STDK (Smart Things Develop Kit) is one of the features of the Smart Things ecosystem. This guide describes with an example, how to enable STDK in TizenRT and develop applications using it.
We choose a common example of a blinking Led to demonstrate how to develop a so-called LED Things and control it via a SmartThings mobile app.
- Prerequisites
- Get TizenRT Source
- Create device identity
- Register Device Profile on SmartThings Devworkspace
- Build and Flash
- Try to do EasySetup and Control
- How to develop your STDK device
This section will describe the pre-requisite steps to install and build STDK for the ESP-WROVER-KIT board.
git clone https://github.com/Samsung/TizenRT.git
cd TizenRT
TIZENRT_BASEDIR="$PWD"- Update submodule
git submodule update --init "external/stdk/st-device-sdk-c"
git submodule update --init "external/libsodium/libsodium"Your IoT device needs authentication in order to connect to the SmartThings Cloud. These data usually reside in file format. To create these authentication data, you must know your MNID in the personal information window of Developer Workspace. Please sign in with Samsung Account and then check your MNID first.
Open a terminal window and run the following stdk-keygen command to create a Device Identity.
$ cd external/stdk/st-device-sdk-c/tools/keygen/linux
$ ./stdk-keygen -h
usage: stdk-keygen -m MNID [-f firmware_version]
$ ./stdk-keygen -m **** -f V201910 # replace '****' with your MNID
Go Device Identity of Developer Workspace.
Serial Number:
┌──────────┬──────────┐
│ STDK**** │ ce**2**3 │
└──────────┴──────────┘
Public Key:
1D********a21F********8WwP********yU/n8vFvM=
$ tree
.
├── ed25519.pubkey
├── ed25519.seckey
└── output_STDK****ce**2**3
└── device_info.jsonCopy the Serial Number and Public Key after running the command on your computer. You will need to upload those values to the SmartThings Cloud via Developer Workspace.
After you create a device identity with a command with an option like above, You can get the ready-to-use device_info.json file directly.
Sign-In to Devworkspace.
Select 'Sign-In' where right-top on the page.

You need to register a new project to SmartThings Cloud.
-
Create a Project.
-
Create a Device Profile.
A device profile contains the components, capabilities, and metadata (ID, name, etc.). These information define the actions and attributes that an IoT device can perform. Click the "GO TO DEVICE PROFILE" and then, enter the all remaining information required.- Select 'Add a Device Profile'.


A device profile contains the components, capabilities, and metadata (ID, name, etc.). This information defines the actions and attributes that an IoT device can perform.

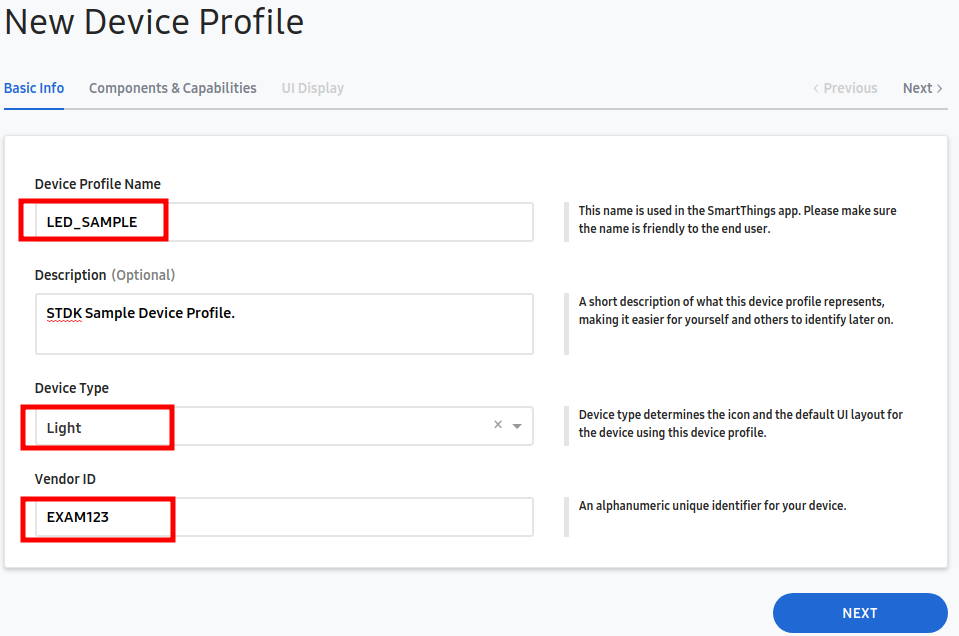
- Create a new profile to add it to project.
