console.log(Math.abs(-10)) //10
//Square root
console.log(Math.sqrt(100)) // 10
console.log(Math.sqrt(2)) //1.4142135623730951
// Power
console.log(Math.pow(3, 2)) // 9
console.log(Math.E) // 2.718
// Logarithm
//Returns the natural logarithm of base E of x, Math.log(x)
console.log(Math.log(2)) // 0.6931471805599453
console.log(Math.log(10)) // 2.302585092994046
// Trigonometry
Math.sin(0)
Math.sin(60)
Math.cos(0)
Math.cos(60)Strings are text which are under single or double quote. To declare a string we need a variable name, assignment operator, a value under a single quote, double quote or back tick. Lets' see some examples of string:
let space = ' ' // an empty space string
let firstName = 'Asabeneh'
let lastName = 'Yetayeh'
let country = 'Finland'
let city = 'Helsinki'
let language = 'JavaScript'
let job = 'teacher'Connect two or more strings together is called concatenation.
// Declaring different variables of different data types
let space = ' '
let firstName = 'Asabeneh'
let lastName = 'Yetayeh'
let country = 'Finland'
let city = 'Helsinki'
let language = 'JavaScript'
let job = 'teacher'let fullName = firstName + space + lastName; // concatenation, merging two string together.
console.log(fullName);// out
Asabeneh YetayehWe can concatenate string in different ways.
Concatenating using addition operator is an old way. This way of concatenating is tedious and error prone. It is good to know, how to concatenate this way but I strongly suggest to use the second way.
// Declaring different variables of different data types
let space = ' '
let firstName = 'Asabeneh'
let lastName = 'Yetayeh'
let country = 'Finland'
let city = 'Helsinki'
let language = 'JavaScript'
let job = 'teacher'
let age = 250
let fullName = firstName + space + lastName
let personInfoOne = fullName + '. I am ' + age + '. I live in ' + country; // ES5
console.log(personInfoOne)Asabeneh Yetayeh. I am 250. I live in FinlandTo create a template string we use back two back ticks. We can inject data as expression inside a template string. To inject data we enclose the expression with curly bracket({}) followed by $ sign. See the syntax blow.
//Syntax
`String literal text`
`String literal text ${expression}`Example: 1
console.log(`The sum of 2 and 3 is 5`)
let a = 2
let b = 3
console.log(`The sum of ${a} and ${b} is ${a + b}`)Example:2
let firstName = 'Asabeneh'
let lastName = 'Yetayeh'
let country = 'Finland'
let city = 'Helsinki'
let language = 'JavaScript'
let job = 'teacher'
let age = 250
let fullName = firstName + ' ' + lastName
let personInfoTwo = `I am ${fullName}. I am ${age}. I live in ${country}.` //ES6 - String interpolation method
let personInfoThree = `I am ${fullName}. I live in ${city}, ${country}. I am a ${job}. I teach ${language}.`
console.log(personInfoTwo)
console.log(personInfoThree)I am Asabeneh Yetayeh. I am 250. I live in Finland.
I am Asabeneh Yetayeh. I live in Helsinki, Finland. I am a teacher. I teach JavaScript.Using string template or string interpolation method we can add expression which could be a value or some operations(comparison, arithmetic operations, ternary operation)
let a = 2
let b = 3
console.log(`${a} is greater than ${b}: ${a > b}`)2 is greater than 3: falseEverything in JavaScript is an object. String is a primitive data type that means we can not modify once it is created. String object has many string methods. There many string methods which can help us to work with strings.
- length: The string length method returns the number of characters in a string included empty space.
Example:
let js = 'JavaScript' console.log(js.length) // 10 let firstName = 'Asabeneh' console.log(firstName.length) // 8
- Accessing characters in a string: We can access each characters in a string using its index. In programming counting starts from 0. The first index of the string is zero and the last index is one minus the length of the string
 Let us access the first character in 'JavaScript' string.
