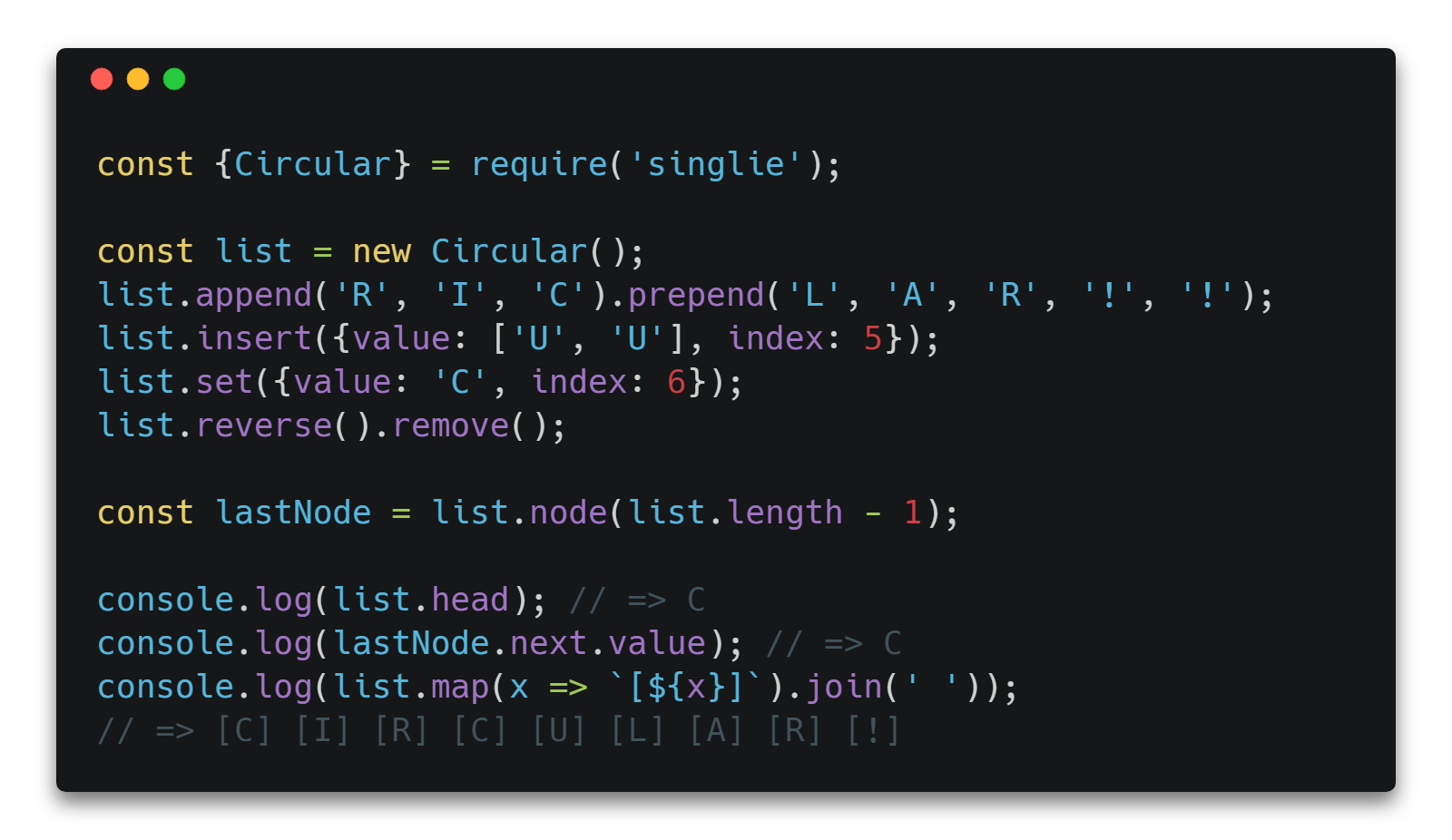
Progressive implementation of the circular and linear singly linked list data structures in modern ES6.
Come over to Gitter or Twitter to share your thoughts on the project.
Visit the contributing guidelines to learn more on how to translate this document into more languages.
npm install singlieSinglie exposes a progressive and composable API, that can be utilized through a simple and minimal syntax, allowing you to combine and chain methods effectively.