Fill properties of device and select 'NEXT'.
- Add copabilities for device.
Select 'ADD CAPABILITY'. And add Capabilities like switch, switch level, color control and health check.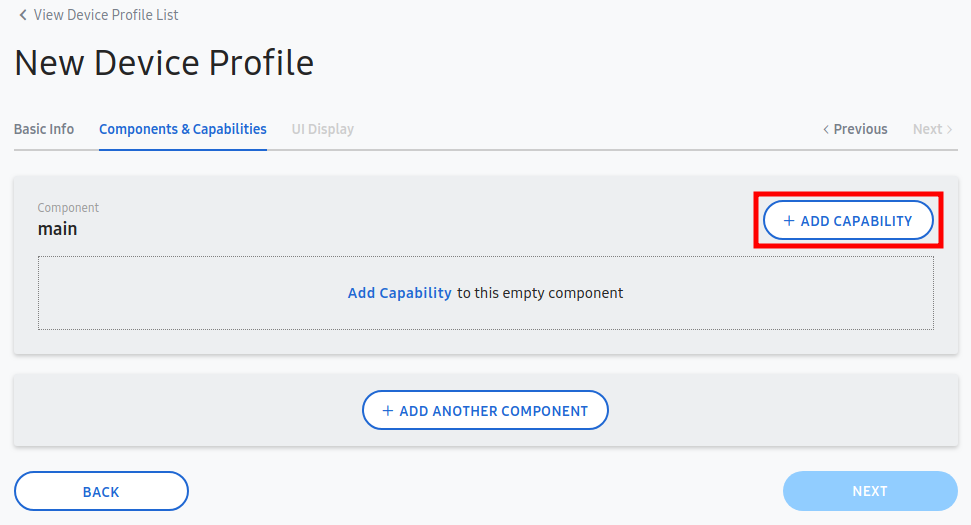
At this time, please note that you will need to add a "Health Check" capability to update the connectivity status of a device. It is only required on the main component.
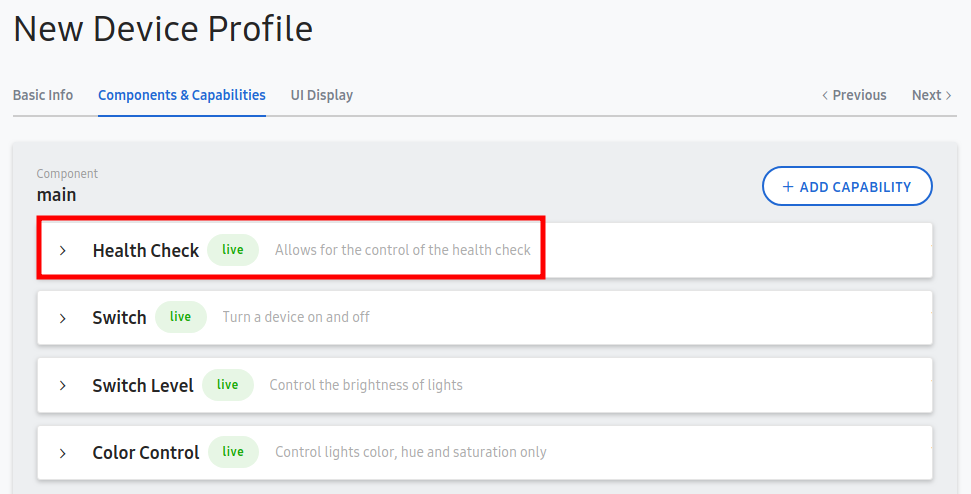
- Select UI Display.
Select Main State and Action.

- Create a new profile to add it to project.
- Select 'Add Device Onboarding'.
This defines information to support the initial connection process between IoT device and SmartThings Cloud.
Click the "GO TO DEVICE ONBOARDING" and then, enter the all remaining information required.