Let us access the first character in 'JavaScript' string.
let string = 'JavaScript'
let firstLetter = string[0]
console.log(firstLetter) // J
let secondLetter = string[1] // a
let thirdLetter = string[2]
let lastLetter = string[9]
console.log(lastLetter) // t
let lastIndex = string.length - 1
console.log(lastIndex) // 9
console.log(string[lastIndex]) // t- toUpperCase(): this method changes the string to uppercase letters.
let string = 'JavaScript'
console.log(string.toUpperCase()) // JAVASCRIPT
let firstName = 'Asabeneh'
console.log(firstName.toUpperCase()) // ASABENEH
let country = 'Finland'
console.log(country.toUpperCase()) // FINLAND- toLowerCase(): this method changes the string to lowercase letters.
let string = 'JavasCript'
console.log(string.toLowerCase()) // javascript
let firstName = 'Asabeneh'
console.log(firstName.toLowerCase()) // asabeneh
let country = 'Finland'
console.log(country.toLowerCase()) // finland- substr(): It takes two arguments,the starting index and number of characters to slice.
let string = 'JavaScript'
console.log(string.substr(4,6)) // Script
let country = 'Finland'
console.log(country.substr(3, 4)) // land- substring(): It takes two arguments,the starting index and the stopping index but it doesn't include the stopping index.
let string = 'JavaScript'
console.log(string.substring(0,4)) // Java
console.log(string.substring(4,10)) // Script
console.log(string.substring(4)) // Script
let country = 'Finland'
console.log(country.substring(0, 3)) // Fin
console.log(country.substring(3, 7)) // land
console.log(country.substring(3)) // land- split(): The split method splits a string at a specified place.
let string = '30 Days Of JavaScipt'
console.log(string.split()) // ["30 Days Of JavaScript"]
console.log(string.split(' ')) // ["30", "Days", "Of", "JavaScript"]
let firstName = 'Asabeneh'
console.log(firstName.split()) // ["Asabeneh"]
console.log(firstName.split('')) // ["A", "s", "a", "b", "e", "n", "e", "h"]
let countries = 'Finland, Sweden, Norway, Denmark, and Iceland'
console.log(countries.split(',')) // ["Finland", " Sweden", " Norway", " Denmark", " and Iceland"]
console.log(countries.split(', ')) // ["Finland", "Sweden", "Norway", "Denmark", "and Iceland"]- trim(): Removes trailing space in the beginning or the end of a string.
let string = ' 30 Days Of JavaScript '
console.log(string) //
console.log(string.trim(' ')) //
let firstName = ' Asabeneh '
console.log(firstName)
console.log(firstName.trim()) // 30 Days Of JavasCript
30 Days Of JavasCript
Asabeneh
Asabeneh- includes(): It takes a substring argument and it check if substring argument exists in the string. includes() returns a boolean. It checks if a substring exist in a string and it returns true if it exists and false if it doesn't exist.
let string = '30 Days Of JavaScript'
console.log(string.includes('Days')) // true
console.log(string.includes('days')) // false
console.log(string.includes('Script')) // true
console.log(string.includes('script')) // false
console.log(string.includes('java')) // false
console.log(string.includes('Java')) // true
let country = 'Finland'
console.log(country.includes('fin')) // false
console.log(country.includes('Fin')) // true
console.log(country.includes('land')) // true
console.log(country.includes('Land')) // false- replace(): takes to parameter the old substring and new substring.
string.replace(oldsubstring, newsubstring)let string = '30 Days Of JavaScript'
console.log(string.replace('JavaScript', 'Python')) // 30 Days Of Python
let country = 'Finland'
console.log(country.replace('Fin', 'Noman')) Nomanland- charAt(): Takes index and it returns the value at that index
string.charAt(index)let string = '30 Days Of JavaScript'
console.log(string.charAt(0)) // 3
let lastIndex = string.length - 1
console.log(string.charAt(lastIndex)) // t- charCodeAt(): Takes index and it returns char code(ASCII number) of the value at that index
string.charCodeAt(index)let string = '30 Days Of JavaScript'
console.log(string.charCodeAt(3)) // D ASCII number is 51
let lastIndex = string.length - 1
console.log(string.charCodeAt(lastIndex)) // t ASCII is 116- indexOf(): Takes takes a substring and if the substring exists in a string it returns the first position of the substring if does not exist it returns -1
string.indexOf(substring)let string = '30 Days Of JavaScript'
console.log(string.indexOf('D')) // 3
console.log(string.indexOf('Days')) // 3
console.log(string.indexOf('days')) // -1
console.log(string.indexOf('a')) // 4
console.log(string.indexOf('JavaScript')) // 11
console.log(string.indexOf('Script')) //15
console.log(string.indexOf('script')) // -1- lastIndexOf(): Takes takes a substring and if the substring exists in a string it returns the last position of the substring if it does not exist it returns -1
string.lastIndexOf(index)let string = 'I love JavaScript. If you do not love JavaScript what else can you love.'