Usage examples can be also found at the test directory.
const {Circular, Linear} = require('singlie');
const linear = new Linear();
linear.prepend('A').append('B');
linear.node(0);
// => Node { value: 'A', next: Node { value: 'B', next: null } }
linear.node(0).next;
// => Node { value: 'B', next: null }
linear.node(0).next.next;
// => null
linear.map(x => `[${x}]`).reverse().join(' -> ');
// => [B] -> [A]
const circular = new Circular();
circular.append('B').prepend('A');
circular.node(0);
// => Node { value: 'A', next: Node { value: 'B', next: [Circular] } }
circular.node(0).next;
// => Node { value: 'B', next: Node { value: 'A', next: [Circular] } }
circular.node(0).next.next;
// => Node { value: 'A', next: Node { value: 'B', next: [Circular] } }
circular.map(x => `[${x}]`).reverse().toArray();
// => [ '[B]', '[A]' ]Linear singly linked lists can contain multiple nodes, where each node has only a value and a next attribute. The value attribute holds the value stored inside of the node, and the next attribute points to the next node in line. The only exception, is that the last node of the list has null stored to its next attribute, which indicates the lack of further nodes down the line, thus the end of the list. The following example demonstrates the operations that can be performed on any linear singly linked list.
const {Linear} = require('singlie');
const linear = new Linear();
const {log} = console;
// Append a node holding the value `E`
linear.append('E');
linear.head; // => E
linear.last; // => E
linear.get(0); // => E
// Return the node corresponding to the index
linear.node(0); // => Node { value: 'E', next: null }
linear.node(0).value; // => E
linear.node(0).next; // => null
// Append multiple nodes at once
linear.append('F', 'G');
linear.length; // => 3
linear.node(0).next.value; // => F
linear.node(0).next.next.value; // => G
linear.toArray(); // => [ 'E', 'F', 'G' ]
// Prepend multiple nodes at once
linear.prepend('B', 'A');
linear.join(' '); // => A B E F G
// Insert multiple nodes to the given index
linear.insert({value: ['D', 'C', 'X'], index: 2});
linear.join(' '); // => A B X C D E F G
// Remove the node corresponding to the index
linear.remove(2);
linear.join(' '); // => A B C D E F G
// Update the value of the node corresponding to the index
linear.node(linear.length - 1).value = '!';
linear.join(' '); // => A B C D E F !
linear.set({value: 'G', index: linear.length - 1});
linear.join(' '); // => A B C D E F G
// Iterate over the list
const array = [];
linear.forEach(x => array.push(x));
log(array);
// => [ 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G' ]
// Chain multiple methods
linear.reverse().map(x => `[${x}]`).join('->');
// => [G]->[F]->[E]->[D]->[C]->[B]->[A]
// Clear the list
linear.clear(); // => Linear { head: null, length: 0 }Circular singly linked lists can also contain multiple nodes, where again each node has the same value and next attributes. The only difference compared to linear lists, is that the last node always points back to the first node / head of the list, thus the list is said to be circular or circularly linked. The following example demonstrates the operations that can be performed on any circular singly linked list.
const {Circular} = require('singlie');
const circular = new Circular();
const {log} = console;
// Append a node holding the value `E`
circular.append('E');
circular.head; // => E
circular.last; // => E
circular.get(0); // => E
// Return the node corresponding to the index
circular.node(0); // => Node { value: 'E', next: [Circular] }
circular.node(0).value; // => E
circular.node(0).next.value; // => E
circular.node(0).next.next.value; // => E
// Append multiple nodes at once
circular.append('F', 'G');
circular.length; // => 3
circular.node(0).next.value; // => F
circular.node(0).next.next.value; // => G
circular.node(0).next.next.next.value; // => E
circular.toArray(); // => [ 'E', 'F', 'G' ]
// Prepend multiple nodes at once
circular.prepend('B', 'A');
circular.join(' '); // => A B E F G
// Insert multiple nodes to the given index
circular.insert({value: ['D', 'C', 'X'], index: 2});
circular.join(' '); // => A B X C D E F G
// Remove the node corresponding to the index
circular.remove(2);
circular.join(' '); // => A B C D E F G
// Update the value of the node corresponding to the index
circular.node(circular.length - 1).value = '!';
circular.join(' '); // => A B C D E F !
circular.set({value: 'G', index: circular.length - 1});
circular.join(' '); // => A B C D E F G
// Iterate over the list
const array = [];
circular.forEach(x => array.push(x));
log(array);
// => [ 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G' ]
// Chain multiple methods
circular.reverse().map(x => `[${x}]`).join('->');
// => [G]->[F]->[E]->[D]->[C]->[B]->[A]
// Clear the list
circular.clear(); // => Circular { head: null, length: 0 }The following documentation holds for both circular & linear lists. The described list instance is used to depict the same methods that are applicable to both a linear and a circular linked list, without overlooking their above described differences and unique qualities.