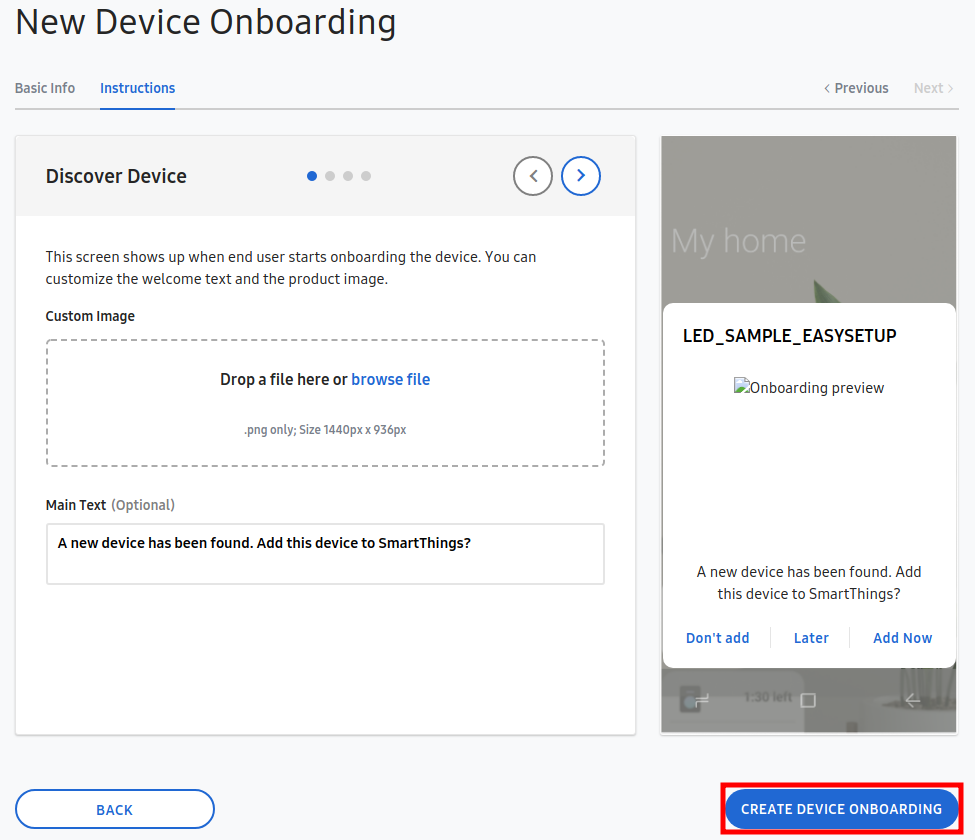
- Select 'Deploy Device Profile to test'.
You can publish your device to the SmartThings platform for testing. And then you will be able to access your device through the SmartThings app. Actually this step is for self-testing. If you want to officially publish your device with enrolled organizations ID(e.g. company MNID), please refer to the process below.
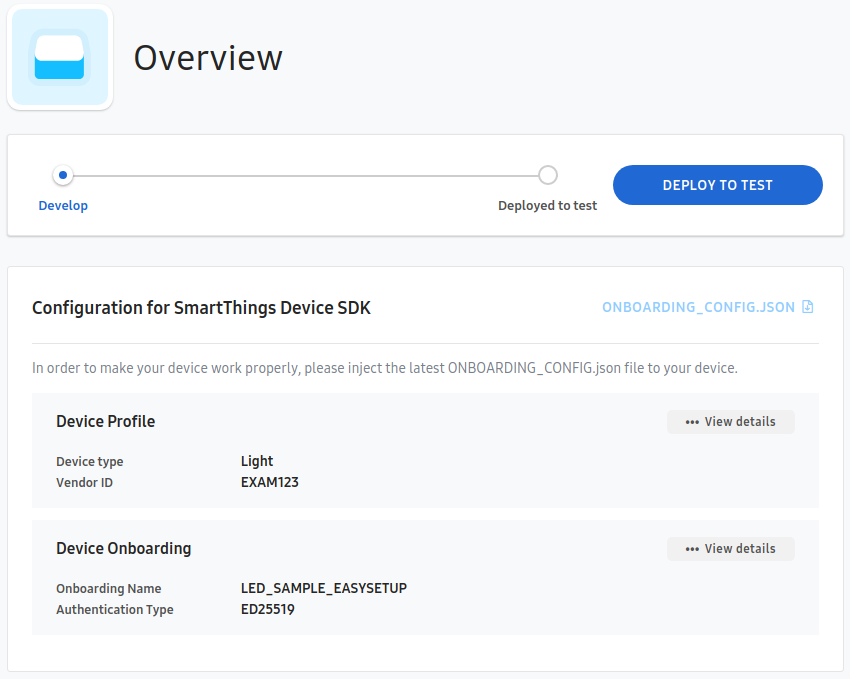
- Register Device Identity.