console.log(string.lastIndexOf('love')) // 67
console.log(string.lastIndexOf('you')) // 63
console.log(string.lastIndexOf('JavaScript')) // 38- concat(): it takes many substrings and creates concatenation.
string.concat(substring, substring, substring)let string = '30'
console.log(string.concat("Days", "Of", "JavaScript")) // 30DaysOfJavaScript
let country = 'Fin'
console.log(country.concat("land")) // Finland- startsWith: it takes a substring as an argument and it checks if the string starts with that specified substring. It returns a boolean(true or false).
string.startsWith(substring)let string = 'Love is the best to in this world'
console.log(string.startsWith('Love')) // true
console.log(string.startsWith('love')) // false
console.log(string.startsWith('world')) // false
let country = 'Finland'
console.log(country.startsWith('Fin')) // true
console.log(country.startsWith('fin')) // false
console.log(country.startsWith('land')) // false- endsWith: it takes a substring as an argument and it checks if the string starts with that specified substring. It returns a boolean(true or false).
string.endsWith(substring)let string = 'Love is the best to in this world'
console.log(string.endsWith('world')) // true
console.log(string.endsWith('love')) // false
console.log(string.endsWith('in this world')) // true
let country = 'Finland'
console.log(country.endsWith('land')) // true
console.log(country.endsWith('fin')) // false
console.log(country.endsWith('Fin')) // false- search: it takes a substring as an argument and it returns the index of the first match.
string.search(substring)let string = 'I love JavaScript. If you do not love JavaScript what else can you love.'
console.log(string.search('love')) // 2- match: it takes a substring or regular expression pattern as an argument and it returns an array if there is match if not it returns null. Let us see how a regular expression pattern looks like. It starts with / sign and ends with / sign.
let string = 'love'
let patternOne = /love/ // with out any flag
let patternTwo = /love/gi // g-means to search in the whole text, i - case insensitivestring.match(substring)let string = 'I love JavaScript. If you do not love JavaScript what else can you love.'
console.log(string.match('love')) //
/*
output
["love", index: 2, input: "I love JavaScript. If you do not love JavaScript what else can you love.", groups: undefined]
*/
let pattern = /love/gi
console.log(string.match(pattern)) // ["love", "love", "love"]Let us extract numbers from text using regular expression. This is not regular expression section, no panic.
let txt = 'In 2019, I run 30 Days of Pyhton. Now, in 2020 I super exited to start this challenge'
let regEx = /\d+/ // d with escape character means d not a normal d instead acts a digit
// + means one or more digit numbers,
// if there is g after that it means global, search everywhere.
console.log(text.match(regEx)) // ["2", "0", "1", "9", "3", "0", "2", "0", "2", "0"]
console.log(text.match(/\d+/g)) // ["2019", "30", "2020"]- repeat(): it takes a number argument and it returned the repeated version of the string.
string.repeat(n)let string = 'love'
console.log(string.repeat(10)) // lovelovelovelovelovelovelovelovelovelove
# Booleans
A boolean data type represents one of the two values:_true_ or _false_. Boolean value is either true or false. The use of these data types will be clear when you start the comparison operator. Any comparisons return a boolean value which is either true or false.
**Example: Boolean Values**
```js
let isLightOn = true;
let isRaining = false;
let isHungery = false;
let isMarried = true;If we declare a variable and if we do not assign a value, the value will be undefined. In addition to this, if a function is not returning the value will be undefined.
let firstName;
console.log(firstName); //not defined, because it is not assigned to a value yetlet empty = null;
console.log(empty); // -> null , means no valueAn equal sign in JavaScript is an assignment operator. It uses to assign a variable.
let firstName = 'Asabeneh'
let country = 'Finland'Arithmetic operators are mathematical operators.
- Addition(+): a + b
- Subtraction(-): a - b
- Multiplication(*):a * b
- Division(/): a / b
- Modulus(%):a % b
- Exponential(**):a ** b
let numOne = 4;
let numTwo = 3;
let sum = numOne + numTwo;
let diff = numOne - numTwo;
let mult = numOne * numTwo;
let div = numOne / numTwo;
let remainder = numOne % numTwo;
let powerOf = numOne ** numTwo
console.log(sum, diff, mult, div, remainder, powerOf); // ->7,1,12,1.33,1, 64
let PI = 3.14;
let radius = 100; // length in meter
const gravity = 9.81; // in m/s2
let mass = 72; // in Kilogram
const boilingPoint = 100; // temperature in oC, boiling point of water
const bodyTemp = 37; // body temperature in oC
//Let us calculate area of a circle
const areaOfCircle = PI * radius * radius;
console.log(areaOfCircle); // -> 314 m
// Let us calculate weight of an object
const weight = mass * gravity;
console.log(weight); // -> 706.32 N(Newton)
//Concatenating string with numbers using string interpolation
/*
The boiling point of water is 100 oC.