- Return Type:
Linked List
Appends one of more nodes to the list.
- Type:
any
Can be one or more comma delimited values. Each value corresponds to a single node.
list.append('A', 'B', 'C', 'D');
// => { value: 'A', next: { value: 'B', next: [List] } }- Return Type:
Linked List
Prepends one of more nodes to the list.
- Type:
any
Can be one or more comma delimited values. Each value corresponds to a single node.
list.append('C' , 'D');
// => { value: 'C', next: [List] }
list.prepend('B', 'A');
// => { value: 'A', next: { value: 'B', next: { value: 'C', next: [List] } } }- Return Type:
any
Returns the value of the first node / head on the list.
list.append('A', 'B');
list.head;
// => A- Return Type:
any
Returns the value of the last node on the list.
list.append('A', 'B');
list.last;
// => B- Return Type:
Integer
Returns the length of the list.
list.append('A', 'B');
list.length;
// => 2- Return Type:
Boolean
Checks whether or not the list is empty.
list.append('A', 'B');
list.isEmpty();
// => false- Return Type:
Linked List
Inserts one or more nodes to the given index.
- Type:
any
Can be one or more comma delimited values. Each value corresponds to a single node.
- Type:
Integer
Can be an integer corresponding to a list index.
list.append('A', 'B', 'E');
list.insert({value: ['C', 'D'], index: 1});
// => { value: 'A', next: { value: 'D', next: { value: 'C', next: { value: 'B', next: [List] } } } }- Return Type:
Node
Return the node corresponding to the given index.
- Type:
Integer
Can be an integer corresponding to a list index.
list.append('A', 'B', 'C', 'D');
const node = list.node(0);
// => { value: 'A', next: { value: 'B', next: [List] } }
node.value;
// => A
node.next;
// => { value: 'B', next: [List] }- Return Type:
any
Return the value of node corresponding to the given index.
- Type:
Integer
Can be an integer corresponding to a list index.
list.append('A', 'B');
list.get(0);
// => A
list.get(0);
// => B- Return Type:
Linked List
Removes from the list the node located to the given index.
- Type:
Integer - Default:
list.length - 1
Can be an integer corresponding to a list index.
If not provided, the last node of the list will be removed.
list.append('A', 'B', 'C', 'D');
// => { value: 'A', next: [List] }
list.remove(0);
// => { value: 'B', next: [List] }
list.remove(0);
// => { value: 'C', next: [List] }- Return Type:
Array
Converts the list into an array.
list.append('A', 'B', 'C');
// => { value: 'A', next: { value: 'B', next: [List] } }
const array = list.toArray();
// => [ 'A', 'B', 'C' ]- Return Type:
Empty Linked List
Removes all nodes from the list.
list.append('A', 'B', 'C');
// => { value: 'A', next: { value: 'B', next: [List] } }
list.clear();
// => null- Return Type:
String
Joins the values of all nodes on the list into a string and returns the string.
- Type:
String - Default:
Comma ','
Specifies a string to separate each pair of adjacent node values of the array.
If omitted, the node values are separated with a comma ','.
list.append('A', 'B', 'C');
// => { value: 'A', next: { value: 'B', next: [List] } }
list.join();
// => 'A,B,C'
list.join('');
// => 'ABC'
list.join(' ');
// => 'A B C'- Return Type:
undefined
Executes a provided function once for each node value.
- Type:
Function
Function to execute for each node value.
const array = [];
list.append('A', 'B', 'C');
// => { value: 'A', next: { value: 'B', next: [List] } }
list.forEach(x => array.push(x));
console.log(array);
// => [ 'A', 'B', 'C' ];- Return Type:
Linked List
Executes a provided function once for each node value.
- Type:
Function
Function that produces a new node value for the new list.
list.append('A', 'B', 'C');
// => { value: 'A', next: { value: 'B', next: [List] } }
const mapped = list.map(x => `[${x}]`);
array.join(' ');
// => '[A] [B] [C]'For more info on how to contribute to the project, please read the contributing guidelines.
- Fork the repository and clone it to your machine
- Navigate to your local fork:
cd singlie - Install the project dependencies:
npm installoryarn install - Lint the code and run the tests:
npm testoryarn test
- Klaus Sinani (@klaussinani)