This step uploads device identity data generated in the Create device identity phase.

Paste the public key that copied key in the Public Key value box that appears. And then, click ADD button.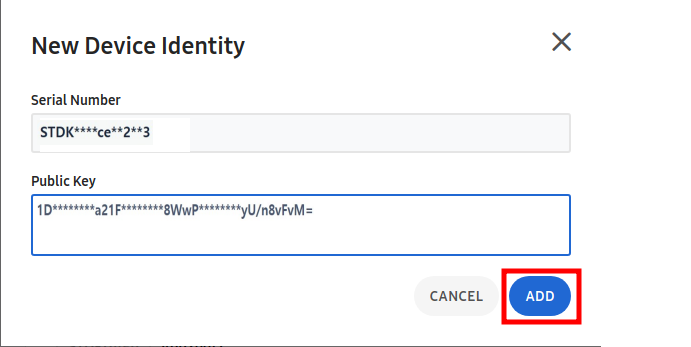
- Select 'Add a Device Profile'.
- Download onboarding data.
Download "onboarding_config.json" file into "[TizenRT]/apps/examples/stdk_smart_lamp/"

- Copy Device Identity file into application folder.
// in [TizenRT]/external/stdk/st-device-sdk-c/tools/keygen/linux
$ cd external/stdk/st-device-sdk-c/tools/keygen/linux
$ cat output_STDK****ce**2**3/device_info.json
{
"deviceInfo": {
"firmwareVersion": "V201910",
"privateKey": "3d********AOyY********ezJQ********TMKLGxzbQ=",
"publicKey": "1D********a21F********8WwP********yU/n8vFvM=",
"serialNumber": "STDK****ce**2**3"
}
}
// Copy device info file under "[TizenRT]/apps/examples/stdk_smart_lamp/apps/examples/stdk_smart_lamp/".
$ cp ./output_STDK****ce**2**3/device_info.json ../../../../../../apps/examples/stdk_smart_lamp/apps/examples/stdk_smart_lamp/ We will use 'esp_wrover_kit/stdk' config which is included the smart led application. and you can set it through "./dbuild menu" command.
Please follow below steps.
- Configuration
// In [TizenRT]/os
$ ./dbuild.sh menu
======================================================
"Select Board"
======================================================
...
"6. esp_wrover_kit"
...
"x. EXIT"
======================================================
6 // Select 'esp_wrover_kit'.
esp_wrover_kit is selected
==================================================
"Select Configuration of esp_wrover_kit"
==================================================
...
"6. STDK"
...
==================================================
6 // Select "STDK".
STDK is selected
Copy build environment files
CAUTION!! To download esp_wrover_kit/STDK built image, genromfs should be installed
Find details at https://github.com/Samsung/TizenRT/blob/master/docs/HowToUseROMFS.md
Configuration is Done!
======================================================
"Select build Option"
======================================================
"1. Build with Current Configurations"
"2. Re-configure"
"3. Menuconfig"
"4. Build Clean"
"5. Build Dist-Clean"
"6. Build SmartFS Image"
"x. Exit"
======================================================
1 // Select "Build with Current Configurations"
...
######################################
## Library Sizes ##
######################################
.data .bss .text Total
356 12560 222108 235024 libexternal.a
340 8544 118702 127586 libnet80211.a
...
0 1036 2164 3200 NOLIB
24 380 2076 2480 libmm.a
4 4 1904 1912 librtc.a
0 24 980 1004 libwque.a
0 42 800 842 libcore.a
0 0 796 796 libboard.a
0 0 102 102 libsoc.a
4 1 0 5 libwpa2.a
0 1 0 1 libwps.a
======================================================
"Select build Option"
======================================================
"1. Build with Current Configurations"
"2. Re-configure"
"3. Menuconfig"
"4. Build Clean"
"5. Build Dist-Clean"
"6. Build SmartFS Image"
"d. Download"
"x. Exit"
======================================================
d // Select "Download"
==================================================
"Select download option"
==================================================
"1. ALL"
"2. OS"
"4. BOOTLOADER"
"5. ROMFS"
"6. ERASE_ALL"
"u. USBrule"
"x. Exit"
==================================================
1 // Select "All"
ALL
make -C ../build/tools/esp32 ALL
...
Leaving...