Human body temperature is 37 oC.
The gravity of earth is 9.81 m/s2.
*/
console.log(
`The boiling point of water is ${boilingPoint} oC.\nHuman body temperature is ${body} oC.\nThe gravity of earth is ${gravity} m / s2.`
);In programming we compare values, we use comparison operators to compare two values. We check if a value is greater or less or equal to other value.
console.log(3 > 2) // true, because 3 is greater than 2
console.log(3 >= 2) // true, because 3 is greater than 2
console.log(3 < 2) // false, because 3 is greater than 2
console.log(2 < 3) // true, because 2 is less than 3
console.log(2 <= 3) // true, because 2 is less than 3
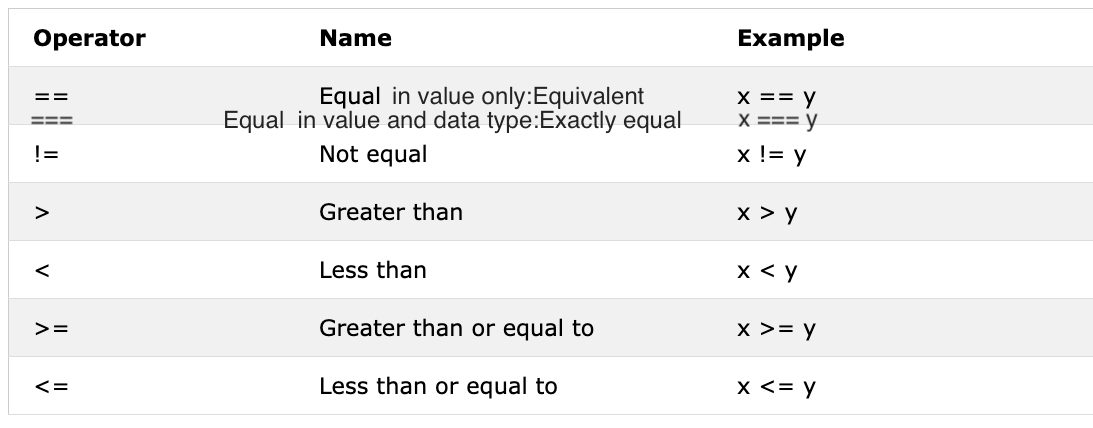
console.log(3 == 2) // false, because 3 is not equal to 2
console.log(3 != 2) // true, because 3 is not equal to 2
console.log(3 == '3') // true, compare only value
console.log(3 === '3') // false, compare both value and data type
console.log(3 !== '3') // true, compare both value and data type
console.log(3 !== '3') // true, compare both value and data type
console.log(3 != 3) // false, compare only value
console.log(3 !== 3) // false, compare both value and data type
console.log('mango'.length == 'avocado'.length) // false
console.log('mango'.length != 'avocado'.length) // true
console.log('mango'.length < 'avocado'.length) // true
console.log('milk'.length != 'meat'.length) // false
console.log('milk'.length == 'meat'.length) // true
console.log('tomato'.length == 'potato'.length) // true
console.log('python'.length > 'dragon'.length) // falseThe following symbols are the common logical operators: &&(ampersand) , ||(pipe) and !(negation). && gets true only if the two operands are true. || gets true either of the operand is true. ! negates true to false, false to true.
//&& ampersand example
const check = 4 > 3 && 10 > 5; // true and true -> true
const check = 4 > 3 && 10 < 5; // true and false -> false
const check = 4 < 3 && 10 < 5; // false and false -> false
//|| pipe or, example
const check = 4 > 3 || 10 > 5; // true and true -> true
const check = 4 > 3 || 10 < 5; // true and false -> true
const check = 4 < 3 || 10 < 5; // false and false -> false
//! Negation examples
let check = 4 > 3; // -> true
let check = !(4 > 3); // -> false
let isLightOn = true;
let isLightOff = !isLightOn; // -> false
let isMarried = !false; // -> true- Declare a variable name challenge and assign it to an initial value '30 Days Of JavaScript'.