Hard resetting via RTS pin...
make[1]: Leaving directory '/home/tizenrt/ws/public/priv/TizenRT/build/tools/esp32'
// DONENow, the device is ready onboarding.
You can download SmartThings Application via Google play app store.
Developer mode should be enabled through settings of app before try to make a connection between mobile and your device via easysetup.
Try to do easysetup.
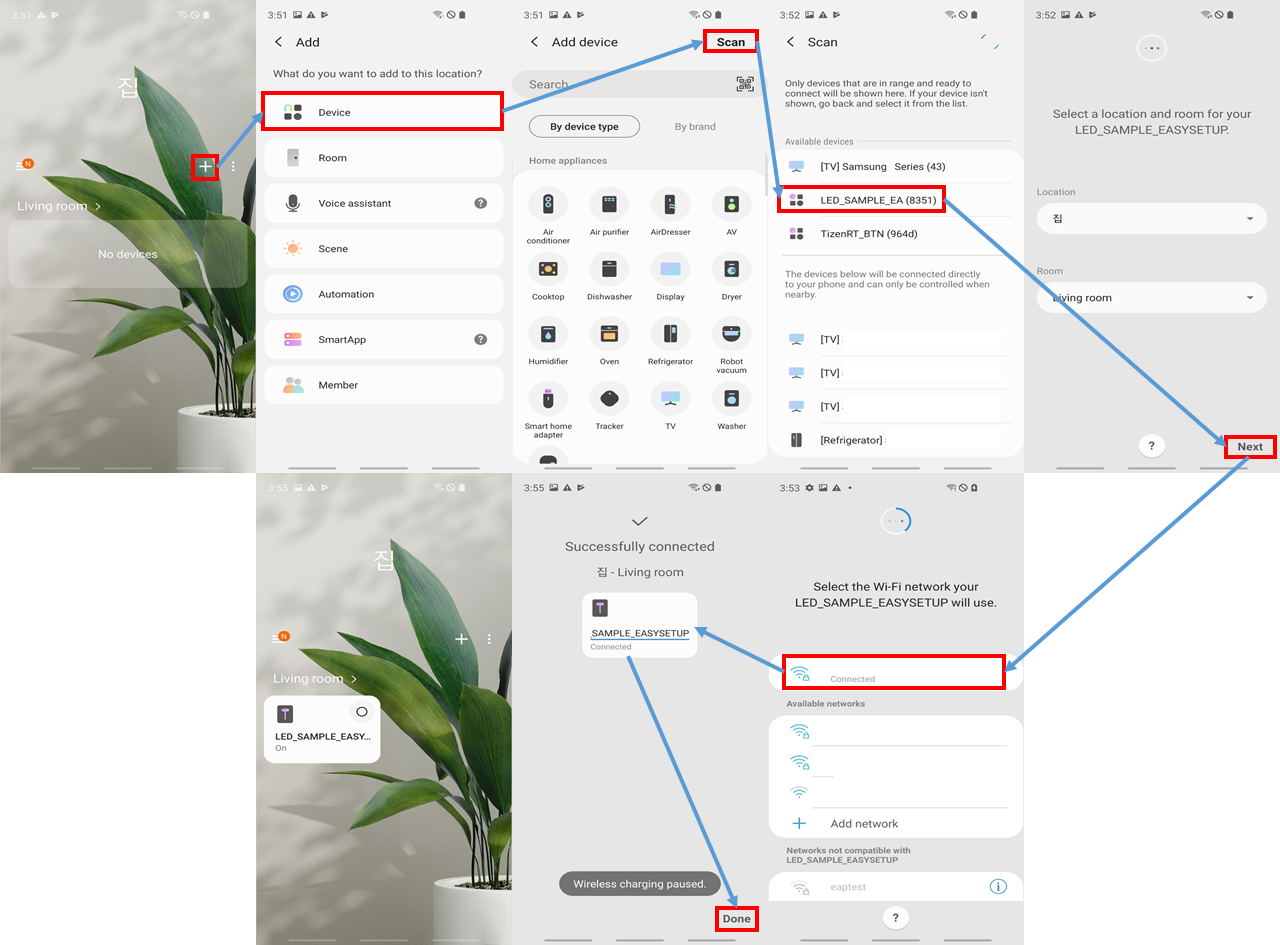
Now you can control smart led device(sample) through SmartThings mobile application.
You can see a more detailed build approach in 'Getting started'.