- Print the string on the browser console using console.log()
- Print the length of the string on the browser console using console.log()
- Change all the string to capital letters using toUpperCase() method
- Change all the string to lowercase letters using toLowerCase() method
- Cut(slice) out the first word of the string using substr() or substring() method
- Slice out the phrase Days Of JavaScript from 30 Days Of JavaScript.
- Use substr to slice out the phase because because because in the following sentence:'You cannot end a sentence with because because because is a conjunction'
- Check if the string contains a word Script using includes() method
- Split the string into array using split() method
- Split the string 30 Days Of JavaScript at the space using split() method
- 'Facebook, Google, Microsoft, Apple, IBM, Oracle, Amazon' split the string at the comma and change it to an array.
- Change 30 Days Of JavaScript to 30 Days Of Python using replace() method.
- What is character at index 15 in '30 Days Of JavaScript' string use charAt() method.
- What is the character code of J in '30 Days Of JavaScript' string using charCodeAt()
- Use indexOf to determine the position of the first occurrence of a in 30 Days Of JavaScript
- Use lastIndexOf to determine the position of the last occurrence of a in 30 Days Of JavaScript.
- Use indexOf to find the position of the first occurrence of the word because in the following sentence:'You cannot end a sentence with because because because is a conjunction'
- Use lastIndexOf to find the position of the first occurrence of the word because in the following sentence:'You cannot end a sentence with because because because is a conjunction'
- Use search to find the position of the first occurrence of the word because in the following sentence:'You cannot end a sentence with because because because is a conjunction'
- Use trim() to remove if there is trailing whitespace at the beginning and the end of a string.E.g ' 30 Days Of JavaScript '.
- Use startsWith() method with the string 30 Days Of JavaScript make the result true
- Use endsWith() method with the string 30 Days Of JavaScript make the result true
- Use match() method to find all the a’s in 30 Days Of JavaScript
- Use match() to count the number all because's in the following sentence:'You cannot end a sentence with because because because is a conjunction'
- Use concat() and merge '30 Days of' and 'JavaScript' to a single string, '30 Days Of JavaScript'
- Use repeat() method to print 30 Days Of JavaScript 2 times
- Love is the best thing in this world. Some found their love and some are still looking for their love. Count the number of word love in this sentence.
- Calculate the total annual income of the person by extract the numbers from the following text. 'He earns 5000 euro from salary per month, 10000 euro annual bonus, 15000 euro online courses per month.'
- Clean the following text and find the most frequent word(hint, use replace and regular express).
const sentence = '%I $am@% a %tea@cher%, &and& I lo%#ve %tea@ching%;. There $is nothing; &as& mo@re rewarding as educa@ting &and& @emp%o@wering peo@ple. ;I found tea@ching m%o@re interesting tha@n any other %jo@bs. %Do@es thi%s mo@tivate yo@u to be a tea@cher!? %Th#is 30#Days&OfJavaScript &is also $the $result of &love& of tea&ching'-
Declare firstName, lastName, country, city, age, isMarried, year variable and assign value to it
-
The JavaScript typeof operator uses to check different data types. Check the data type of each variables from question number 1.
JavaScript arithmetic operators are addition(+), subtraction(-), multiplication(*), division(/), modulus(%), exponential(**), increment(++) and decrement(--).
let operandOne = 4;
let operandTwo = 3;Using the above operands apply different JavaScript arithmetic operations.
Boolean value is either true or false.
- Write three JavaScript statement which provide truthy value.
- Write three JavaScript statement which provide falsy value.
Figure out the result of the following comparison expression first without using console.log(). After you decide the result confirm it using console.log()
- 4 > 3
- 4 >= 3
- 4 < 3
- 4 <= 3
- 4 == 4
- 4 === 4
- 4 != 4
- 4 !== 4
- 4 != '4'
- 4 == '4'
- 4 === '4'
Figure out the result of the following expressions first without using console.log(). After you decide the result confirm it by using console.log()
- 4 > 3 && 10 < 12
- 4 > 3 && 10 > 12
- 4 > 3 || 10 < 12
- 4 > 3 || 10 > 12
- !(4 > 3)
- !(4 < 3)
- !(false)
- !(4 > 3 && 10 < 12)
- !(4 > 3 && 10 > 12)
- !(4 === '4')